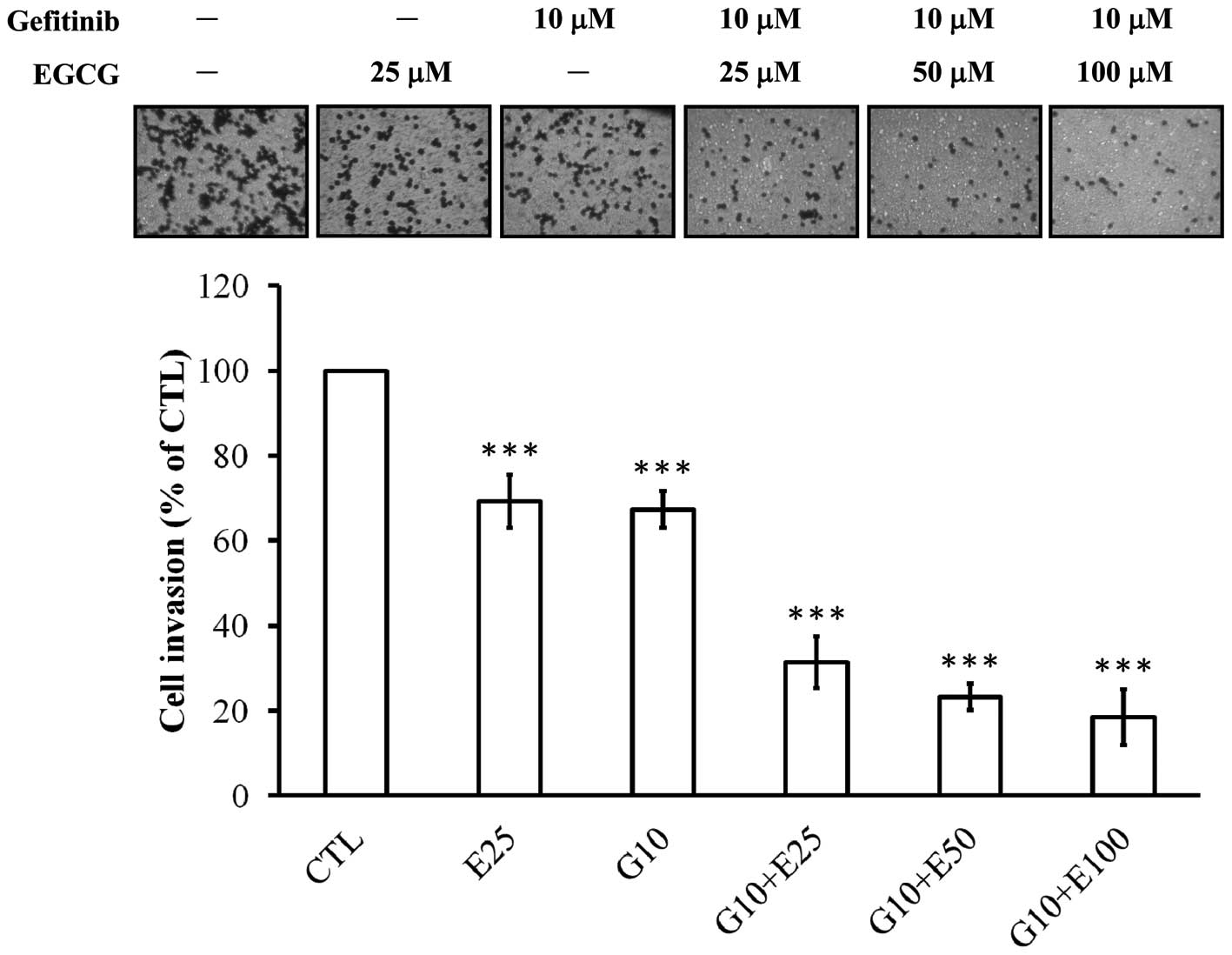
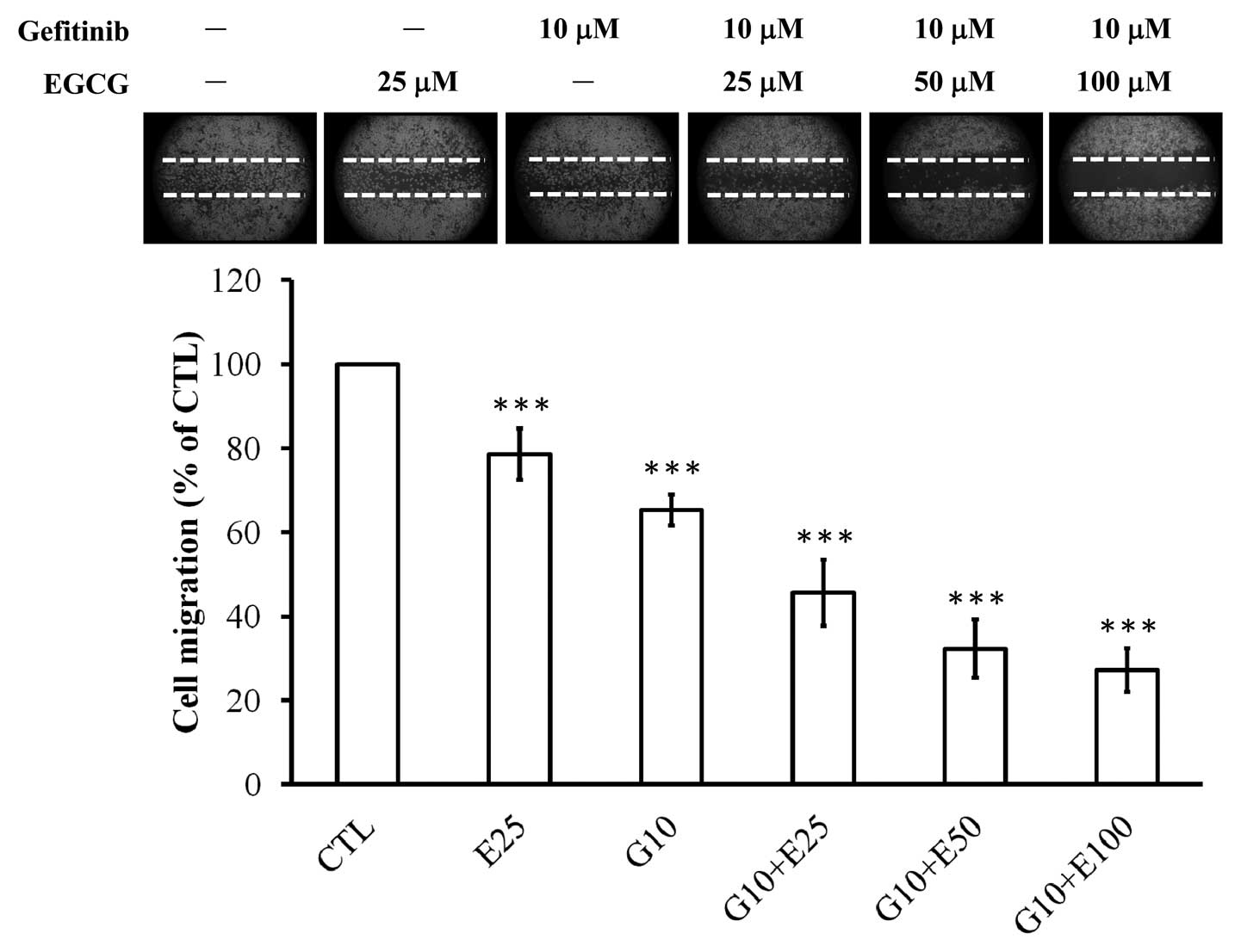
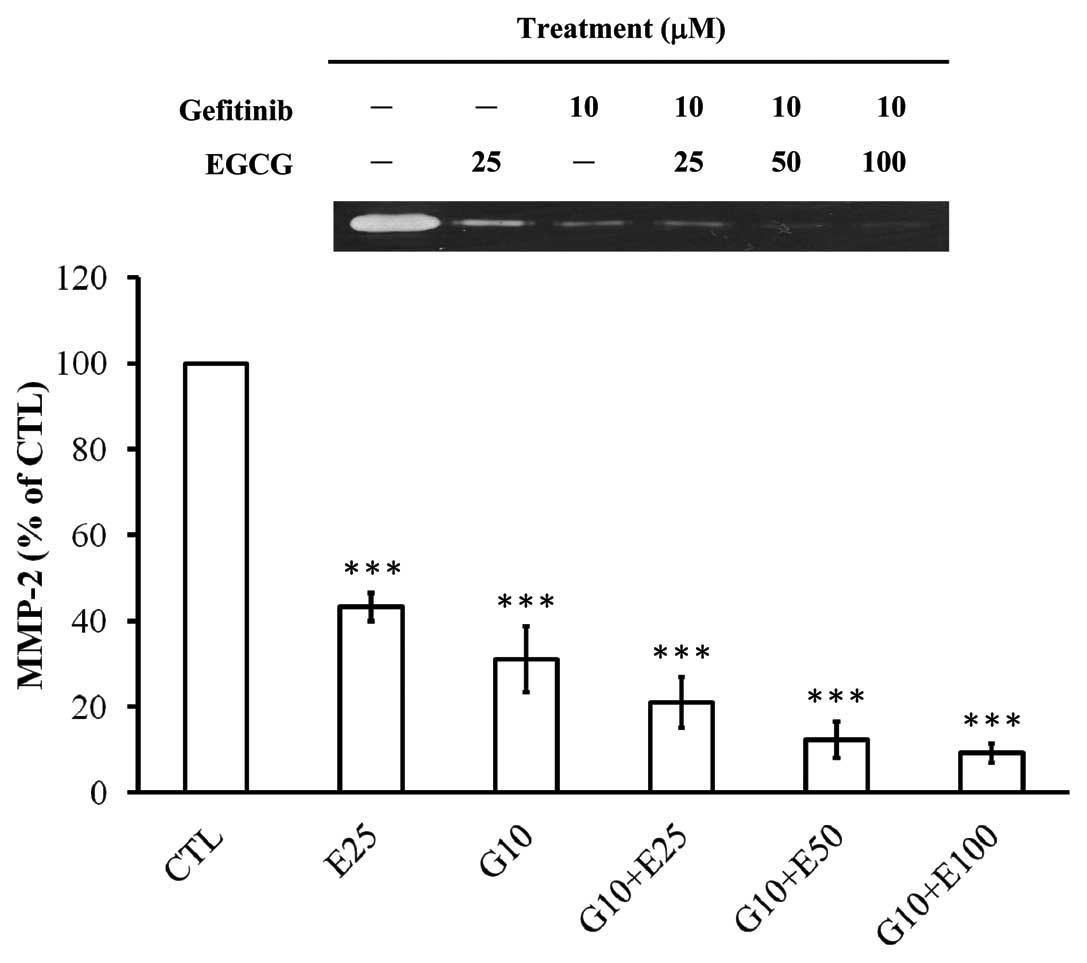
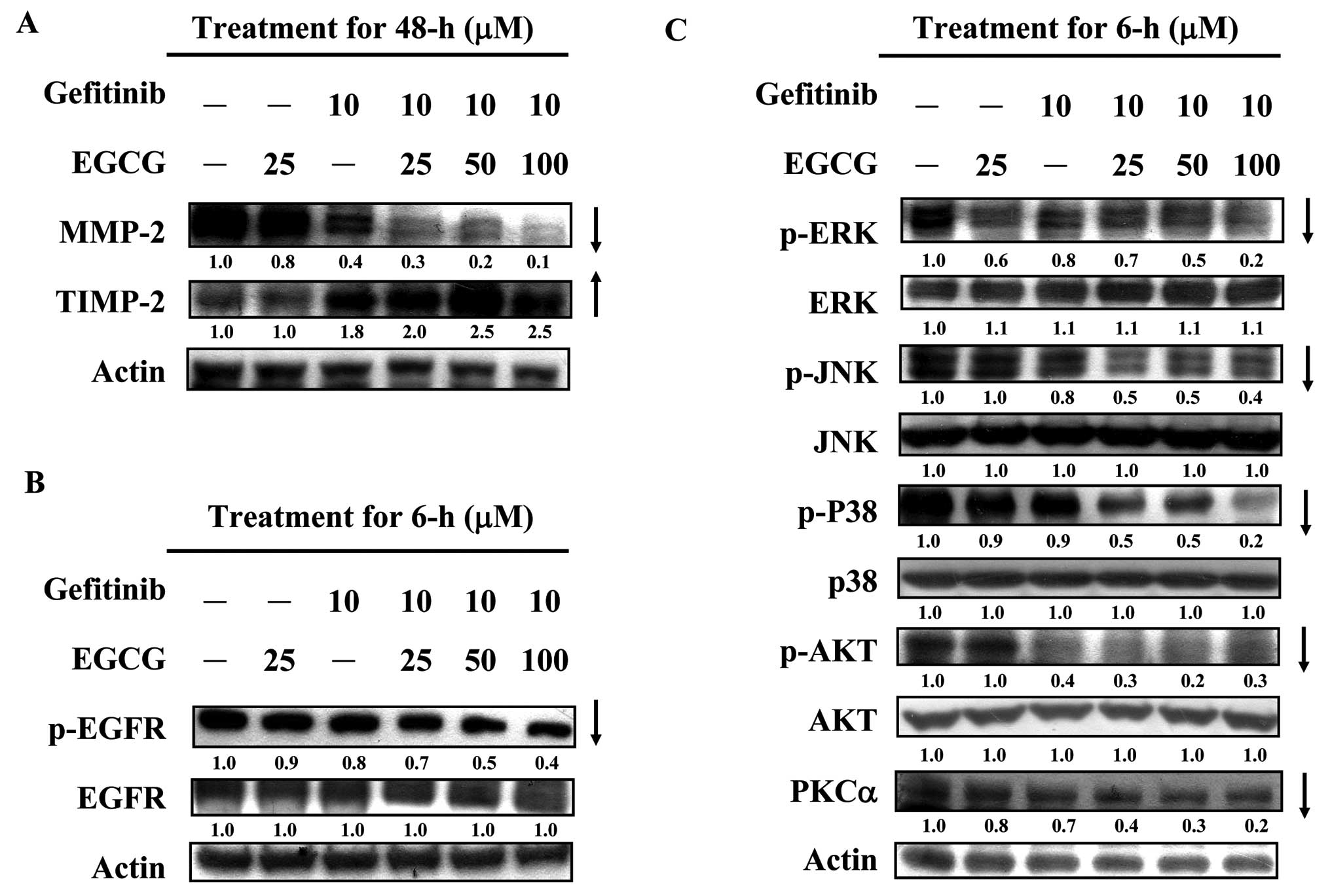
|
1
|
Liu SY, Lu CL, Chiou CT, et al: Surgical
outcomes and prognostic factors of oral cancer associated with
betel quid chewing and tobacco smoking in Taiwan. Oral Oncol.
46:276–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen PT, Kuan FC, Huang CE, et al:
Incidence and patterns of second primary malignancies following
oral cavity cancers in a prevalent area of betel-nut chewing: a
population-based cohort of 26,166 patients in Taiwan. Jpn J Clin
Oncol. 41:1336–1343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang SC, Tsai CC, Huang ST and Hong YJ:
Betel nut chewing and related factors in adolescent students in
Taiwan. Public Health. 117:339–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu FS, Yang JS, Yu CS, et al: Safrole
induces apoptosis in human oral cancer HSC-3 cells. J Dent Res.
90:168–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi Y, Kim SY, Kim SH, Yang J, Park K and
Byun Y: Inhibition of tumor growth by biodegradable microspheres
containing all-trans-retinoic acid in a human head-and-neck cancer
xenograft. Int J Cancer. 107:145–148. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Muir C and Weiland L: Upper aerodigestive
tract cancers. Cancer. 75:147–153. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Funk GF, Karnell LH, Robinson RA, Zhen WK,
Trask DK and Hoffman HT: Presentation, treatment, and outcome of
oral cavity cancer: a National Cancer Data Base report. Head Neck.
24:165–180. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sommer G, Rossa C, Chi AC, Neville BW and
Heise T: Implication of RNA-binding protein La in proliferation,
migration and invasion of lymph node-metastasized hypopharyngeal
SCC cells. PLoS One. 6:e254022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu Z, Lu N, Li C, et al: Oroxylin A
inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 expression and activation by
up-regulating tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and
suppressing the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett.
209:211–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ni L, Feng Y, Wan H, et al:
Angiotensin-(1–7) inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 human
lung adenocarcinoma cells through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt and
MAPK signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 27:783–790. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Kim SA, Kwon SM, Kim JA, Kang KW, Yoon JH
and Ahn SG: 5′-Nitro-indirubinoxime, an indirubin derivative,
suppresses metastatic ability of human head and neck cancer cells
through the inhibition of Integrin beta1/FAK/Akt signaling. Cancer
Lett. 306:197–204. 2011.
|
|
12
|
Liang X, Yang X, Tang Y, et al:
RNAi-mediated downregulation of urokinase plasminogen activator
receptor inhibits proliferation, adhesion, migration and invasion
in oral cancer cells. Oral Oncol. 44:1172–1180. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ono M and Kuwano M: Molecular mechanisms
of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation and response
to gefitinib and other EGFR-targeting drugs. Clin Cancer Res.
12:7242–7251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Normanno N, De Luca A, Bianco C, et al:
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling in cancer. Gene.
366:2–16. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schuler PJ, Boeckers P, Engers R, et al:
EGFR-specific T cell frequencies correlate with EGFR expression in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 9:1682011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chiang WF, Liu SY, Yen CY, et al:
Association of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene copy
number amplification with neck lymph node metastasis in
areca-associated oral carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 44:270–276. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Korner A, Mudduluru G, Manegold C and
Allgayer H: Enzastaurin inhibits invasion and metastasis in lung
cancer by diverse molecules. Br J Cancer. 103:802–811. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matsuo M, Sakurai H and Saiki I: ZD1839, a
selective epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor, shows antimetastatic activity using a hepatocellular
carcinoma model. Mol Cancer Ther. 2:557–561. 2003.
|
|
19
|
Yamaoka T, Frey MR, Dise RS, Bernard JK
and Polk DB: Specific epidermal growth factor receptor
autophosphorylation sites promote mouse colon epithelial cell
chemotaxis and restitution. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 301:G368–G376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hwang YP, Yun HJ, Choi JH, et al:
Suppression of EGF-induced tumor cell migration and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by capsaicin via the inhibition of
EGFR-mediated FAK/Akt, PKC/Raf/ERK, p38 MAPK, and AP-1 signaling.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:594–605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rebucci M, Peixoto P, Dewitte A, et al:
Mechanisms underlying resistance to cetuximab in the HNSCC cell
line: role of AKT inhibition in bypassing this resistance. Int J
Oncol. 38:189–200. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dias JD, Guse K, Nokisalmi P, et al:
Multimodal approach using oncolytic adenovirus, cetuximab,
chemotherapy and radiotherapy in HNSCC low passage tumour cell
cultures. Eur J Cancer. 46:625–635. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wagenblast J, Baghi M, Arnoldner C, et al:
Effect of bortezomib and cetuximab in EGF-stimulated HNSCC.
Anticancer Res. 28:2239–2243. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jouan-Hureaux V, Boura C, Merlin JL and
Faivre B: Modulation of endothelial cell network formation in vitro
by molecular signaling of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
(HNSCC) exposed to cetuximab. Microvasc Res. 83:131–137. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu Y, Liu P, Van den Bergh F, et al:
Modulation of gene expression and cell-cycle signaling pathways by
the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib (Iressa) in rat urinary bladder
cancer. Cancer Prev Res. 5:248–259. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Normanno N, De Luca A, Maiello MR, et al:
The MEK/MAPK pathway is involved in the resistance of breast cancer
cells to the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor gefitinib. J Cell
Physiol. 207:420–427. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Milano G, Spano JP and Leyland-Jones B:
EGFR-targeting drugs in combination with cytotoxic agents: from
bench to bedside, a contrasted reality. Br J Cancer. 99:1–5. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peng G, Wargovich MJ and Dixon DA:
Anti-proliferative effects of green tea polyphenol EGCG on
Ha-Ras-induced transformation of intestinal epithelial cells.
Cancer Lett. 238:260–270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Collins QF, Liu HY, Pi J, Liu Z, Quon MJ
and Cao W: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), a green tea
polyphenol, suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis through
5′-AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 282:30143–30149.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo S, Yang S, Taylor C and Sonenshein GE:
Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3 gallate (EGCG) affects gene
expression of breast cancer cells transformed by the carcinogen
7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene. J Nutr. 135:S2978–S2986.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahmed S, Wang N, Lalonde M, Goldberg VM
and Haqqi TM: Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate
(EGCG) differentially inhibits interleukin-1 beta-induced
expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -13 in human
chondrocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 308:767–773. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Annabi B, Currie JC, Moghrabi A and
Beliveau R: Inhibition of HuR and MMP-9 expression in
macrophage-differentiated HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells by green tea
polyphenol EGCg. Leuk Res. 31:1277–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu L, Lai CQ, Nie L, et al: The
modulation of endothelial cell gene expression by green tea
polyphenol-EGCG. Mol Nutr Food Res. 52:1182–1192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Siddiqui IA, Malik A, Adhami VM, et al:
Green tea polyphenol EGCG sensitizes human prostate carcinoma LNCaP
cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis and synergistically inhibits
biomarkers associated with angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene.
27:2055–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Masuda M, Wakasaki T, Toh S, Shimizu M and
Adachi S: Chemoprevention of head and neck cancer by green tea
extract: EGCG-the role of EGFR signaling and ‘Lipid Raft’. J Oncol.
2011:5401482011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Multitargeted
therapy of cancer by green tea polyphenols. Cancer Lett.
269:269–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen PN, Chu SC, Kuo WH, Chou MY, Lin JK
and Hsieh YS: Epigallocatechin-3 gallate inhibits invasion,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and tumor growth in oral cancer
cells. J Agric Food Chem. 59:3836–3844. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang L, Ji N, Zhou Y, et al: CAL 27 is an
oral adenosquamous carcinoma cell line. Oral Oncol. 45:e204–e207.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fan MJ, Lin YC, Shih HD, et al: Crude
extracts of Agaricus brasiliensis induce apoptosis in human oral
cancer CAL 27 cells through a mitochondria-dependent pathway. In
Vivo. 25:355–366. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chien MH, Ying TH, Hsieh YS, et al:
Dioscorea nipponica Makino inhibits migration and invasion of human
oral cancer HSC-3 cells by transcriptional inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinase-2 through modulation of CREB and AP-1 activity.
Food Chem Toxicol. 50:558–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lai KC, Huang AC, Hsu SC, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate (BITC) inhibits migration and invasion of human
colon cancer HT29 cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
and urokinase plasminogen (uPA) through PKC and MAPK signaling
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 58:2935–2942. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yu FS, Huang AC, Yang JS, et al: Safrole
induces cell death in human tongue squamous cancer SCC-4 cells
through mitochondria-dependent caspase activation cascade apoptotic
signaling pathways. Environ Toxicol. 27:433–444. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Troeberg L and Nagase H: Zymography of
metalloproteinases. Curr Protoc Protein Sci. Chapter 21(Unit 21):
152004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lin JJ, Hsu HY, Yang JS, et al: Molecular
evidence of anti-leukemia activity of gypenosides on human myeloid
leukemia HL-60 cells in vitro and in vivo using a HL-60 cells
murine xenograft model. Phytomedicine. 18:1075–1085. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chang YC, Lai TY, Yu CS, et al: Emodin
induces apoptotic death in murine myelomonocytic leukemia WEHI-3
cells in vitro and enhances phagocytosis in leukemia mice in vivo.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:5235962011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chou ST, Peng HY, Chang CT, et al:
Zanthoxylum ailanthoides Sieb and Zucc. extract inhibits growth and
induces cell death through G2/M-phase arrest and activation of
apoptotic signals in colo 205 human colon adenocarcinoma cells.
Anticancer Res. 31:1667–1676. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Huang AC, et al:
Chrysophanol induces necrosis through the production of ROS and
alteration of ATP levels in J5 human liver cancer cells. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 54:967–976. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Ma CY, et al:
Danthron, an anthraquinone derivative, induces DNA damage and
caspase cascades-mediated apoptosis in SNU-1 human gastric cancer
cells through mitochondrial permeability transition pores and
Bax-triggered pathways. Chem Res Toxicol. 24:20–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chung JG, Chang HL, Lin WC, Yeh FT and
Hung CF: Effects of ibuprofen on arylamine N-acetyltransferase
activity in human colon tumor cells. J Appl Toxicol. 19:1–6. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gardina PJ, Clark TA, Shimada B, et al:
Alternative splicing and differential gene expression in colon
cancer detected by a whole genome exon array. BMC Genomics.
7:3252006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yeh MH, Tsai TC, Kuo HP, et al: Lentiviral
short hairpin RNA screen of human kinases and phosphatases to
identify potential biomarkers in oral squamous cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 39:1221–1231. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Saeed AI, Sharov V, White J, et al: TM4: a
free, open-source system for microarray data management and
analysis. Biotechniques. 34:374–378. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang HL, Kuo YH, Tsai CT, et al:
Anti-metastatic activities of Antrodia camphorata against human
breast cancer cells mediated through suppression of the MAPK
signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:290–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Deng YT and Lin JK: EGCG inhibits the
invasion of highly invasive CL1–5 lung cancer cells through
suppressing MMP-2 expression via JNK signaling and induces G2/M
arrest. J Agric Food Chem. 59:13318–13327. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sok JC, Coppelli FM, Thomas SM, et al:
Mutant epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFRvIII) contributes to
head and neck cancer growth and resistance to EGFR targeting. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:5064–5073. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Barnes EL and
Tweardy DJ: Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis of
transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor
receptor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and
neck. Cancer. 78:1284–1292. 1996.
|
|
57
|
Rubin Grandis J, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, et
al: Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma and patient survival. J Natl Cancer Inst.
90:824–832. 1998.
|
|
58
|
Zhang X, Zhang H, Tighiouart M, et al:
Synergistic inhibition of head and neck tumor growth by green tea
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Int J Cancer. 123:1005–1014. 2008.
|
|
59
|
Wu PP, Kuo SC, Huang WW, et al:
(−)-Epigallocatechin gallate induced apoptosis in human adrenal
cancer NCI-H295 cells through caspase-dependent and
caspase-independent pathway. Anticancer Res. 29:1435–1442.
2009.
|
|
60
|
Chen NG, Lu CC, Lin YH, et al: Proteomic
approaches to study epigallocatechin gallate-provoked apoptosis of
TSGH-8301 human urinary bladder carcinoma cells: roles of AKT and
heat shock protein 27-modulated intrinsic apoptotic pathways. Oncol
Rep. 26:939–947. 2011.
|