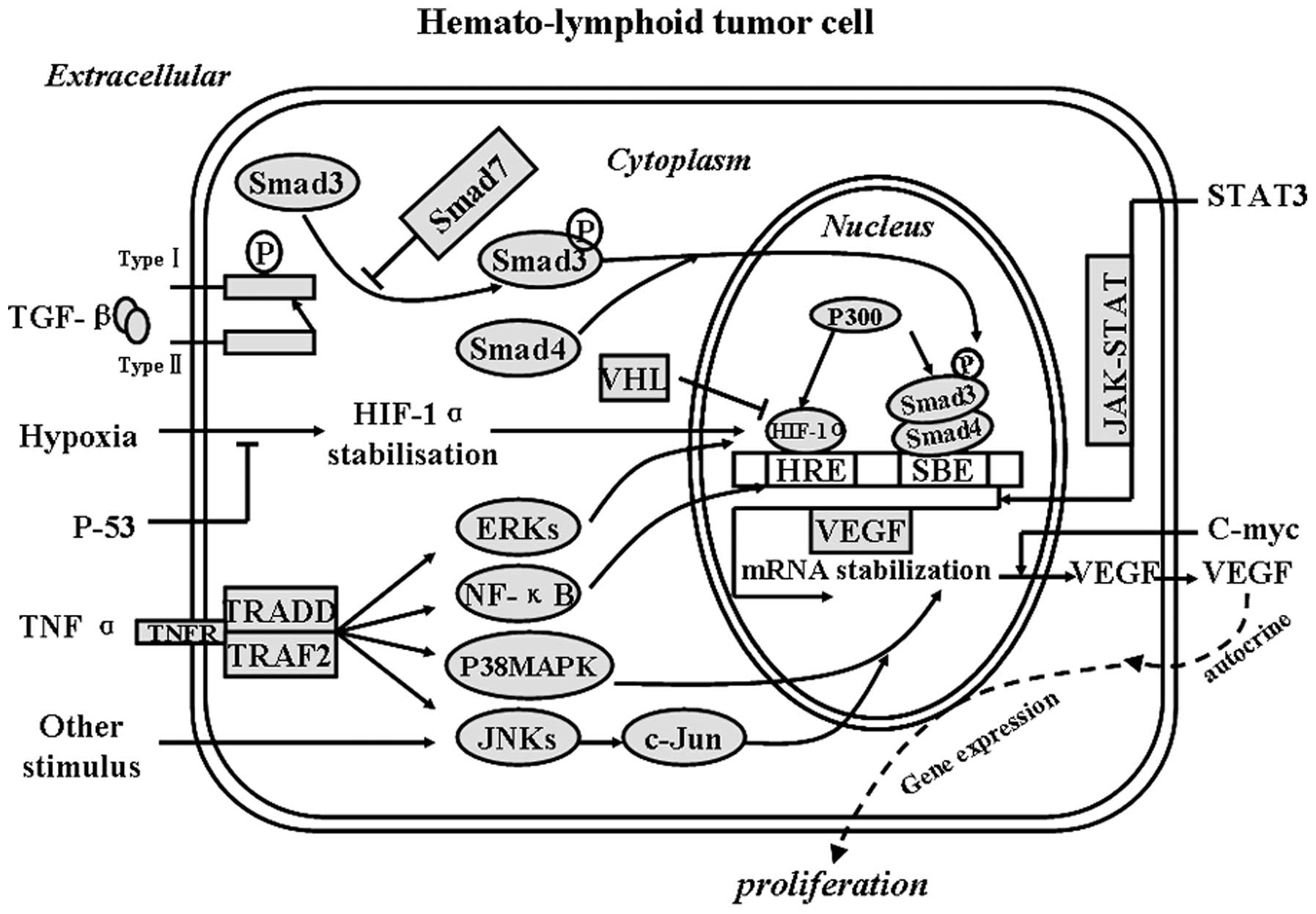
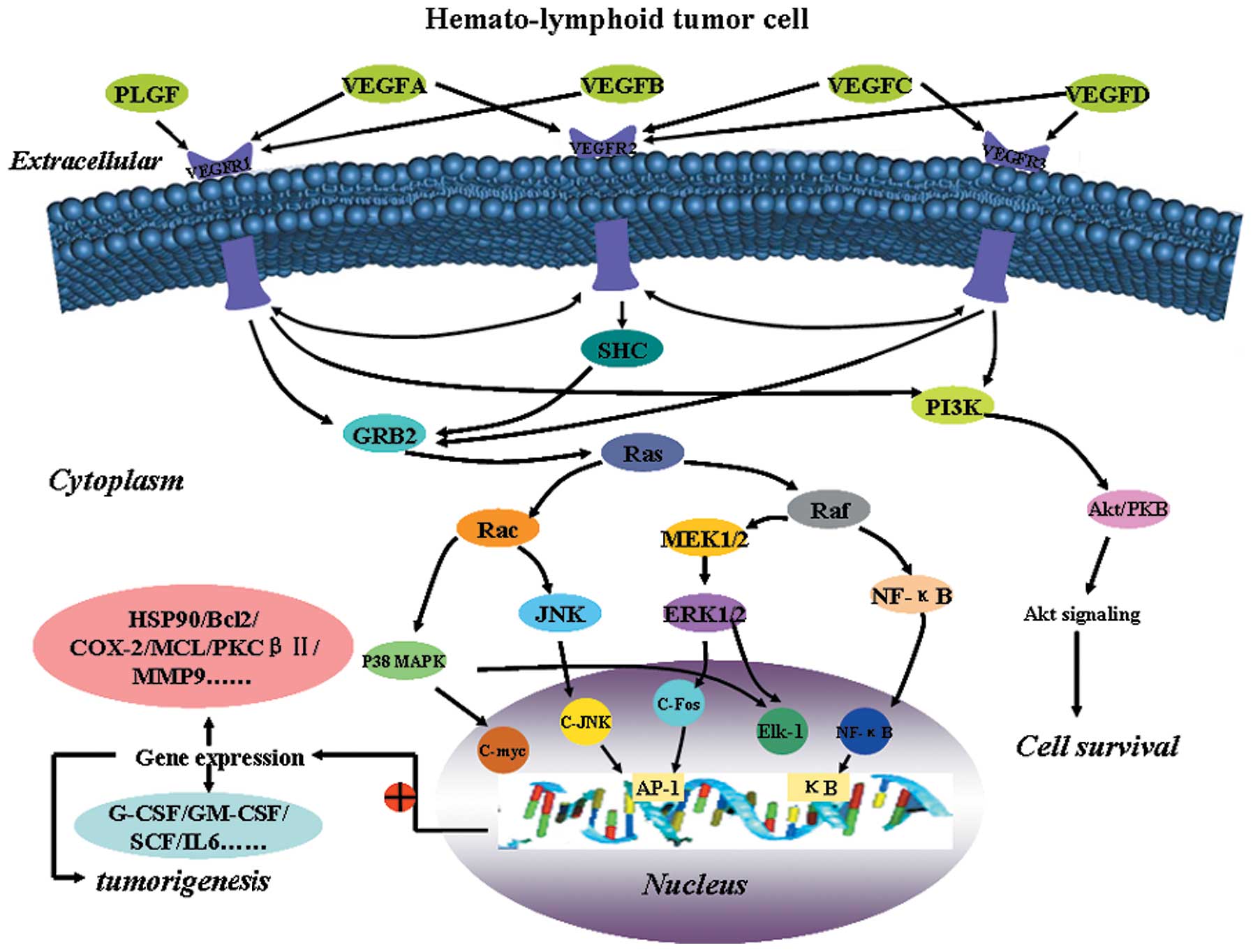
|
1
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ellis LM and Hicklin DJ: VEGF-targeted
therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:579–591. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Medinger M, Fischer N and Tzankov A:
Vascular endothelial growth factor-related pathways in
hemato-lymphoid malignancies. J Oncol. 2010:7297252010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Aguayo A, Kantarjian HM, Estey EH, et al:
Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor levels have prognostic
significance in patients with acute myeloid leukemia but not in
patients with myelodysplastic syndromes. Cancer. 95:1923–1930.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhu Z, Hattori K, Zhang H, et al:
Inhibition of human leukemia in an animal model with human
antibodies directed against vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2. Correlation between antibody affinity and biological
activity. Leukemia. 17:604–611. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Benouchan M and Colombo BM:
Anti-angiogenic strategies for cancer therapy. Int J Oncol.
27:563–571. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferrara N and Henzel WJ: Pituitary
follicular cell secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor
specific for vascular endothelial cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
161:8511989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao Y: Positive and negative modulation of
angiogenesis by VEGFR1 ligands. Sci Signal. 2:re12009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Zhou F, Han W, et al: VEGFR-3
ligand-binding and kinase activity are required for
lymphangiogenesis but not for angiogenesis. Cell Res. 20:1319–1331.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Y, Hooper AT, Zhong Z, et al: The
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR-1) supports
growth and survival of human breast carcinoma. Int J Cancer.
119:1519–1529. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Autiero M, Luttun A, Tjwa M and Carmeliet
P: Placental growth factor and its receptor, vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor-1: novel targets for stimulation of ischemic
tissue revascularization and inhibition of angiogenic and
inflammatory disorders. J Thromb Haemost. 1:1356–1370. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Holmes K, Roberts OL, Thomas AM and Cross
MJ: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: structure,
function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell
Signal. 19:2003–2012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Brekken RA, Overholser JP, Stastny VA,
Waltenberger J, Minna JD and Thorpe PE: Selective inhibition of
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor 2 (KDR/Flk-1)
activity by a monoclonal anti-VEGF antibody blocks tumor growth in
mice. Cancer Res. 60:5117–5124. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katoh O, Tauchi H, Kawaishi K, Kimura A
and Satow Y: Expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) receptor gene, KDR, in hematopoietic cells and inhibitory
effect of VEGF on apoptotic cell death caused by ionizing
radiation. Cancer Res. 55:5687–5692. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cursiefen C, Chen L, Borges LP, et al:
VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in
inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment. J Clin
Invest. 113:1040–1050. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Adams J, Carder PJ, Downey S, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in breast cancer:
comparison of plasma, serum and tissue VEGF and microvessel density
and effects of tamoxifen. Cancer Res. 60:2898–2905. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kay NE, Bone ND, Tschumper RC, et al:
B-CLL cells are capable of synthesis and secretion of both pro- and
anti-angiogenic molecules. Leukemia. 16:911–919. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rafii S, Lyden D, Benezra R, Hattori K and
Heissig B: Vascular and haematopoietic stem cells: novel targets
for anti-angiogenesis therapy? Nat Rev Cancer. 2:826–835. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shweiki D, Itin A, Soffer D and Keshet E:
Vascular endothelial growth factor induced by hypoxia may mediate
hypoxia-initiated angiogenesis. Nature. 359:843–845. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dor Y, Porat R and Keshet E: Vascular
endothelial growth factor and vascular adjustments to perturbations
in oxygen homeostasis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 280:C1367–C1374.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kaelin WG Jr: The von Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor protein and clear cell renal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
13:680s–682s. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cong XL, Li B, Yang RC, Feng SZ, Chen SJ
and Han ZC: Enhanced growth suppression of Philadephia1 leukemia
cells by targeting bcr3/abl2 and VEGF through antisense strategy.
Leukemia. 19:1517–1524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghosh AK, Shanafelt TD, Cimmino A, et al:
Aberrant regulation of pVHL levels by microRNA promotes the
HIF/VEGF axis in CLL B cells. Blood. 113:5568–5574. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Withey JM, Marley SB, Kaeda J, Harvey AJ,
Crompton MR and Gordon MY: Targeting primary human leukemia cells
with RNA interference: Bcr-Abl targeting inhibits myeloid
progenitor self-renewal in chronic myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J
Haematol. 129:377–380. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ghosh AK, Secreto CR, Knox TR, Ding W,
Mukhopadhyay D and Kay NE: Circulating microvesicles in B-cell
chronic lymphocytic leukemia can stimulate marrow stromal cells:
implications for disease progression. Blood. 115:1755–1764. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Ahn KS, et al:
Targeting signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for
prevention and therapy of cancer:modern target but ancient
solution. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1091:151–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eriksen KW, Kaltoft K, Mikkelsen G, et al:
Constitutive STAT3-activation in Sezary syndrome: tyrphostin AG490
inhibits STAT3-activation, interleukin-2 receptor expression and
growth of leukemic Sezary cells. Leukemia. 15:787–793. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nielsen M, Nissen MH, Gerwien J, et al:
Spontaneous interleukin-5 production in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
lines is mediated by constitutively activated Stat3. Blood.
99:973–977. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Minet E, Michel G, Mottet D, et al: c-JUN
gene induction and AP-1 activity is regulated by a JNK-dependent
pathway in hypoxic HepG2 cells. Exp Cell Res. 265:114–124. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pages G, Berra E, Milanini J, Levy AP and
Pouyssegur J: Stress-activated protein kinases (JNK and p38/HOG)
are essential for vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA
stability. J Biol Chem. 275:26484–26491. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Krejsgaard T, Vetter-Kauczok CS, Woetmann
A, et al: Jak3- and JNK-dependent vascular endothelial growth
factor expression in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia.
20:1759–1766. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kumar SA, Hu X, Brown M, et al:
Lysophosphatidic acid receptor expression in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia leads to cell survival mediated though vascular
endothelial growth factor expression. Leuk Lymphoma. 50:2038–2048.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hu X, Mendoza FJ, Sun J, Banerji V,
Johnston JB and Gibson SB: Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) induces the
expression of VEGF leading to protection against apoptosis in
B-cell derived malignancies. Cell Signal. 20:1198–1208. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aguayo A, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T, et
al: Angiogenesis in acute and chronic leukemias and myelodysplastic
syndromes. Blood. 96:2240–2245. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bellamy WT, Richter L, Sirjani D, et al:
Vascular endothelial cell growth factor is an autocrine promoter of
abnormal localized immature myeloid precursors and leukemia
progenitor formation in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood.
97:1427–1434. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Braun T, Carvalho G, Fabre C, Grosjean J,
Fenaux P and Kroemer G: Targeting NF-kappaB in hematologic
malignancies. Cell Death Differ. 13:748–758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao T, Yasunaga J, Satou Y, et al: Human
T-cell leukemia virus type 1 bZIP factor selectively suppresses the
classical pathway of NF-kappaB. Blood. 113:2755–2764. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sujobert P, Bardet V, Cornillet-Lefebvre
P, et al: Essential role for the p110delta isoform in
phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation and cell proliferation in
acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 106:1063–1066. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ramos AM, Fernandez C, Amran D, Sancho P,
de Blas E and Aller P: Pharmacologic inhibitors of PI3K/Akt
potentiate the apoptotic action of the antileukemic drug arsenic
trioxide via glutathione depletion and increased peroxide
accumulation in myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 105:4013–4020. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Shi Q, Le X, Abbruzzese JL, et al:
Constitutive Sp1 activity is essential for differential
constitutive expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in
human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 61:4143–4154.
2001.
|
|
43
|
Hsu TC, Young MR, Cmarik J and Colburn NH:
Activator protein 1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappa
B)-dependent transcriptional events in carcinogenesis. Free Radic
Biol Med. 28:1338–1348. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Angel P and Karin M: The role of Jun, Fos
and the AP-1 complex in cell proliferation and transformation.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1072:129–157. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pollmann C, Huang X, Mall J, Bech-Otschir
D, Naumann M and Dubiel W: The constitutive photomorphogenesis 9
signalosome directs vascular endothelial growth factor production
in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 61:8416–8421. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Poulaki V, Mitsiades CS, McMullan C, et
al: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression by
insulin-like growth factor I in thyroid carcinomas. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 88:5392–5398. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chuang CH, Huang CS and Hu ML: Vitamin E
and rutin synergistically inhibit expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor through down-regulation of binding
activity of activator protein-1 in human promyelocytic leukemia
(HL-60) cells. Chem Biol Interact. 183:434–441. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rho SB, Choi K, Park K and Lee JH:
Inhibition of angiogenesis by the BTB domain of promyelocytic
leukemia zinc finger protein. Cancer Lett. 294:49–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Konopka JB, Watanabe SM and Witte ON: An
alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells
unmasks associated tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 37:1035–1042.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pendergast AM, Quilliam LA, Cripe LD, et
al: BCR-ABL-induced oncogenesis is mediated by direct interaction
with the SH2 domain of the GRB-2 adaptor protein. Cell. 75:175–185.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Carlesso N, Frank DA and Griffin JD:
Tyrosyl phosphorylation and DNA binding activity of signal
transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) proteins in
hematopoietic cell lines transformed by Bcr/Abl. J Exp Med.
183:811–820. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sillaber C, Gesbert F, Frank DA, Sattler M
and Griffin JD: STAT5 activation contributes to growth and
viability in Bcr/Abl-transformed cells. Blood. 95:2118–2125.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Wasik MA, Slupianek
A, Salomoni P, Kitamura T, Calabretta B and Skorski T: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)5 activation by
BCR/ABL is dependent on intact Src homology (SH)3 and SH2 domains
of BCR/ABL and is required for leukemogenesis. J Exp Med.
189:1229–1242. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Skorski T, Bellacosa A,
Nieborowska-Skorska M, Majewski M, Martinez R, Choi JK, et al:
Transformation of hematopoietic cells by BCR/ABL requires
activation of a PI-3k/Akt-dependent pathway. EMBO J. 16:6151–6161.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hwan D, Kim, Xu W, et al: Lipton genetic
variants in the candidate genes of the apoptosis pathway and
susceptibility to chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 113:2517–2525.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li L, Zhang R, Fang ZY, Chen JN and Zhu
ZL: Suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
expression by targeting the Bcr-Abl oncogene and protein tyrosine
kinase activity in Bcr-Abl-positive leukaemia cells. J Int Med Res.
37:426–437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Böhm A, Aichberger KJ, Mayerhofer M, et
al: Targeting of mTOR is associated with decreased growth and
decreased VEGF expression in acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Eur J
Clin Invest. 39:395–405. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Venables JP: Unbalanced alternative
splicing and its significance in cancer. Bioessays. 28:378–386.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Podar K, Tai YT and Davies FE: Vascular
endothelial growth factor triggers signaling cascades mediating
multiple myeloma cell growth and migration. Blood. 98:428–435.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hussong JW, Rodgers GM and Shami PJ:
Evidence of increased angiogenesis in patients with acute myeloid
leukemia. Blood. 95:390–313. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Padró T, Ruiz S, Bieker R, Bürger H,
Steins M, Kienast J, et al: Increased angiogenesis in the bone
marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
95:2637–2644. 2000.
|
|
62
|
Abrams ST, Lakum T, Lin K, et al: B-cell
receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells is
regulated by overexpressed active protein kinase CβII. Blood.
109:1193–1201. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gora-Tybor J, Blonski JZ and Robak T:
Circulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its
soluble receptors in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Eur Cytokine Netw. 16:41–46. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Abrams ST, Brown BR, Zuzel M and Slupsky
JR: Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates protein kinase
CβII expression in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells. Blood.
115:4447–4454. 2010.
|
|
65
|
Ugarte-Berzal E, Redondo-Muñoz J, Eroles
P, et al: VEGF/VEGFR2 interaction down-regulates matrix
metalloproteinase-9 via STAT1 activation and inhibits B chronic
lymphocytic leukemia cell migration. Blood. 115:846–849. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hata AN and Breyer RM: Pharmacology and
signaling of prostaglandin receptors: multiple roles in
inflammation and immune modulation. Pharmacol Ther. 103:147–166.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wu G, Luo J, Rana JS, Laham R, Sellke FW
and Li J: Involvement of COX-2 in VEGF-induced angiogenesis via P38
and JNK pathways in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc.
69:512–519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Su JL, Shih JY, Yen ML, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 induces EP1- and HER-2/Neu-dependent vascular
endothelial growth factor-C up-regulation: a novel mechanism of
lymphangiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 64:554–564.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Véronèse L, Tournilhac O, Verrelle P, et
al: Low MCL-1 mRNA expression correlates with prolonged survival in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 22:1291–1293.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pepper C, Lin TT, Pratt G, et al: Mcl-1
expression has in vitro and in vivo significance in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia and is associated with other poor prognostic
markers. Blood. 112:3807–3817. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Véronèse L, Tournilhac O, Verrelle P, et
al: Strong correlation between VEGF and MCL-1 mRNA expression
levels in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Res.
33:1623–1626. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Perez-Atayde AR, Sallan SE, Tedrow U,
Connors S, Allred E and Folkman J: Spectrum of tumor angiogenesis
in the bone marrow of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Am J Pathol. 150:815–821. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yetgin S, Yenicesu I, Etin MC and Tuncer
M: Clinical importance of serum vascular endothelial and basic
fibroblast growth factors in children with acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 42:83–88. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dong X, Han ZC and Yang R: Angiogenesis
and antiangiogenic therapy in hematologic malignancies. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 62:105–118. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Frater JL, Kay NE, Goolsby CL, Crawford
SE, Dewald GW and Peterson LC: Dysregulated angiogenesis in
B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia: morphologic, immunohistochemical,
and flow cytometric evidence. Diagn Pathol. 3:162008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Norén-Nyström U, Heyman M, Frisk P, et al:
Vascular density in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
correlates to biological factors and outcome. Br J Haematol.
146:521–530. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chen H, Treweeke AT, West DC, Till KJ,
Cawley JC, Zuzel M and Toh CH: In vitro and in vivo production of
vascular endothelial growth factor by chronic lymphocytic leukemia
cells. Blood. 96:3181–3187. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Folkman J: Fundamental concepts of the
angiogenic process. Curr Mol Med. 3:643–651. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Verstovsek S, Lunin S, Kantarjian H, et
al: Clinical relevance of VEGF receptors 1 and 2 in patients with
chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Res. 27:661–669. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Hayashibara T, Yamada Y, Miyanishi T, et
al: Vascular endothelial growth factor and cellular chemotaxis: a
possible autocrine pathway in adult T-cell leukemia cell invasion.
Clin Cancer Res. 7:2719–2726. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Demacq C, Vasconcellos VB, Izidoro-Toledo
TC, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and
endothelial nitric oxide synthase (NOS3) polymorphisms are
associated with high relapse risk in childhood acute lymphoblastic
leukemia (ALL). Clin Chim Acta. 411:1335–1405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Fragoso R, Elias AP and Dias S: Autocrine
VEGF loops, signaling pathways, and acute leukemia regulation. Leuk
Lymphoma. 48:481–488. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bellamy WT: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor and its receptors in multiple myeloma and
other hematopoietic malignancies. Semin Oncol. 28:551–559. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Bairey O, Boycov O, Kaganovsky E, Zimra Y,
Shaklai M and Rabizadeh E: All three receptors for vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are expressed on B-chronic
lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Leuk Res. 28:243–248. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
de Bont ES, Neefjes VM, Rosati S, Vellenga
E and Kamps WA: New vessel formation and aberrant VEGF/VEGFR
signaling in acute leukemia: does it matter? Leuk Lymphoma.
43:1901–1909. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Aguayo A, Estey E, Kantarjian H, et al:
Cellular vascular endothelial growth factor is a predictor of
outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
94:3717–3721. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fu J, Fu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Gu H and Bai
Y: CD147 and VEGF co-expression predicts prognosis in patients with
acute myeloid leukemia. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:1046–1052. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Fiedler W, Graeven U, Ergün S, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor, a possible paracrine growth
factor in human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 89:1870–1875.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Koistinen P, Siitonen T, Mäntymaa P, et
al: Regulation of the acute myeloid leukemia cell line OCI/AML-2 by
endothelial nitric oxide synthase under the control of a vascular
endothelial growth factor signaling system. Leukemia. 15:1433–1441.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Fielder W, Graeven U, Ergün S, et al:
Expression of FLT4 and its ligand VEGF-C in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 11:1234–1237. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
de Jonge HJ, Valk PJ, Veeger NJ, et al:
High VEGFC expression is associated with unique gene expression
profiles and predicts adverse prognosis in pediatric and adult
acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 116:1747–1754. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Molica S, Vitelli G, Levato D, Gandolfo GM
and Liso V: Increased serum levels of vascular endothelial growth
factor predict risk of progression in early B-cell chronic
lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 107:605–610. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ferrajoli A, Manshouri T, Estrov Z, et al:
High levels of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2
correlate with shortened survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Clin Cancer Res. 7:795–799. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Dias S, Hattori K, Zhu Z, et al: Autocrine
stimulation of VEGFR-2 activates human leukemic cell growth and
migration. J Clin Invest. 106:511–521. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Dias S, Hattori K, Heissig B, et al:
Inhibition of both paracrine and autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling
pathways is essential to induce long-term remission of
xenotransplanted human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10857–10862. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Schuch G, Machluf M, Bartsch G Jr, et al:
In vivo administration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
and its antagonist, soluble neuropilin-1, predicts a role of VEGF
in the progression of acute myeloid leukemia in vivo. Blood.
100:4622–4628. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Liu P, Wang Y, Li YH, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated gene therapy with an antiangiogenic fragment of
thrombospondin-1 inhibits human leukemia xenograft growth in nude
mice. Leuk Res. 27:701–708. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Cervi D, Haeri
M, Li Y, Nagy A and Ben-David Y: Vascular endothelial growth factor
- a positive and negative regulator of tumor growth. Cancer Res.
70:863–867. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Cervi D, Shaked Y, Haeri M, et al:
Enhanced natural-killer cell and erythropoietic activities in
VEGF-A-overexpressing mice delay F-MuLV-induced erythroleukemia.
Blood. 109:2139–2146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W, Bjarnason
GA, Christensen JG and Kerbel RS: Accelerated metastasis after
short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis.
Cancer Cell. 15:232–239. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, et
al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil and leucovorin for
metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 350:2335–2342. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, et al:
Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 357:2666–2676. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Escudier B, Eisen T, Stadler WM, et al:
Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 356:125–134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P, et al:
Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Karp JE, Gojo I, Pili R, et al: Targeting
vascular endothelial growth factor for relapsed and refractory
adult acute myelogenous leukemias: therapy with sequential
1-β-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine, mitoxantrone, and bevacizumab. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:3577–3585. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Presta LG, Chen H, O’Connor SJ, et al:
Humanization of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
monoclonal antibody for the therapy of solid tumors and other
disorders. Cancer Res. 57:4593–4599. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
D’Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E and
Folkman J: Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:4082–4085. 1994.
|
|
109
|
Teo SK: Properties of thalidomide and its
analogues: implications for anticancer therapy. AAPS J. 7:E14–E19.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Dredge K, Marriott JB, Macdonald CD, et
al: Novel thalidomide analogues display anti-angiogenic activity
independently of immunomodulatory effects. Br J Cancer.
87:1166–1172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Thomas DA, Estey E, Giles FJ, et al:
Single agent thalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory
acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 123:436–441. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Steins MB, Padró T, Bieker R, et al:
Efficacy and safety of thalidomide in patients with acute myeloid
leukemia. Blood. 99:834–839. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Barr P, Fu P, Lazarus H, et al:
Antiangiogenic activity of thalidomide in combination with
fludarabine, carboplatin and topotecan for high-risk acute
myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 48:1940–1949. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Drevs J, Müller-Driver R, Wittig C, et al:
PTK787/ZK 222584, a specific vascular endothelial growth
factor-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, affects the anatomy of
the tumor vascular bed and the functional vascular properties as
detected by dynamic enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer
Res. 62:4015–4022. 2002.
|
|
115
|
Roboz GJ, Giles FJ, List AF, et al: Phase
1 study of PTK787/ZK 222584, a small molecule tyrosine kinase
receptor inhibitor, for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and
myelodysplastic syndrome. Leukemia. 20:952–957. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wedge SR, Kendrew J, Hennequin LF, et al:
AZD2171: a highly potent, orally bioavailable, vascular endothelial
growth factor receptor-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the
treatment of cancer. Cancer Res. 65:4389–4400. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fiedler W, Mesters R, Heuser M, et al: An
open-label, phase I study of cediranib (RECENTIN) in patients with
acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 34:196–202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Raza A, Mehdi M, Mumtaz M, Ali F, Lascher
S and Galili N: Combination of 5-azacytidine and thalidomide for
the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid
leukemia. Cancer. 113:1596–1604. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|