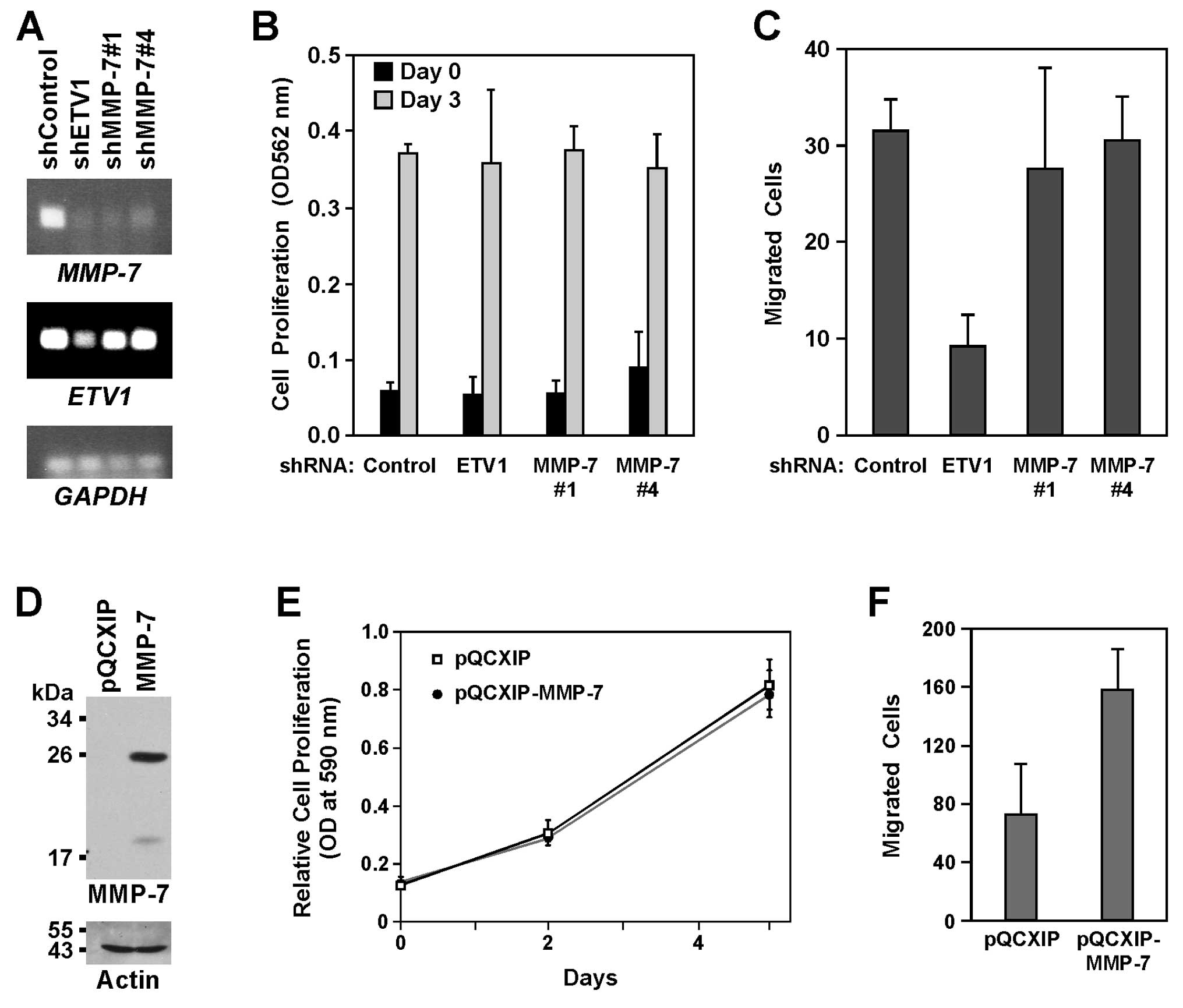
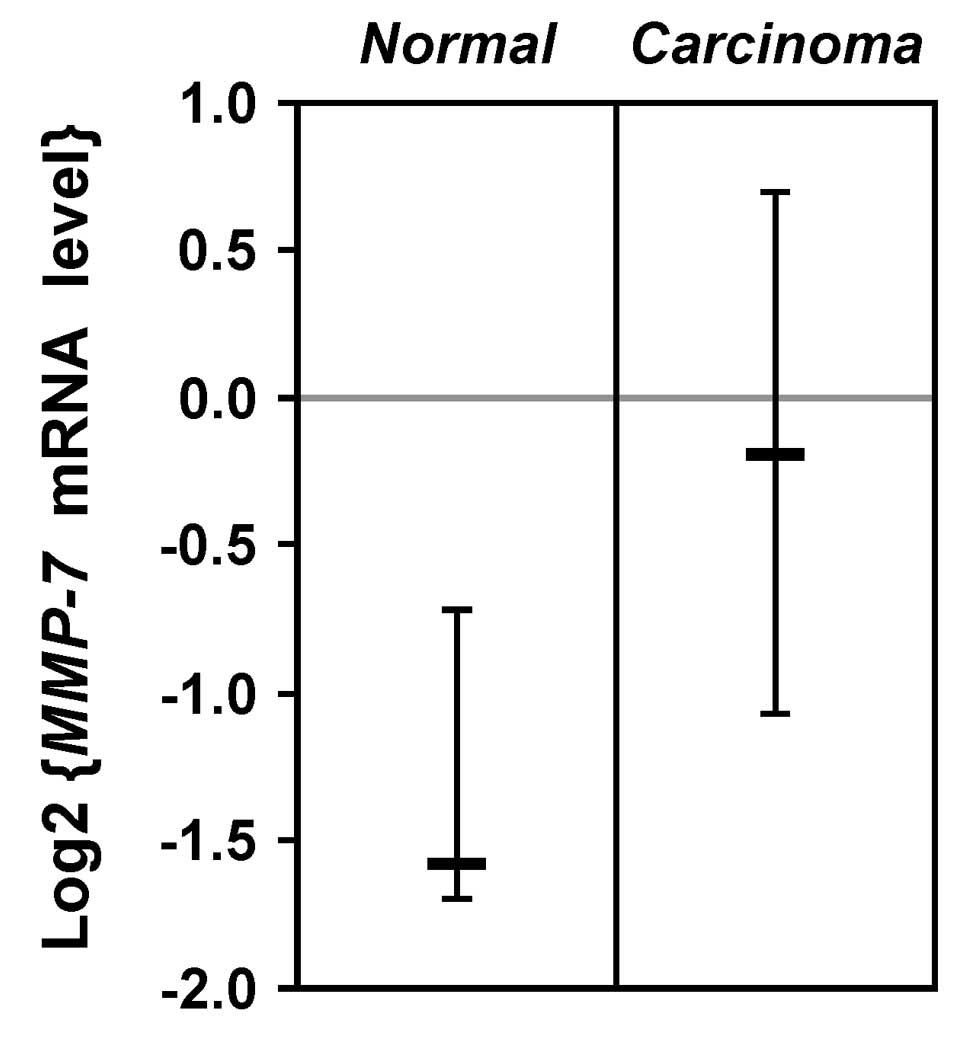
|
1
|
Brown TA and McKnight SL: Specificities of
protein-protein and protein-DNA interaction of GABP alpha and two
newly defined ets-related proteins. Genes Dev. 6:2502–2512. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coutte L, Monte D, Imai K, Pouilly L,
Dewitte F, Vidaud M, Adamski J, Baert JL and de Launoit Y:
Characterization of the human and mouse ETV1/ER81 transcription
factor genes: role of the two alternatively spliced isoforms in the
human. Oncogene. 18:6278–6286. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharrocks AD: The ETS-domain transcription
factor family. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:827–837. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hollenhorst PC, McIntosh LP and Graves BJ:
Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS
transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 80:437–471. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oh S, Shin S and Janknecht R: ETV1, 4 and
5: An oncogenic subfamily of ETS transcription factors. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1826:1–12. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jeon IS, Davis JN, Braun BS, Sublett JE,
Roussel MF, Denny CT and Shapiro DN: A variant Ewing’s sarcoma
translocation (7;22) fuses the EWS gene to the ETS gene ETV1.
Oncogene. 10:1229–1234. 1995.
|
|
7
|
Monte D, Coutte L, Baert JL, Angeli I,
Stehelin D and de Launoit Y: Molecular characterization of the
ets-related human transcription factor ER81. Oncogene. 11:771–779.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chotteau-Lelievre A, Desbiens X, Pelczar
H, Defossez PA and de Launoit Y: Differential expression patterns
of the PEA3 group transcription factors through murine embryonic
development. Oncogene. 15:937–952. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chotteau-Lelievre A, Dolle P, Peronne V,
Coutte L, de Launoit Y and Desbiens X: Expression patterns of the
Ets transcription factors from the PEA3 group during early stages
of mouse development. Mech Dev. 108:191–195. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arber S, Ladle DR, Lin JH, Frank E and
Jessell TM: ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional
connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons.
Cell. 101:485–498. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kucera J, Cooney W, Que A, Szeder V,
Stancz-Szeder H and Walro J: Formation of supernumerary muscle
spindles at the expense of Golgi tendon organs in ER81-deficient
mice. Dev Dyn. 223:389–401. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Janknecht R: Analysis of the
ERK-stimulated ETS transcription factor ER81. Mol Cell Biol.
16:1550–1556. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bosc DG, Goueli BS and Janknecht R:
HER2/Neu-mediated activation of the ETS transcription factor ER81
and its target gene MMP-1. Oncogene. 20:6215–6224. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Janknecht R: Cell type-specific inhibition
of the ETS transcription factor ER81 by mitogen-activated protein
kinase-activated protein kinase 2. J Biol Chem. 276:41856–41861.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu J and Janknecht R: Regulation of the
ETS transcription factor ER81 by the 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase 1
and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem. 277:42669–42679. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Janknecht R: Regulation of the ER81
transcription factor and its coactivators by mitogen- and
stress-activated protein kinase 1 (MSK1). Oncogene. 22:746–755.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Papoutsopoulou S and Janknecht R:
Phosphorylation of ETS transcription factor ER81 in a complex with
its coactivators CREB-binding protein and p300. Mol Cell Biol.
20:7300–7310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goel A and Janknecht R:
Acetylation-mediated transcriptional activation of the ETS protein
ER81 by p300, P/CAF, and HER2/Neu. Mol Cell Biol. 23:6243–6254.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Janknecht R: The versatile functions of
the transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP and their roles in
disease. Histol Histopathol. 17:657–668. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee KK and Workman JL: Histone
acetyltransferase complexes: one size doesn’t fit all. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:284–295. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Goel A and Janknecht R: Concerted
activation of ETS protein ER81 by p160 coactivators, the
acetyltransferase p300 and the receptor tyrosine kinase HER2/Neu. J
Biol Chem. 279:14909–14916. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Font de Mora J and Brown M: AIB1 is a
conduit for kinase-mediated growth factor signaling to the estrogen
receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 20:5041–5047. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu J, Wu RC and O’Malley BW: Normal and
cancer-related functions of the p160 steroid receptor co-activator
(SRC) family. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:615–630. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Janknecht R: EWS-ETS oncoproteins: the
linchpins of Ewing tumors. Gene. 363:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Toomey EC, Schiffman JD and Lessnick SL:
Recent advances in the molecular pathogenesis of Ewing’s sarcoma.
Oncogene. 29:4504–4516. 2010.
|
|
26
|
Rossow KL and Janknecht R: The Ewing’s
sarcoma gene product functions as a transcriptional activator.
Cancer Res. 61:2690–2695. 2001.
|
|
27
|
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S,
Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun XW, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J,
Kuefer R, et al: Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription
factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 310:644–648. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomlins SA, Laxman B, Dhanasekaran SM,
Helgeson BE, Cao X, Morris DS, Menon A, Jing X, Cao Q, Han B, et
al: Distinct classes of chromosomal rearrangements create oncogenic
ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nature. 448:595–599. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Attard G, Clark J, Ambroisine L, Mills IG,
Fisher G, Flohr P, Reid A, Edwards S, Kovacs G, Berney D, et al:
Heterogeneity and clinical significance of ETV1 translocations in
human prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:314–320. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hermans KG, van der Korput HA, van Marion
R, van de Wijngaart DJ, Ziel-van der Made A, Dits NF, Boormans JL,
van der Kwast TH, van Dekken H, Bangma CH, et al: Truncated ETV1,
fused to novel tissue-specific genes, and full-length ETV1 in
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:7541–7549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Clark JP and Cooper CS: ETS gene fusions
in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 6:429–439. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shin S, Kim TD, Jin F, van Deursen JM,
Dehm SM, Tindall DJ, Grande JP, Munz JM, Vasmatzis G and Janknecht
R: Induction of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and modulation
of androgen receptor by ETS variant 1/ETS-related protein 81.
Cancer Res. 69:8102–8110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jane-Valbuena J, Widlund HR, Perner S,
Johnson LA, Dibner AC, Lin WM, Baker AC, Nazarian RM, Vijayendran
KG, Sellers WR, et al: An oncogenic role for ETV1 in melanoma.
Cancer Res. 70:2075–2084. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Goueli BS and Janknecht R: Upregulation of
the catalytic telomerase subunit by the transcription factor ER81
and oncogenic HER2/Neu, Ras, or Raf. Mol Cell Biol. 24:25–35. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hiyama E and Hiyama K: Telomerase as tumor
marker. Cancer Lett. 194:221–233. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Janknecht R: On the road to immortality:
hTERT upregulation in cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 564:9–13. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bosc DG and Janknecht R: Regulation of
HER2/Neu promoter activity by the ETS transcription factor, ER81. J
Cell Biochem. 86:174–183. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Signoretti S, Montironi R, Manola J,
Altimari A, Tam C, Bubley G, Balk S, Thomas G, Kaplan I, Hlatky L,
et al: Her-2-neu expression and progression toward androgen
independence in human prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
92:1918–1925. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Osman I, Mikhail M, Shuch B, Clute M,
Cheli CD, Ghani F, Thiel RP and Taneja SS: Serum levels of shed
Her2/neu protein in men with prostate cancer correlate with disease
progression. J Urol. 174:2174–2177. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nishio Y, Yamada Y, Kokubo H, Nakamura K,
Aoki S, Taki T, Honda N, Nakagawa A, Saga S and Hara K: Prognostic
significance of immunohistochemical expression of the HER-2/neu
oncoprotein in bone metastatic prostate cancer. Urology.
68:110–115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dowdy SC, Mariani A and Janknecht R:
HER2/Neu- and TAK1-mediated up-regulation of the transforming
growth factor beta inhibitor Smad7 via the ETS protein ER81. J Biol
Chem. 278:44377–44384. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Massague J: TGFbeta in cancer. Cell.
134:215–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yan X and Chen YG: Smad7: not only a
regulator, but also a cross-talk mediator of TGF-beta signalling.
Biochem J. 434:1–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
De Haro L and Janknecht R: Functional
analysis of the transcription factor ER71 and its activation of the
matrix metalloproteinase-1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res.
30:2972–2979. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
De Haro L and Janknecht R: Cloning of the
murine ER71 gene (Etsrp71) and initial characterization of its
promoter. Genomics. 85:493–502. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Goueli BS and Janknecht R: Regulation of
telomerase reverse transcriptase gene activity by upstream
stimulatory factor. Oncogene. 22:8042–8047. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Concerted
activation of the Mdm2 promoter by p72 RNA helicase and the
coactivators p300 and P/CAF. J Cell Biochem. 101:1252–1265. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kim TD, Oh S, Shin S and Janknecht R:
Regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and HCT116 cell physiology by
histone demethylase JMJD2D/KDM4D. PLoS One. 7:e346182012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kim TD, Shin S and Janknecht R: Repression
of Smad3 activity by histone demethylase SMCX/JARID1C. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 366:563–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rossow KL and Janknecht R: Synergism
between p68 RNA helicase and the transcriptional coactivators CBP
and p300. Oncogene. 22:151–156. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ben-Levy R, Paterson HF, Marshall CJ and
Yarden Y: A single autophosphorylation site confers oncogenicity to
the Neu/ErbB-2 receptor and enables coupling to the MAP kinase
pathway. EMBO J. 13:3302–3311. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Knebel J, De Haro L and Janknecht R:
Repression of transcription by TSGA/Jmjd1a, a novel interaction
partner of the ETS protein ER71. J Cell Biochem. 99:319–329. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mooney SM, Goel A, D’Assoro AB, Salisbury
JL and Janknecht R: Pleiotropic effects of p300-mediated
acetylation on p68 and p72 RNA helicase. J Biol Chem.
285:30443–30452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim J, Shin S, Subramaniam M, Bruinsma E,
Kim TD, Hawse JR, Spelsberg TC and Janknecht R: Histone demethylase
JARID1B/KDM5B is a corepressor of TIEG1/KLF10. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 401:412–416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Activation of
androgen receptor by histone demethylases JMJD2A and JMJD2D.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:742–746. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mooney SM, Grande JP, Salisbury JL and
Janknecht R: Sumoylation of p68 and p72 RNA helicases affects
protein stability and transactivation potential. Biochemistry.
49:1–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shin S and Janknecht R: Diversity within
the JMJD2 histone demethylase family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
353:973–977. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shin S, Bosc DG, Ingle JN, Spelsberg TC
and Janknecht R: Rcl is a novel ETV1/ER81 target gene upregulated
in breast tumors. J Cell Biochem. 105:866–874. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shin S, Rossow KL, Grande JP and Janknecht
R: Involvement of RNA helicases p68 and p72 in colon cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:7572–7578. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Oh S and Janknecht R: Histone demethylase
JMJD5 is essential for embryonic development. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 420:61–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim TD, Shin S, Berry WL, Oh S and
Janknecht R: The JMJD2A demethylase regulates apoptosis and
proliferation in colon cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 113:1368–1376.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ozaki I, Mizuta T, Zhao G, Yotsumoto H,
Hara T, Kajihara S, Hisatomi A, Sakai T and Yamamoto K: Involvement
of the Ets-1 gene in overexpression of matrilysin in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 60:6519–6525. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Crawford HC, Fingleton B, Gustavson MD,
Kurpios N, Wagenaar RA, Hassell JA and Matrisian LM: The PEA3
subfamily of Ets transcription factors synergizes with
beta-catenin-LEF-1 to activate matrilysin transcription in
intestinal tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 21:1370–1383. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wei GH, Badis G, Berger MF, Kivioja T,
Palin K, Enge M, Bonke M, Jolma A, Varjosalo M, Gehrke AR, et al:
Genome-wide analysis of ETS-family DNA-binding in vitro and in
vivo. EMBO J. 29:2147–2160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Janknecht R, Monte D, Baert JL and de
Launoit Y: The ETS-related transcription factor ERM is a nuclear
target of signaling cascades involving MAPK and PKA. Oncogene.
13:1745–1754. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Holbro T, Civenni G and Hynes NE: The ErbB
receptors and their role in cancer progression. Exp Cell Res.
284:99–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cai C, Hsieh CL, Omwancha J, Zheng Z, Chen
SY, Baert JL and Shemshedini L: ETV1 is a novel androgen
receptor-regulated gene that mediates prostate cancer cell
invasion. Mol Endocrinol. 21:1835–1846. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kumar-Sinha C, Tomlins SA and Chinnaiyan
AM: Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:497–511. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yu YP, Landsittel D, Jing L, Nelson J, Ren
B, Liu L, McDonald C, Thomas R, Dhir R, Finkelstein S, et al: Gene
expression alterations in prostate cancer predicting tumor
aggression and preceding development of malignancy. J Clin Oncol.
22:2790–2799. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pajouh MS, Nagle RB, Breathnach R, Finch
JS, Brawer MK and Bowden GT: Expression of metalloproteinase genes
in human prostate cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 117:144–150.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Hashimoto K, Kihira Y, Matuo Y and Usui T:
Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 in human prostate. J Urol. 160:1872–1876. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ouyang XS, Wang X, Lee DT, Tsao SW and
Wong YC: Up-regulation of TRPM-2, MMP-7 and ID-1 during sex
hormone-induced prostate carcinogenesis in the Noble rat.
Carcinogenesis. 22:965–973. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Asamoto M, Hokaiwado N, Cho YM, Takahashi
S, Ikeda Y, Imaida K and Shirai T: Prostate carcinomas developing
in transgenic rats with SV40 T antigen expression under probasin
promoter control are strictly androgen dependent. Cancer Res.
61:4693–4700. 2001.
|
|
74
|
Szarvas T, Becker M, Vom Dorp F, Meschede
J, Scherag A, Bankfalvi A, Reis H, Schmid KW, Romics I, Rubben H
and Ergun S: Elevated serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 levels
predict poor prognosis after radical prostatectomy. Int J Cancer.
128:1486–1492. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wilson CL, Heppner KJ, Labosky PA, Hogan
BL and Matrisian LM: Intestinal tumorigenesis is suppressed in mice
lacking the metalloproteinase matrilysin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:1402–1407. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Rudolph-Owen LA, Chan R, Muller WJ and
Matrisian LM: The matrix metalloproteinase matrilysin influences
early-stage mammary tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 58:5500–5506.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Crawford HC, Scoggins CR, Washington MK,
Matrisian LM and Leach SD: Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is expressed
by pancreatic cancer precursors and regulates acinar-to-ductal
metaplasia in exocrine pancreas. J Clin Invest. 109:1437–1444.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hollenhorst PC, Ferris MW, Hull MA, Chae
H, Kim S and Graves BJ: Oncogenic ETS proteins mimic activated
RAS/MAPK signaling in prostate cells. Genes Dev. 25:2147–2157.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Powell WC, Knox JD, Navre M, Grogan TM,
Kittelson J, Nagle RB and Bowden GT: Expression of the
metalloproteinase matrilysin in DU-145 cells increases their
invasive potential in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer
Res. 53:417–422. 1993.
|
|
80
|
Wroblewski LE, Noble PJ, Pagliocca A,
Pritchard DM, Hart CA, Campbell F, Dodson AR, Dockray GJ and Varro
A: Stimulation of MMP-7 (matrilysin) by Helicobacter pylori
in human gastric epithelial cells: role in epithelial cell
migration. J Cell Sci. 116:3017–3026. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Remy L, Trespeuch C, Bachy S, Scoazec JY
and Rousselle P: Matrilysin 1 influences colon carcinoma cell
migration by cleavage of the laminin-5 beta3 chain. Cancer Res.
66:11228–11237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lee SK, Han YM, Yun J, Lee CW, Shin DS, Ha
YR, Kim J, Koh JS, Hong SH, Han DC and Kwon BM: Phosphatase of
regenerating liver-3 promotes migration and invasion by
upregulating matrix metalloproteinases-7 in human colorectal cancer
cells. Int J Cancer. 131:E190–E203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ii M, Yamamoto H, Adachi Y, Maruyama Y and
Shinomura Y: Role of matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) in
human cancer invasion, apoptosis, growth, and angiogenesis. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 231:20–27. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Wang Y, Wang L, Chen Y, Li L, Yang X, Li
B, Song S, Yang L, Hao Y and Yang J: ER81 expression in breast
cancers and hyperplasia. Pathology Res Int. 2011:9805132011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Chi P, Chen Y, Zhang L, Guo X, Wongvipat
J, Shamu T, Fletcher JA, Dewell S, Maki RG, Zheng D, et al: ETV1 is
a lineage survival factor that cooperates with KIT in
gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Nature. 467:849–853. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|