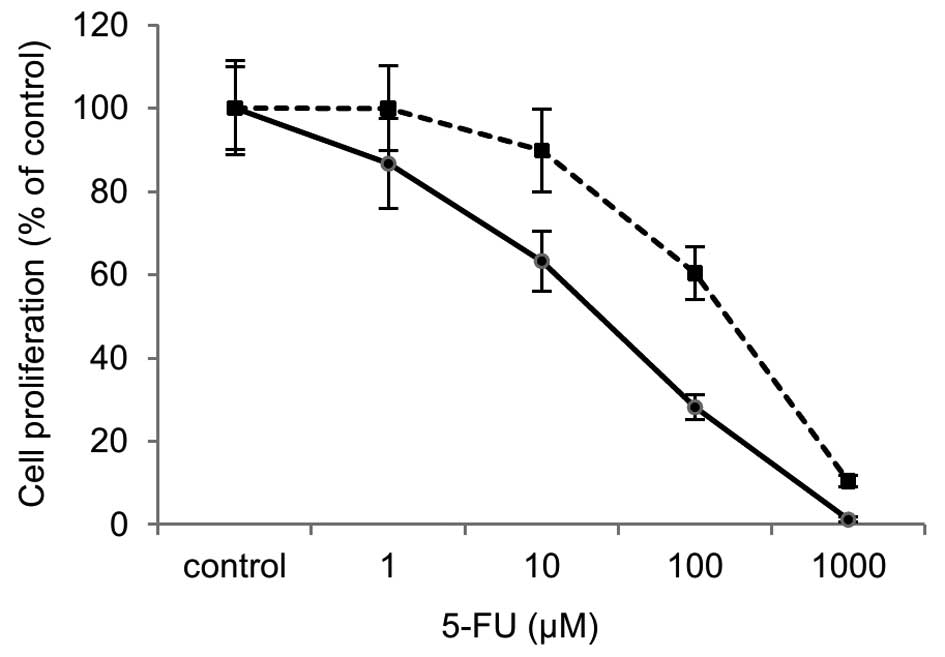
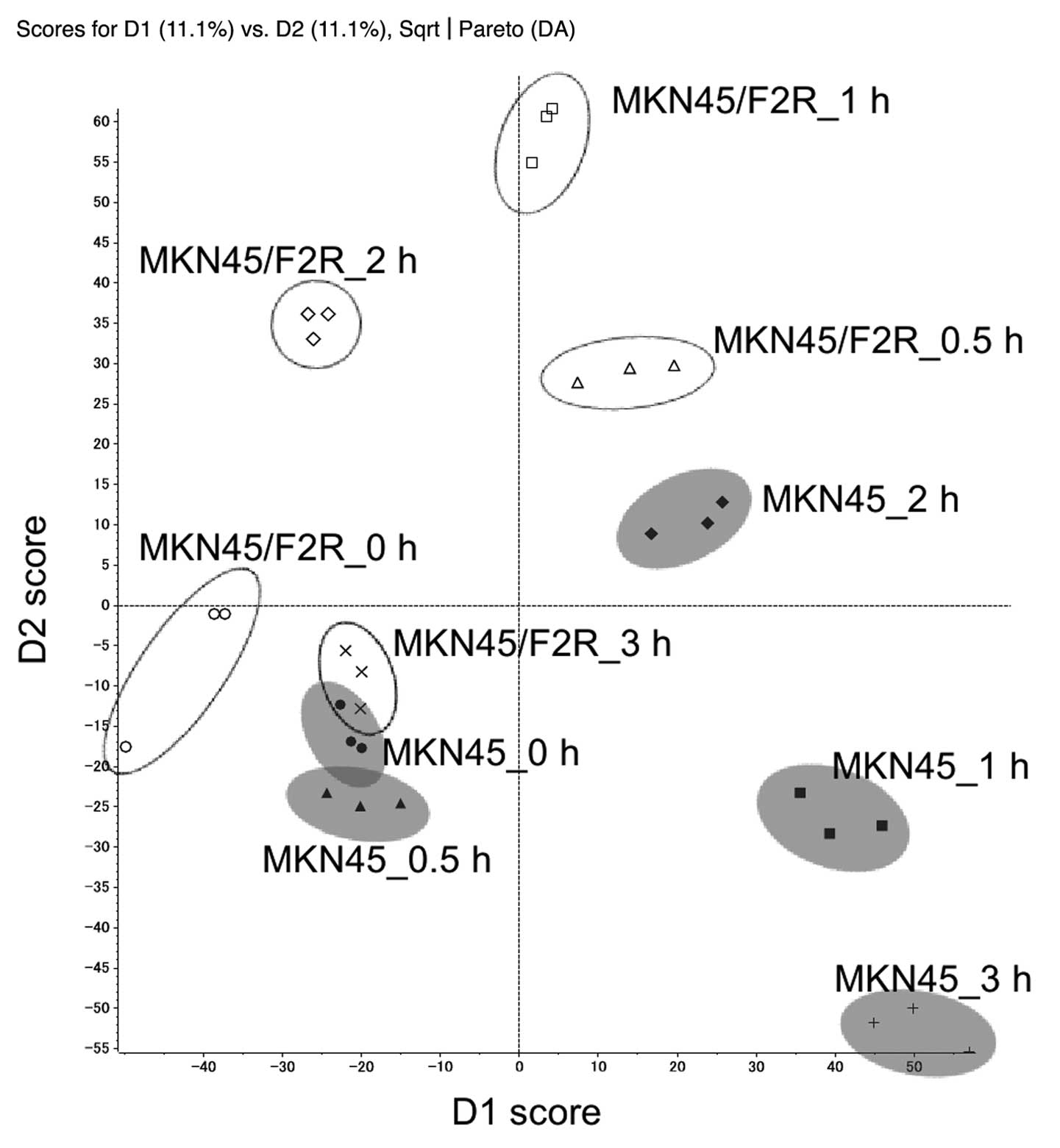
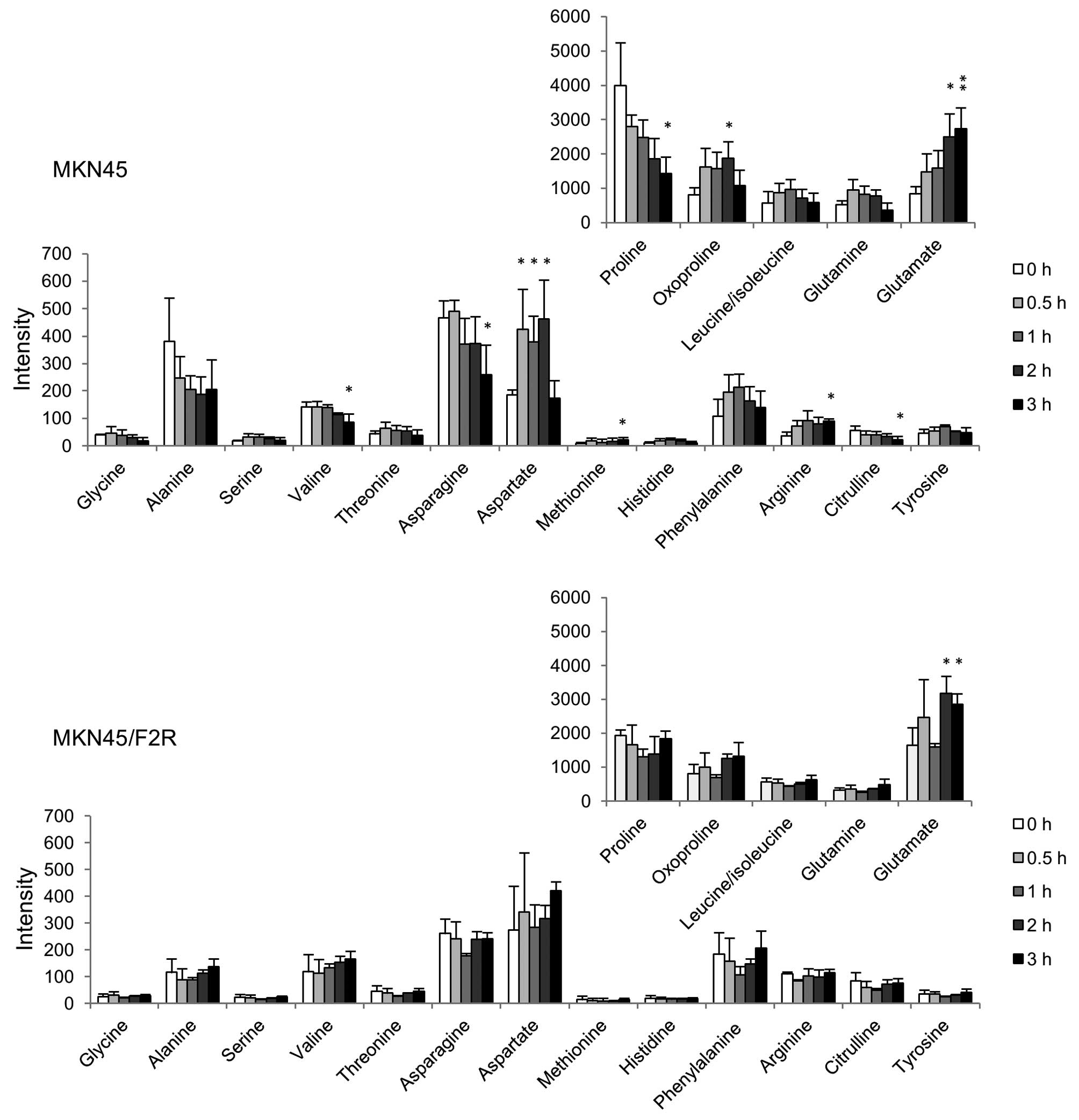
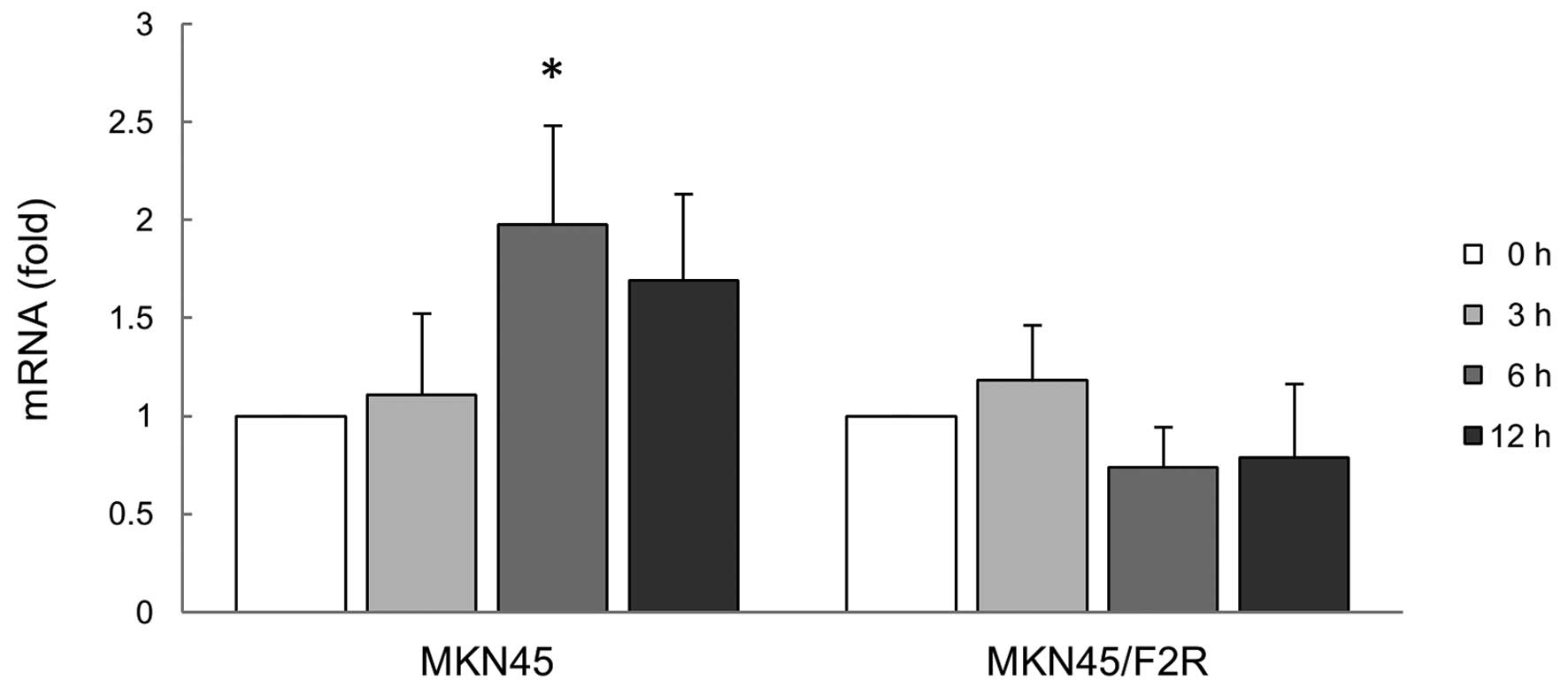
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 56:106–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Koizumi W, Narahara H, Hara T, et al: S-1
plus cisplatin versus S-1 alone for first-line treatment of
advanced gastric cancer (SPIRITS trial): a phase III trial. Lancet
Oncol. 9:215–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, et al:
Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N
Eng J Med. 358:36–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S,
et al: Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil
compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for
advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 Study Group. J Clin
Oncol. 24:4991–4997. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sumner LW, Mendes P and Dixon RA: Plant
metabolomics: large-scale phytochemistry in the functional genomics
era. Phytochemistry. 62:817–836. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schauer N, Semel Y, Roessner U, et al:
Comprehensive metabolic profiling and phenotyping of interspecific
introgression lines for tomato improvement. Nat Biotechnol.
24:447–454. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Plumb R, Granger J, Stumpf C, Wilson ID,
Evans JA and Lenz EM: Metabonomic analysis of mouse urine by
liquid-chromatography-time of flight mass spectrometry (LC-TOFMS):
detection of strain, diurnal and gender differences. Analyst.
128:819–823. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Opstad KS, Bell BA, Griffiths JR and Howe
FA: An assessment of the effects of sample ischaemia and spinning
time on the metabolic profile of brain tumour biopsy specimens as
determined by high-resolution magic angle spinning (1)H NMR. NMR
Biomed. 21:1138–1147. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bayet-Robert M, Loiseau D, Rio P, et al:
Quantitative two-dimentional HRMAS 1H-NMR
spectroscopy-based metabolite profiling of human cancer cell lines
and response to chemotherapy. Magn Reson Med. 63:1172–1183.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bayet-Robert M, Lim S, Barthomeuf C and
Morvan D: Biochemical disorders induced by cytotoxic marine natural
products in breast cancer cells as revealed by proton NMR
spectroscopy-based metabolomics. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1170–1179.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Morvan D and Demidem A: Metabolomics by
proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the response to
chloroethylnitrosourea reveals drug efficacy and tumor adaptive
metabolic pathways. Cancer Res. 67:2150–2159. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tsutani Y, Yoshida K, Sanada Y, et al:
Decreased orotate phosphoribosyltransferase activity produces
5-fluorouracil resistance in a human gastric cancer cell line.
Oncol Rep. 99:2268–2273. 2008.
|
|
13
|
Hirayama A, Kami K, Sugimoto M, et al:
Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer
microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass
spectrometry. Cancer Res. 69:4918–4925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen JL, Tang HQ, Hu JD, et al:
Metabolomics of gastric cancer metastasis detected by gas
chromatography and mass spectrometry. World J Gastroenterol.
16:5874–5880. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mohamed R, Varesio E, Ivosev G, et al:
Comprehensive analytical strategy for biomarker identification
based on liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry and new
candidate confirmation tools. Anal Chem. 81:7677–7694. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomics.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Horai H, Arita M, Kanaya S, et al:
MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for
life sciences. J Mass Spectrom. 45:703–714. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Griffin JL and Shockcor JP: Metabolic
profiles of cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:551–561. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dang CV and Semenza GL: Oncogenic
alterations of metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:68–72. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fox CJ, Hammerman PS and Thompson CB: Fuel
feeds function: energy metabolism and the T-cell response. Nut Rev
Immunol. 5:844–852. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Phang JM, Liu W and Zabirnyk O: Proline
metabolism and microenvironmental stress. Annu Rev Nutr.
30:441–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cascino A, Muscaritoli M, Cangiano C, et
al: Plasma amino acid imbalance in patients with lung and breast
cancer. Anticancer Res. 15:507–510. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Phang JM: The regulatory functions of
proline and pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid. Curr Top Cell Regul.
25:91–132. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
White TA, Krishnan N, Becker DF and Tanner
JJ: Structure and kinetics of monofunctional proline dehydrogenase
from Thermus thermophilius. J Biol Chem. 282:14316–14327.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Surazynski A and Phang
JM: Proline oxidase, a p53-induced gene, targets COX-2/PDE2
signaling to induce apoptosis and inhibit tumor growth in
colorectal cancers. Oncogene. 27:6729–6737. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pandhare J, Cooper SK and Phang JM:
Proline oxidase, a proapoptotic gene, is induced by triglitazone:
evidence for both peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor
gamma-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem.
281:2044–2052. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Borchert GL, Donald SP, Diwan BA,
Anver M and Phang JM: Proline oxidase functions as a mitochondrial
tumor suppressor in human cancers. Cancer Res. 69:6414–6422. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|