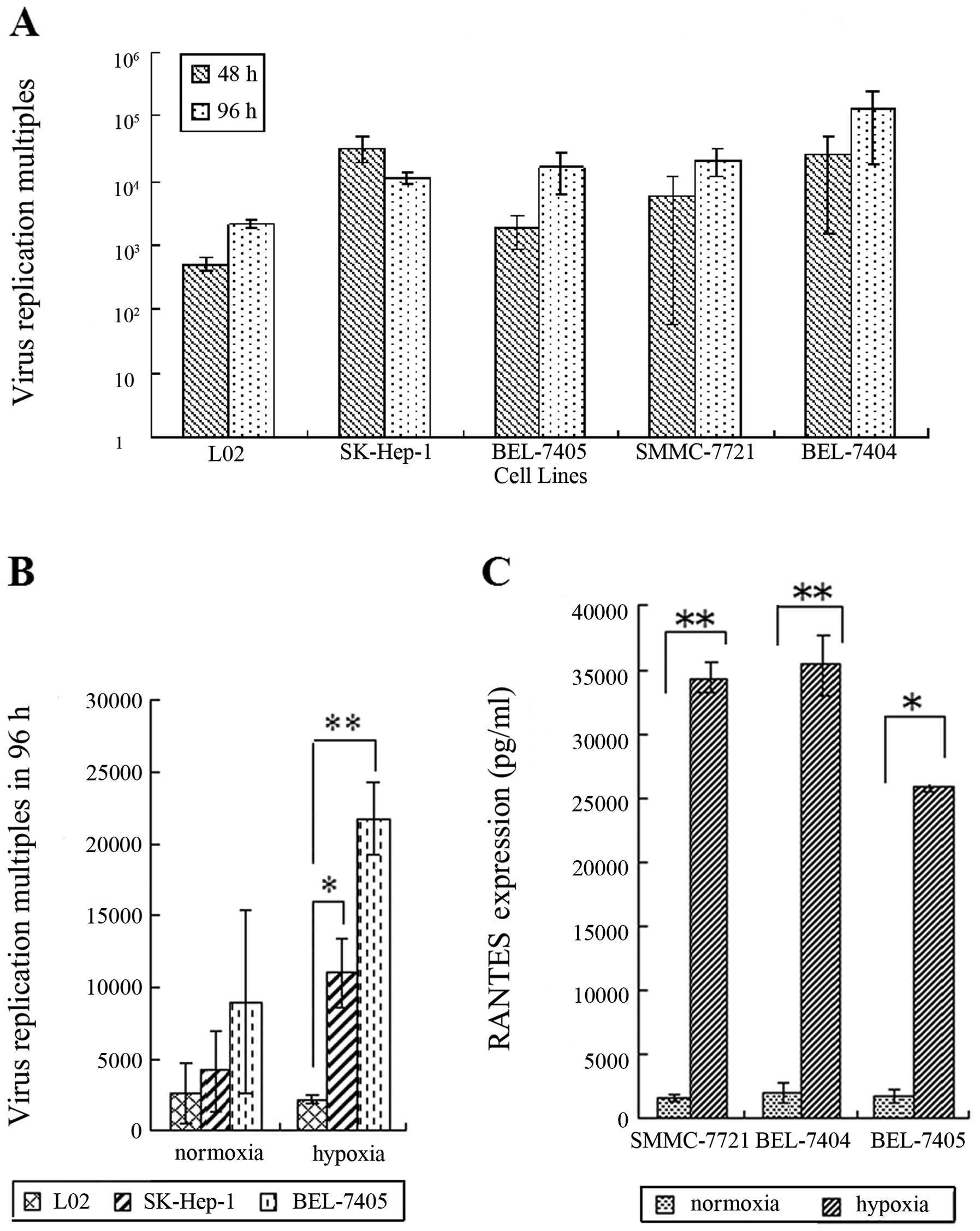
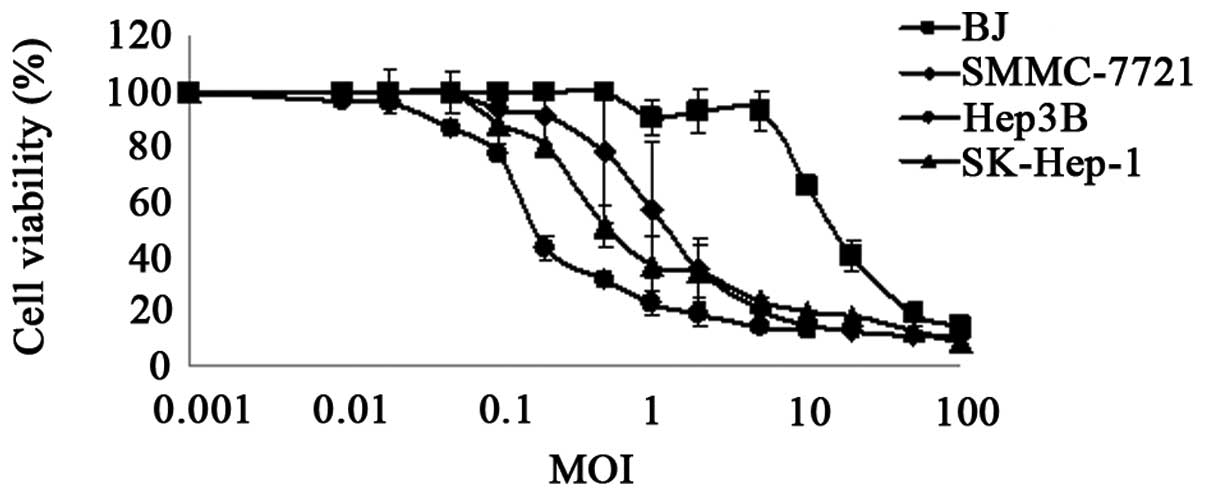
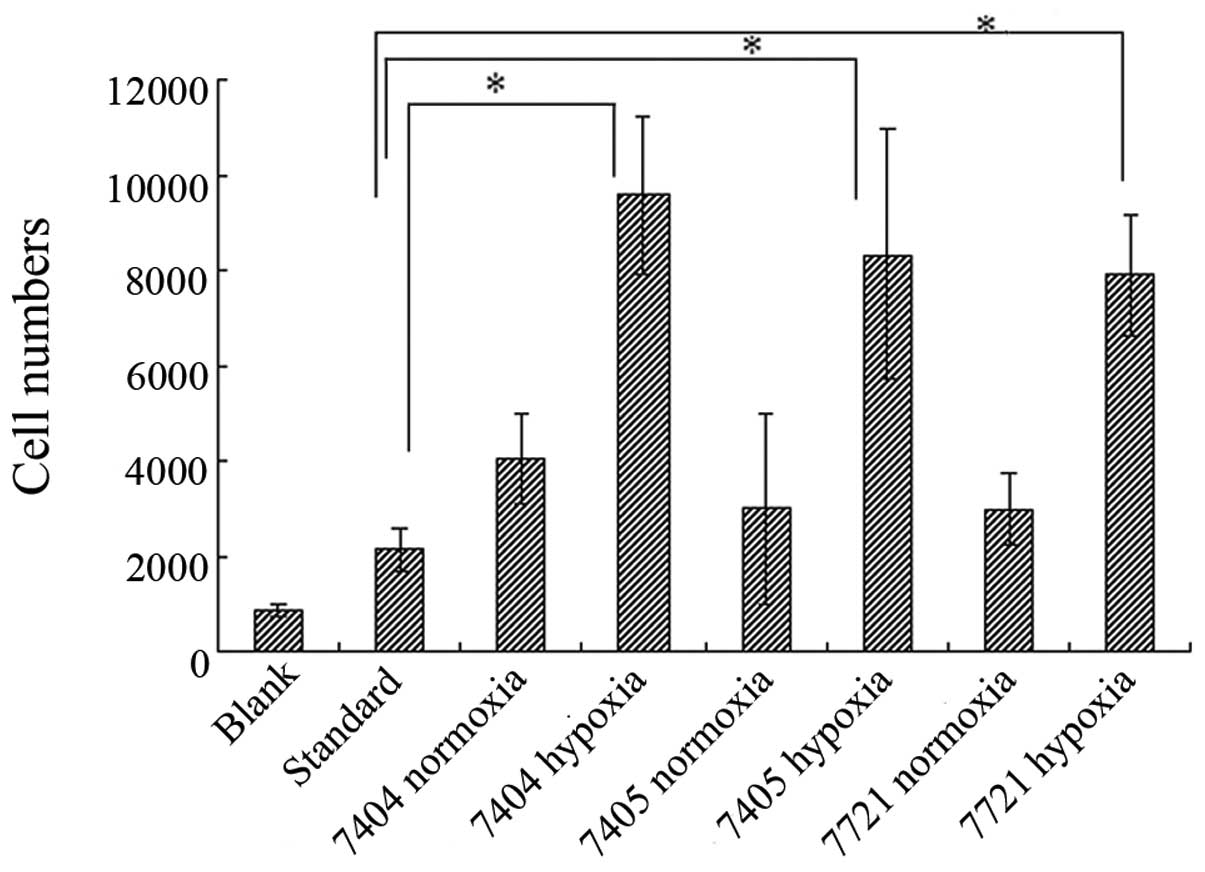
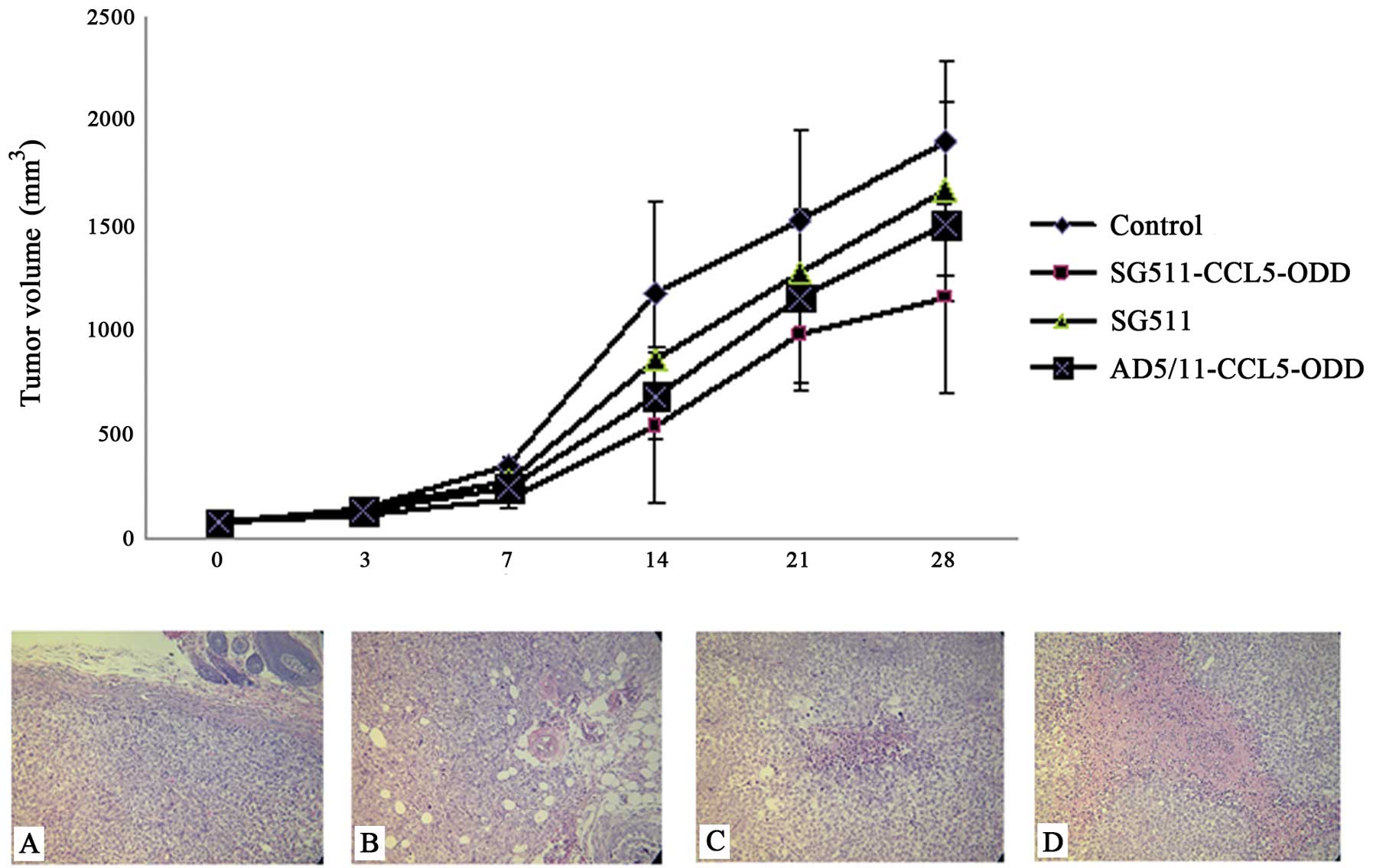
|
1
|
Dudley ME, Yang JC, Sherry R, Hughes MS,
Royal R, Kammula U, Robbins PF, Huang J, Citrin DE, Leitman SF,
Wunderlich J, Restifo NP, Thomasian A, Downey SG, Smith FO, Klapper
J, Morton K, Laurencot C, White DE and Rosenberg SA: Adoptive cell
therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: evaluation of
intensive myeloablative chemoradiation preparative regimens. J Clin
Oncol. 26:5233–5239. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Shelton TE, Even
J and Rosenberg SA: Generation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
cultures for use in adoptive transfer therapy for melanoma
patients. J Immunother. 26:332–342. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Yang JC, Sherry
RM, Topalian SL, Restifo NP, Royal RE, Kammula U, White DE,
Mavroukakis SA, Rogers LJ, Gracia GJ, Jones SA, Mangiameli DP,
Pelletier MM, Gea-Banacloche J, Robinson MR, Berman DM, Filie AC,
Abati A and Rosenberg SA: Adoptive cell transfer therapy following
non-myeloablative but lymphodepleting chemotherapy for the
treatment of patients with refractory metastatic melanoma. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2346–2357. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wrzesinski C, Paulos CM, Kaiser A,
Muranski P, Palmer DC, Gattinoni L, Yu Z, Rosenberg SA and Restifo
NP: Increased intensity lymphodepletion enhances tumor treatment
efficacy of adoptively transferred tumor-specific T cells. J
Immunother. 33:1–7. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Kammula
US, Hughes MS, Phan GQ, Citrin DE, Restifo NP, Robbins PF,
Wunderlich JR, Morton KE, Laurencot CM, Steinberg SM, White DE and
Dudley ME: Durable complete responses in heavily pretreated
patients with metastatic melanoma using T-cell transfer
immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 17:4550–4557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ripley RT, Davis JL, Klapper JA, Mathur A,
Kammula U, Royal RE, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Hughes MS, Libutti SK,
White DE, Steinberg SM, Dudley ME, Rosenberg SA and Avital I: Liver
resection for metastatic melanoma with postoperative
tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:163–170.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosenberg SA and Dudley ME: Adoptive cell
therapy for the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma.
Curr Opin Immunol. 21:233–240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pittet MJ and Mempel TR: Regulation of
T-cell migration and effector functions: insights from in vivo
imaging studies. Immunol Rev. 221:107–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Braun SE, Chen K, Foster RG, Kim CH,
Hromas R, Kaplan MH, Broxmeyer HE and Cornetta K: The CC chemokine
CK beta-11/MIP-3 beta/ELC/Exodus 3 mediates tumor rejection of
murine breast cancer cells through NK cells. J Immunol.
164:4025–4031. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hromas R, Cripe L, Hangoc G, Cooper S and
Broxmeyer HE: The exodus subfamily of CC chemokines inhibits the
proliferation of chronic myelogenous leukemia progenitors. Blood.
95:1506–1508. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sharma S, Stolina M, Luo J, Strieter RM,
Burdick M, Zhu LX, Batra RK and Dubinett SM: Secondary lymphoid
tissue chemokine mediates T cell-dependent antitumor responses in
vivo. J Immunol. 164:4558–4563. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kudo T, Lu H, Wu JY, Graham DY, Casola A
and Yamaoka Y: Regulation of RANTES promoter activation in gastric
epithelial cells infected with Helicobacter pylori. Infect
Immun. 73:7602–7612. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lebovic DI, Chao VA and Taylor RN:
Peritoneal macrophages induce RANTES (regulated on activation,
normal T cell expressed and secreted) chemokine gene transcription
in endometrial stromal cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
89:1397–1401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Veillard NR, Kwak B, Pelli G, Mulhaupt F,
James RW, Proudfoot AE and Mach F: Antagonism of RANTES receptors
reduces atherosclerotic plaque formation in mice. Circ Res.
94:253–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rojas-Ramos E, Avalos AF, Pérez-Fernandez
L, Cuevas-Schacht F, Valencia-Maqueda E and Terán LM: Role of the
chemokines RANTES, monocyte chemotactic proteins-3 and -4 and
eotaxins-1 and -2 in childhood asthma. Eur Respir J. 22:310–316.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen CJ, Chen JH, Chen SY, Liao SL and
Raung SL: Upregulation of RANTES gene expression in neuroglia by
Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J Virol. 78:12107–12119.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oltmanns U, Issa R, Sukkar MB, John M and
Chung KF: Role of c-jun N-terminal kinase in the induced release of
GM-CSF, RANTES and IL-8 from human airway smooth muscle cells. Br J
Pharmacol. 139:1228–1234. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teichmann JV, Ludwig WD and Thiel E:
Cytotoxicity of interleukin 2-induced lymphokine-activated killer
(LAK) cells against human leukemia and augmentation of killing by
interferons and tumor necrosis factor. Leuk Res. 16:287–298. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pawelec G: MHC-unrestricted immune
surveillance of leukemia. Cancer Biother. 9:265–288. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dokhelar MC, Wiels J, Lipinski M, Tetaud
C, Devergie A, Gluckman E and Tursz T: Natural killer cell activity
in human bone marrow recipients: early reappearance of peripheral
natural killer activity in graft-versus-host disease.
Transplantation. 31:61–65. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cerwenka A and Lanier LL: Natural killer
cells, viruses and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:41–49. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lanier LL: NK cell recognition. Annu Rev
Immunol. 23:225–274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Drexler HG and Matsuo Y: Malignant
hematopoietic cell lines: in vitro models for the study of natural
killer cell leukemia-lymphoma. Leukemia. 14:777–782. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yan Y, Steinherz P, Klingemann HG, Dennig
D, Childs BH, McGuirk J and O’Reilly RJ: Antileukemia activity of a
natural killer cell line against human leukemias. Clin Cancer Res.
4:2859–2868. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gong JH, Maki G and Klingemann HG:
Characterization of a human cell line (NK-92) with phenotypical and
functional characteristics of activated natural killer cells.
Leukemia. 8:652–658. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reid GS, Bharya S, Klingemann HG and
Schultz KR: Differential killing of pre-B acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia cells by activated NK cells and the NK-92 ci cell line.
Clin Exp Immunol. 129:265–271. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tam YK, Miyagawa B, Ho VC and Klingemann
HG: Immunotherapy of malignant melanoma in a SCID mouse model using
the highly cytotoxic natural killer cell line NK-92. J Hematother.
8:281–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tonn T, Becker S, Esser R, Schwabe D and
Seifried E: Cellular immunotherapy of malignancies using the clonal
natural killer cell line NK-92. J Hematother Stem Cell Res.
10:535–544. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G,
Kurt-Jones EA, Krithivas A, Hong JS, Horwitz MS, Crowell RL and
Finberg RW: Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses
and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science. 275:1320–1323. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tomko RP, Xu R and Philipson L: HCAR and
MCAR: the human and mouse cellular receptors for subgroup C
adenoviruses and group B coxsackieviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:3352–3356. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim M, Zinn KR, Barnett BG, Sumerel LA,
Krasnykh V, Curiel DT and Douglas JT: The therapeutic efficacy of
adenoviral vectors for cancer gene therapy is limited by a low
level of primary adenovirus receptors on tumour cells. Eur J
Cancer. 38:1917–1926. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsumoto K, Shariat SF, Ayala GE, Rauen
KA and Lerner SP: Loss of coxsackie and adenovirus receptor
expression is associated with features of aggressive bladder
cancer. Urology. 66:441–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Sakamoto H, Nakajima
Y, Une Y, Hinoda Y and Imai K: Association of reduced cell adhesion
regulator messenger RNA expression with tumor progression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 74:251–254. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gaggar A, Shayakhmetov DM and Lieber A:
CD46 is a cellular receptor for group B adenoviruses. Nat Med.
9:1408–1412. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hara T, Kojima A, Fukuda H, Masaoka T,
Fukumori Y, Matsumoto M and Seya T: Levels of complement regulatory
proteins, CD35 (CR1), CD46 (MCP) and CD55 (DAF) in human
haematological malignancies. Br J Haematol. 82:368–373. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kinugasa N, Higashi T, Nouso K,
Nakatsukasa H, Kobayashi Y, Ishizaki M, Toshikuni N, Yoshida K,
Uematsu S and Tsuji T: Expression of membrane cofactor protein
(MCP, CD46) in human liver diseases. Br J Cancer. 80:1820–1825.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murray KP, Mathure S, Kaul R, Khan S,
Carson LF, Twiggs LB, Martens MG and Kaul A: Expression of
complement regulatory proteins-CD 35, CD 46, CD 55 and CD 59-in
benign and malignant endometrial tissue. Gynecol Oncol. 76:176–182.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Thorsteinsson L, O’Dowd GM, Harrington PM
and Johnson PM: The complement regulatory proteins CD46 and CD59,
but not CD55, are highly expressed by glandular epithelium of human
breast and colorectal tumour tissues. APMIS. 106:869–878. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vähä-Koskela MJ, Heikkilä JE and Hinkkanen
AE: Oncolytic viruses in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 254:178–216.
2007.
|
|
40
|
Liu X, Qian Q, Xu P, Wolf F, Zhang J,
Zhang D, Li C and Huang Q: A novel conditionally replicating
‘armed’ adenovirus selectively targeting gastrointestinal tumors
with aberrant wnt signaling. Hum Gene Ther. 22:427–437. 2011.
|
|
41
|
Xie M, Niu JH, Chang Y, Qian QJ, Wu HP, Li
LF, Zhang Y, Li JL, Huang XJ and Ruan GR: A novel triple-regulated
oncolytic adenovirus carrying PDCD5 gene exerts potent antitumor
efficacy on common human leukemic cell lines. Apoptosis.
14:1086–1094. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Harada H, Hiraoka M and Kizaka-Kondoh S:
Antitumor effect of TAT-oxygen-dependent degradation-caspase-3
fusion protein specifically stabilized and activated in hypoxic
tumor cells. Cancer Res. 62:2013–2018. 2002.
|
|
43
|
Teicher BA: Hypoxia and drug resistance.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 13:139–168. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kung AL, Wang S, Klco JM, Kaelin WG and
Livingston DM: Suppression of tumor growth through disruption of
hypoxia-inducible transcription. Nat Med. 6:1335–1340. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Helmlinger G, Yuan F, Dellian M and Jain
RK: Interstitial pH and pO2 gradients in solid tumors in vivo:
high-resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation. Nat Med.
3:177–182. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M,
Hilton DA, Zagzag D, Buechler P, Isaacs WB, Semenza GL and Simons
JW: Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common
human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang Q, Chen G, Peng L, Wang X, Yang Y,
Liu C, Shi W, Su C, Wu H, Liu X, Wu M and Qian Q: Increased safety
with preserved antitumoral efficacy on hepatocellular carcinoma
with dual-regulated oncolytic adenovirus. Clin Cancer Res.
12:6523–6531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|