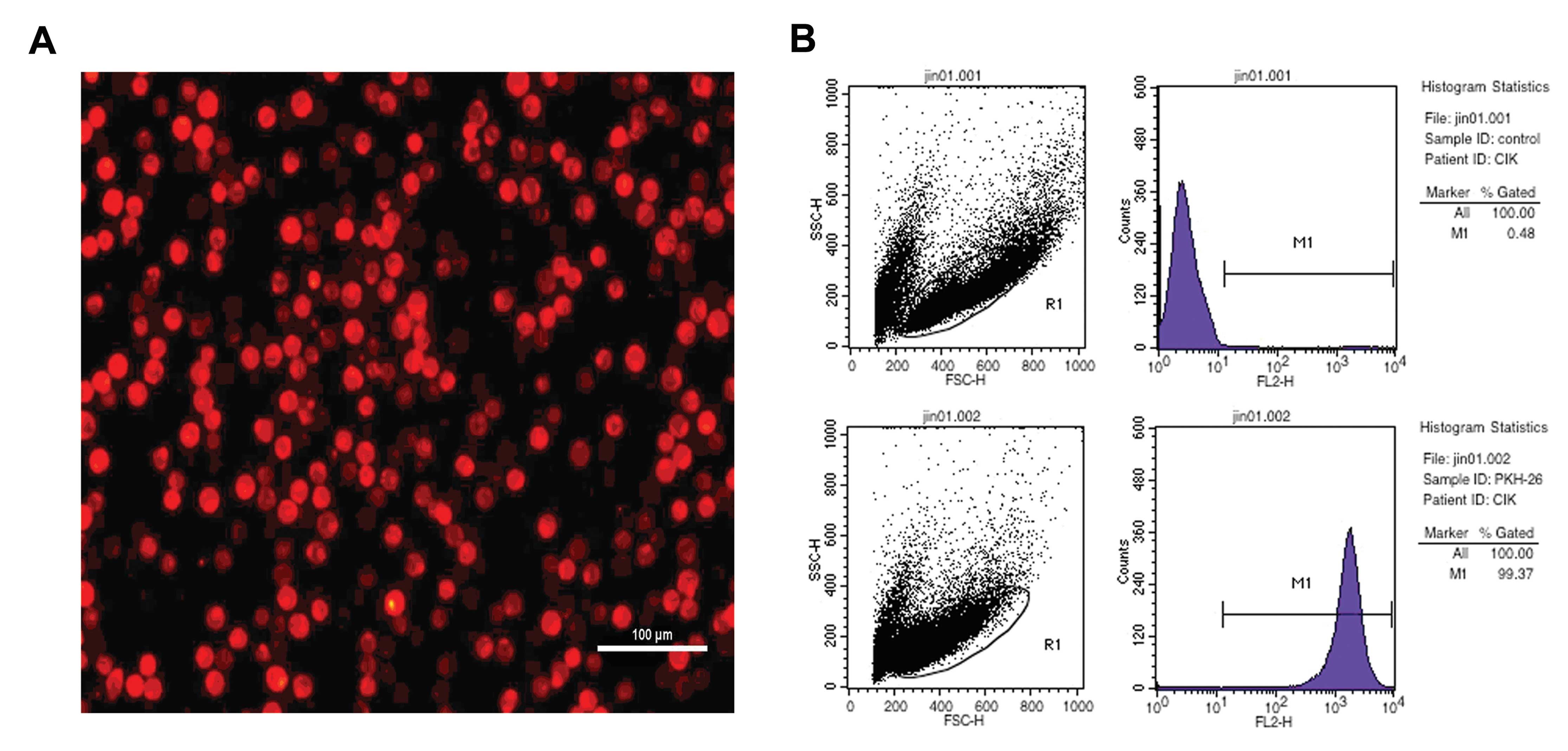
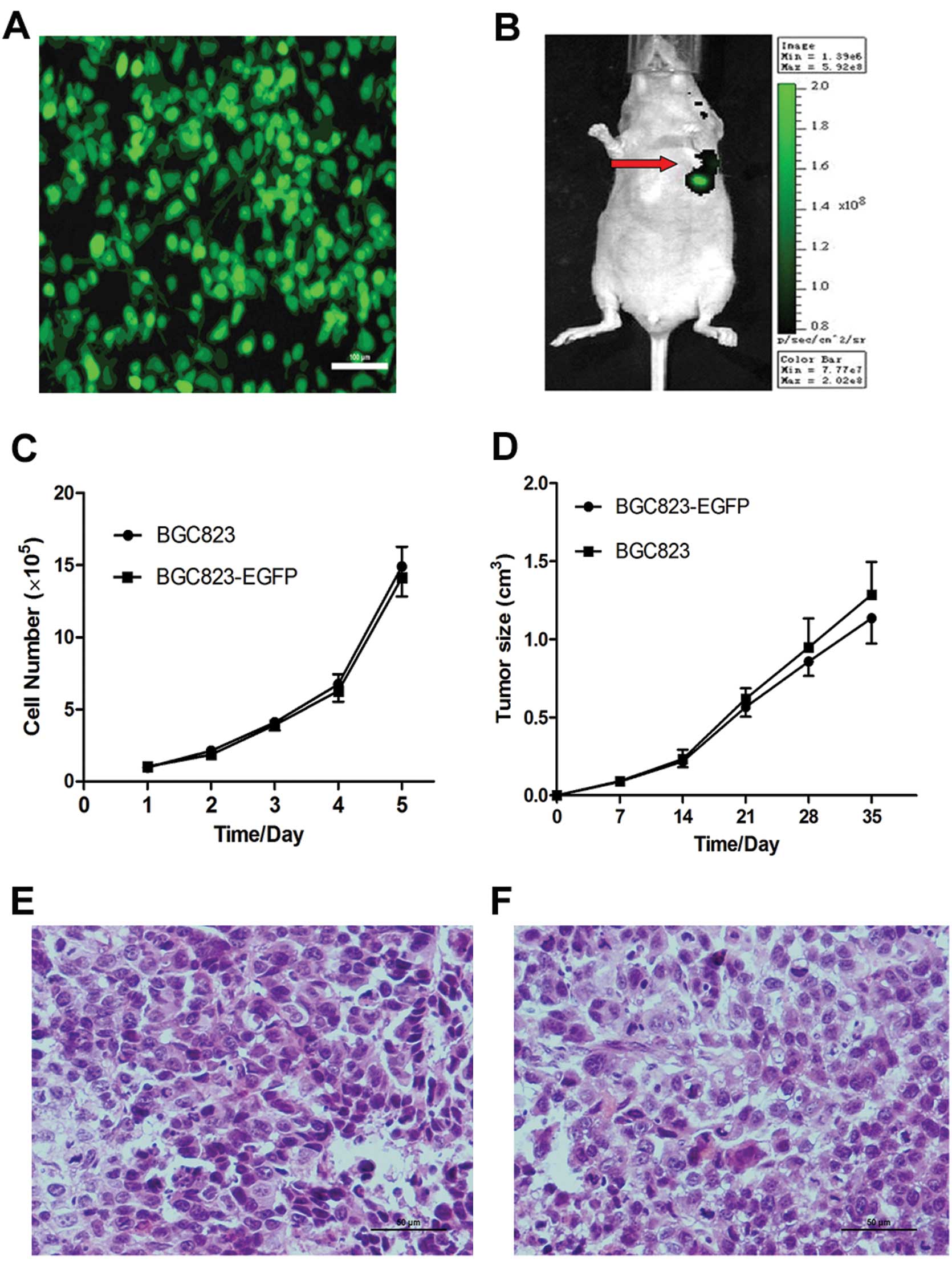
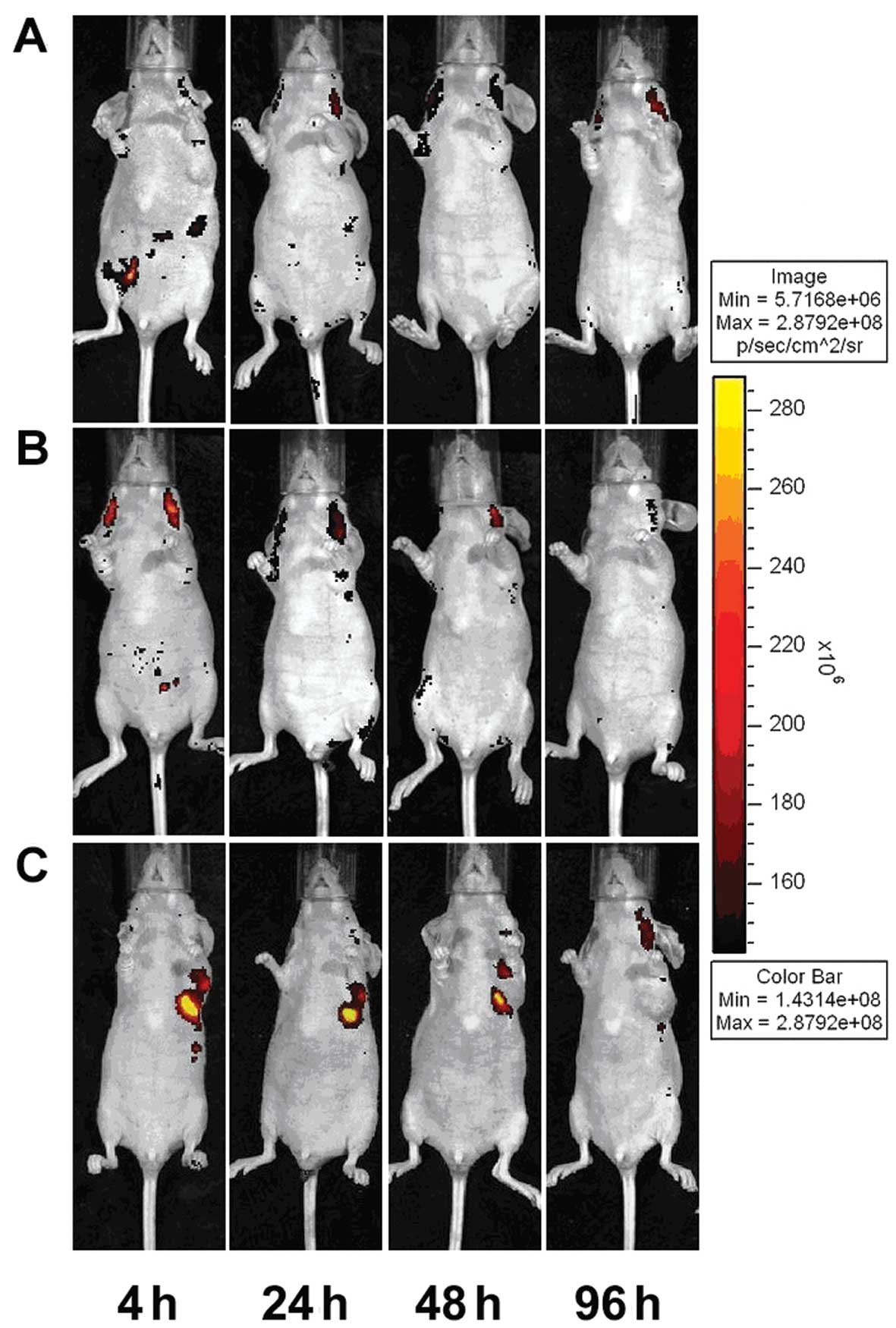
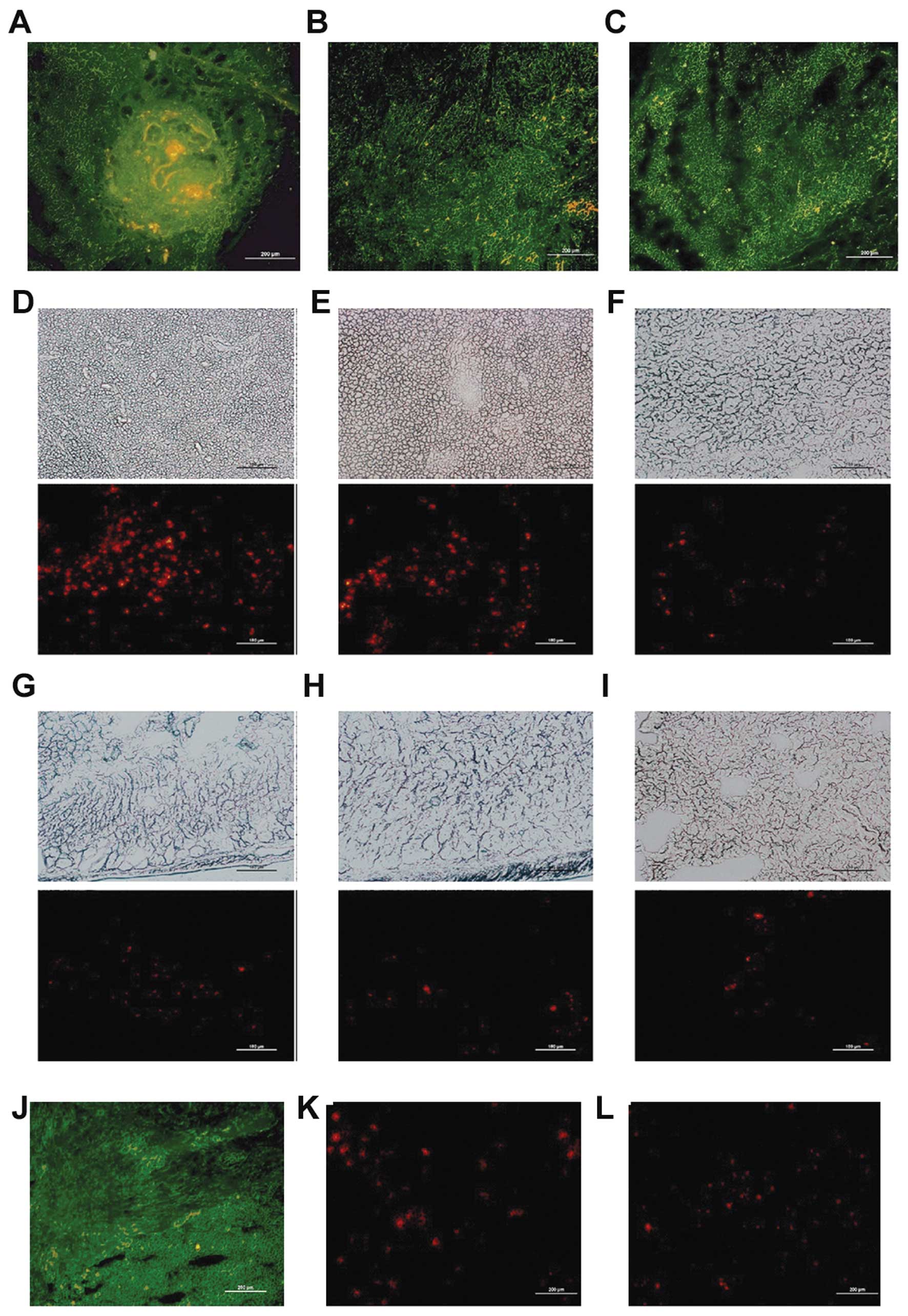
|
1
|
Kamangar F, Dores GM and Anderson WF:
Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five
continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in
different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol.
24:2137–2150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kim HM, Kang JS, Lim J, et al: Antitumor
activity of cytokine-induced killer cells in nude mouse xenograft
model. Arch Pharm Res. 32:781–787. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Klebanoff CA, Gattinoni L, Palmer DC, et
al: Determinants of successful CD8+ T-cell adoptive
immunotherapy for large established tumors in mice. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:5343–5352. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marcus A and Eshhar Z: Tumor-specific
allogeneic cells for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
11:1551–1554. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
June CH: Adoptive T cell therapy for
cancer in the clinic. J Clin Invest. 117:1466–1476. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Stasi A, Tey SK, Dotti G, et al:
Inducible apoptosis as a safety switch for adoptive cell therapy. N
Engl J Med. 365:1673–1683. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhong JH, Ma L, Wu LC, et al: Adoptive
immunotherapy for postoperative hepatocellular carcinoma: a
systematic review. Int J Clin Pract. 66:21–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Toh U, Fujii T, Mishima M, et al:
Conventional chemotherapy combined with the repetitive immune cell
transfer for patients with refractory advanced gastric cancer. Gan
To Kagaku Ryoho. 34:1931–1933. 2007.(In Japanese).
|
|
9
|
Linn YC and Hui KM: Cytokine-induced
NK-like T cells: from bench to bedside. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2010:4357452010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sangiolo D: Cytokine induced killer cells
as promising immunotherapy for solid tumors. J Cancer. 2:363–368.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma Y, Zhang Z, Tang L, et al:
Cytokine-induced killer cells in the treatment of patients with
solid carcinomas: a systematic review and pooled analysis.
Cytotherapy. 14:483–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wright SE, Rewers-Felkins KA, Quinlin IS,
et al: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte immunotherapy for ovarian cancer: a
pilot study. J Immunother. 35:196–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hickey MJ, Malone CC, Erickson KE, et al:
Implementing preclinical study findings to protocol design:
translational studies with alloreactive CTL for gliomas. Am J
Transl Res. 4:114–126. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang M, Baranov E, Jiang P, et al:
Whole-body optical imaging of green fluorescent protein-expressing
tumors and metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:1206–1211. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chishima T, Miyagi Y, Wang X, et al:
Cancer invasion and micrometastasis visualized in live tissue by
green fluorescent protein expression. Cancer Res. 57:2042–2047.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heim R, Cubitt AB and Tsien RY: Improved
green fluorescence. Nature. 373:663–664. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kaneko K, Yano M, Tsujinaka T, et al:
Establishment of a visible peritoneal micrometastatic model from a
gastric adenocarcinoma cell line by green fluorescent protein. Int
J Oncol. 16:893–898. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaneko K, Yano M, Yamano T, et al:
Detection of peritoneal micrometastases of gastric carcinoma with
green fluorescent protein and carcinoembryonic antigen promoter.
Cancer Res. 61:5570–5574. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmidt-Wolf IG, Negrin RS, Kiem HP, Blume
KG and Weissman IL: Use of a SCID mouse/human lymphoma model to
evaluate cytokine-induced killer cells with potent antitumor cell
activity. J Exp Med. 174:139–149. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Linn YC, Lau LC and Hui KM: Generation of
cytokine-induced killer cells from leukaemic samples with in vitro
cytotoxicity against autologous and allogeneic leukaemic blasts. Br
J Haematol. 116:78–86. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lopez RD, Waller EK, Lu PH and Negrin RS:
CD58/LFA-3 and IL-12 provided by activated monocytes are critical
in the in vitro expansion of CD56+ T cells. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 49:629–640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Niam M, Linn YC, Fook Chong S, et al:
Clinical scale expansion of cytokine-induced killer cells is
feasible from healthy donors and patients with acute and chronic
myeloid leukemia at various stages of therapy. Exp Hematol.
39:897–903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hazelrigg MR, Hirsch JI and Merchant RE:
Distribution of adoptively transferred, tumor-sensitized
lymphocytes in the glioma-bearing rat. J Neurooncol. 60:143–150.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Skitzki J, Craig RA, Okuyama R, et al:
Donor cell cycling, trafficking, and accumulation during adoptive
immunotherapy for murine lung metastases. Cancer Res. 64:2183–2191.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Edinger M, Cao YA, Verneris MR, Bachmann
MH, Contag CH and Negrin RS: Revealing lymphoma growth and the
efficacy of immune cell therapies using in vivo bioluminescence
imaging. Blood. 101:640–648. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Nishimura R, Baker J, Beilhack A, et al:
In vivo trafficking and survival of cytokine-induced killer cells
resulting in minimal GVHD with retention of antitumor activity.
Blood. 112:2563–2574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Brandau S and Bohle A: Activation of
natural killer cells by Bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Eur Urol.
39:518–524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Akagi J, Takai E, Tamori Y and Ogawa M:
CD3+CD56+CD8+ cells demonstrating
a suppressor T cell-like function in the peripheral blood of colon
cancer patients. Int J Oncol. 19:561–566. 2001.
|
|
29
|
Nagaraj S, Ziske C and Schmidt-Wolf IG:
Human cytokine-induced killer cells have enhanced in vitro
cytolytic activity via non-viral interleukin-2 gene transfer. Genet
Vaccines Ther. 2:122004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marten A, Renoth S, von Lilienfeld-Toal M,
et al: Enhanced lytic activity of cytokine-induced killer cells
against multiple myeloma cells after co-culture with
idiotype-pulsed dendritic cells. Haematologica. 86:1029–1037.
2001.
|
|
31
|
Ziske C, Marten A, Schottker B, et al:
Resistance of pancreatic carcinoma cells is reversed by coculturing
NK-like T cells with dendritic cells pulsed with tumor-derived RNA
and CA 19-9. Mol Ther. 3:54–60. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van Spriel AB, van Ojik HH and van De
Winkel JG: Immunotherapeutic perspective for bispecific antibodies.
Immunol Today. 21:391–397. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Flieger D, Kufer P, Beier I, Sauerbruch T
and Schmidt-Wolf IG: A bispecific single-chain antibody directed
against EpCAM/CD3 in combination with the cytokines interferon
alpha and interleukin-2 efficiently retargets T and
CD3+CD56+ natural-killer-like T lymphocytes
to EpCAM-expressing tumor cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
49:441–448. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lutterbuese R, Raum T, Kischel R, et al:
Potent control of tumor growth by CEA/CD3-bispecific single-chain
antibody constructs that are not competitively inhibited by soluble
CEA. J Immunother. 32:341–352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Savage P, Millrain M, Dimakou S, Stebbing
J and Dyson J: Expansion of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells in
vitro and in vivo using MHC class I tetramers. Tumour Biol.
28:70–76. 2007.
|
|
36
|
Morishima N, Mizoguchi I, Okumura M, et
al: A pivotal role for interleukin-27 in CD8+ T cell
functions and generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2010:6054832010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yee C, Thompson JA, Byrd D, et al:
Adoptive T cell therapy using antigen-specific CD8+ T
cell clones for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma:
in vivo persistence, migration, and antitumor effect of transferred
T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:16168–16173. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mackensen A, Meidenbauer N, Vogl S, Laumer
M, Berger J and Andreesen R: Phase I study of adoptive T-cell
therapy using antigen-specific CD8+ T cells for the
treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol.
24:5060–5069. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Butler MO, Lee JS, Ansen S, et al:
Long-lived antitumor CD8+ lymphocytes for adoptive
therapy generated using an artificial antigen-presenting cell. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:1857–1867. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamaguchi Y, Ohshita A, Hironaka K, et al:
Adoptive immunotherapy using autologous lymphocytes sensitized with
HLA class I-matched allogeneic tumor cells. Oncol Rep. 16:165–169.
2006.
|