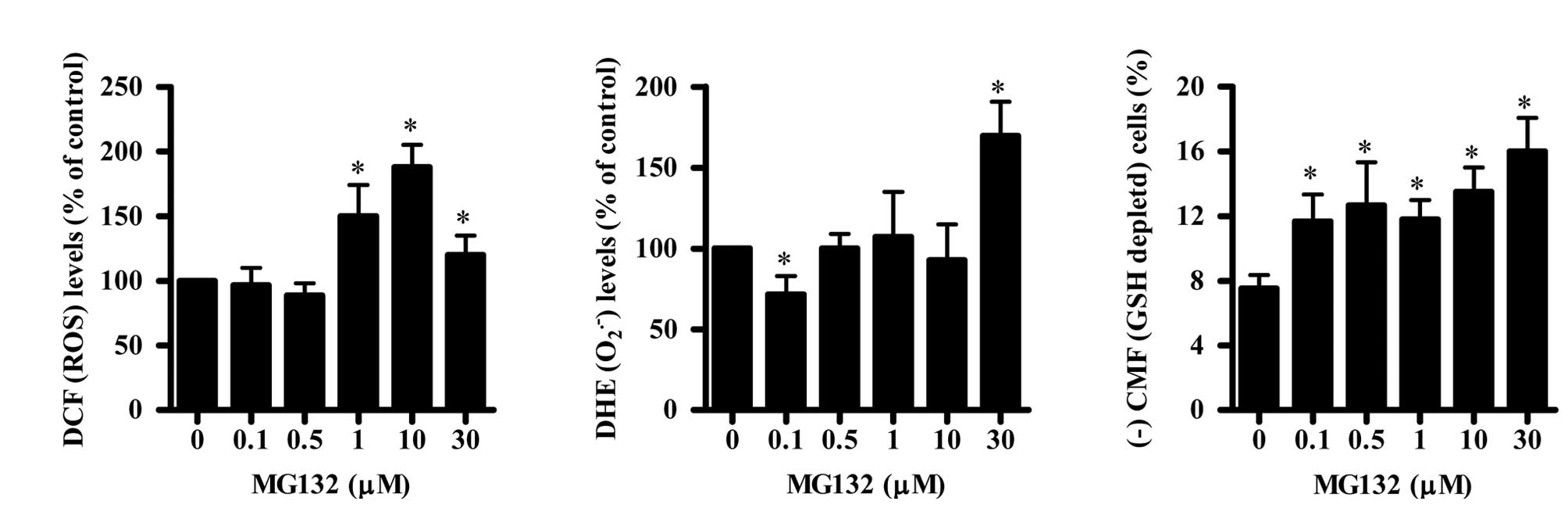
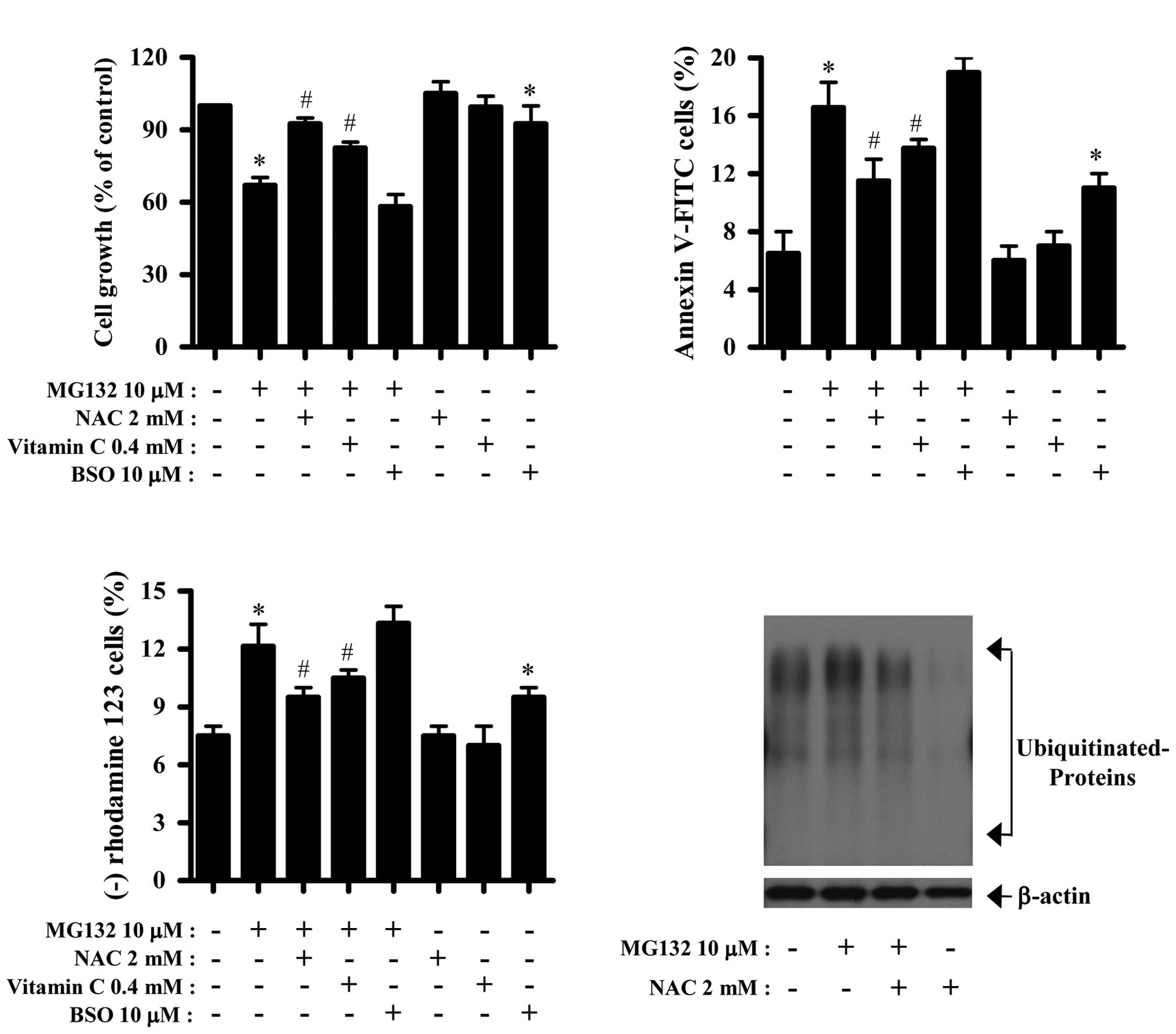
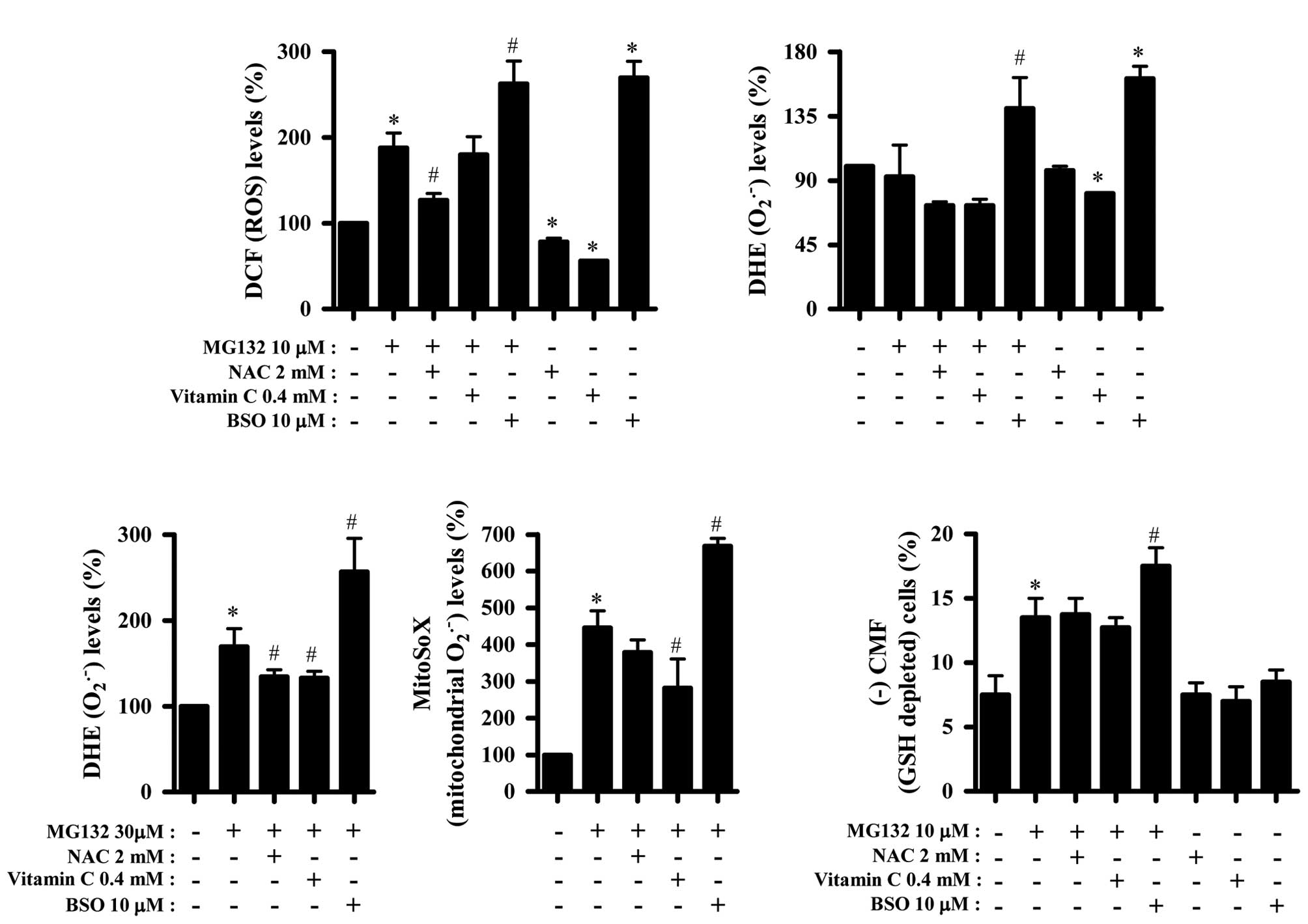
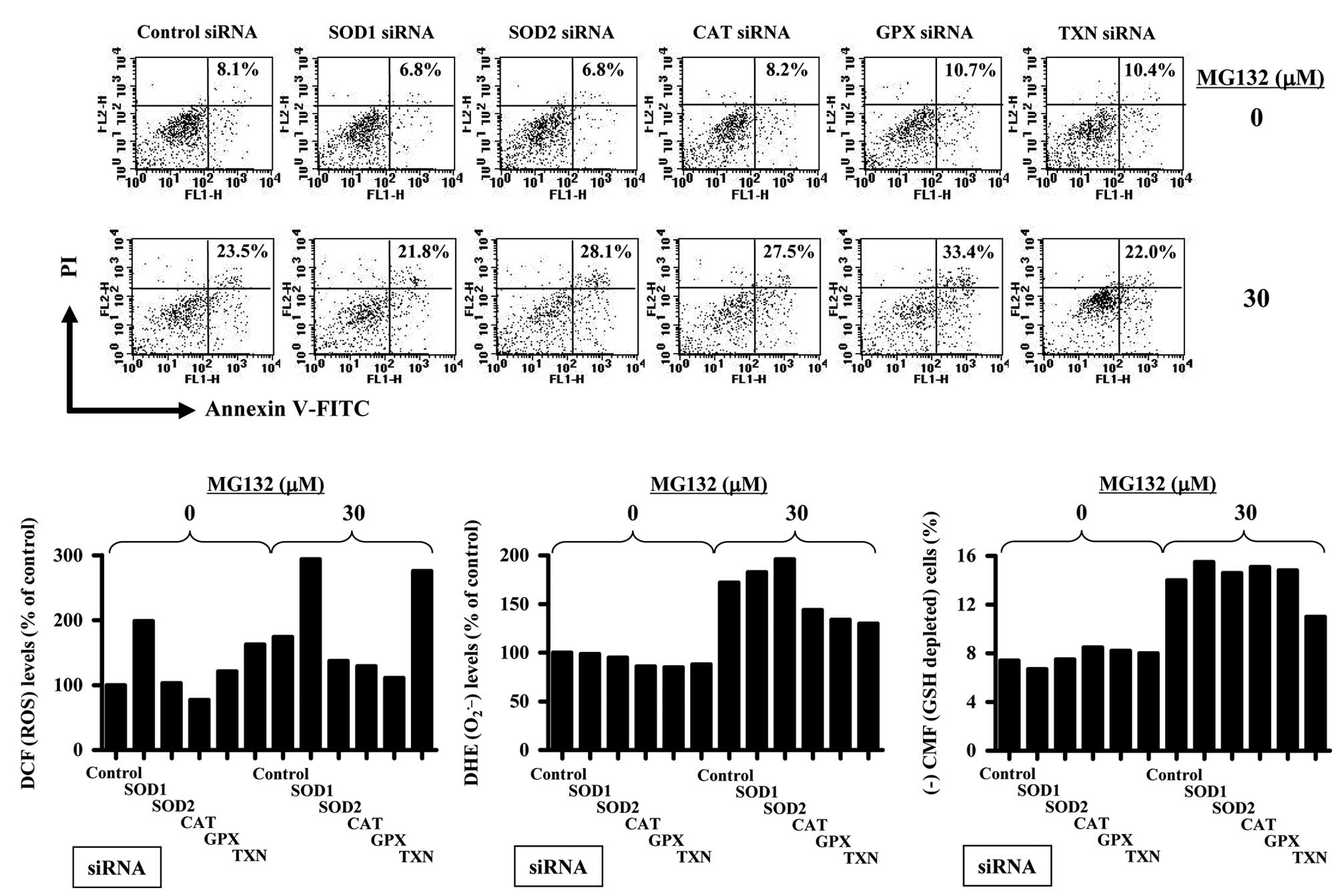
|
1
|
Gonzalez C, Sanz-Alfayate G, Agapito MT,
Gomez-Nino A, Rocher A and Obeso A: Significance of ROS in oxygen
sensing in cell systems with sensitivity to physiological hypoxia.
Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 132:17–41. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baran CP, Zeigler MM, Tridandapani S and
Marsh CB: The role of ROS and RNS in regulating life and death of
blood monocytes. Curr Pharm Des. 10:855–866. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: an update and review.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1757:509–517. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zelko IN, Mariani TJ and Folz RJ:
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD
(SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures,
evolution, and expression. Free Radic Biol Med. 33:337–349. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wilcox CS: Reactive oxygen species: roles
in blood pressure and kidney function. Curr Hypertens Rep.
4:160–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Marks PA: Thioredoxin in cancer - role of
histone deacetylase inhibitors. Semin Cancer Biol. 16:436–443.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen TJ, Jeng JY, Lin CW, Wu CY and Chen
YC: Quercetin inhibition of ROS-dependent and -independent
apoptosis in rat glioma C6 cells. Toxicology. 223:113–126. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dasmahapatra G, Rahmani M, Dent P and
Grant S: The tyrphostin adaphostin interacts synergistically with
proteasome inhibitors to induce apoptosis in human leukemia cells
through a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent mechanism. Blood.
107:232–240. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wallach-Dayan SB, Izbicki G, Cohen PY,
Gerstl-Golan R, Fine A and Breuer R: Bleomycin initiates apoptosis
of lung epithelial cells by ROS but not by Fas/FasL pathway. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L790–L796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Orlowski RZ: The role of the
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ.
6:303–313. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Voges D, Zwickl P and Baumeister W: The
26S proteasome: a molecular machine designed for controlled
proteolysis. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:1015–1068. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Adams J: The proteasome: a suitable
antineoplastic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:349–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Drexler HC: Activation of the cell death
program by inhibition of proteasome function. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:855–860. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shah SA, Potter MW and Callery MP:
Ubiquitin proteasome pathway: implications and advances in cancer
therapy. Surg Oncol. 10:43–52. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee DH and Goldberg AL: Proteasome
inhibitors: valuable new tools for cell biologists. Trends Cell
Biol. 8:397–403. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu HM, Chi KH and Lin WW: Proteasome
inhibitors stimulate activator protein-1 pathway via reactive
oxygen species production. FEBS Lett. 526:101–105. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Perez-Galan P, Roue G, Villamor N,
Montserrat E, Campo E and Colomer D: The proteasome inhibitor
bortezomib induces apoptosis in mantle-cell lymphoma through
generation of ROS and Noxa activation independent of p53 status.
Blood. 107:257–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ling YH, Liebes L, Zou Y and Perez-Soler
R: Reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial dysfunction
in the apoptotic response to Bortezomib, a novel proteasome
inhibitor, in human H460 non-small cell lung cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 278:33714–33723. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qiu JH, Asai A, Chi S, Saito N, Hamada H
and Kirino T: Proteasome inhibitors induce cytochrome
c-caspase-3-like protease-mediated apoptosis in cultured cortical
neurons. J Neurosci. 20:259–265. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Petty RD, Nicolson MC, Kerr KM,
Collie-Duguid E and Murray GI: Gene expression profiling in
non-small cell lung cancer: from molecular mechanisms to clinical
application. Clin Cancer Res. 10:3237–3248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mortenson MM, Schlieman MG, Virudachalam S
and Bold RJ: Effects of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib alone
and in combination with chemotherapy in the A549 non-small-cell
lung cancer cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 54:343–353.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ling YH, Liebes L, Jiang JD, Holland JF,
Elliott PJ, Adams J, Muggia FM and Perez-Soler R: Mechanisms of
proteasome inhibitor PS-341-induced G(2)-M-phase arrest and
apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:1145–1154. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han YH and Park WH: MG132 as a proteasome
inhibitor induces cell growth inhibition and cell death in A549
lung cancer cells via influencing reactive oxygen species and GSH
level. Hum Exp Toxicol. 29:607–614. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Han YH and Park WH: MG132, a proteasome
inhibitor decreased the growth of Calu-6 lung cancer cells via
apoptosis and GSH depletion. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:1237–1242. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bailey HH: L-S,R-buthionine sulfoximine:
historical development and clinical issues. Chem Biol Interact.
111–112:239–254. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han YH and Park WH: Propyl gallate
inhibits the growth of HeLa cells via regulating intracellular GSH
level. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2531–2538. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
You BR and Park WH: Gallic acid-induced
lung cancer cell death is related to glutathione depletion as well
as reactive oxygen species increase. Toxicol In Vitro.
24:1356–1362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Pyrogallol as a glutathione depletor induces apoptosis in HeLa
cells. Int J Mol Med. 21:721–730. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park WH, Seol JG, Kim ES, Hyun JM, Jung
CW, Lee CC, Kim BK and Lee YY: Arsenic trioxide-mediated growth
inhibition in MC/CAR myeloma cells via cell cycle arrest in
association with induction of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor,
p21, and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 60:3065–3071. 2000.
|
|
30
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Arsenic trioxide inhibits growth of As4.1 juxtaglomerular cells via
cell cycle arrest and caspase-independent apoptosis. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 293:F511–F520. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Lendeckel W,
Yalcin A, Weber K and Tuschl T: Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs
mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature.
411:494–498. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, Kim CN, Ibrado
AM, Cai J, Peng TI, Jones DP and Wang X: Prevention of apoptosis by
Bcl-2: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria blocked. Science.
275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cocco D, Calabrese L, Rigo A, Argese E and
Rotilio G: Re-examination of the reaction of diethyldithiocarbamate
with the copper of superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem.
256:8983–8986. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jahngen-Hodge J, Obin MS, Gong X, Shang F,
Nowell TR Jr, Gong J, Abasi H, Blumberg J and Taylor A: Regulation
of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes by glutathione following oxidative
stress. J Biol Chem. 272:28218–2826. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lewis-Wambi JS, Kim HR, Wambi C, Patel R,
Pyle JR, Klein-Szanto AJ and Jordan VC: Buthionine sulfoximine
sensitizes antihormone-resistant human breast cancer cells to
estrogen-induced apoptosis. Breast Cancer Res. 10:R1042008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ramos AM and Aller P: Quercetin decreases
intracellular GSH content and potentiates the apoptotic action of
the antileukemic drug arsenic trioxide in human leukemia cell
lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:1912–1923. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gallegos A, Gasdaska JR, Taylor CW,
Paine-Murrieta GD, Goodman D, Gasdaska PY, Berggren M, Briehl MM
and Powis G: Transfection with human thioredoxin increases cell
proliferation and a dominant-negative mutant thioredoxin reverses
the transformed phenotype of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
56:5765–5770. 1996.
|
|
38
|
Kim SJ, Miyoshi Y, Taguchi T, Tamaki Y,
Nakamura H, Yodoi J, Kato K and Noguchi S: High thioredoxin
expression is associated with resistance to docetaxel in primary
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8425–8430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|