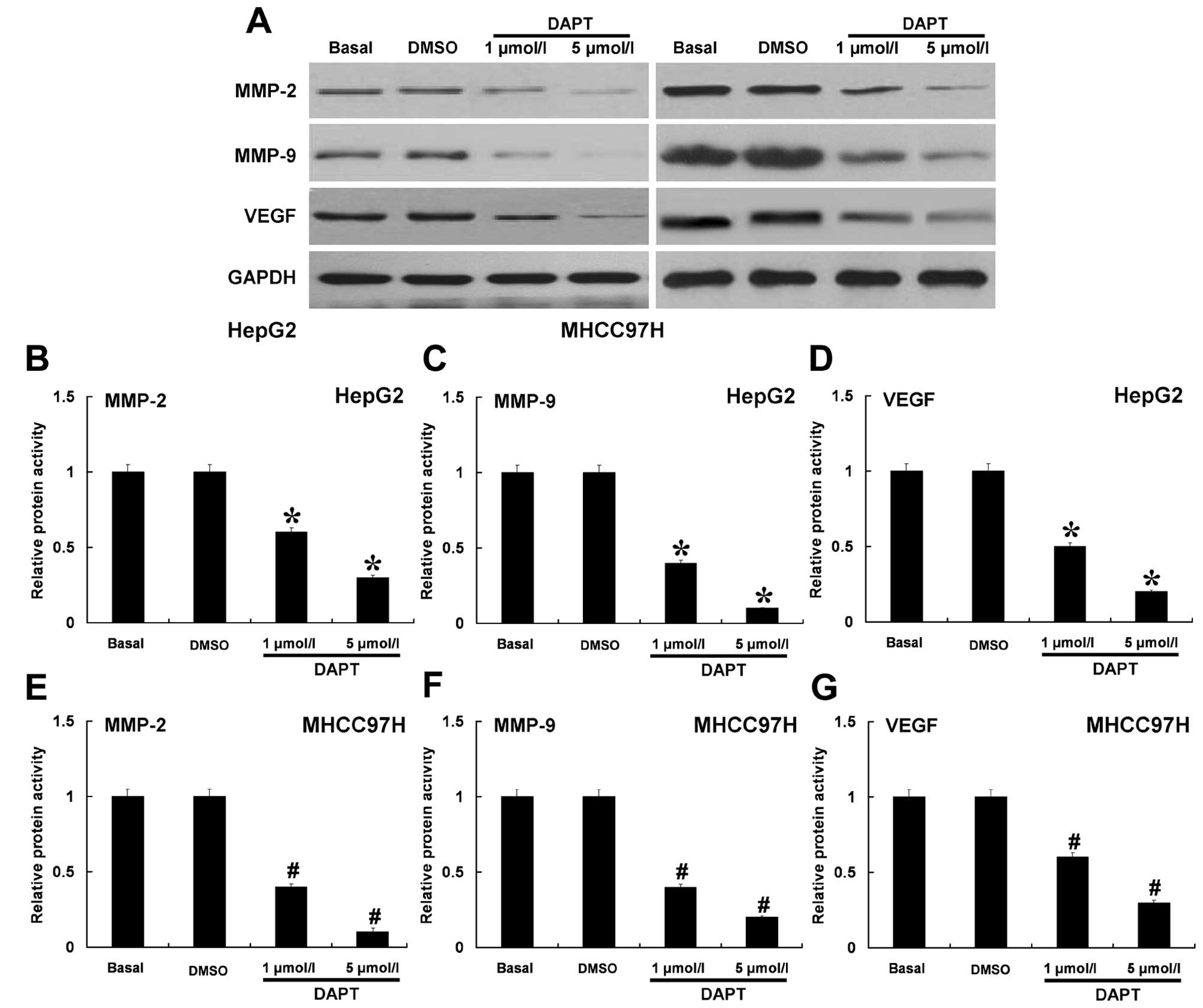
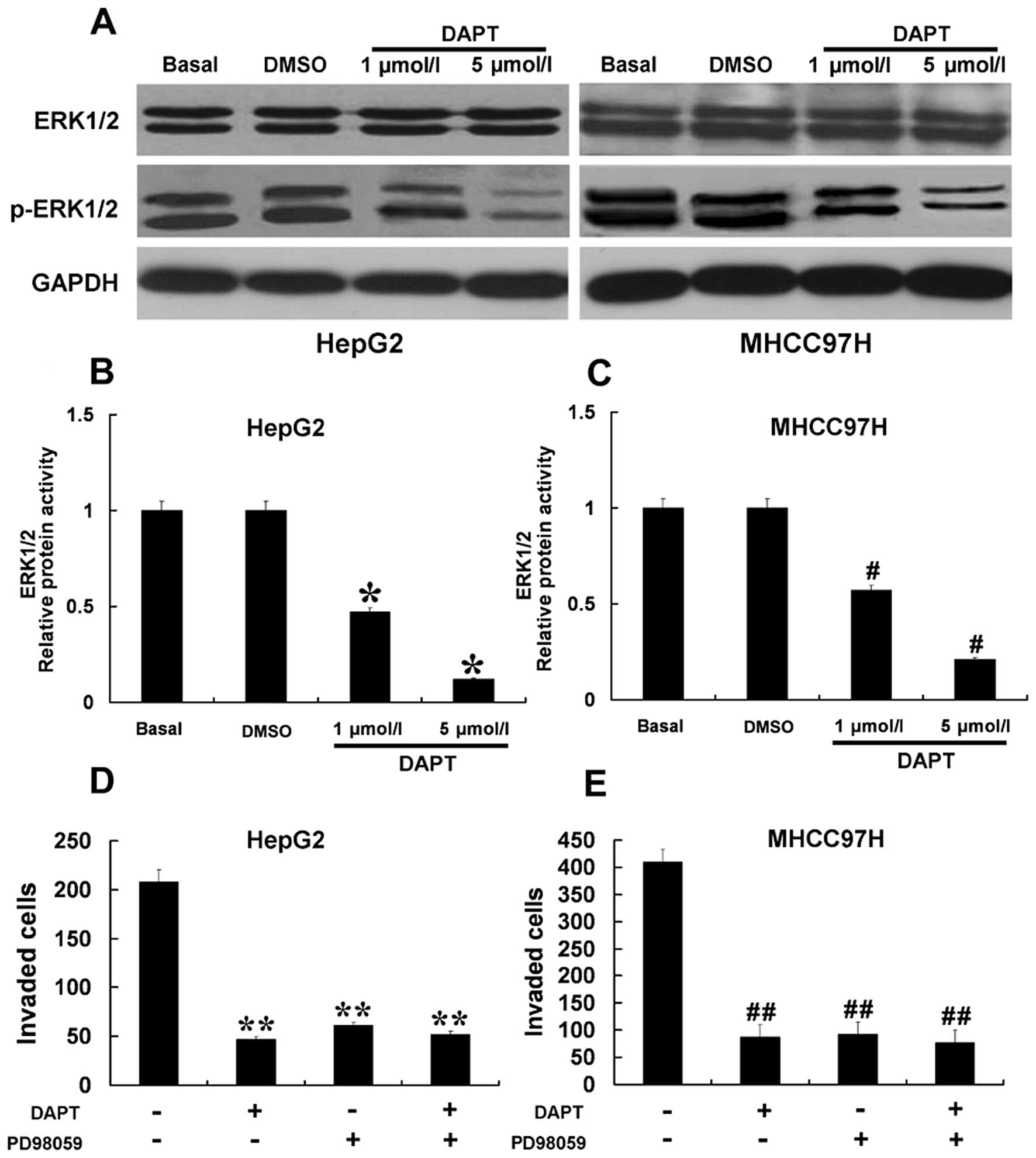
|
1
|
Yang JD, Nakamura I and Roberts LR: The
tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: current status
and therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer Biol. 21:35–43. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thomas MB and Zhu AX: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: the need for progress. J Clin Oncol. 23:2892–2899. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, et al:
Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell
motility and promotes tumor metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 51:1255–1263. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Itoh Y and Nagase H: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer. Essays Biochem. 38:21–36.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng ZS, Cohen AM and Guillem JG: Loss of
basement membrane type IV collagen is associated with increased
expression of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) during
human colorectal tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 20:749–755. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Komatsu K, Nakanishi Y, Nemoto N, Hori T,
Sawada T and Kobayashi M: Expression and quantitative analysis of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human gliomas. Brain Tumor
Pathol. 21:105–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Folkman J: What is the evidence that
tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:4–6.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Joo YE, Sohn YH, Lee WS, et al: Expression
of vascular endothelial growth factor and p53 in pancreatic
carcinomas. Korean J Intern Med. 17:153–159. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zeng H, Datta K, Neid M, Li J, Parangi S
and Mukhopadhyay D: Requirement of different signaling pathways
mediated by insulin-like growth factor-I receptor for
proliferation, invasion, and VPF/VEGF expression in a pancreatic
carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 302:46–55. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miele L and Osborne B: Arbiter of
differentiation and death: Notch signaling meets apoptosis. J Cell
Physiol. 181:393–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Allenspach EJ, Maillard I, Aster JC and
Pear WS: Notch signaling in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 1:466–476.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nickoloff BJ, Osborne BA and Miele L:
Notch signaling as a therapeutic target in cancer: a new approach
to the development of cell fate modifying agents. Oncogene.
22:6598–6608. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leong KG and Karsan A: Recent insights
into the role of Notch signaling in tumorigenesis. Blood.
107:2223–2233. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Radtke F and Raj K: The role of Notch in
tumorigenesis: oncogene or tumour suppressor? Nat Rev Cancer.
3:756–767. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zweidler-McKay PA, He Y, Xu L, et al:
Notch signaling is a potent inducer of growth arrest and apoptosis
in a wide range of B-cell malignancies. Blood. 106:3898–3906. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kunnimalaiyaan M and Chen H: Tumor
suppressor role of Notch-1 signaling in neuroendocrine tumors.
Oncologist. 12:535–542. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Proweller A, Tu L, Lepore JJ, et al:
Impaired notch signaling promotes de novo squamous cell carcinoma
formation. Cancer Res. 66:7438–7444. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seiffert D, Bradley JD, Rominger CM, et
al: Presenilin-1 and -2 are molecular targets for gamma-secretase
inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 275:34086–34091. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tung-Ping Poon R, Fan ST and Wong J: Risk
factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence
after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 232:10–24.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sahlgren C, Gustafsson MV, Jin S,
Poellinger L and Lendahl U: Notch signaling mediates
hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:6392–6397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Li Y, Rahman KM, Zhang
Y and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by
inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB, vascular endothelial growth
factor, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 66:2778–2784. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of cancer
metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:453–458. 2003.
|
|
24
|
Weiss L: Metastasis of cancer: a
conceptual history from antiquity to the 1990s. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 19:193–383. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vihinen P and Kahari VM: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer: prognostic markers and therapeutic
targets. Int J Cancer. 99:157–166. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Curran S and Murray GI: Matrix
metalloproteinases: molecular aspects of their roles in tumour
invasion and metastasis. Eur J Cancer. 36:1621–1630. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
John A and Tuszynski G: The role of matrix
metalloproteinases in tumor angiogenesis and tumor metastasis.
Pathol Oncol Res. 7:14–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cockett MI, Murphy G, Birch ML, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinases and metastatic cancer. Biochem Soc Symp.
63:295–313. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bianco FJ Jr, Gervasi DC, Tiguert R, et
al: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in bladder washes from
bladder cancer patients predicts pathological stage and grade. Clin
Cancer Res. 4:3011–3016. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murphy AN, Unsworth EJ and
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2
inhibits bFGF-induced human microvascular endothelial cell
proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 157:351–358. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wey JS, Fan F, Gray MJ, et al: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 promotes migration and
invasion in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer. 104:427–438.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary
KR and Ellis LM: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor
and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and
proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 55:3964–3968.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Balint K, Xiao M, Pinnix CC, et al:
Activation of Notch1 signaling is required for
beta-catenin-mediated human primary melanoma progression. J Clin
Invest. 115:3166–3176. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jundt F, Anagnostopoulos I, Forster R,
Mathas S, Stein H and Dorken B: Activated Notch1 signaling promotes
tumor cell proliferation and survival in Hodgkin and anaplastic
large cell lymphoma. Blood. 99:3398–3403. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Buchler P, Gazdhar A, Schubert M, et al:
The Notch signaling pathway is related to neurovascular progression
of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 242:791–801. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu B, Wei J, Qian X, Lei D, Ma Q and Liu
Y: Notch1 signaling pathway participates in cancer invasion by
regulating MMPs in lingual squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
27:547–552. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, Fu L, Gu F and Ma Y: Notch1 is
involved in migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 26:1295–1303. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Delbosc S, Glorian M, Le Port AS, Bereziat
G, Andreani M and Limon I: The benefit of docosahexanoic acid on
the migration of vascular smooth muscle cells is partially
dependent on Notch regulation of MMP-2/-9. Am J Pathol.
172:1430–1440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiong HQ, Abbruzzese JL, Lin E, Wang L,
Zheng L and Xie K: NF-kappaB activity blockade impairs the
angiogenic potential of human pancreatic cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 108:181–188. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Funahashi Y, Shawber CJ, Sharma A,
Kanamaru E, Choi YK and Kitajewski J: Notch modulates VEGF action
in endothelial cells by inducing Matrix Metalloprotease activity.
Vasc Cell. 3:22011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chan-Hui PY and Weaver R: Human
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase mediates the
stress-induced activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase
cascades. Biochem J. 336:599–609. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Trusolino L and Comoglio PM:
Scatter-factor and semaphorin receptors: cell signalling for
invasive growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:289–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen PN, Hsieh YS, Chiou HL and Chu SC:
Silibinin inhibits cell invasion through inactivation of both
PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact.
156:141–150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Arai K, Lee SR and Lo EH: Essential role
for ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase in matrix
metalloproteinase-9 regulation in rat cortical astrocytes. Glia.
43:254–264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zeigler ME, Chi Y, Schmidt T and Varani J:
Role of ERK and JNK pathways in regulating cell motility and matrix
metalloproteinase 9 production in growth factor-stimulated human
epidermal keratinocytes. J Cell Physiol. 180:271–284. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Giuliani N, Lunghi P, Morandi F, et al:
Downmodulation of ERK protein kinase activity inhibits VEGF
secretion by human myeloma cells and myeloma-induced angiogenesis.
Leukemia. 18:628–635. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Okajima E and Thorgeirsson UP: Different
regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by the
ERK and p38 kinase pathways in v-ras, v-raf, and v-myc transformed
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 270:108–111. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Banerjee S and Sarkar FH:
Exploitation of the Notch signaling pathway as a novel target for
cancer therapy. Anticancer Res. 28:3621–3630. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|