|
1
|
Parkin DM: The global health burden of
infection-associated cancers in the year 2002. Int J Cancer.
118:3030–3044. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
But DY, Lai CL and Yuen MF: Natural
history of hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:1652–1656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu S, Xie J, Yin J, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Pu
R, Li C, Ni W, Wang H and Cao G: A matched case-control study of
hepatitis B virus mutations in the preS and core promoter regions
associated independently with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med
Virol. 83:45–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huwiler A, Kolter T, Pfeilschifter J and
Sandhoff K: Physiology and pathophysiology of sphingolipid
metabolism and signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1485:63–99. 2000.
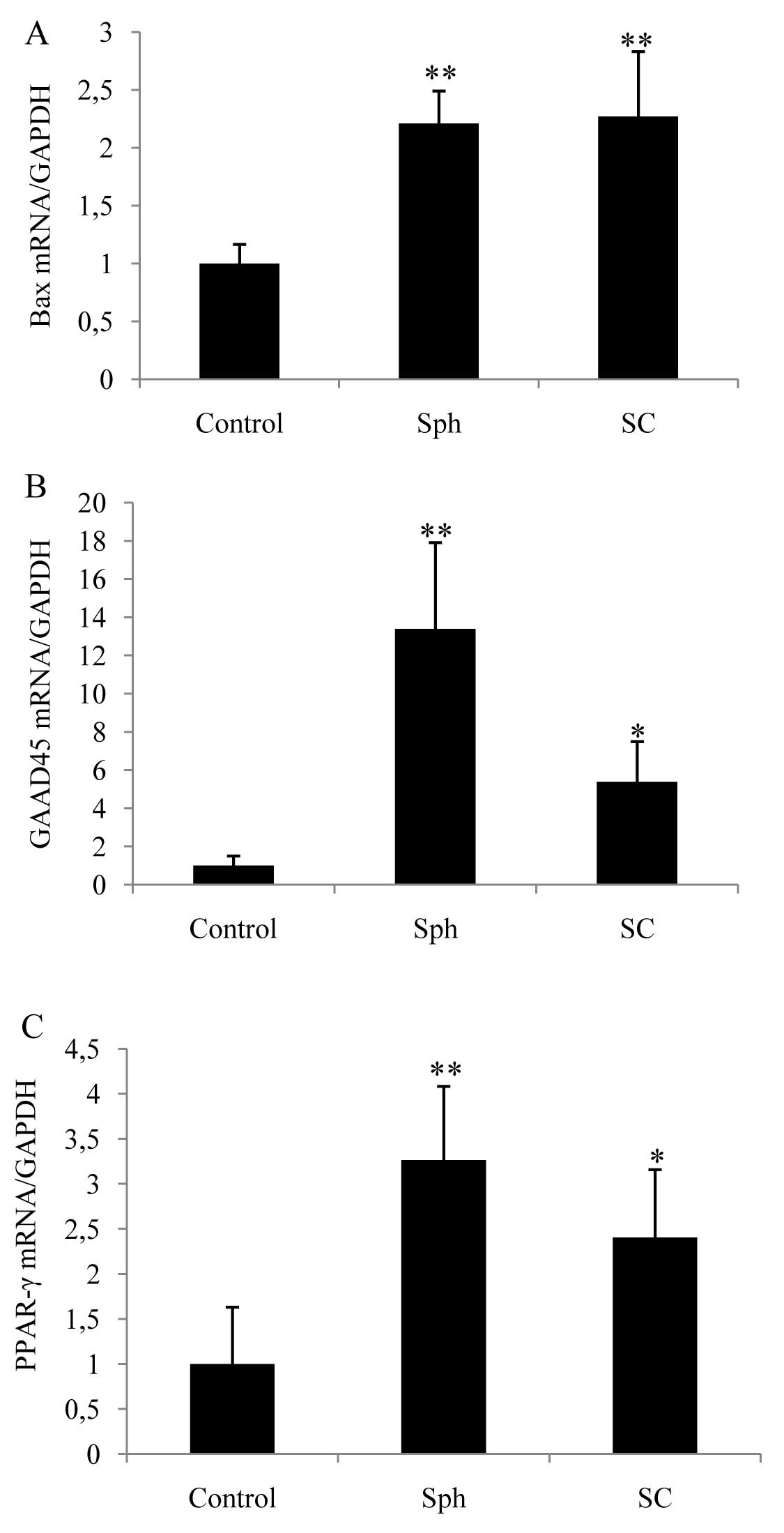
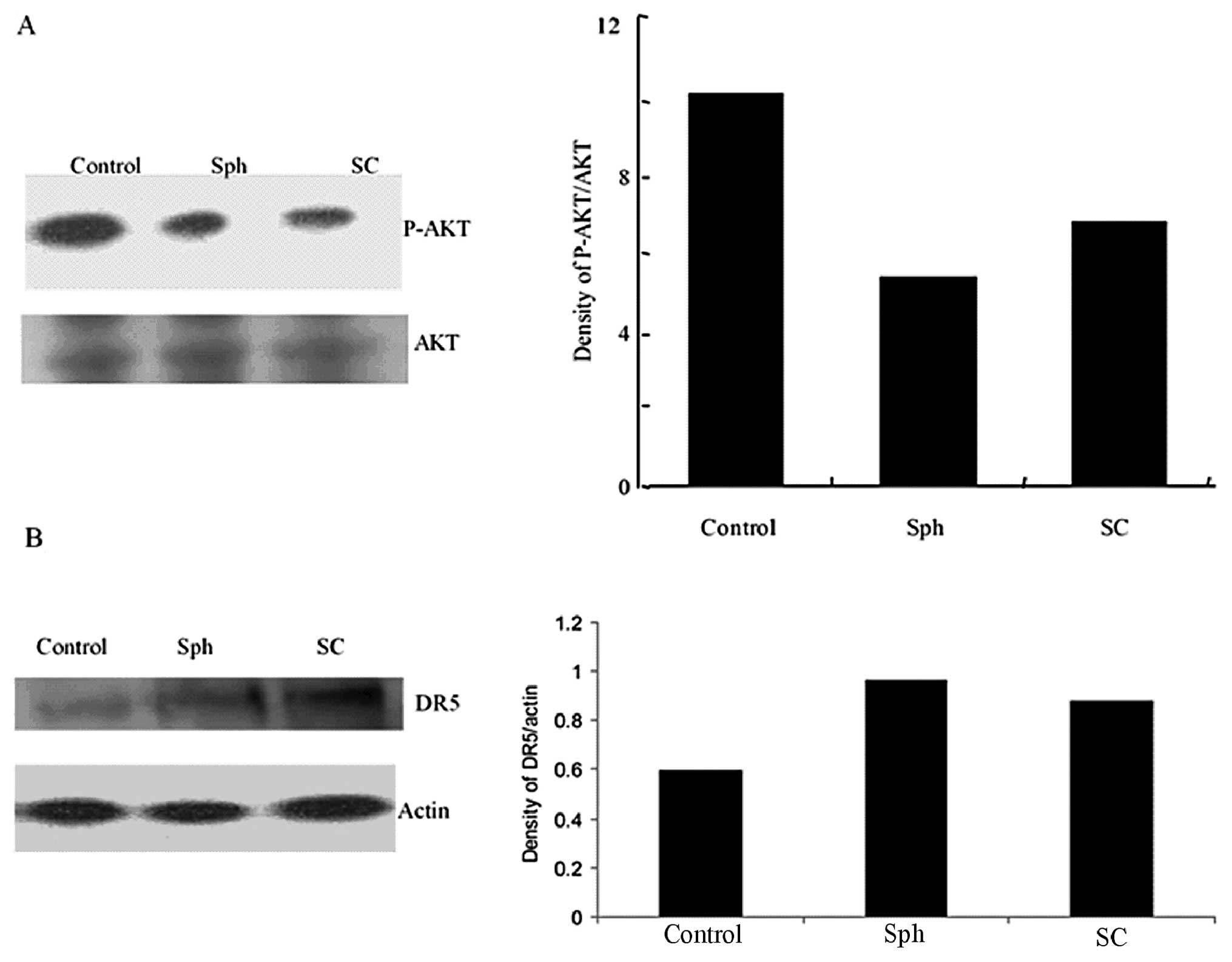
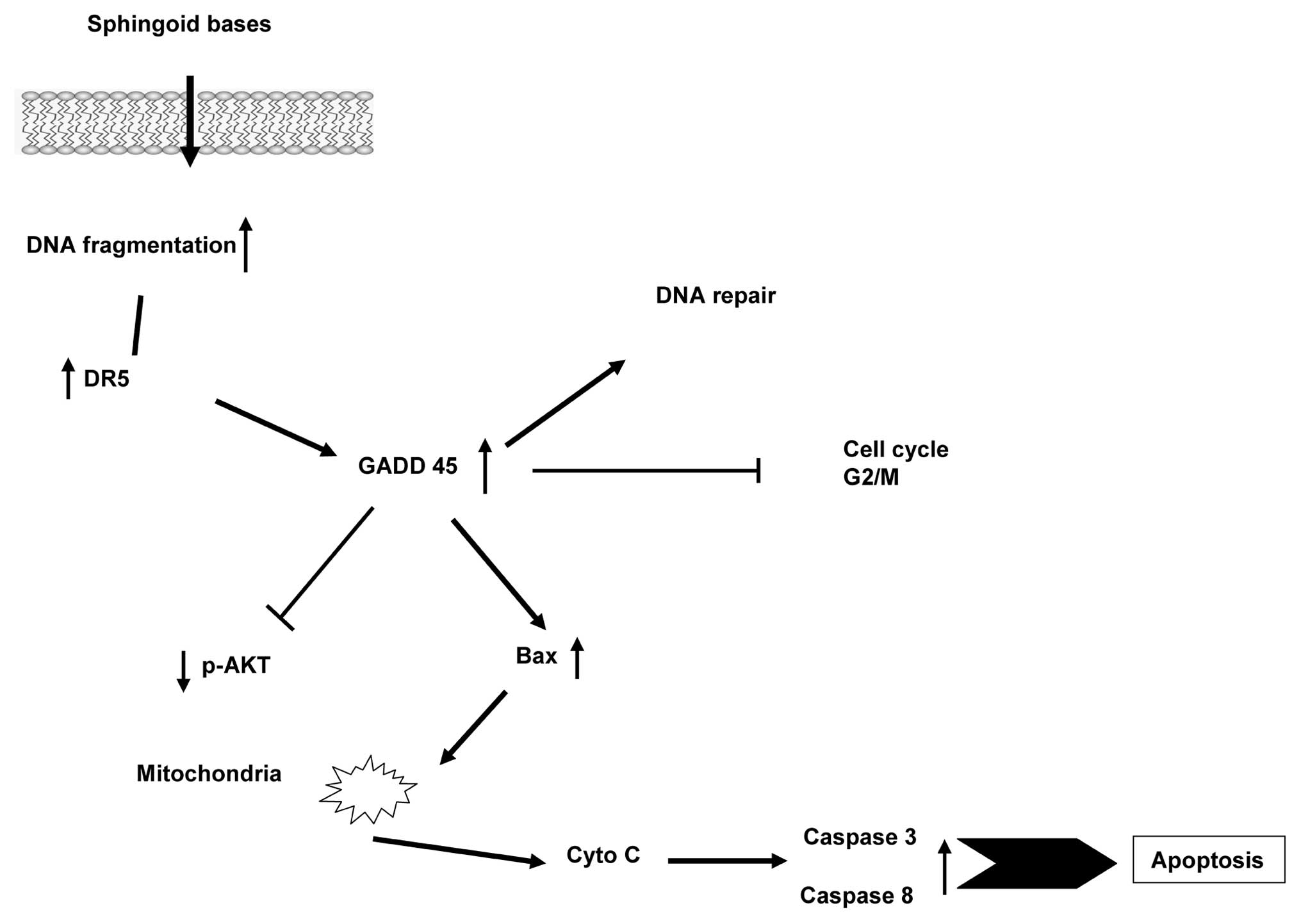
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang HC, Tsai LH, Chuang LY and Hung WC:
Role of AKT kinase in sphingosine-induced apoptosis in human
hepatoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 188:188–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruvolo PP: Intracellular signal
transduction pathways activated by ceramide and its metabolites.
Pharmacol Res. 47:383–392. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maceyka M, Payne SG, Milstien S and
Spiegel S: Sphingosine kinase, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1585:193–201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Orgetmen B and Hannun YA: Biologically
active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 4:604–616. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamada K: Chemo-pharmaceutical studies on
the glycosphingolipid constituents from echinoderm, sea cucumbers,
as medicinal materials. Yakugaku Zasshi. 122:1133–1143. 2002.(In
Japanese).
|
|
10
|
Yamada K, Hamada A, Kisa F, Miyamoto T and
Higuchi R: Constituents of holothuroidea, 13. Structure of
neuritogenic active ganglioside molecular species from the sea
cucumber Stichopus chloronotus. Chem Pharm Bull. 51:46–52.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sugawara T, Zaima N, Yamamoto A, Sakai S,
Noguchi R and Hirata T: Isolation of sphingoid bases of sea
cucumber cerebrosides and their cytotoxicity against human colon
cancer cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 70:2906–2912. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sugawara T and Miyazawa T: Separation and
determination of glycolipids from edible plant sources by
high-performance liquid chromatography and evaporative
light-scattering detection. Lipids. 34:1231–1237. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sugawara T, Aida K, Duan J and Hirata T:
Analysis of glucosylceramides from various sources by liquid
chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. J Oleo Sci. 59:387–394.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hossain Z, Sugawara T, Aida K and Hirata
T: Effect of dietary glucosylceramides from sea cucumber on plasma
and liver lipids in cholesterol-fed mice. Fish Sci. 77:1081–1085.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sugawara T, Kinoshita M, Ohnishi M and
Miyazawa T: Apoptosis induction by wheat-flour sphingoid bases in
DLD-1 human colon cancer cells. Biosci Biotech Biochem.
66:2228–2231. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aida K, Kinoshita M, Sugawara T, Ono J,
Miyazawa T and Ohnishi M: Apoptosis inducement by plant and fungus
sphingoid bases in human colon cancer cells. J Oleo Sci.
53:503–510. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kanno T and Nishizaki T: Sphingosine
induces apoptosis in hippocampal neurons and astrocytes by
activating caspase−3/−9 via a mitochondrial pathway linked to
SDK/14-3-3 protein/Bax/cytochrome c. J Cell Physiol.
226:2329–2337. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clay CE, Atsumi GI, High KP and Chilton
FH: Early de novo gene expression is required for 15-deoxy-Delta
12,14-prostaglandin J2-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 276:47131–47135. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Debrock G, Vanhentenrijk V, Sciot R,
Debiec-Rychter M, Oyen R and Van Oosterom A: A phase II trial with
rosiglitazone in liposarcoma patients. Br J Cancer. 89:1409–1412.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grommes C, Landreth GE and Heneka MT:
Antineoplastic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma agonists. Lancet Oncol. 5:419–429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Date M, Fukuchi K, Morita S, Takahashi H
and Ohura K: 15-Deoxy-delta12,14-prostaglandin J2, a ligand for
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma, induces apoptosis
in human hepatoma cells. Liver Int. 23:460–466. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Han S, Sidell N, Fisher PB and Roman J:
Up-regulation of p21 gene expression by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human lung carcinoma
cells. Clin Cancer Res. 10:1911–1919. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang FG, Zhang ZW, Xin DQ, Shi CJ, Wu JP,
Guo YL and Guan YF: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma ligands induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human renal
carcinoma cell lines. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:753–761. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shigeto T, Yokoyama Y, Xin B and Mizunuma
H: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and gamma
ligands inhibit the growth of human ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep.
18:833–840. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin MS, Chen WC, Bai X and Wang YD:
Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
inhibits cell growth via apoptosis and arrest of the cell cycle in
human colorectal cancer. J Dig Dis. 8:82–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sporn MB, Suh N and Mangelsdorf DJ:
Prospects for prevention and treatment of cancer with selective
PPARγ modulators (SPARMs). Trends Mol Med. 7:395–400.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gupta RA and Dubois RN: Controversy: PPARγ
as a target for treatment of colorectal cancer. Am J Physiol.
283:G266–G269. 2002.
|
|
28
|
Girnun GD, Smith WM, Drori S, Sarraf P,
Mueller E, Eng C, Nambiar P, Rosenberg DW, Bronson RT, Edelmann W,
Kucherlapati R, Gonzalez FJ and Spiegelman BM: APC- dependent
suppression of colon carcinogenesis by PPARγ. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:13771–13776. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yasui Y, Hosokawa M, Sahara T, Suzuki R,
Ohgiya S, Kohno H, Tanaka T and Miyashita K: Bitter gourd seed
fatty acid rich in 9c,11t,13t-conjugated linolenic acid induces
apoptosis and up-regulates the GADD45, p53 and PPARgamma in human
colon cancer Caco-2 cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty
Acids. 73:113–119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han C, Demetris AJ, Michalopoulos GK, Zhan
Q, Shelhamer JH and Wu T: PPARγ ligands inhibit cholangiocarcinoma
cell growth through p53-dependent GADD45 and p21 WAF1/Cip1 pathway.
Hepatology. 38:167–177. 2003.
|
|
31
|
Nagamine M, Okumura T, Tanno S, Sawamukai
M, Motomura W, Takahashi N and Kohgo Y: PPARγ ligand-induced
apoptosis through a p53-dependent mechanism in human gastric cancer
cells. Cancer Sci. 94:338–343. 2003.
|
|
32
|
Okumura T, Nakamura M, Takata Y, Watanabe
S, Kitami Y and Hiwada K: Troglitazone induces apoptosis via the
p53 and Gadd45 pathway in vascular muscle cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
407:227–235. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin F, Bruemmer D, Blaschke F, Hsueh WA,
Law RE and Van Herle AJ: Signaling pathways involved in induction
of GADD45 gene expression and apoptosis by troglitazone in human
MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 23:4614–4623. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aida K, Kinoshita M, Tanji M, Sugawara T,
Tamura M, Ono J, Ueno N and Ohnishi M: Prevention of aberrant crypt
foci formation by dietary maize and yeast cerebrosides in
1,2-dimethylhydrazine-treated mice. J Oleo Sci. 54:45–49. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Merrill AH Jr, Schmelz EM, Dillehay DL,
Spiegel S, Shayman JA, Schroeder JJ, Riley RT, Voss KA and Wang E:
Sphingolipids: the enigmatic lipid class: biochemistry, physiology,
and pathophysiology. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 142:208–225. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schmelz EM, Sullards MS, Dillehay DL and
Merrill AH Jr: Colonic cell proliferation and aberrant crypt foci
formation are inhibited by dairy glycosphingolipids in
1,2-dimethylhydrazine-treated CF1 mice. J Nutr. 130:522–527.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sprick MR and Walczak H: The interplay
between the Bcl-2 family and death receptor-mediated apoptosis.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1644:125–132. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Willis SN and Adams JM: Life in the
balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 17:617–625. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dejean LM, Martinez-Caballero S, Guo L,
Hughes C, Teijido O, Ducret T, Ichas F, Korsmeyer SJ, Antonsson B,
Jonas EA and Kinnally KW: Oligomeric Bax is a component of the
putative cytochrome c release channel MAC, mitochondrial
apoptosis-induced channel. Mol Biol Cell. 16:2424–2432. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Zha J, Korsmeyer
SJ, Krammer PH and Peter ME: Differential modulation of apoptosis
sensitivity in CD95 type I and type II cells. J Biol Chem.
274:22532–22538. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC and Korsmeyer
SJ: Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation,
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J. 17:3878–3885.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Laurora S, Pizzimenti S, Briatore F,
Fraioli A, Maggio M, Reffo P, Ferretti C, Dianzani MU and Barrera
G: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor ligands affect
growth-related gene expression in human leukemic cells. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 305:932–942. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu H, Zang C, Fenner MH, Liu D, Possinger
K, Koeffler HP and Elstner E: Growth inhibition and apoptosis in
human Philadelphia chromosome-positive lymphoblastic leukemia cell
lines by treatment with the dual PPARα/γ ligand TZD18. Blood.
107:3683–3692. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shimada T, Kojima K, Yoshiura K, Hiraishi
H and Terano A: Characteristics of the peroxisome proliferator
activated receptor γ (PPARγ) ligand induced apoptosis in colon
cancer cells. Gut. 50:658–664. 2002.
|
|
46
|
Toyoda M, Takagi H, Horiguchi N, Kakizaki
S, Sato K, Takayama H and Mori M: A ligand for peroxisome
proliferator activated receptor gamma inhibits cell growth and
induces apoptosis in human liver cancer cells. Gut. 50:563–567.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang W, Huper G, Guo Y, Murphy SK, Olson
JA Jr and Marks JR: Analysis of methylation-sensitive transcriptome
identifies GADD45α as a frequently methylated gene in breast
cancer. Oncogene. 24:2705–2714. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mita H, Tsutsui J, Takekawa M, Witten EA
and Saito H: Regulation of MTK1/MEKK4 kinase activity by its
N-terminal autoinhibitory domain and GADD45 binding. Mol Cell Biol.
22:4544–4555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tront JS, Hoffman B and Liebermann DA:
Gadd45α suppresses Ras driven mammary tumorigenesis by activation
of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p38 stress signaling resulting in
apoptosis and senescence. Cancer Res. 66:8448–8454. 2006.
|
|
50
|
Zerbini LF and Libermann TA: ADD45
deregulation in cancer: frequently methylated tumor suppressors and
potential therapeutic targets. Clin Cancer Res. 11:6409–6413. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tong T, Ji J, Jin S, Li X, Fan W, Song Y,
Wang M, Liu Z, Wu M and Zhan Q: Gadd45α expression induces Bim
dissociation from the cytoskeleton and translocation to
mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol. 25:4488–4500. 2005.
|
|
52
|
Hildesheim J, Bulavin DV, Anver MR, Alvord
WG, Hollander MC, Vardanian L and Fornace AJ Jr: Gadd45α protects
against UV irradiation-induced skin tumors, and promotes apoptosis
and stress signaling via MAPK and p53. Cancer Res. 62:7305–7315.
2002.
|
|
53
|
Zhou H, Li XM, Meinkoth J and Pittman RN:
Akt regulates cell survival and apoptosis at a postmitochondrial
level. J Cell Biol. 151:483–494. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Testa JR and Bellacosa A: Akt plays a
central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10983–10985. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Xin M and Deng X: Nicotine inactivation of
proapoptotic function of Bax through phosphorylation. J Biol Chem.
280:10781–10789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|