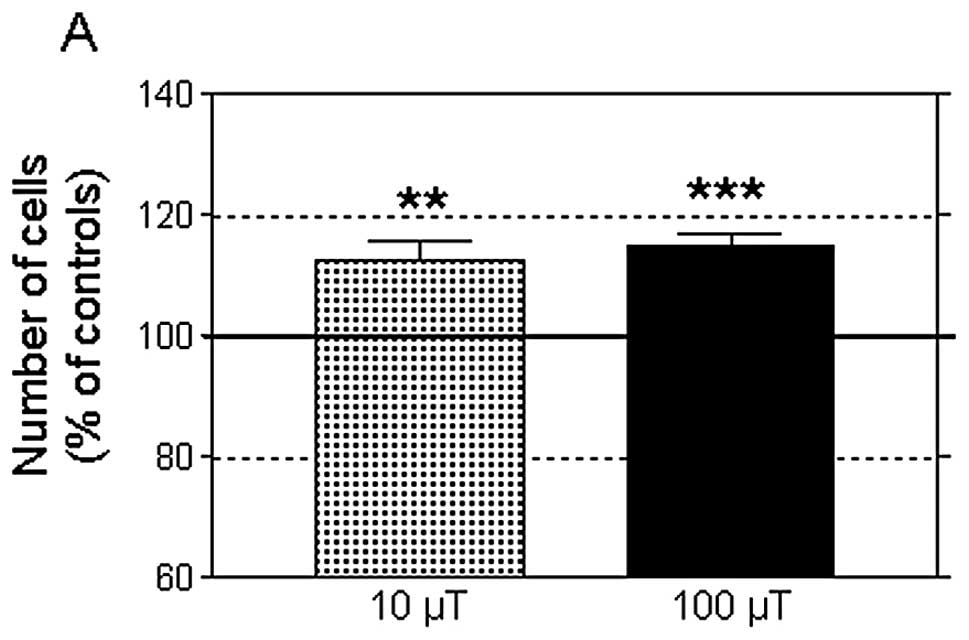
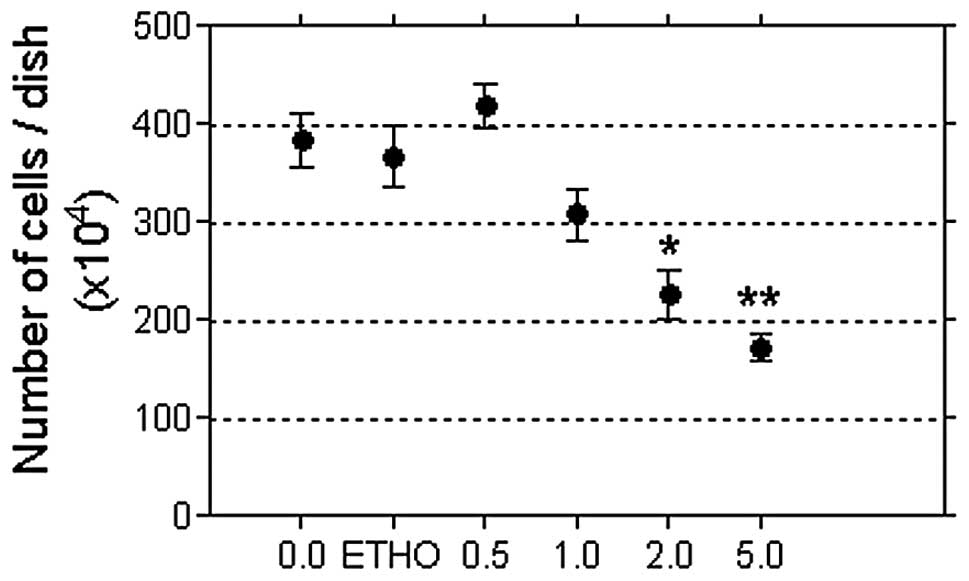
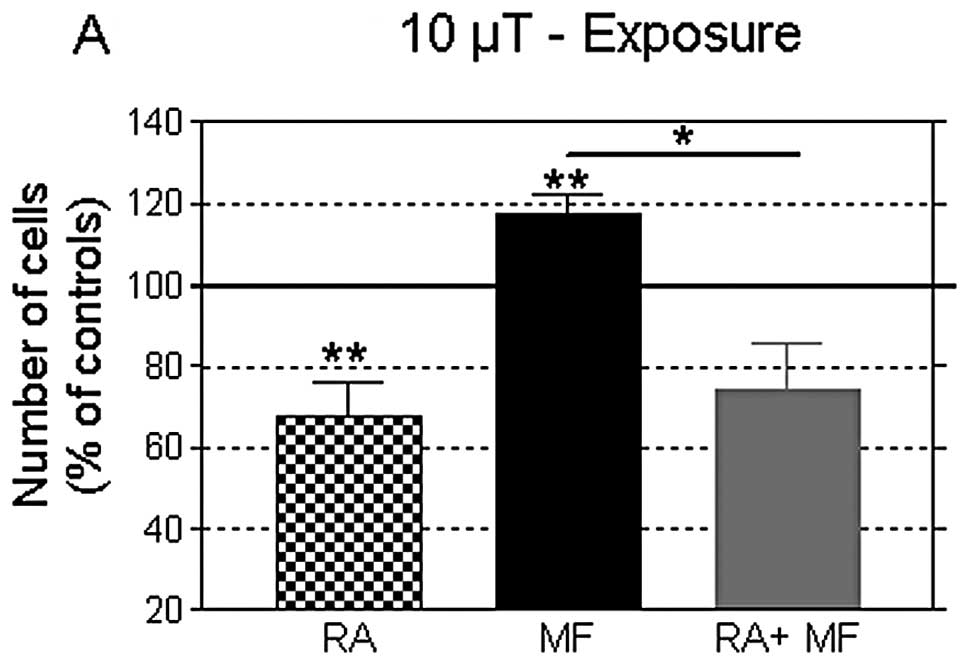
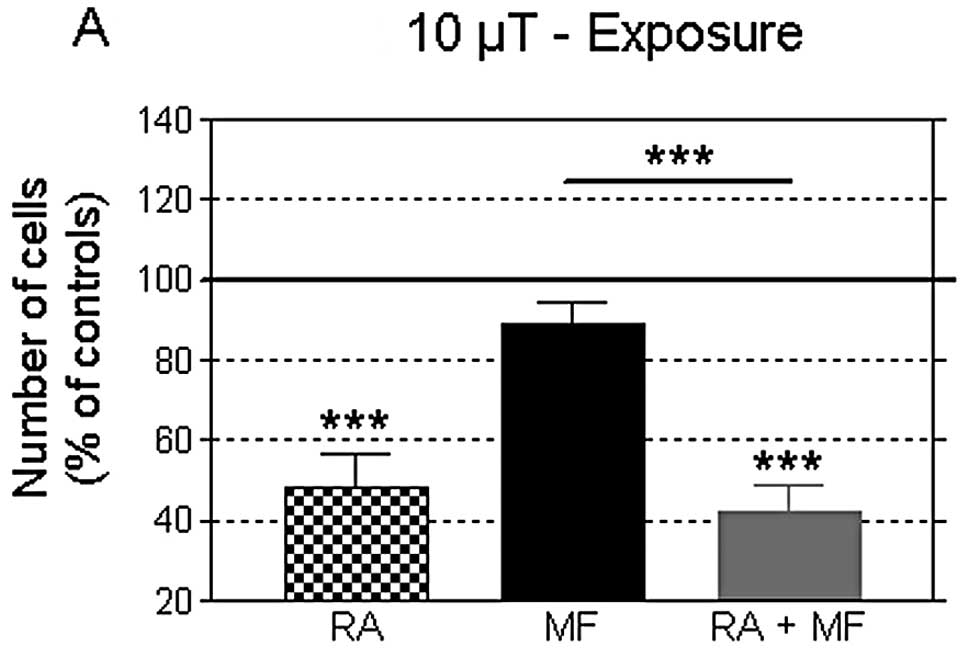
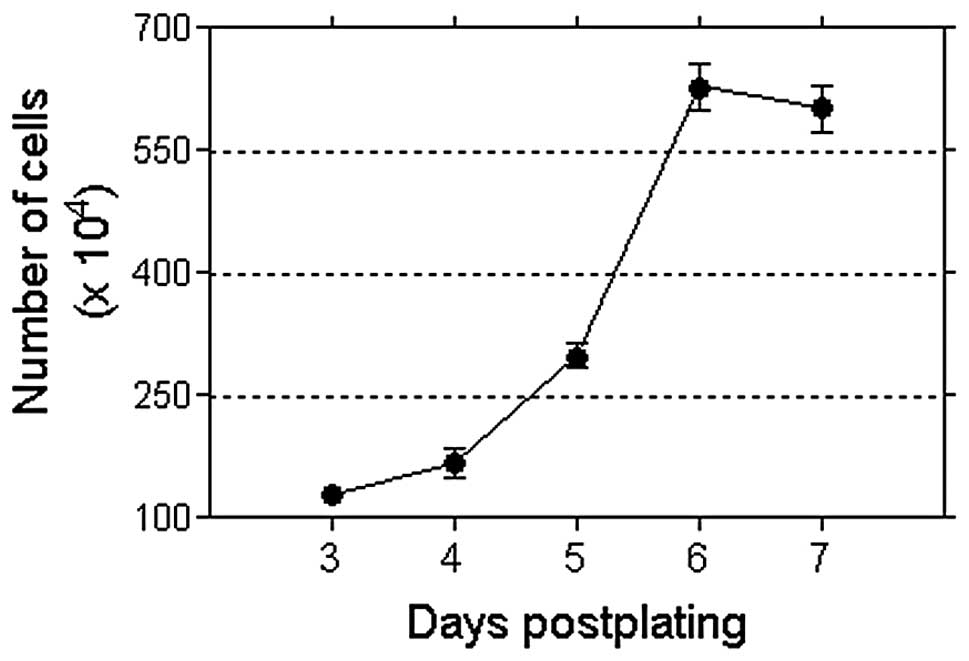
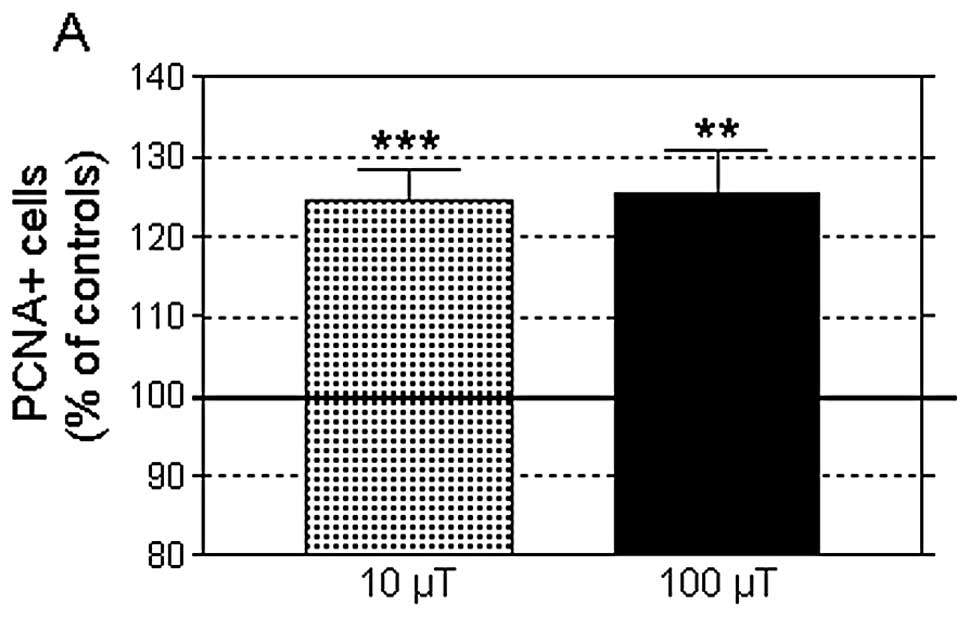
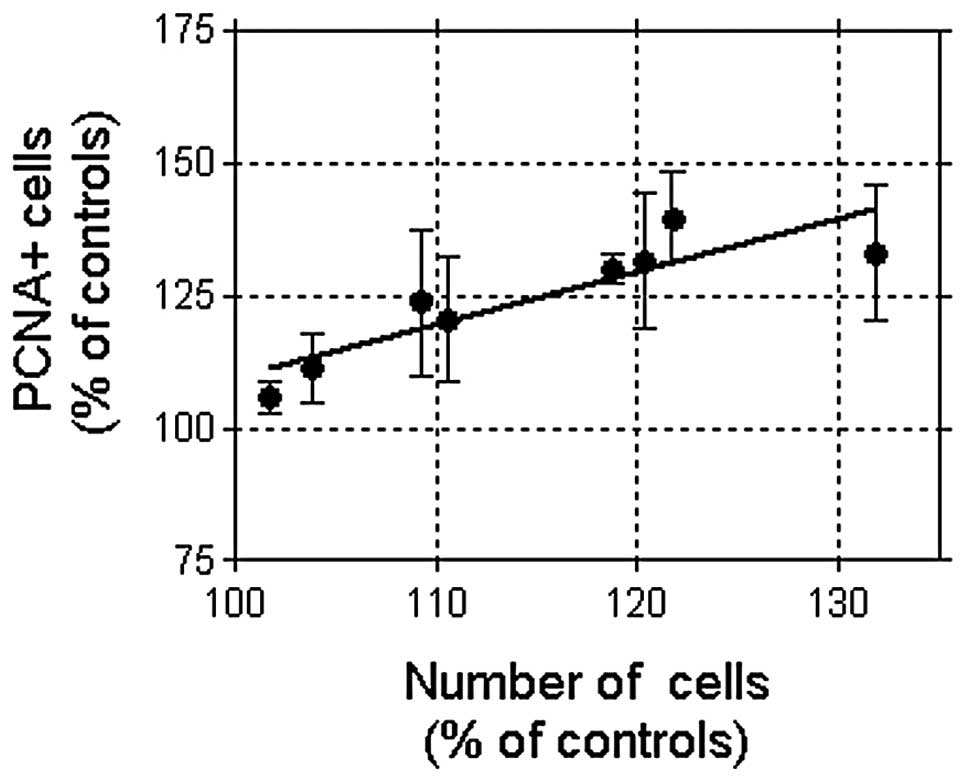
|
1
|
Kheifets LI, Afifi AA, Buffler PA and
Zhang ZW: Occupational electric and magnetic field exposure and
brain cancer: a meta-analysis. J Occup Environ Med. 37:1327–1341.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kliukiene J, Tynes T and Andersen A:
Residential and occupational exposures to 50-Hz magnetic fields and
breast cancer in women: a population-based study. Am J Epidemiol.
159:852–861. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Davanipour Z and Sobel E: Long-term
exposure to magnetic fields and the risks of Alzheimer’s disease
and breast cancer: further biological research. Pathophysiology.
16:149–156. 2009.
|
|
4
|
Hakansson N, Gustavsson P, Johansen C and
Floderus B: Neurodegenerative diseases in welders and other workers
exposed to high levels of magnetic fields. Epidemiology.
14:420–426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huss A, Spoerri A, Egger M and Röösli M:
Residence near power lines and mortality from neurodegenerative
diseases: longitudinal study of the Swiss population. Am J
Epidemiol. 169:167–175. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Feychting M and Forssen U: Electromagnetic
fields and female breast cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 17:553–558.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kheifets L, Bowman JD, Checkoway H,
Feychting M, Harrington JM, Kavet R, Marsh G, Mezei G, Renew DC and
van Wijngaarden E: Future needs of occupational epidemiology of
extremely low frequency electric and magnetic fields: review and
recommendations. Occup Environ Med. 66:72–80. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
International Agency for Research of
Cancer (IARC). IARC monograph on the evaluation of carcinogenic
risks to humans. 80:Non-ionizing radiation, Part 1: Static and
extremely low-frequency (ELF) electric and magnetic fields. IARC
Press; Lyon, France: 2002, Retrieved from: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol80/mono80.pdf.
Last accessed 1 August 2012
|
|
9
|
International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for limiting exposure to
time varying electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields. Health
Phys. 74:494–522. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
International Commission on Non-Ionizing
Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). Guidelines for limiting exposure to
time varying electric and magnetic fields (1 Hz to 100 kHz). Health
Phys. 99:818–836. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fedrowitz M and Loscher W: Exposure of
Fischer 344 rats to a weak power frequency magnetic field
facilitates mammary tumorigenesis in the DMBA model of breast
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 29:186–193. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiménez-García MN, Arellanes-Robledo J,
Aparicio-Bautista DI, Rodríguez-Segura MA, Villa-Trevino S and
Godina-Nava JJ: Anti-proliferative effect of extremely low
frequency electromagnetic field on preneoplastic lesions formation
in the rat liver. BMC Cancer. 10:159–170. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wen J, Jiang S and Chen B: The effect of
100 Hz magnetic field combined with X-ray on hepatoma-implanted
mice. Bioelectromagnetics. 32:322–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Juutilainen J: Do electromagnetic fields
enhance the effects of environmental carcinogens? Radiat Prot
Dosimetry. 132:228–231. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Santini MT, Rainaldi G and Indovina PL:
Cellular effects of extremely low frequency (ELF) electromagnetic
fields. Int J Radiat Biol. 85:294–313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li H, Zeng Q, Weng Y, Lu D, Jiang H and Xu
Z: Effects of ELF magnetic fields on protein expression profile of
human breast cancer cells MCF7. Sci China C Life Sci. 48:506–514.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lupke M, Frahm J, Lantow M, Maercker C,
Remondini D, Bersani F and Simko M: Gene expression analysis of
ELF-MF exposed human monocytes indicating the involvement of the
alternative activation pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1763:402–412.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vianale G, Reale M, Amerio P, Stefanachi
M, Di Luzio S and Muraro R: Extremely low frequency electromagnetic
field enhances human keratinocyte cell growth and decreases
proinflammatory chemokine production. Br J Dermatol. 158:1189–1196.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Simko M, Kriehuber R, Weiss DG and Luben
RA: Effects of 50 Hz EMF exposure on micronucleus formation and
apoptosis in transformed and non-transformed human cell lines.
Bioelectromagnetics. 19:85–91. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nikolova T, Czyz J, Rolletschek A,
Blyszczuk P, Fuchs J, Jovtchev G, Schuderer J, Kuster N and Wobus
AM: Electromagnetic fields affect transcript levels of
apoptosis-related genes in embryonic stem cell-derived neural
progenitor cells. FASEB J. 19:1686–1688. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Manikonda PK, Rajendra P, Devendranath D,
Gunasekaran B, Channakeshava, Aradhya RS, Sashidhar RB and
Subramanyam C: Influence of extremely low frequency magnetic fields
on Ca2+ signaling and NMDA receptor functions in rat
hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 413:145–149. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gaetani R, Ledda M, Barile L, Chimenti I,
De Carlo F, Forte E, Ionta V, Giuliani L, D’Emilia E, Frati G,
Miraldi F, Pozzi D, Messina E, Grimaldi S, Giacomello A and Lisi A:
Differentiation of human adult cardiac stem cells exposed to
extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Cardiovasc Res.
82:411–420. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Di Loreto S, Falone S, Caracciolo V,
Sebastiani P, D’Alessandro A, Mirabilio A, Zimmitti V and
Amicarelli F: Fifty hertz extremely low-frequency magnetic field
exposure elicits redox and trophic response in rat-cortical
neurons. J Cell Physiol. 219:334–343. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pirozzoli MC, Marino C, Lovisolo GA,
Laconi C, Mosiello L and Negroni A: Effects of 50 Hz
electromagnetic field exposure on apoptosis and differentiation in
a neuroblastoma cell line. Bioelectromagnetics. 24:510–516. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Falone S, Grossi MR, Cinque B, D’Angelo B,
Tettamanti E, Cimini A, Di Ilio C and Amicarelli F: Fifty hertz
extremely low-frequency electromagnetic field causes changes in
redox and differentiative status in neuroblastoma cells. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 39:2093–2106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eleuteri AM, Amici M, Bonfili L, Cecarini
V, Cuccioloni M, Grimaldi S, Giuliani L, Angeletti M and Fioretti
E: 50 Hz extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields enhance
protein carbonyl groups content in cancer cells: effects on
proteasomal systems. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009:8342392009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Simko M, Kriehuber R and Lange S:
Micronucleus formation in human amnion cells after exposure to 50
Hz MF applied horizontally and vertically. Mutat Res. 418:101–111.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Pilger A, Rudiger HW
and Jahn O: Induction of DNA strand breaks by intermittent exposure
to extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic fields in human diploid
fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 519:1–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Jahn O and Rudiger
HW: Intermittent extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields
cause DNA damage in a dose-dependent way. Int Arch Occup Environ
Health. 76:431–436. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ivancsits S, Diem E, Jahn O and Rudiger
HW: Age-related effects on induction of DNA strand breaks by
intermittent exposure to electromagnetic fields. Mech Ageing Dev.
124:847–850. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fatigoni C, Dominici L, Moretti M,
Villarini M and Monarca S: Genotoxic effects of extremely low
frequency (ELF) magnetic fields (MF) evaluated by the
Tradescantia-micronucleus assay. Environ Toxicol. 20:585–591. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Simko M and Mattsson MO: Extremely low
frequency electromagnetic fields as effectors of cellular responses
in vitro: possible immune cell activation. J Cell Biochem.
93:83–92. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mannerling AC, Simkó M, Mild KH and
Mattsson MO: Effects of 50-Hz magnetic field exposure on superoxide
radical anion formation and HSP70 induction in human K562 cells.
Radiat Environ Biophys. 49:731–741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Trillo MA, Martínez MA, Cid MA, Leal J and
Úbeda A: Influence of a 50 Hz magnetic field and of
all-trans-retinol on the proliferation of human cancer cell lines.
Int J Oncol. 40:1405–1413. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tulachan SS, Doi R, Kawaguchi Y, Tsuji S,
Nakajima S, Masui T, Koizumi M, Toyoda E, Mori T, Ito D, Kami K,
Fujimoto K and Imamura M: All-trans retinoic acid induces
differentiation of ducts and endocrine cells by
mesenchymal/epithelial interactions in embryonic pancreas.
Diabetes. 52:76–84. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Schenk T, Chen WC, Göllner S, Howell L,
Jin L, Hebestreit K, Klein HU, Popescu AC, Burnett A, Mills K,
Casero RA Jr, Marton L, Woster P, Minden MD, Dugas M, Wang JC, Dick
JE, Müller-Tidow C, Petrie K and Zelent A: Inhibition of the LSD1
(KDM1A) demethylase reactivates the all-trans-retinoic acid
differentiation pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med.
18:605–611. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang QJ, Zhou LY, Mu YQ, Zhou QX, Luo JY,
Cheng L, Deng ZL, He TC, Haydon RC and He BC: All-trans retinoic
acid inhibits tumor growth of human osteosarcoma by activating Smad
signaling-induced osteogenic differentiation. Int J Oncol.
41:153–160. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Handler A, Lobo MD, Alonso FJ, Paíno CL
and Mena MA: Functional implications of the
noradrenergic-cholinergic switch induced by retinoic acid in NB69
neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci Res. 60:311–320. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hölzel M, Huang S, Koster J, Ora I,
Lakeman A, Caron H, Nijkamp W, Xie J, Callens T, Asgharzadeh S,
Seeger RC, Messiaen L, Versteeg R and Bernards R: NF1 is a tumor
suppressor in neuroblastoma that determines retinoic acid response
and disease outcome. Cell. 142:218–229. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shih YY, Lee H, Nakagawara A, Juan HF,
Jeng YM, Tsay YG, Lin DT, Hsieh FJ, Pan CY, Hsu WM and Liao YF:
Nuclear GRP75 binds retinoic acid receptors to promote neuronal
differentiation of neuroblastoma. PLoS One. 6:e262362011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Di Nallo AM, Strigari L, Giliberti C,
Bedini A, Palomba R and Benassi M: Monitoring of people and workers
exposure to the electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields in an
Italian National Cancer Institute. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
27:162008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Blackman CF, Benane SG and House DE:
Evidence for direct effect of magnetic fields on neurite outgrowth.
FASEB J. 7:801–806. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing
the principle of protein dye-binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Burton K: Study of the conditions and
mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric
estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 62:315–323.
1956.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Woods AL, Hall PA, Shepherd NA, Hanby AM,
Waseem NH, Lane DP and Levison DA: The assessment of proliferating
cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining in primary
gastrointestinal lymphomas and its relationship to histological
grade, S+G2+M phase fraction (flow cytometric analysis) and
prognosis. Histopathology. 19:21–27. 1991.
|
|
46
|
Tan Z, Wortman M, Dillehay KL, Seibel WL,
Evelyn CR, Smith SJ, Malkas LH, Zheng Y, Lu S and Dong Z: Small
molecule targeting of PCNA chromatin association inhibits tumor
cell growth. Mol Pharmacol. 81:811–819. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Martínez MA, Úbeda A, Cid MA and Trillo
MA: The proliferative response of NB69 human neuroblastoma cells to
a 50 Hz magnetic field is mediated by ERK1/2 signaling. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 29:675–686. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kawasaki H, Mukai K, Yajima S, Tanaka R,
Takayama J, Takasaki Y and Ohira M: Prognostic value of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining in
neuroblastoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 24:300–304. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Stoimenov I and Helleday T: PCNA on the
crossroad of cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:605–613. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Delle Monache S, Alessandro R, Iorio R,
Gualtieri G and Colonna R: Extremely low frequency electromagnetic
fields (ELF-EMFs) induce in vitro angiogenesis process in human
endothelial cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 29:640–648. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wolf FI, Torsello A, Tedesco B, Fasanella
S, Boninsegna A, D’Ascenzo M, Grassi C, Azzena GB and Cittadini A:
50-Hz extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields enhance cell
proliferation and DNA damage: possible involvement of a redox
mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1743:120–129. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sulpizio M, Falone S, Amicarelli F,
Marchisio M, Di Giuseppe F, Eleuterio E, Di Ilio C and Angelucci S:
Molecular basis underlying the biological effects elicited by
extremely low-frequency magnetic field (ELF-MF) on neuroblastoma
cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:3797–3806. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yoshizawa H, Tsuchiya T, Mizoe H, Ozeki H,
Kanao S, Yomori H, Sakane C, Hasebe S, Motomura T, Yamakawa T,
Mizuno F, Hirose H and Otaka Y: No effect of extremely
low-frequency magnetic field observed on cell growth or initial
response of cell proliferation in human cancer cell lines.
Bioelectromagnetics. 23:355–368. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grassi C, D’Ascenzo M, Torsello A,
Martinotti G, Wolf F, Cittadini A and Azzena GB: Effects of 50 Hz
electromagnetic fields on voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
and their role in modulation of neuroendocrine cell proliferation
and death. Cell Calcium. 35:307–315. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bułdak RJ, Polaniak R, Bułdak L,
Zwirska-Korczala K, Skonieczna M, Monsiol A, Kukla M, Duława-Bułdak
A and Birkner E: Short-term exposure to 50 Hz ELF-EMF alters the
cisplatin-induced oxidative response in AT478 murine squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 33:641–651. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hong MN, Han NK, Lee HC, Ko YK, Chi SG,
Lee YS, Gimm YM, Myung SH and Lee JS: Extremely low frequency
magnetic fields do not elicit oxidative stress in MCF10A cells. J
Radiat Res. 53:79–86. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ivancsits S, Pilger A, Diem E, Jahn O and
Rüdiger HW: Cell type-specific genotoxic effects of intermittent
extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields. Mutat Res.
583:184–188. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Focke F, Schuermann D, Kuster N and Schär
P: DNA fragmentation in human fibroblasts under extremely low
frequency electromagnetic field exposure. Mutat Res. 683:74–83.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Repacholi M: Concern that ‘EMF’ magnetic
fields from power lines cause cancer. Sci Total Environ.
426:454–458. 2012.
|
|
60
|
Ba F, Pang PK and Benishin CG: The
establishment of a reliable cytotoxic system with SK-N-SH
neuroblastoma cell culture. J Neurosci Methods. 123:11–22. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Úbeda A, Trillo MA, House DE and Blackman
CF: A 50 Hz magnetic field blocks melatonin-induced enhancement of
junctional transfer in normal C3H/10T1/2 cells. Carcinogenesis.
16:2945–2949. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Blackman CF, Benane SG and House DE: The
influence of 1.2 microT, 60 Hz magnetic fields on melatonin- and
tamoxifen-induced inhibition of MCF-7 cell growth.
Bioelectromagnetics. 22:122–128. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tonini R, Baroni MD, Masala E, Micheletti
M, Ferroni A and Mazzanti M: Calcium protects differentiating
neuroblastoma cells during 50 Hz electromagnetic radiation. Biophys
J. 81:2580–2589. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Reynolds CP, Matthay KK, Villablanca JG
and Maurer BJ: Retinoid therapy of high-risk neuroblastoma. Cancer
Lett. 197:185–192. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kanemaru KK, Tuthill MC, Takeuchi KK,
Sidell N and Wada RK: Retinoic acid induced downregulation of MYCN
is not mediated through changes in Sp1/Sp3. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
50:806–811. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tanaka K, Tamiya-Koizumi K, Hagiwara K,
Ito H, Takagi A, Kojima T, Suzuki M, Iwaki S, Fujii S, Nakamura M,
Banno Y, Kannagi R, Tsurumi T, Kyogashima M and Murate T: Role of
down-regulated neutral ceramidase during all-trans retinoic
acid-induced neuronal differentiation in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma
cells. J Biochem. 151:611–620. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cetinkaya C, Hultquist A, Su Y, Wu S,
Bahram F, Påhlman S, Guzhova I and Larsson LG: Combined IFN-gamma
and retinoic acid treatment targets the N-Myc/Max/Mad1 network
resulting in repression of N-Myc target genes in MYCN-amplified
neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2634–2641. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Masiá S, Alvarez S, de Lera AR and
Barettino D: Rapid, nongenomic actions of retinoic acid on
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase signaling pathway mediated by the
retinoic acid receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 21:2391–2402.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wegert J, Bausenwein S, Kneitz S, Roth S,
Graf N, Geissinger E and Gessler M: Retinoic acid pathway activity
in Wilms tumors and characterization of biological responses in
vitro. Mol Cancer. 10:1362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Jiao RQ, Li G and Chiu JF: Comparative
proteomic analysis of differentiation of mouse F9 embryonic
carcinoma cells induced by retinoic acid. J Cell Biochem.
113:1811–1819. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li X, Li H, Bi J, Chen Y, Jain S and Zhao
Y: Human cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (CB-SCs) treated
with all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) give rise to dopamine neurons.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 419:110–116. 2012.
|
|
72
|
Marzinke MA and Clagett-Dame M: The
all-trans retinoic acid (atRA)-regulated gene Calmin (Clmn)
regulates cell cycle exit and neurite outgrowth in murine
neuroblastoma (Neuro2a) cells. Exp Cell Res. 318:85–93. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Marcantonio P, Del Re B, Franceschini A,
Capri M, Lukas S, Bersani F and Giorgi G: Synergic effect of
retinoic acid and extremely low frequency magnetic field exposure
on human neuroblastoma cell line BE(2)C. Bioelectromagnetics.
31:425–433. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lin H, Head M, Blank M, Han L, Jin M and
Goodman R: Myc-mediated transactivation of HSP70 expression
following exposure to magnetic fields. J Cell Biochem. 69:181–188.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shaul YD and Seger R: The MEK/ERK cascade:
from signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1773:1213–1226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Karsy M, Albert L, Tobias ME, Murali R and
Jhanwar-Uniyal M: All-trans retinoic acid modulates cancer stem
cells of glioblastoma multiforme in an MAPK-dependent manner.
Anticancer Res. 30:4915–4920. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
De Melo M, Gerbase MW, Curran J and Pache
JC: Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinases are
significantly increased in malignant mesothelioma. J Histochem
Cytochem. 54:855–861. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Menakongka A and Suthiphongchai T:
Involvement of PI3K and ERK1/2 pathways in hepatocyte growth
factor-induced cholangiocarcinoma cell invasion. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:713–722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Webster B, Hansen L, Adame A, Crews L,
Torrance M, Thal L and Masliah E: Astroglial activation of
extracellular-regulated kinase in early stages of Alzheimer
disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 65:142–151. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Dagda RK, Zhu J, Kulich SM and Chu CT:
Mitochondrially localized ERK2 regulates mitophagy and autophagic
cell stress: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Autophagy.
4:770–782. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kawamata J and Shimohama S: Stimulating
nicotinic receptors trigger multiple pathways attenuating
cytotoxicity in models of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J
Alzheimers Dis. 24(Suppl 2): 95–109. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Jin M, Blank M and Goodman R: ERK1/2
phosphorylation, induced by electromagnetic fields, diminishes
during neoplastic transformation. J Cell Biochem. 78:371–379. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Friedman J, Kraus S, Hauptman Y, Schiff Y
and Seger R: Mechanism of short-term ERK activation by
electromagnetic fields at mobile phone frequencies. Biochem J.
405:559–568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Schmidt-Ullrich RK, Contessa JN, Lammering
G, Amorino G and Lin PS: ERBB receptor tyrosine kinases and
cellular radiation responses. Oncogene. 22:5855–5865. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Winker R, Ivancsits S, Pilger A, Adlkofer
F and Rudiger HW: Chromosomal damage in human diploid fibroblasts
by intermittent exposure to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic
fields. Mutat Res. 585:43–49. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Wahab MA, Podd JV, Rapley BI and Rowland
RE: Elevated sister chromatid exchange frequencies in dividing
human peripheral blood lymphocytes exposed to 50 Hz magnetic
fields. Bioelectromagnetics. 28:281–288. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Stronati L, Testa A, Villani P, Marino C,
Lovisolo GA, Conti D, Russo F, Fresegna AM and Cordelli E: Absence
of genotoxicity in human blood cells exposed to 50 Hz magnetic
fields as assessed by comet assay, chromosome aberration,
micronucleus, and sister chromatid exchange analyses.
Bioelectromagnetics. 25:41–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Scarfi MR, Sannino A, Perrotta A, Sarti M,
Mesirca P and Bersani F: Evaluation of genotoxic effects in human
fibroblasts after intermittent exposure to 50 Hz electromagnetic
fields: a confirmatory study. Radiat Res. 164:270–276. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Adair RK: Extremely low frequency
electromagnetic fields do not interact directly with DNA.
Bioelectromagnetics. 19:136–138. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Wan C, Fiebig T, Schiemann O, Barton JK
and Zewail AH: Femtosecond direct observation of charge transfer
between bases in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:14052–14055. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Porath D, Bezryadin A, De Vries S and
Dekker C: Direct measurement of electrical transport through DNA
molecules. Nature. 403:635–638. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Giese B: Electron transfer through DNA and
peptides. Bioorg Med Chem. 14:6139–6143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|