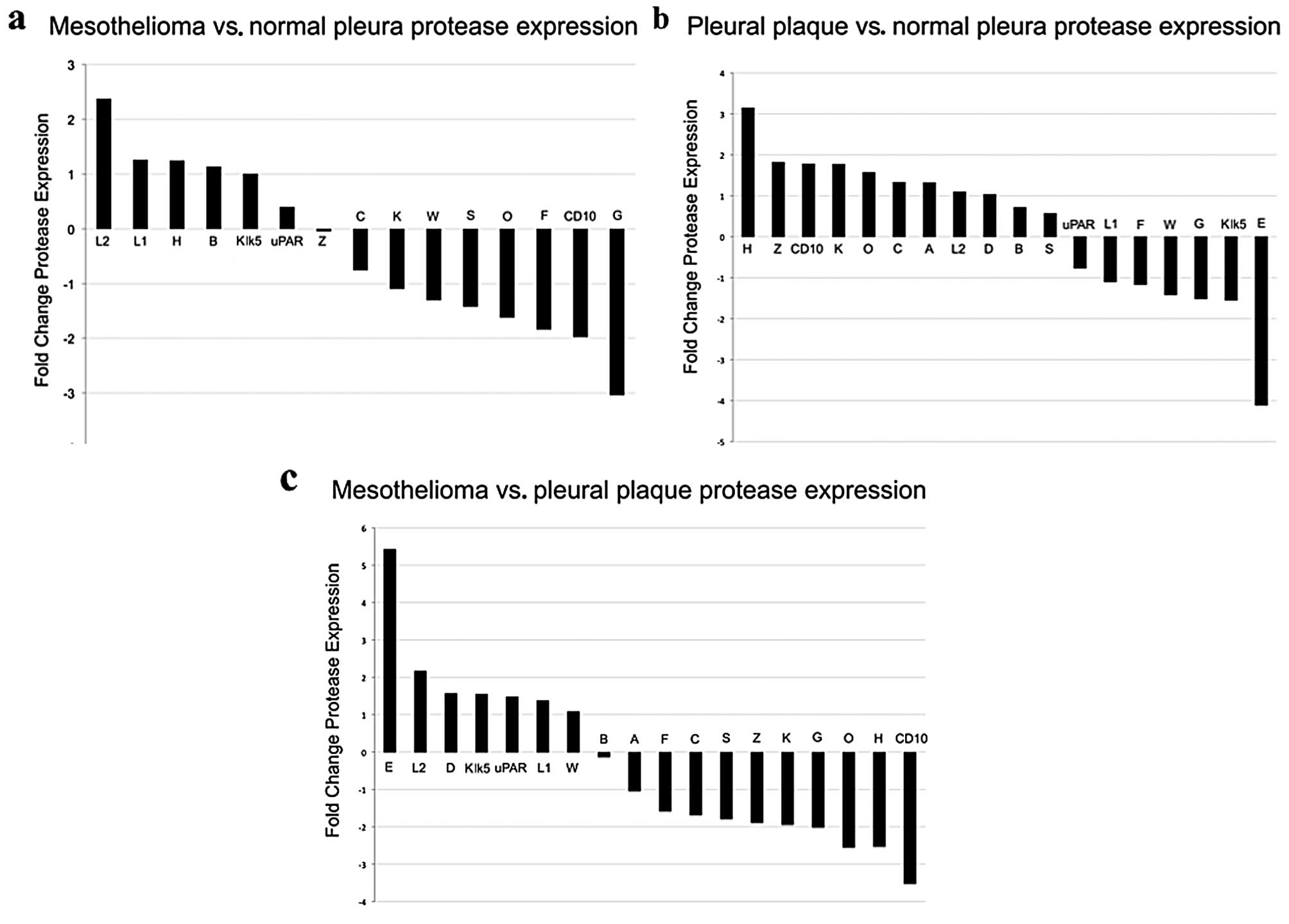
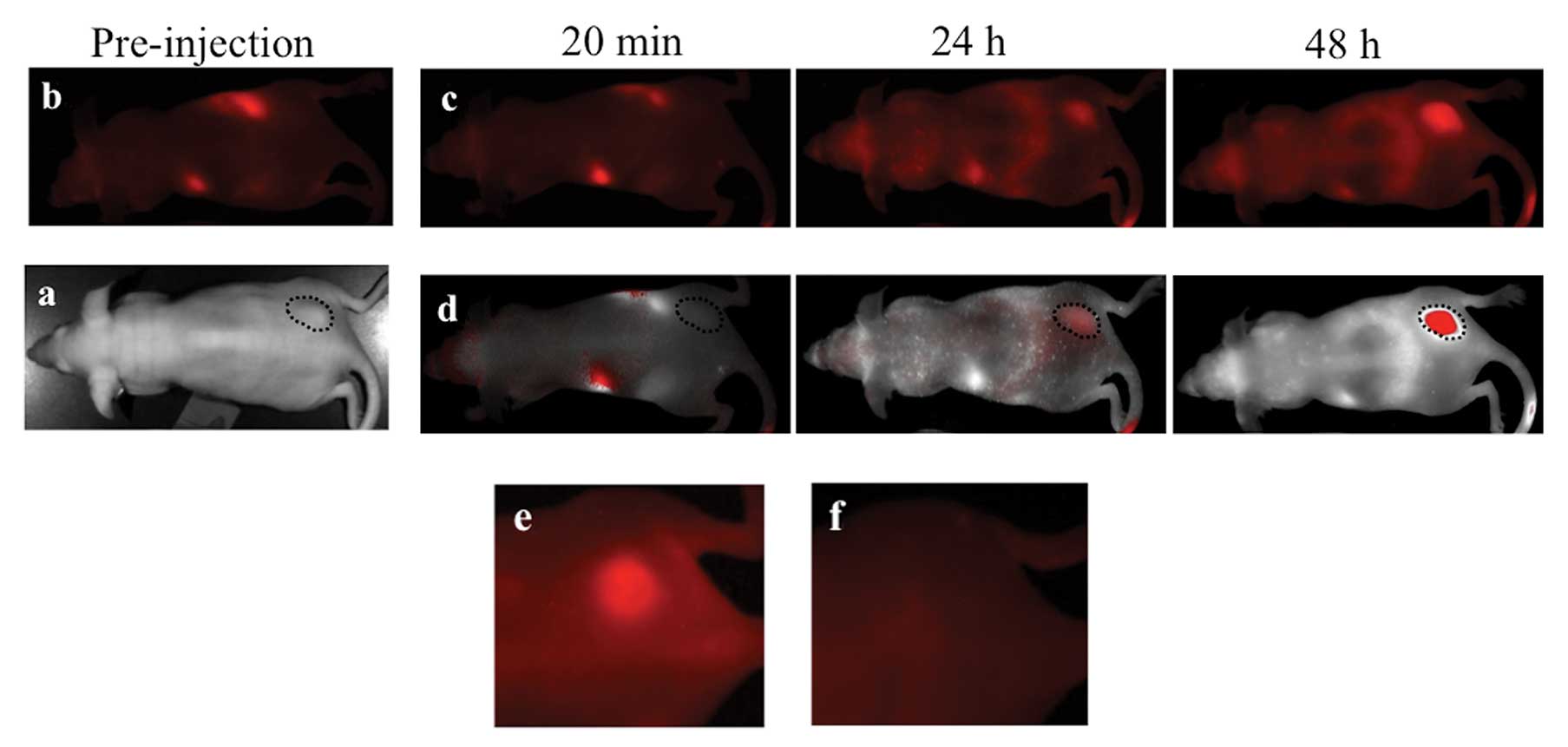
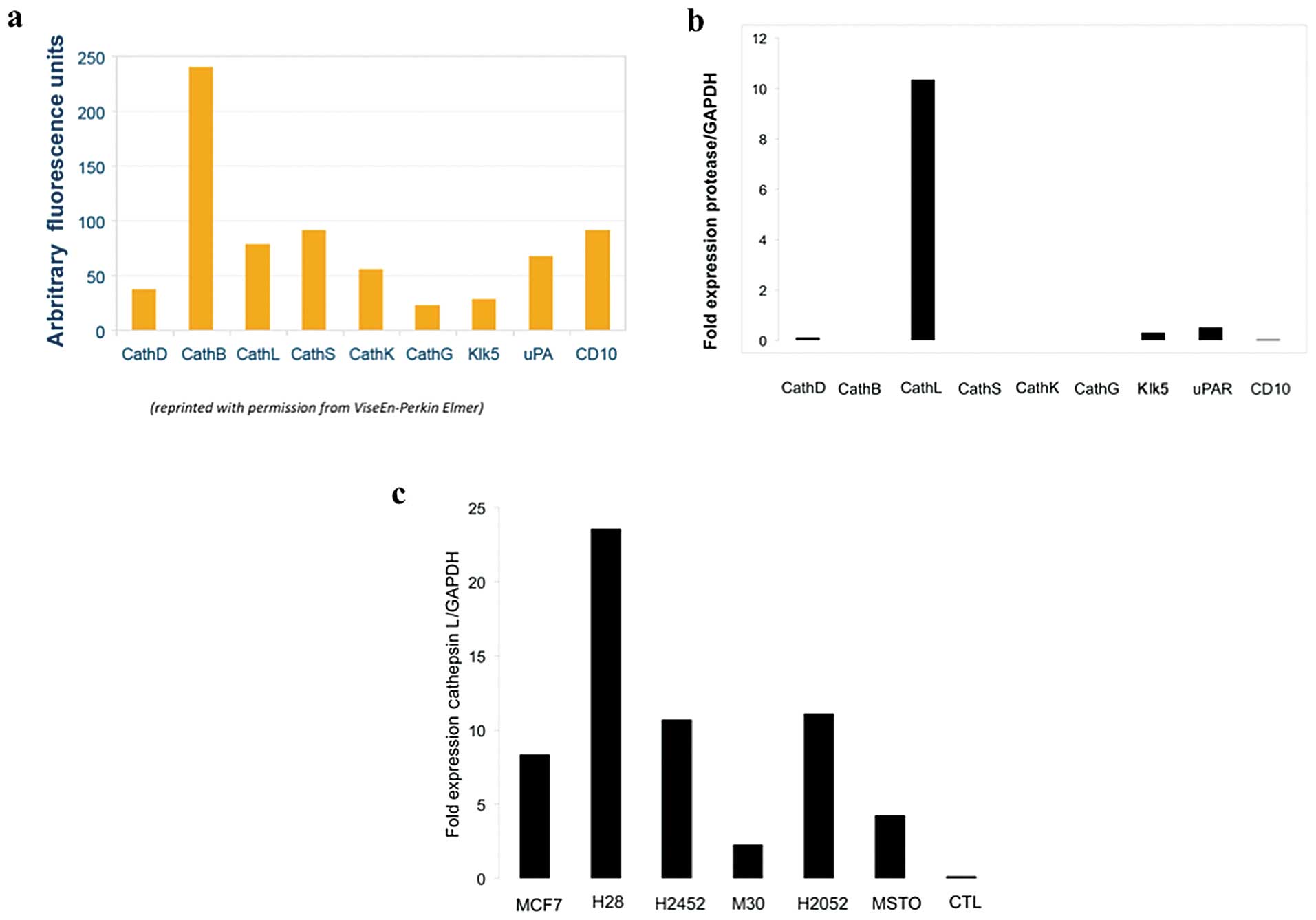
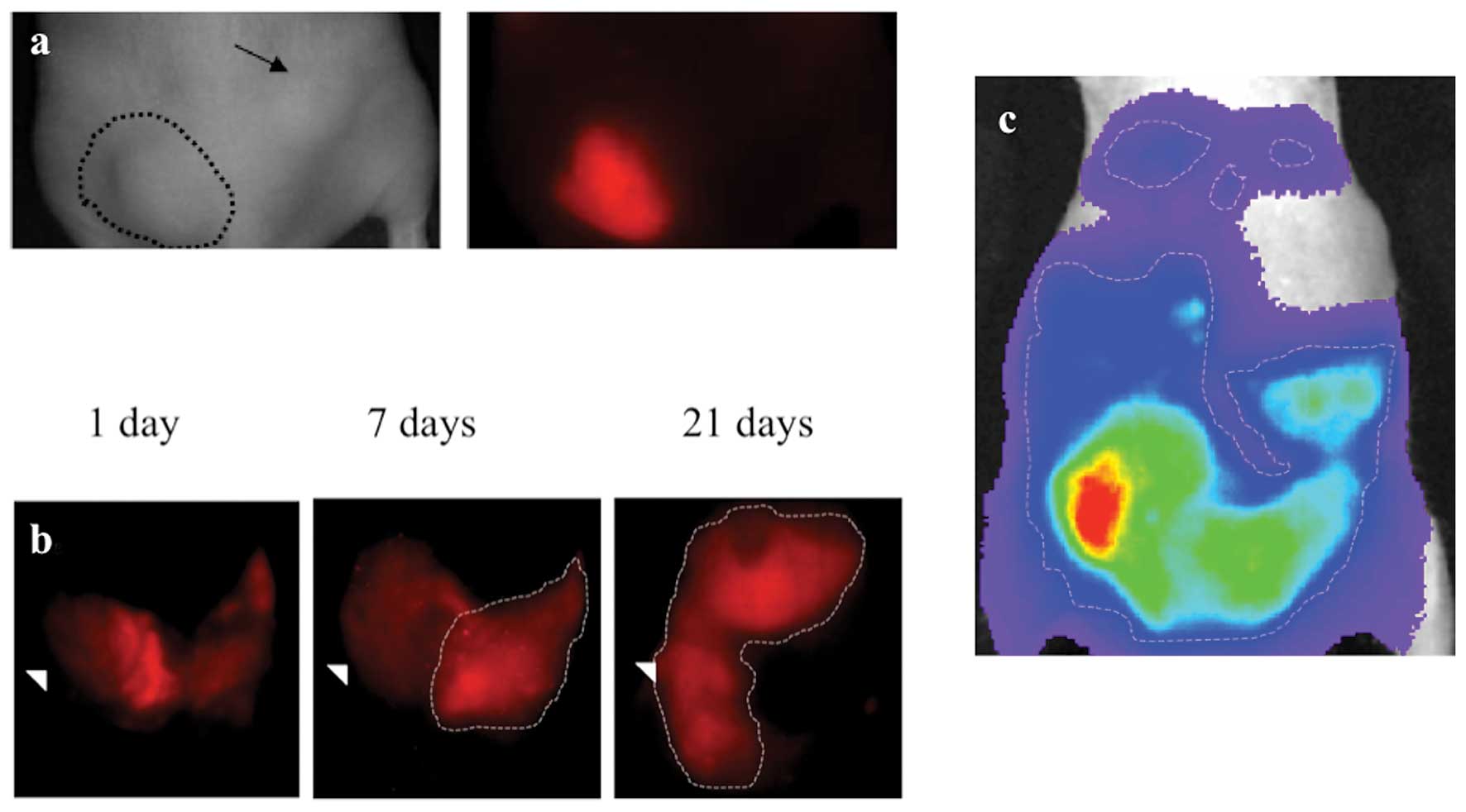
|
1
|
Bibby MC: Orthotopic models of cancer for
preclinical drug evaluation: advantages and disadvantages. Eur J
Cancer. 40:852–857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grisanzio C, Seeley A, Chang M, et al:
Orthotopic xenografts of RCC retain histological, immunophenotypic
and genetic features of tumours in patients. J Pathol. 225:212–221.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chan E, Patel A, Heston W and Larchian W:
Mouse orthotopic models for bladder cancer research. BJU Int.
104:1286–1291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hoffman RM: Orthotopic metastatic mouse
models for anticancer drug discovery and evaluation: a bridge to
the clinic. Invest New Drugs. 17:343–359. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang M, Jiang P, Sun FX, et al: A
fluorescent orthotopic bone metastasis model of human prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 59:781–786. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gros SJ, Dohrmann T, Rawnaq T, et al:
Orthotopic fluorescent peritoneal carcinomatosis model of
esophageal cancer. Anticancer Res. 30:3933–3938. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakataki E, Yano S, Matsumori Y, et al:
Novel orthotopic implantation model of human malignant pleural
mesothelioma (EHMES-10 cells) highly expressing vascular
endothelial growth factor and its receptor. Cancer Sci. 97:183–191.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Moolgavkar SH, Meza R and Turim J: Pleural
and peritoneal mesotheliomas in SEER: age effects and temporal
trends, 1973–2005. Cancer Causes Control. 20:935–944.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamaoka N, Kawasaki Y, Xu Y, et al:
Establishment of in vivo fluorescence imaging in mouse
models of malignant mesothelioma. Int J Oncol. 37:273–279.
2010.
|
|
10
|
Sloane BF: Cathepsin B and cystatins:
evidence for a role in cancer progression. Semin Cancer Biol.
1:137–152. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang W and El-Deiry WS: Bioluminescent
molecular imaging of endogenous and exogenous p53-mediated
transcription in vitro and in vivo using an HCT116 human colon
carcinoma xenograft model. Cancer Biol Ther. 2:196–202. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Roe OD, Anderssen E, Helge E, et al:
Genome-wide profile of pleural mesothelioma versus parietal and
visceral pleura: the emerging gene portrait of the mesothelioma
phenotype. PLoS One. 4:e65542004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Klipper-Aurbach Y, Wasserman M,
Braunspiegel-Weintrob N, et al: Mathematical formulae for the
prediction of the residual beta cell function during the first two
years of disease in children and adolescents with insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus. Med Hypotheses. 45:486–490. 1995.
|
|
14
|
Lankelma JM, Voorend DM, Barwari T, et al:
Cathepsin L, target in cancer treatment? Life Sci. 86:225–233.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
DeLong P, Carroll RG, Henry AC, et al:
Regulatory T cells and cytokines in malignant pleural effusions
secondary to mesothelioma and carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
4:342–346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamaguchi T, Naruishi K, Arai H, Nishimura
F and Takashiba S: IL-6/sIL-6R enhances cathepsin B and L
production via caveolin-1-mediated JNK-AP-1 pathway in human
gingival fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 217:423–432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gerber A, Wille A, Welte T, Ansorge S and
Buhling F: Interleukin-6 and transforming growth factor-β1 control
expression of cathepsins B and L in human lung epithelial cells. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 21:11–19. 2001.
|
|
18
|
D'Angelo ME, Bird PI, Peters C, Reinheckel
T, Trapani JA and Sutton VR: Cathepsin H is an additional
convertase of pro-granzyme B. J Biol Chem. 285:20514–20519. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Asagiri M, Hirai T, Kunigami T, et al:
Cathepsin K-dependent toll-like receptor 9 signaling revealed in
experimental arthritis. Science. 319:624–627. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagai A, Murakawa Y, Terashima M, et al:
Cystatin C and cathepsin B in CSF from patients with inflammatory
neurologic diseases. Neurology. 55:1828–1832. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Martin SL, Moffitt KL, McDowell A, et al:
Association of airway cathepsin B and S with inflammation in cystic
fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 45:860–868. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brutkiewicz S, Mendonca M, Stantz K, et
al: The expression level of luciferase within tumour cells can
alter tumour growth upon in vivo bioluminescence imaging.
Luminescence. 22:221–228. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|