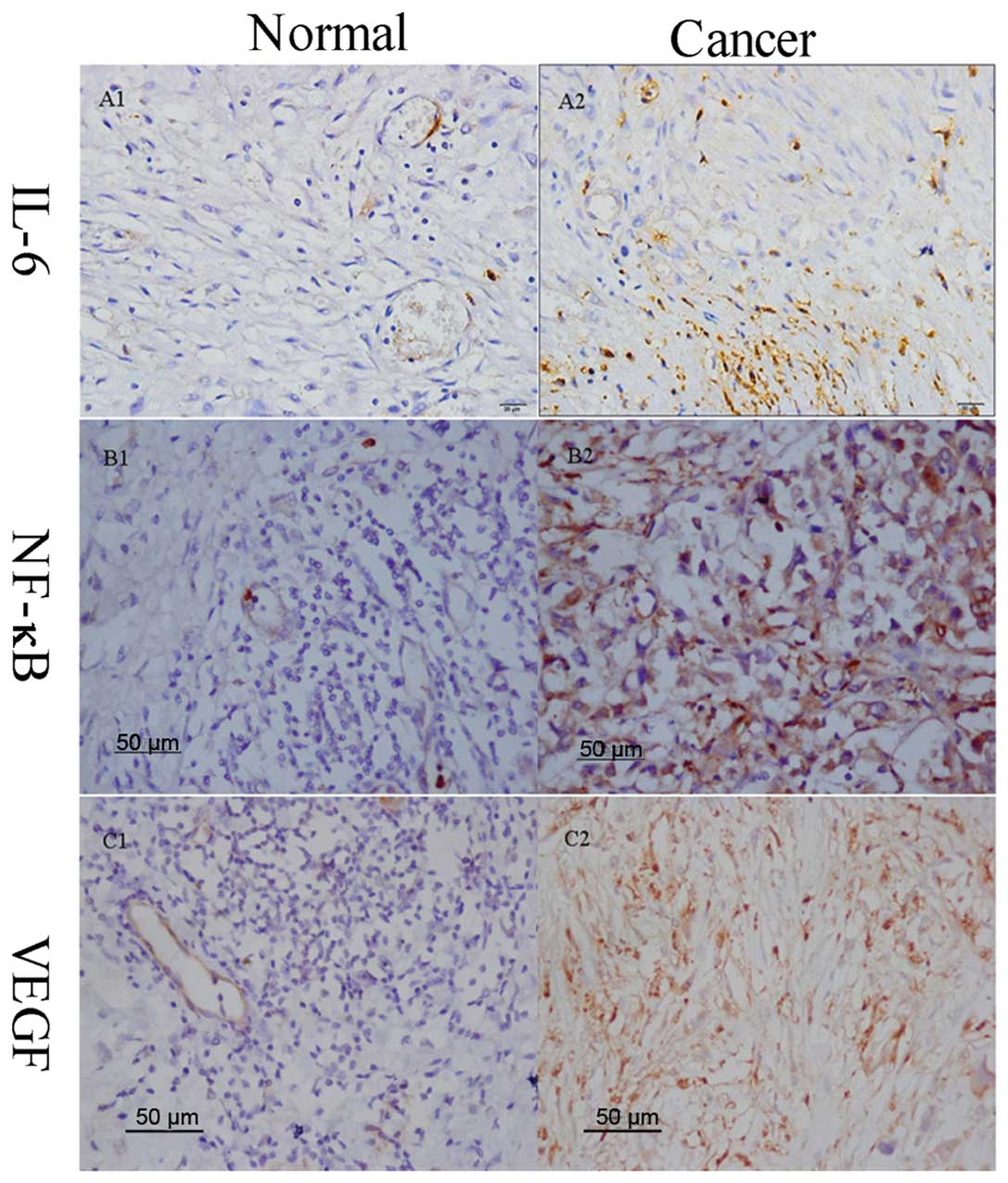
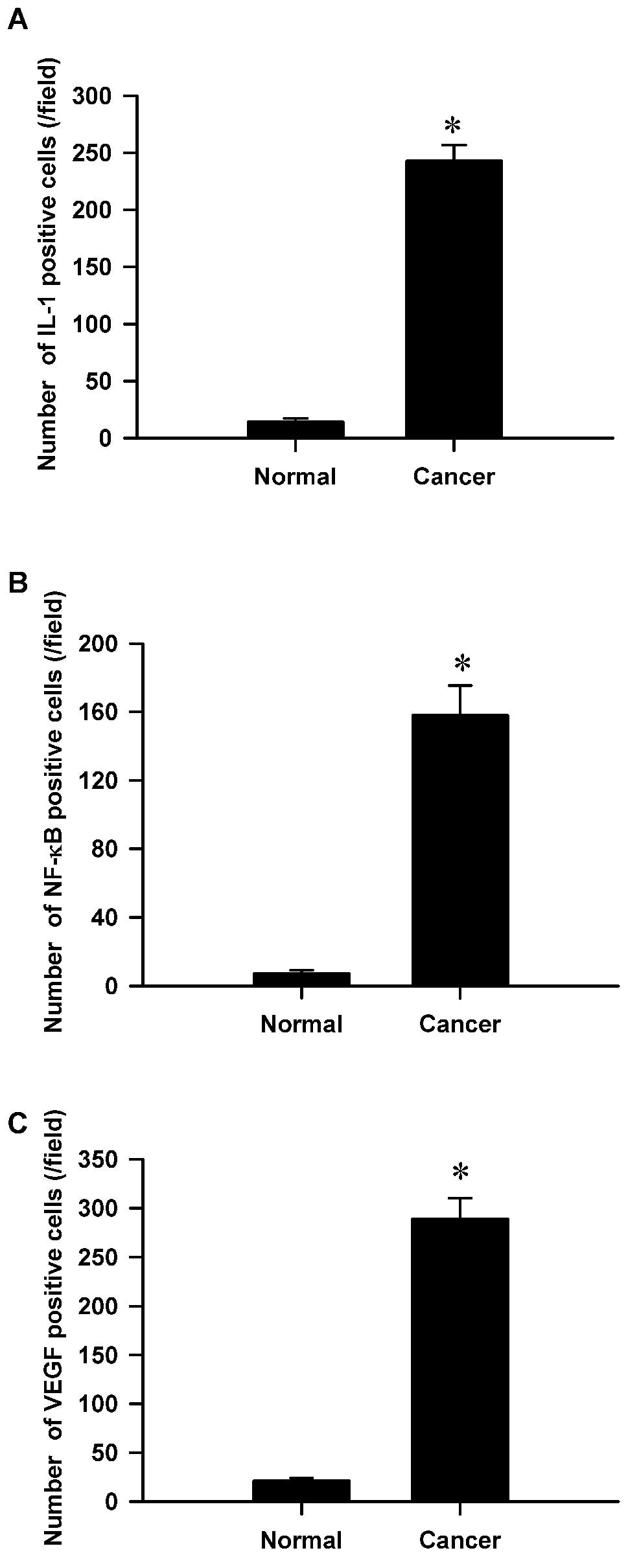
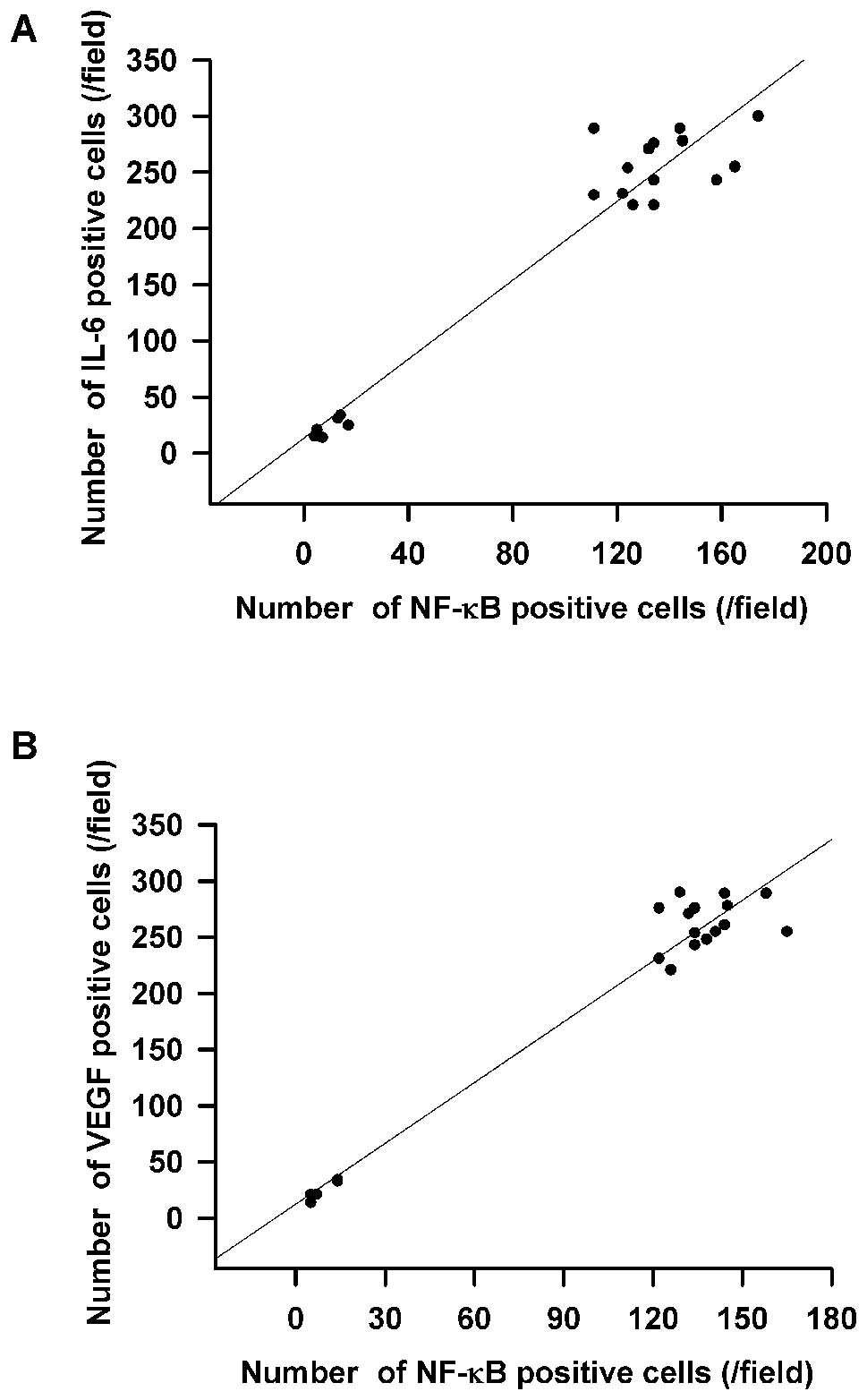
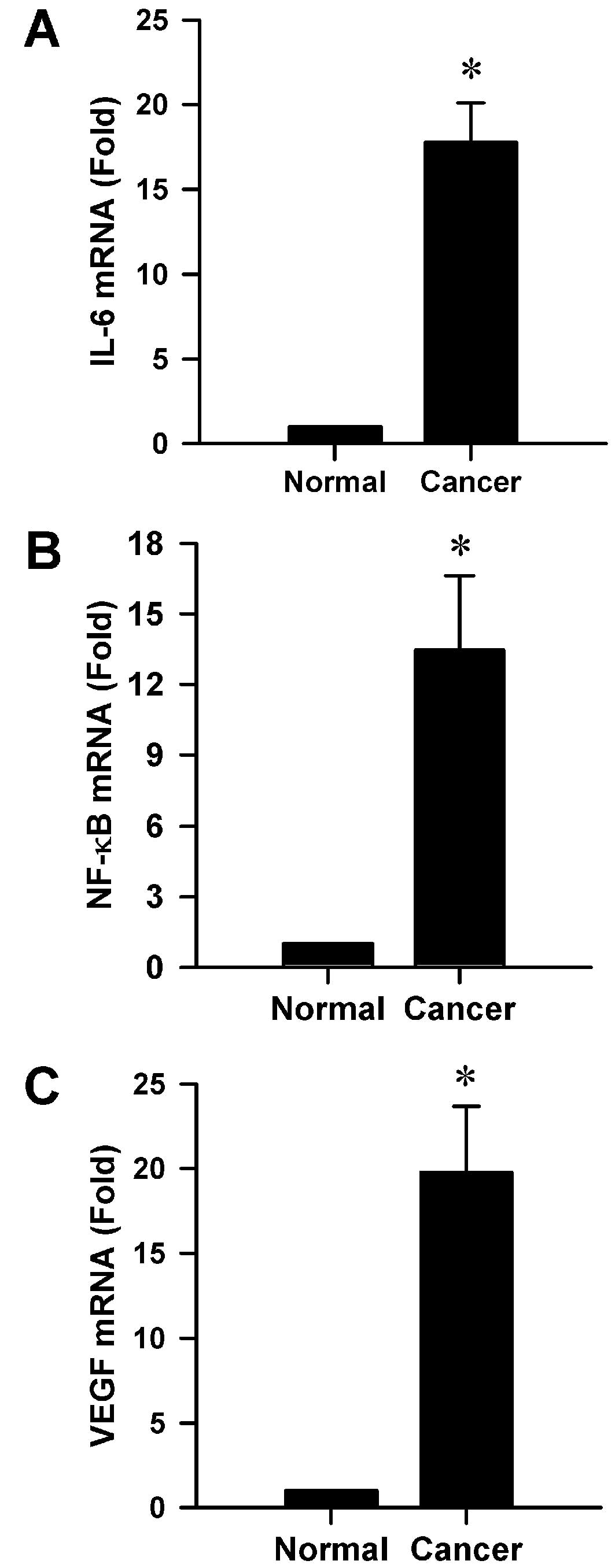
|
1
|
Cohen T, Nahari D, Cerem LW, Neufeld G and
Levi BZ: Interleukin 6 induces the expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor. J Biol Chem. 271:736–741. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thong-Ngam D, Tangkijvanich P, Lerknimitr
R, Mahachai V, Theamboonlers A and Poovorawan Y: Diagnostic role of
serum interleukin-18 in gastric cancer patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:4473–4477. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin MT, Lin BR, Chang CC, Chu CY, Su HJ,
Chen ST, Jeng YM and Kuo ML: IL-6 induces AGS gastric cancer cell
invasion via activation of the c-Src/RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway.
Int J Cancer. 120:2600–2608. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sen R and Baltimore D: Inducibility of
kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein NF-kappa B by a
posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 47:921–928. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Karin M and Delhase M: The I kappa B
kinase (IKK) and NF-kappa B: key elements of proinflammatory
signaling. Semin Immunol. 12:85–98. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR and Li ZW:
NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:301–310. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM,
Li ZW, Egan LJ, Kagnoff MF and Karin M: IKKbeta links inflammation
and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer.
Cell. 118:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Becker C, Fantini MC, Schramm C, Lehr HA,
Wirtz S, Nikolaev A, Burg J, Strand S, Kiesslich R, Huber S, et al:
TGF-beta suppresses tumor progression in colon cancer by inhibition
of IL-6 trans-signaling. Immunity. 21:491–501. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kawano M, Hirano T, Matsuda T, Taga T,
Horii Y, Iwato K, Asaoku H, Tang B, Tanabe O and Tanaka H:
Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6 for human
multiple myelomas. Nature. 332:83–85. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Klein B, Zhang XG, Lu ZY and Bataille R:
Interleukin-6 in human multiple myeloma. Blood. 85:863–872.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oue N, Sentani K, Sakamoto N, Motoshita J,
Nishisaka T, Fukuhara T, Matsuura H, Sasaki H, Nakachi K and Yasui
W: Characteristic gene expression in stromal cells of gastric
cancers among atomic-bomb survivors. Int J Cancer. 124:1112–1121.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ashizawa T, Okada R, Suzuki Y, Takagi M,
Yamazaki T, Sumi T and Aoki T, Ohnuma S and Aoki T: Clinical
significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the spread of gastric
cancer: role of IL-6 as a prognostic factor. Gastric Cancer.
8:124–131. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sethi G, Sung B and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappaB activation: from bench to bedside. Exp Biol Med.
233:21–31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bargou RC, Emmerich F, Krappmann D,
Bommert K, Mapara MY, Arnold W, Royer HD, Grinstein E, Greiner A,
Scheidereit C and Dörken B: Constitutive nuclear factor-kappaB-RelA
activation is required for proliferation and survival of Hodgkin’s
disease tumor cells. J Clin Invest. 100:2961–2969. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akira S and Kishimoto T: The evidence for
interleukin-6 as an autocrine growth factor in malignancy. Semin
Cancer Biol. 3:17–26. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang SP, Wu MS, Shun CT, Wang HP, Lin MT,
Kuo ML and Lin JT: Interleukin-6 increases vascular endothelial
growth factor and angiogenesis in gastric carcinoma. J Biomed Sci.
11:517–527. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim DK, Oh SY, Kwon HC, Lee S, Kwon KA,
Kim BG, Kim SG, Kim SH, Jang JS, Kim MC, et al: Clinical
significances of preoperative serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive
protein level in operable gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:1552009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liao WC, Lin JT, Wu CY, Huang SP, Lin MT,
Wu AS, Huang YJ and Wu MS: Serum interleukin-6 level but not
genotype predicts survival after resection in stages II and III
gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:428–434. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harris PR, Smythies LE, Smith PD and
Dubois A: Inflammatory cytokine mRNA expression during early and
persistent Helicobacter pylori infection in nonhuman
primates. J Infect Dis. 181:783–786. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamaoka Y, Kita M, Kodama T, Sawai N and
Imanishi J: Helicobacter pylori cagA gene and expression of
cytokine messenger RNA in gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology.
110:1744–1752. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Crabtree JE, Shallcross TM, Heatley RV and
Wyatt JI: Mucosal tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-6 in
patients with Helicobacter pylori associated gastritis. Gut.
32:1473–1477. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kopp EB and Ghosh S: NF-κB and Rel
proteins in innate immunity. Adv Immunol. 58:1–27. 1995.
|
|
24
|
Busam K, Gieringer C, Freudenberg M and
Hohmann HP: Staphylococcus aureus and derived exotoxins
induce nuclear factor κB-like activity in murine bone marrow
macrophages. Infect Immun. 60:2008–2015. 1992.
|
|
25
|
Dranoff G: Cytokines in cancer
pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:11–22. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|