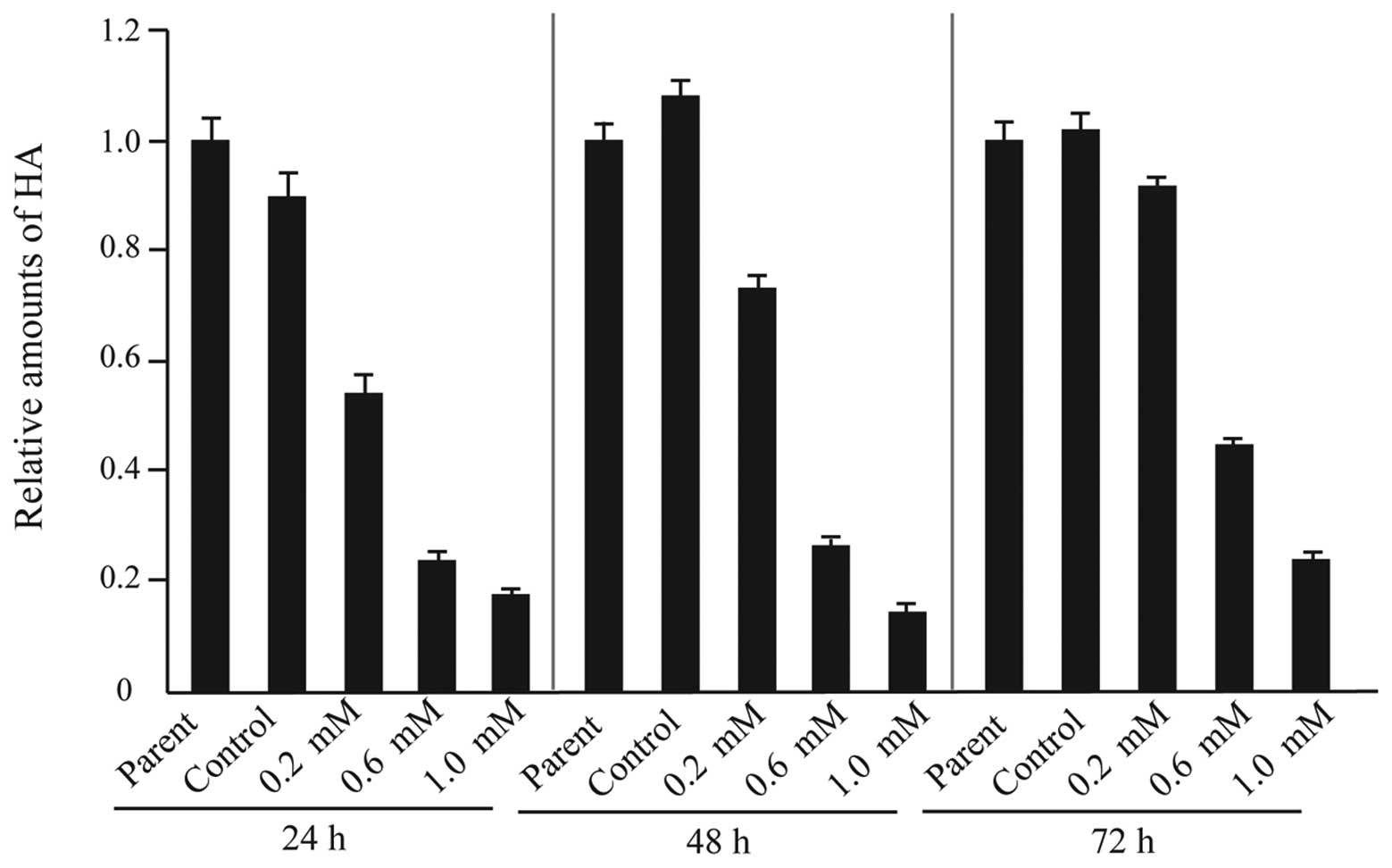
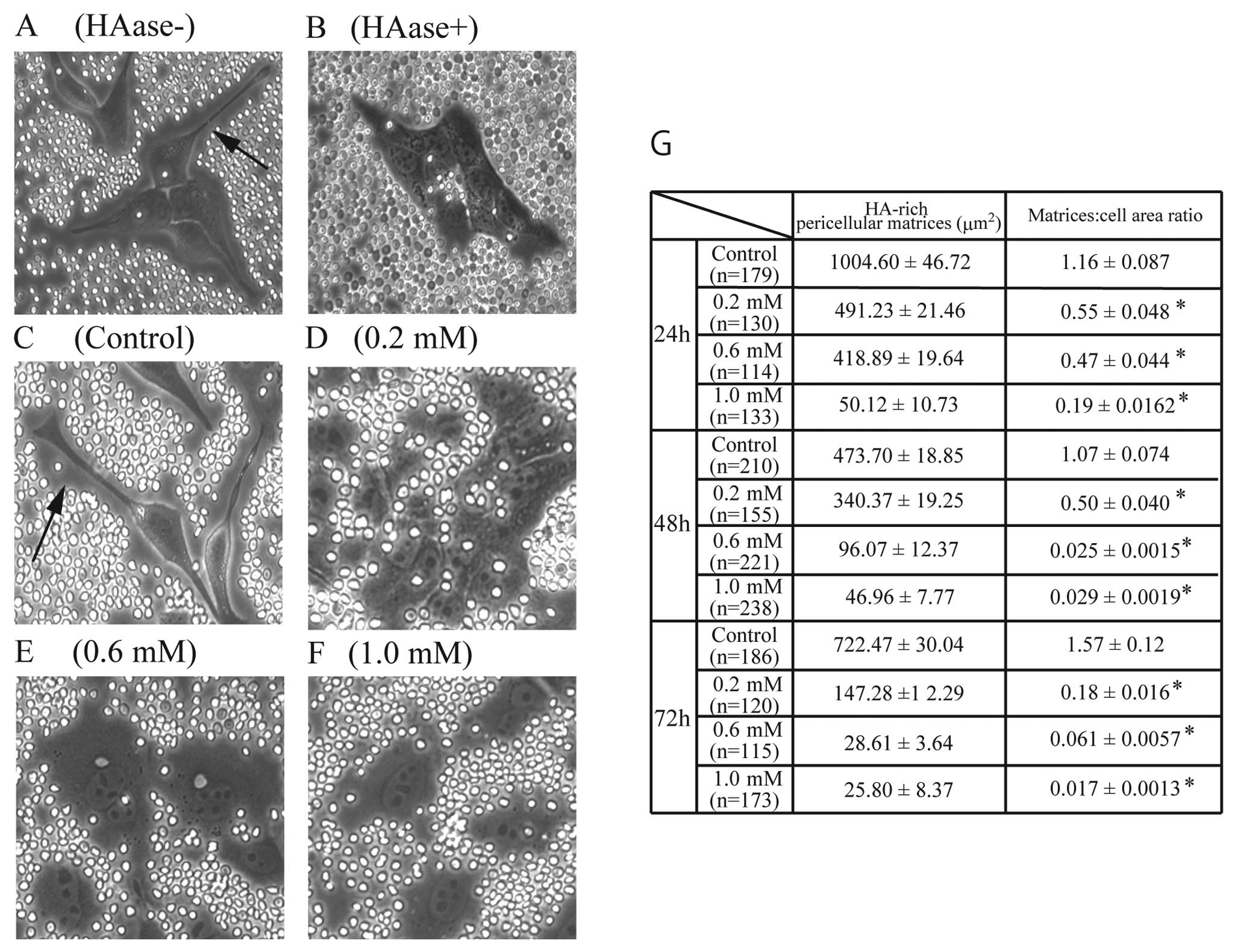
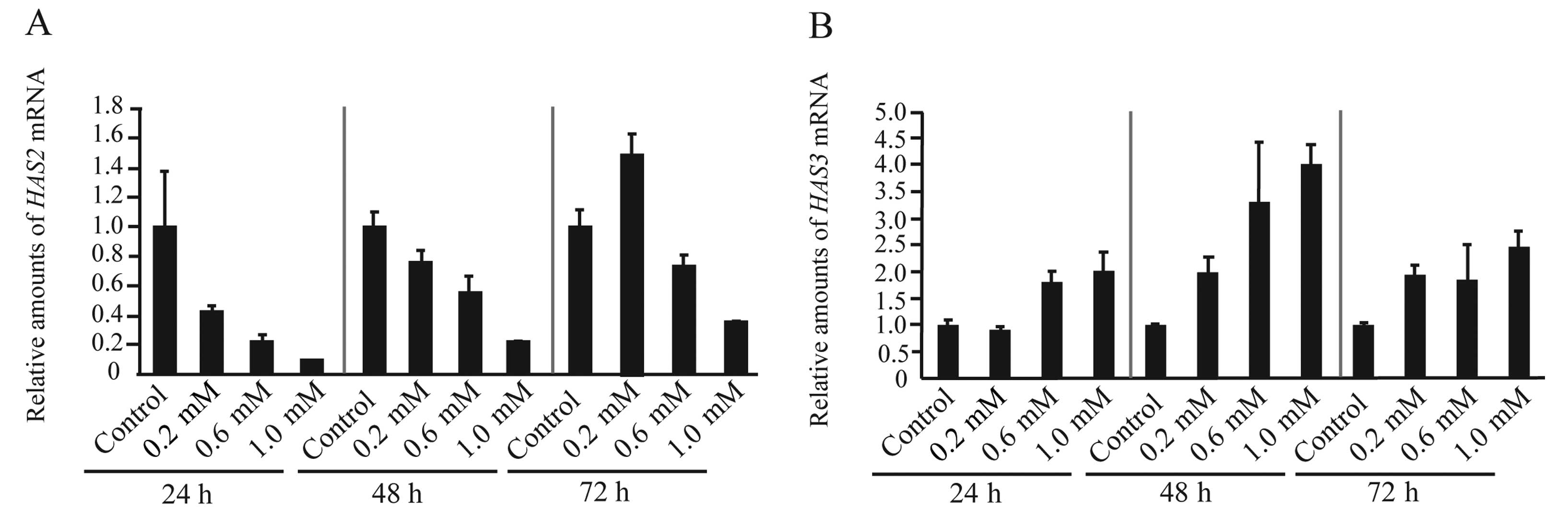
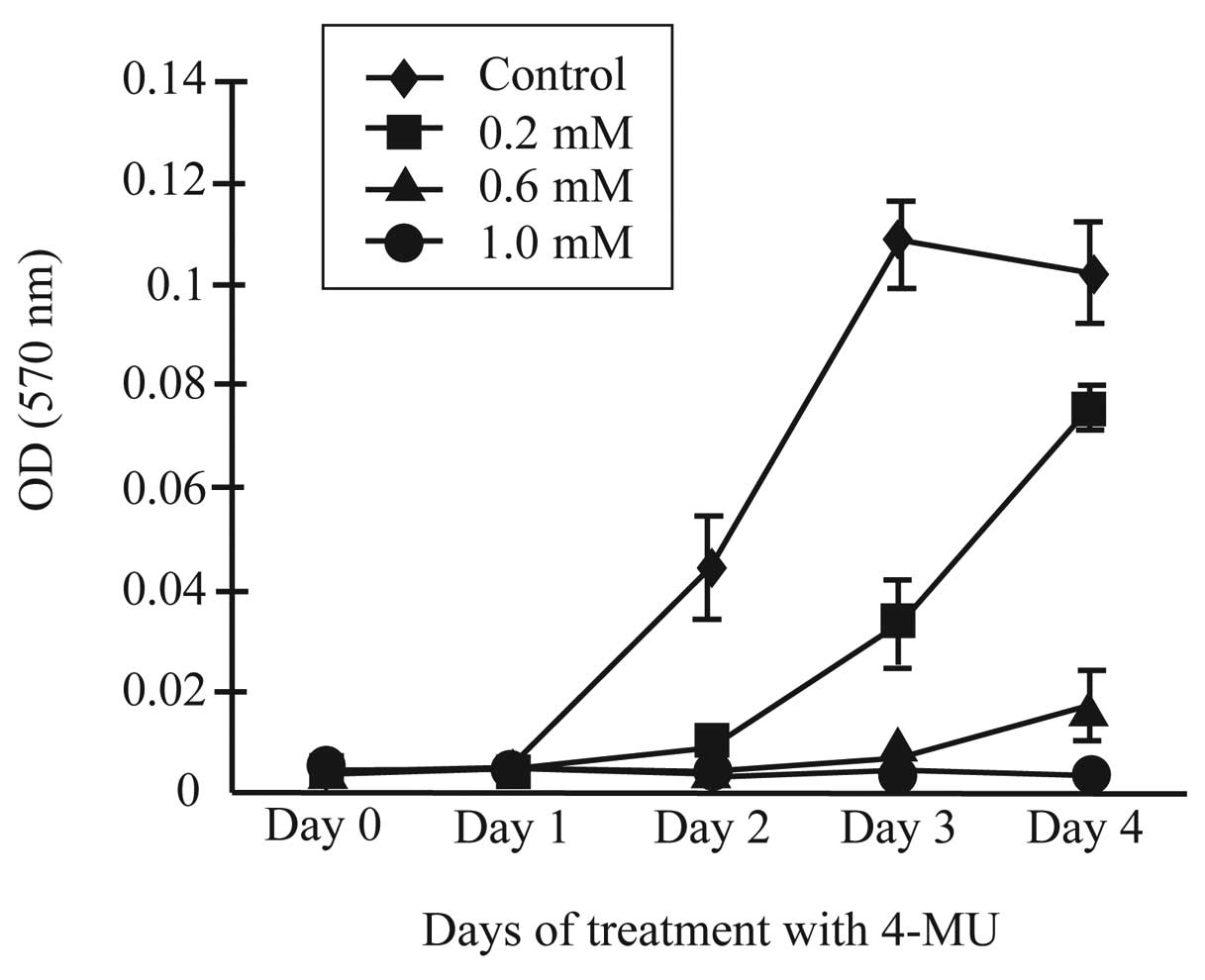
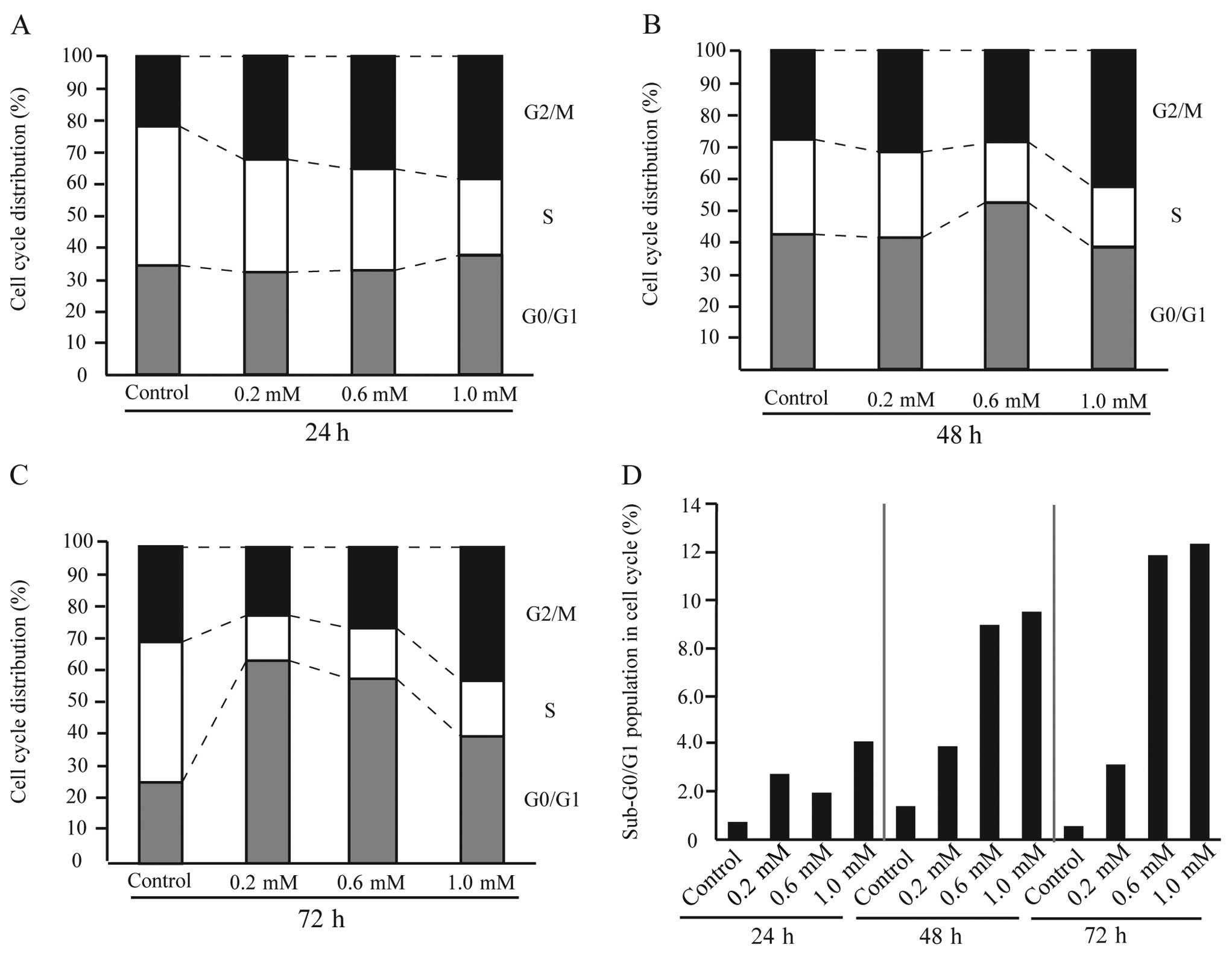
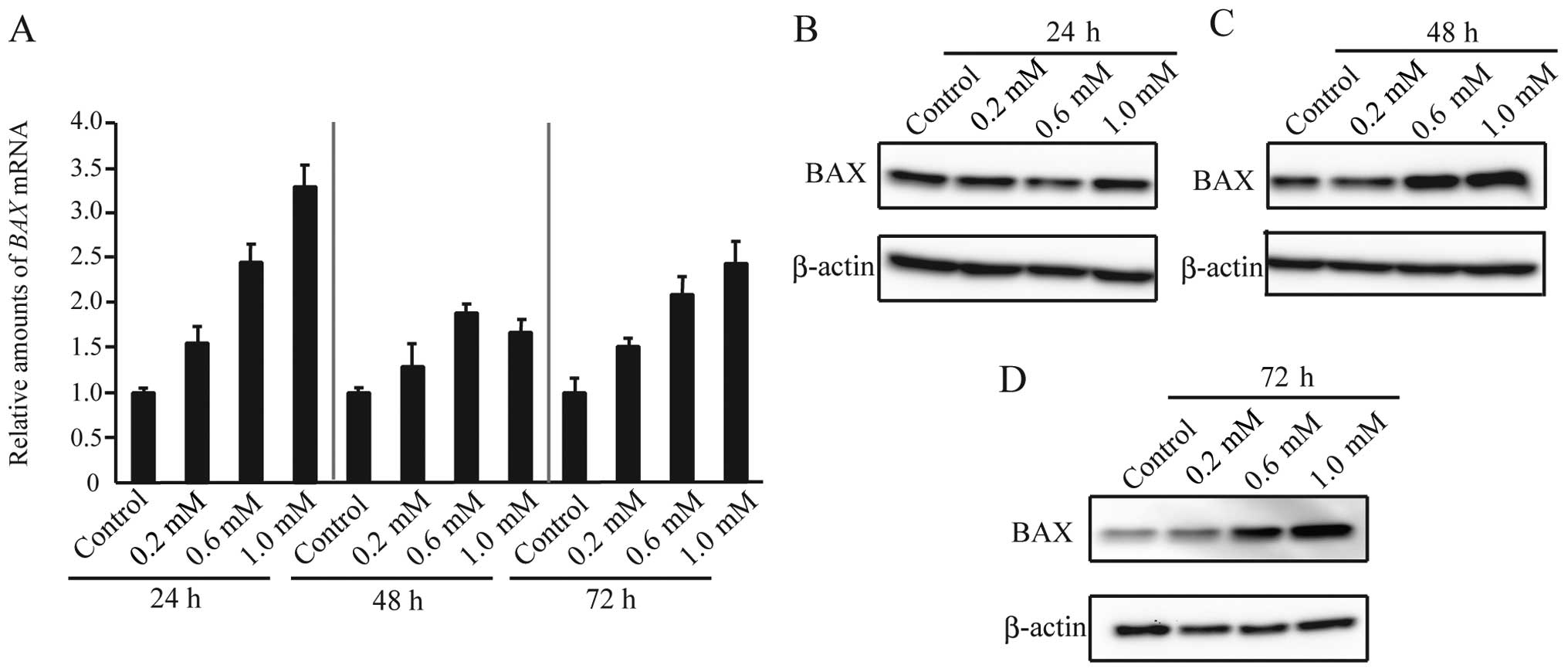
|
1
|
Priester WA and Mantel N: Occurrence of
tumors in domestic animals. Data from 12 United States and Canadian
colleges of veterinary medicine. J Natl Cancer Inst. 47:1333–1344.
1971.
|
|
2
|
Sorenmo K: Canine mammary gland tumors.
Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 33:573–596. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Graham JC and Myers RK: The prognostic
significance of angiogenesis in canine mammary tumors. J Vet Intern
Med. 13:416–418. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nieto A, Pena L, Perez-Alenza MD, Sanchez
MA, Flores JM and Castano M: Immunohistologic detection of estrogen
receptor alpha in canine mammary tumors: clinical and pathologic
associations and prognostic significance. Vet Pathol. 37:239–247.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Uva P, Aurisicchio L, Watters J, Loboda A,
Kulkarni A, Castle J, Palombo F, Viti V, Mesiti G, Zappulli V,
Marconato L, Abramo F, Ciliberto G, Lahm A, La Monica N and de
Rinaldis E: Comparative expression pathways analysis of human and
canine mammary tumors. BMC Genomics. 10:1352009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Standberg JD and Goodman DG: Animal model
of human disease: canine mammary neoplasia. Am J Pathol.
75:225–228. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pinho SS, Carvalho S, Cabral J, Reis CA
and Gartner F: Canine tumors: a spontaneous animal model of human
carcinogenesis. Transl Res. 159:165–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weismann B, Rapport MM, Linker A and Meyer
K: Isolation of the aldobionic acid of umbilical cord hyaluronic
acid. J Biol Chem. 205:205–211. 1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Toole BP: Hyaluronan: from extracellular
glue to pericellular cue. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:528–539. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Turley EA, Noble PW and Bourguignon LY:
Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem.
277:4589–4592. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fraser JR, Laurent TC and Laurent UB:
Hyaluronan: its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J
Intern Med. 242:27–33. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Menzel E and Farr C: Hyaluronidase and its
substrate hyaluronan: biochemistry, biological activities and
therapeutic uses. Cancer Lett. 131:3–11. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Auvinen P, Tammi RH, Parkinen J, Tammi M,
Agren U, Johansson R, Hirvikoski P, Eskelinen M and Kosma VM:
Hyaluronan in peritumoral stroma and malignant cells associates
with breast cancer spreading and predicts survival. Am J Pathol.
156:529–536. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Anttila MA, Tammi RH, Tammi MI, Syrjanen
KJ, Saarikoski SV and Kosma VM: High levels of stromal hyaluronan
predict poor disease outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer
Res. 60:150–155. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lipponen P, Aaltomaa S, Tammi R, Tammi M,
Agren U and Kosma VM: High stromal hyaluronan level is associated
with poor differentiation and metastasis in prostate cancer. Eur J
Cancer. 37:849–856. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Golshani R, Lopez L, Estrella V, Kramer M,
Iida N and Lokeshwar VB: Hyaluronic acid synthase-1 expression
regulates bladder cancer growth, invasion, and angiogenesis through
CD44. Cancer Res. 68:483–491. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Udabage L, Brownlee GR, Waltham M, Blick
T, Walker EC, Heldin P, Nilsson SK, Thompson EW and Brown TJ:
Antisense-mediated suppression of hyaluronan synthase-2 inhibits
the tumorigenesis and progression of breast cancer. Cancer Res.
65:6139–6150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu N, Gao F, Han Z, Xu X, Underhill CB
and Zhang L: Hyaluronan synthase 3 overexpression promotes the
growth of TSU prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 61:5207–5214.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cichy J and Pure E: The liberation of
CD44. J Cell Biol. 161:839–843. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cheung WF, Cruz TF and Turley EA: Receptor
for hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM), a hyaladherin that
regulates cell responses to growth factors. Biochem Soc Trans.
27:135–142. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Itano N, Zhuo L and Kimata K: Impact of
the hyaluronan-rich tumor microenvironment on cancer initiation and
progression. Cancer Sci. 99:1720–1725. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gotte M and Yip GW: Heparanase,
Hyaluronan, and CD44 in cancers: a breast carcinoma perspective.
Cancer Res. 66:10233–10237. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Serra M, Rabanal RM, Miquel L, Domenzain C
and Bassols A: Differential expression of CD44 in canine
melanocytic tumours. J Comp Path. 130:171–180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paltian V, Alldinger S, Baumgartner W and
Wohlsein P: Expression of CD44 in canine mammary tumours. J Comp
Path. 141:237–247. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakamura T, Funahashi M, Takagaki K,
Munakata H, Tanaka K, Saito Y and Endo M: Effect of
4-methylumbelliferone on cell-free synthesis of hyaluronic acid.
Biochem Mol Biol Int. 43:263–268. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kakizaki I, Kojima K, Takagaki K, Endo M,
Kannagi R, Ito M, Maruo Y, Sato H, Yasuda T, Mita S, Kimata K and
Itano N: A novel mechanism for the inhibition of hyaluronan
biosynthesis by 4-Methylumbelliferone. J Biol Chem.
279:33281–33289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kultti A, Pasonen-Seppanen S, Jauhiainen
M, Rilla KJ, Karna R, Pyoria E, Tammi RH and Tammi MI:
4-Methylumbelliferone inhibits hyaluronan synthesis by depletion of
cellular UDP-glucuronic acid and downregulation of hyaluronan
synthase 2 and 3. Exp Cell Res. 315:1914–1923. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lokeshwar VB, Lopez LE, Munoz D, Chi A,
Shirodkar SP, Lokeshwar SD, Escudero DO, Dhir N and Altman N:
Antitumor activity of hyaluronic acid synthesis inhibitor
4-methylumbelliferone in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:2613–2623. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshihara S, Kon A, Kudo D, Nakazawa H,
Kakizaki I, Sasaki M, Endo M and Takagaki K: A hyaluronan synthase
suppressor, 4-methylumbelliferone, inhibits liver metastasis of
melanoma cells. FEBS Lett. 579:2722–2726. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Knudson W and Knudson CB: Assembly of a
chondrocyte-like pericellular matrix on non-chondrogenic cells.
Role of the cell surface hyaluronan receptors in the assembly of a
pericellular matrix. J Cell Sci. 99:227–235. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE and Berg K:
Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye
method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods.
119:203–210. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Twentyman PR and Luscombe M: A study of
some variables in a tetrazolium dye (MTT) based assay for cell
growth and chemosensitivity. Br J Cancer. 56:279–285. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saito T, Kawana H, Azuma K, Toyoda A,
Fujita H, Kitagawa M and Harigaya K: Fragmented hyaluronan is an
autocrine chemokinetic motility factor supported by the
HAS2-HYAL2/CD44 system on the plasma membrane. Int J Oncol.
39:1311–1320. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Simpson M, Reiland J, Burger S, Furcht L,
Spicer A, Oegema T and MaCarthy JB: Hyaluronan synthase elevation
in metastatic prostate carcinoma cells correlates with hyaluronan
surface retention, a prerequisite for rapid adhesion to bone marrow
endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 276:17949–17957. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li Y, Li L, Brown TJ and Heldin P:
Silencing of hyaluronan synthase 2 suppresses the malignant
phenotype of invasive breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer.
120:2557–2567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xia W, Spector S, Hardy L, Zhao S, Saluk
A, Alemane L and Spector NL: Tumor selective G2/M cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis of epithelial and hematological malignancies by
BBL22, a benzazepine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:7494–7499. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Arai E, Nishida Y, Wasa J, Urakawa H, Zhuo
L, Kimata K, Kozawa E, Futamura N and Ishiguro N: Inhibition of
hyaluronan retention by 4-methylumbelliferone suppresses
osteosarcoma cells in vitro and lung metastasis in vivo. Br J
Cancer. 105:1839–1849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Urakawa H, Nishida Y, Wasa J, Arai E, Zhuo
L, Kimata K, Kozawa E, Futamura N and Ishiguro N: Inhibition of
hyaluronan synthesis in breast cancer cells by
4-methylumbelliferone suppresses tumorigenicity in vitro and
metastatic lesions of bone in vivo. Int J Cancer. 130:454–466.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Camenisch TD, Spicer AP, Brehm-Gibson T,
Biesterfeldt J, Agustine ML, Calabro A Jr, Kubalak S, Klewer SE and
McDonald JA: Disruption of hyaluronan synthase-2 abrogates normal
cardiac morphogenesis and hyaluronan-mediated transformation of
epithelium to mesenchyme. J Clin Invest. 106:349–360. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vigetti D, Genasetti A, Karousou E, Viola
M, Moretto P, Clerici M, Deleonibus S, De Luca G, Hascall VC and
Passi A: Proinflammatory cytokines induce hyaluronan synthesis and
monocyte adhesion in human endothelial cells through hyaluronan
synthase 2 (HAS2) and the nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB)
pathway. J Biol Chem. 285:24639–24645. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Itano N and Kimata K: Mammalian hyaluronan
synthases. IUBMB Life. 54:195–199. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Okuda H, Kobayashi A, Xia B, Watabe M, Pai
SK, Hirota S, Xing F, Liu W, Pandey PR, Fukuda K, Modur V, Ghosh A,
Wilber A and Watabe K: Hyaluronan synthase HAS2 promotes tumor
progression in bone by stimulating the interaction of breast cancer
stem-like cells with macrophages and stromal cells. Cancer Res.
72:537–547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sironen RK, Tammi M, Tammi R, Auvinen PK,
Anttila M and Kosma VM: Hyaluronan in human malignancies. Exp Cell
Res. 317:383–391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bourguignon LY, Zhu H, Chu A, Iida N,
Zhang L and Hung MC: Interaction between the adhesion receptor,
CD44, and the oncogene product, p185HER2, promotes human ovarian
tumor cell activation. J Biol Chem. 272:27913–27918. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ouhit A, Abd Elmageed ZY, Abdraboh ME,
Lioe TF and Raj MH: In vivo evidence for the role of CD44s in
promoting breast cancer metastasis to the liver. Am J Pathol.
171:2033–2039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sohara Y, Ishiguro N, Machida K, Kurata H,
Thant AA, Senga T, Matsuda S, Kimata K, Iwata H and Hamaguchi M:
Hyaluronan activates cell motility of v-Src-transformed cells via
Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphoinositide
3-kinase-Akt in a tumor-specific manner. Mol Biol Cell.
12:1859–1868. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|