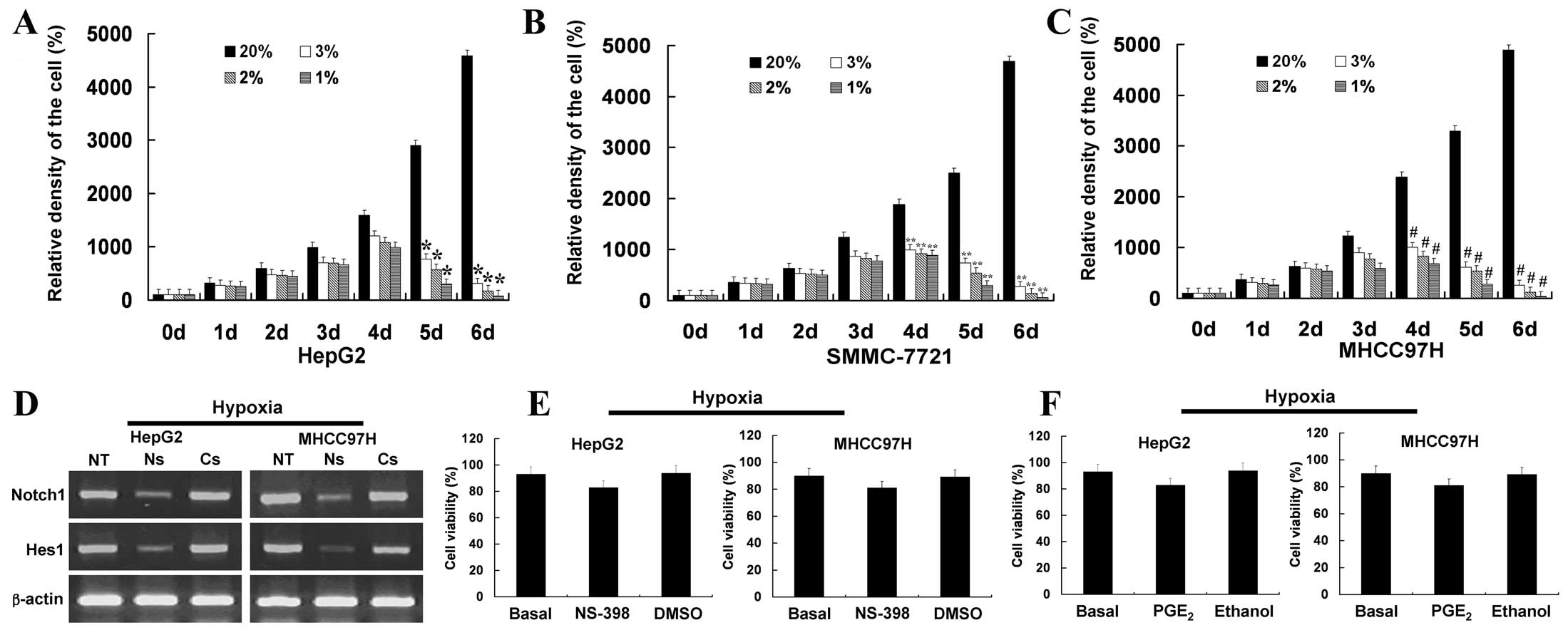
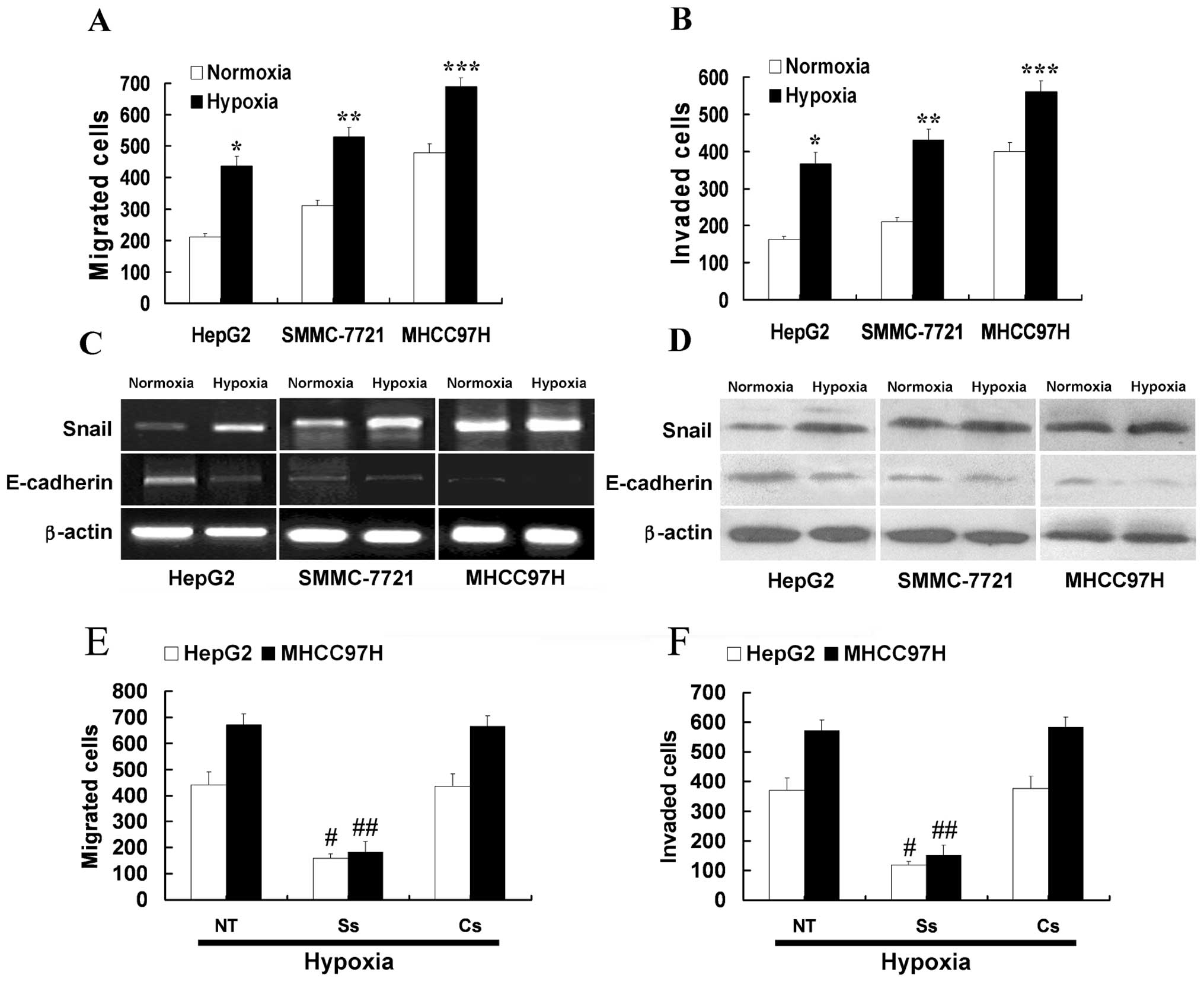
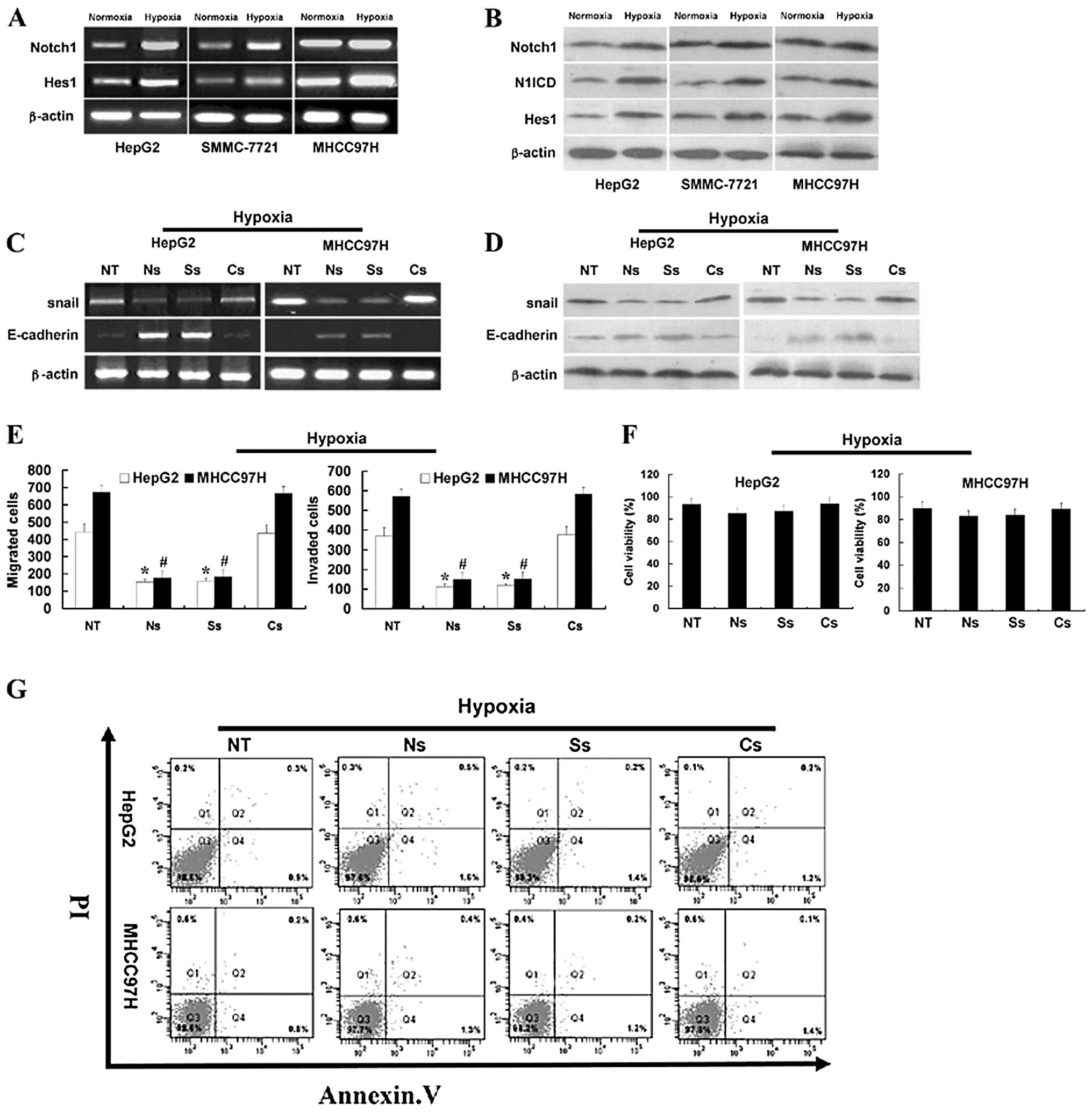
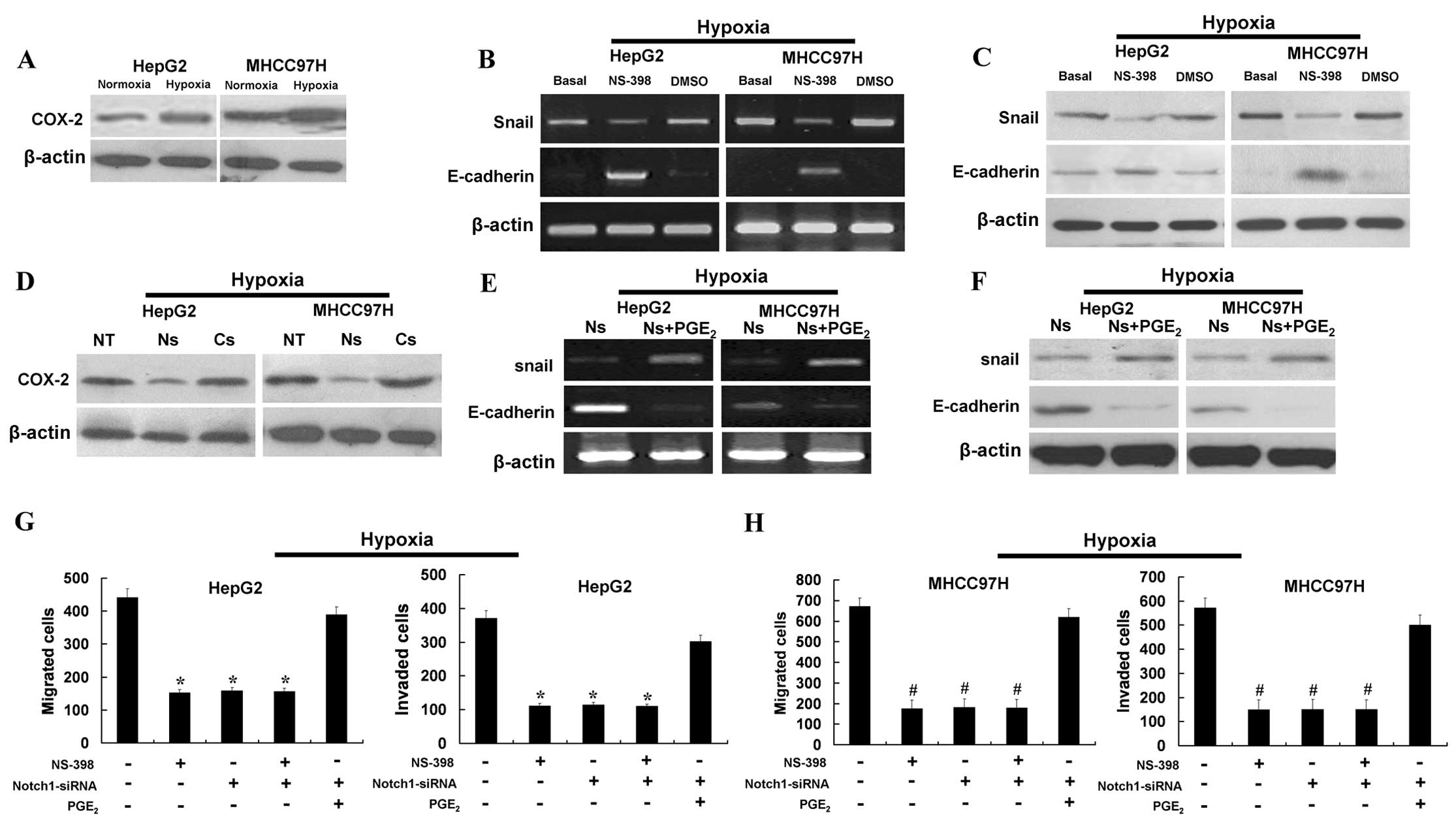
|
1
|
Yu MC, Yuan JM, Govindarajan S and Ross
RK: Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Can J Gastroenterol.
14:703–709. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tung-Ping Poon R, Fan ST and Wong J: Risk
factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence
after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 232:10–24.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J and Pouyssegur
J: Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med. 85:1301–1307. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Graeber TG, Osmanian C, Jacks T, et al:
Hypoxia-mediated selection of cells with diminished apoptotic
potential in solid tumours. Nature. 379:88–91. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cavallaro U and Christofori G: Cell
adhesion and signalling by cadherins and Ig-CAMs in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:118–132. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choi YS, Shim YM, Kim SH, et al:
Prognostic significance of E-cadherin and beta-catenin in resected
stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
24:441–449. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bremnes RM, Veve R, Gabrielson E, et al:
High-throughput tissue microarray analysis used to evaluate biology
and prognostic significance of the E-cadherin pathway in
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:2417–2428. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsujii M and DuBois RN: Alterations in
cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing
prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell. 83:493–501. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu D, Huang C, Kameyama K, et al:
E-cadherin expression associated with differentiation and prognosis
in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg.
71:949–954. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giroldi LA, Bringuier PP, de Weijert M,
Jansen C, van Bokhoven A and Schalken JA: Role of E boxes in the
repression of E-cadherin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
241:453–458. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Perl AK, Wilgenbus P, Dahl U, Semb H and
Christofori G: A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from
adenoma to carcinoma. Nature. 392:190–193. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moody SE, Perez D, Pan TC, et al: The
transcriptional repressor Snail promotes mammary tumor recurrence.
Cancer Cell. 8:197–209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan W, Fu Y, Tian D, et al: PI3 kinase/Akt
signaling mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hypoxic
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
382:631–636. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cannito S, Novo E, Compagnone A, et al:
Redox mechanisms switch on hypoxia-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:2267–2278. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu L, Ren ZG, Shen Y, et al: Influence of
hepatic artery occlusion on tumor growth and metastatic potential
in a human orthotopic hepatoma nude mouse model: relevance of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Sci. 101:120–128. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD and Lake RJ:
Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in
development. Science. 284:770–776. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miele L and Osborne B: Arbiter of
differentiation and death: Notch signaling meets apoptosis. J Cell
Physiol. 181:393–409. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gustafsson MV, Zheng X, Pereira T, et al:
Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the undifferentiated
cell state. Dev Cell. 9:617–628. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao J, Song Z, Chen Y, et al: Deregulated
expression of Notch receptors in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Dig Liver Dis. 40:114–121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zlobin A, Jang M and Miele L: Toward the
rational design of cell fate modifiers: notch signaling as a target
for novel biopharmaceuticals. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 1:83–106.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jang MS, Zlobin A, Kast WM and Miele L:
Notch signaling as a target in multimodality cancer therapy. Curr
Opin Mol Ther. 2:55–65. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sahlgren C, Gustafsson MV, Jin S,
Poellinger L and Lendahl U: Notch signaling mediates
hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:6392–6397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lim SO, Kim HS, Quan X, et al: Notch1
binds and induces degradation of Snail in hepatocellular carcinoma.
BMC Biol. 9:832011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Molecular targeted
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 48:1312–1327.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Postovit LM, Adams MA, Lash GE, Heaton JP
and Graham CH: Oxygen-mediated regulation of tumor cell
invasiveness. Involvement of a nitric oxide signaling pathway. J
Biol Chem. 277:35730–35737. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rofstad EK: Microenvironment-induced
cancer metastasis. Int J Radiat Biol. 76:589–605. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lundgren K, Nordenskjold B and Landberg G:
Hypoxia, Snail and incomplete epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 101:1769–1781. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wells A, Yates C and Shepard CR:
E-cadherin as an indicator of mesenchymal to epithelial reverting
transitions during the metastatic seeding of disseminated
carcinomas. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:621–628. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Osada T, Sakamoto M, Ino Y, et al:
E-cadherin is involved in the intrahepatic metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 24:1460–1467. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hotz B, Arndt M, Dullat S, Bhargava S,
Buhr HJ and Hotz HG: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition:
expression of the regulators snail, slug, and twist in pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4769–4776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Cubillo E, Sarrio D, et
al: Genetic profiling of epithelial cells expressing E-cadherin
repressors reveals a distinct role for Snail, Slug, and E47 factors
in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 66:9543–9556.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cano A, Perez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, et al:
The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, et al: The
transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene
expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yokoyama K, Kamata N, Hayashi E, et al:
Reverse correlation of E-cadherin and snail expression in oral
squamous cell carcinoma cells in vitro. Oral Oncol. 37:65–71. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiao W, Miyazaki K and Kitajima Y: Inverse
correlation between E-cadherin and Snail expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Br J
Cancer. 86:98–101. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Balint K, Xiao M, Pinnix CC, et al:
Activation of Notch1 signaling is required for
beta-catenin-mediated human primary melanoma progression. J Clin
Invest. 115:3166–3176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Buchler P, Gazdhar A, Schubert M, et al:
The Notch signaling pathway is related to neurovascular progression
of pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 242:791–800. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Li Y, Rahman KM, Zhang
Y and Sarkar FH: Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by
inactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB, vascular endothelial growth
factor, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 66:2778–2784. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Qi R, An H, Yu Y, et al: Notch1 signaling
inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction
of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63:8323–8329.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dubinett SM, Sharma S, Huang M, Dohadwala
M, Pold M and Mao JT: Cyclooxygenase-2 in lung cancer. Prog Exp
Tumor Res. 37:138–162. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Dannenberg AJ and Subbaramaiah K:
Targeting cyclooxygenase-2 in human neoplasia: rationale and
promise. Cancer Cell. 4:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brown JR and DuBois RN: Cyclooxygenase as
a target in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:S4266–S4269. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Dannenberg AJ and Zakim D: Chemoprevention
of colorectal cancer through inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Semin
Oncol. 26:499–504. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang M, Stolina M, Sharma S, et al:
Non-small cell lung cancer cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of
cytokine balance in lymphocytes and macrophages: upregulation of
interleukin 10 and down–regulation of interleukin 12 production.
Cancer Res. 58:1208–1216. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park K, Han S, Shin E, Kim HJ and Kim JY:
Cox-2 expression on tissue microarray of breast cancer. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 32:1093–1096. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dohadwala M, Batra RK, Luo J, et al:
Autocrine/paracrine prostaglandin E2 production by non-small cell
lung cancer cells regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 and CD44 in
cyclooxygenase-2-dependent invasion. J Biol Chem. 277:50828–50833.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Dohadwala M, Yang SC, Luo J, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2-dependent regulation of E-cadherin: prostaglandin
E(2) induces transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and snail in non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 66:5338–5345. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yeh TS, Wu CW, Hsu KW, et al: The
activated Notch1 signal pathway is associated with gastric cancer
progression through cyclooxygenase-2. Cancer Res. 69:5039–5048.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Noda M, Tatsumi Y, Tomizawa M, et al:
Effects of etodolac, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, on the
expression of E-cadherin-catenin complexes in gastrointestinal cell
lines. J Gastroenterol. 37:896–904. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee DS and Moss SF: COX-2 inhibition and
the prevention of gastric cancer. Digestion. 74:184–186.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fujimura T, Ohta T, Oyama K, Miyashita T
and Miwa K: Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in the carcinogenesis of
gastrointestinal tract cancers: a review and report of personal
experience. World J Gastroenterol. 12:1336–1345. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|