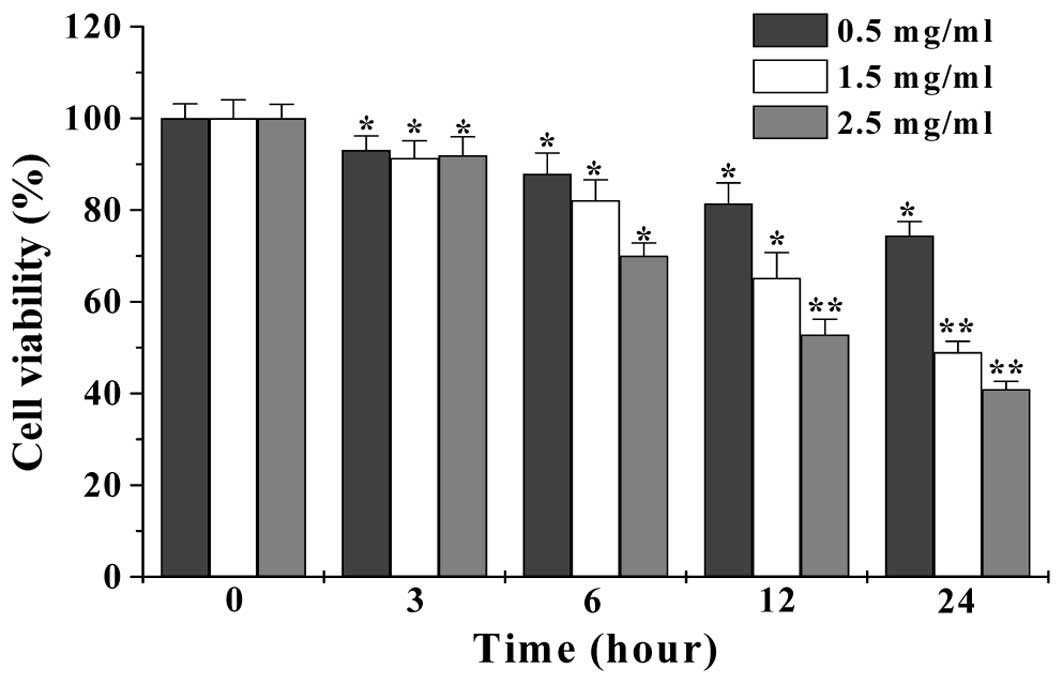
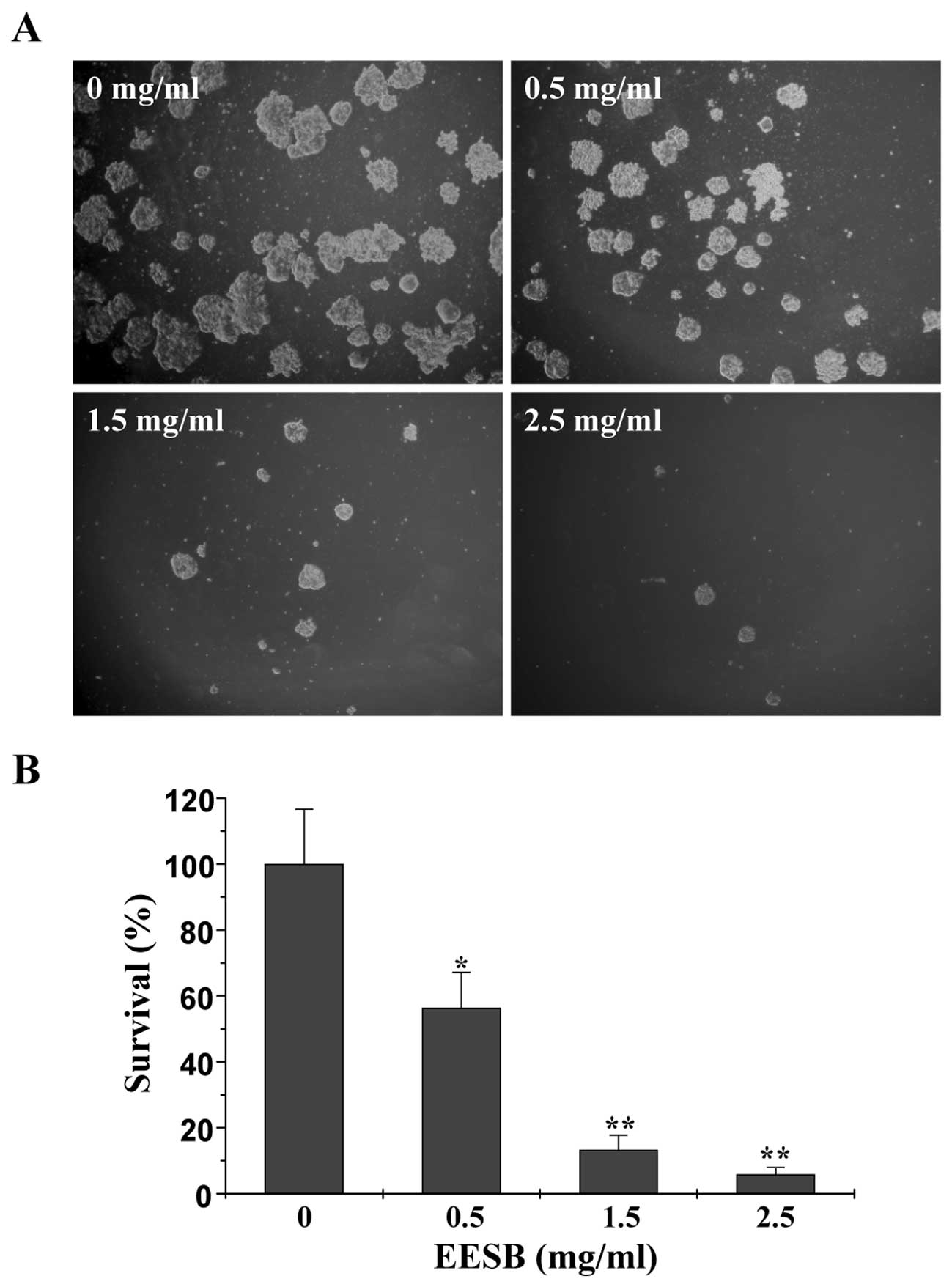
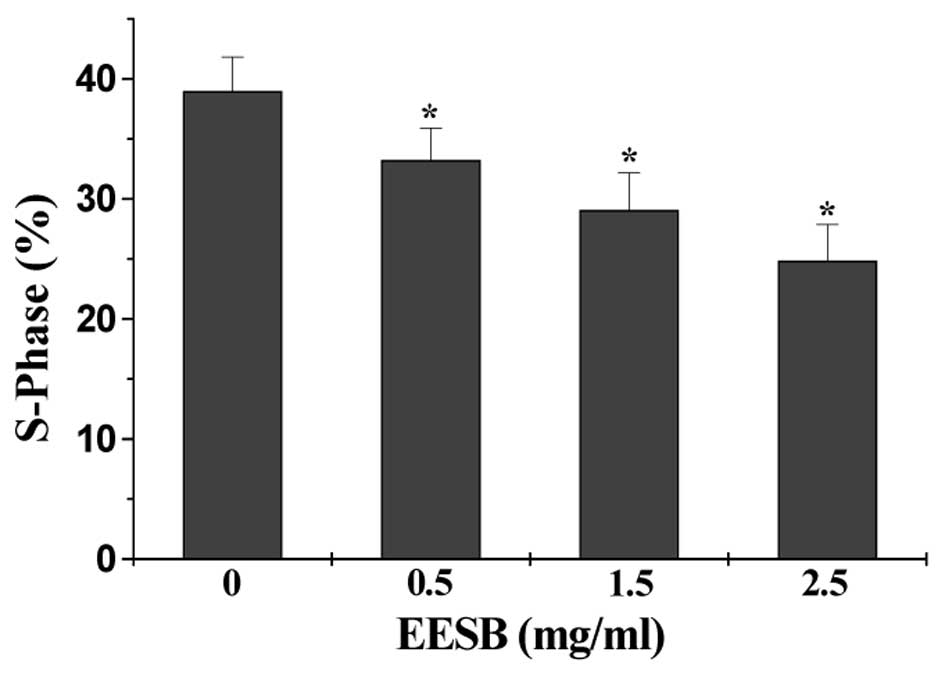
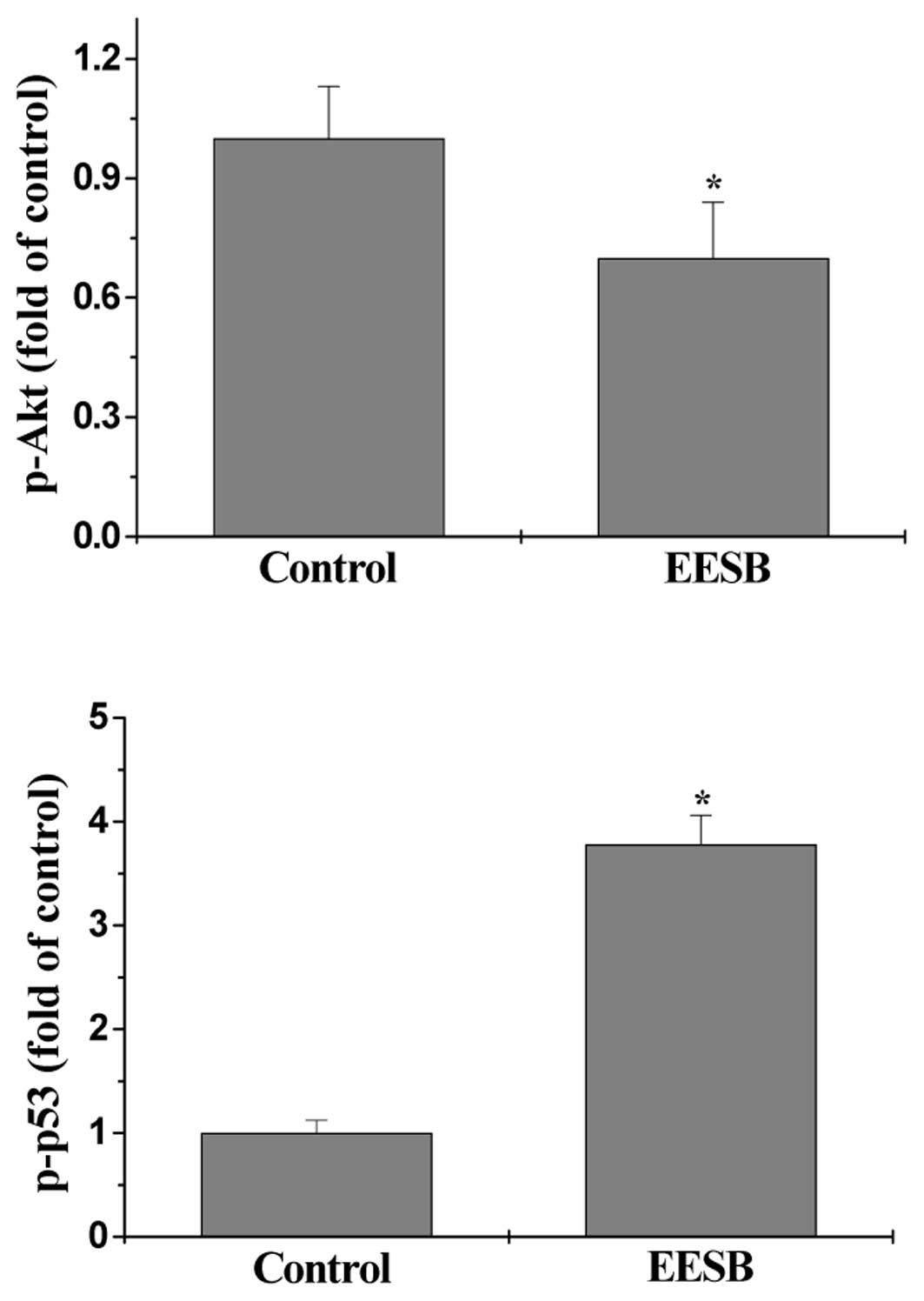
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gorlick R and Bertino JR: Drug resistance
in colon cancer. Semin Oncol. 26:606–611. 1999.
|
|
3
|
Grau MV, Rees JR and Baron JA:
Chemoprevention in gastrointestinal cancers: current status. Basic
Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 98:281–287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Longley DB, Allen WL and Johnston PG: Drug
resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:184–196. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gordaliza M: Natural products as leads to
anticancer drugs. Clin Transl Oncol. 9:767–776. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Harvey AL: Natural products in drug
discovery. Drug Discov Today. 13:894–901. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: The
influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep.
17:215–234. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nurse P: Ordering S phase and M phase in
the cell cycle. Cell. 79:5471994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Y, Robles AI, Martinez LA, Liu F,
Gimenez-Conti IB and Conti CJ: Expression of G1 cyclins,
cyclin-dependent kinases, and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in
androgen-induced prostate proliferation in castrated rats. Cell
Growth Differ. 7:1571–1578. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Graña X and Reddy EP: Cell cycle control
in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases
(CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene. 11:211–219. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kouraklis G, Theocharis S, Vamvakas P, et
al: Cyclin D1 and Rb protein expression and their correlation with
prognosis in patients with colon cancer. World J Surg Oncol.
4:52006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zafonte BT, Hulit J, Amanatullah DF, et
al: Cell-cycle dysregulation in breast cancer: breast cancer
therapies targeting the cell cycle. Front Biosci. 5:D938–D961.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Keyomarsi K, et al:
Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by p21. Mol Biol Cell.
6:387–400. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D and Stillman B:
The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA
replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 369:574–578. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Domagala W, Welcker M, Chosia M, et al:
p21/WAF1/Cip1 expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma:
relationship to p53, proliferation rate, and survival at 5 years.
Virchows Arch. 439:132–140. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC and Toker
A: Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by
phosphatidylinositol-3, 4-bisphosphate. Science. 275:665–668. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, et al:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Clarke RB: p27KIP1 phosphorylation by
PKB/Akt leads to poor breast cancer prognosis. Breast Cancer Res.
5:162–163. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Franke TF, Kaplan DR and Cantley LC: PI3K:
downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell. 88:435–437. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Burqering BM and Coffer PJ: Protein kinase
B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction.
Nature. 376:599–602. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, et al: The
protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the
PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 81:727–736.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, et
al: Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and
IGF-1. EMBO J. 15:6541–6551. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, et al: Akt
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rommel C, Clarke BA, Zimmermann S, et al:
Differentiation stage-specific inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK
pathway by Akt. Science. 286:1738–1741. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Spohn B, Lee MH
and Hung MC: Cytoplasmic localization of p21Cip1/WAF1 by
Akt-induced phosphorylation in HER-2/neu-overexpressing cells. Nat
Cell Biol. 3:245–252. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
review for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV,
Chernova OB and Stark GR: The p53 network. J Biol Chem. 273:1–4.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Schwartz GK and Shah MA: Targeting the
cell cycle: a new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
23:9408–9421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiangsu New Medical College. Dictionary of
Chinese Materia Medica. Shanghai Sci Techno Press; Shanghai:
1997
|
|
33
|
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission.
Pharmacopoeia of the Peoples Republic of China. Chin Med Sci
Technol Press. 1:109–110. 2010.
|
|
34
|
Tan P, Lu BZ and Bao WL: Analysis on the
clinical application of Scutellaria barbata D. Don in the
anti-cancer therapy. J Jiangxi Tradit Chin Med. 37:57–58. 2006.
|
|
35
|
Qian B: Clinical Effect of Anticancer
Chinese Medicine. Shanghai Transl Publ House; Shanghai: pp.
111–112. 1987
|
|
36
|
Cha YY, Lee EO, Lee HJ, et al: Methylene
chloride fraction of Scutellaria barbata induces apoptosis
in human U937 leukemia cells via the mitochondrial signaling
pathway. Clin Chim Acta. 348:41–48. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dai ZJ, Liu XX, Tang W, et al: Antitumor
and immune-modulating effects of Scutellaria barbata extract
in mice bearing hepatocarcinoma H22 cells-derived tumor. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 28:1835–1837. 2008.(in Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Goh D, Lee YH and Ong ES: Inhibitory
effects of a chemically standardized extract from Scutellaria
barbata in human colon cancer cell lines, LoVo. J Agric Food
Chem. 53:8197–8204. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Marconett CN, Morgenstern TJ, San Roman
AK, Sundar SN, Singhal AK and Firestone GL: BZL101, a phytochemical
extract from the Scutellaria barbata plant, disrupts
proliferation of human breast and prostate cancer cells through
distinct mechanisms dependent on the cancer cell phenotype. Cancer
Biol Ther. 10:397–405. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suh SJ, Yoon JW, Lee TK, et al:
Chemoprevention of Scutellaria barbata on human cancer cells
and tumorigenesis in skin cancer. Phytother Res. 21:135–141.
2007.
|
|
41
|
Wong BYY, Nguyen DL, Lin T, et al: Chinese
medicinal herb Scutellaria barbata modulates apoptosis and
cell survival in murine and human prostate cancer cells and tumor
development in TRAMP mice. Eur J Cancer Prev. 18:331–341. 2009.
|
|
42
|
Zhao Z, Holle L, Song W, Wei Y, Wagner TE
and Yu X: Antitumor and anti-angiogenic activities of
Scutellaria barbata extracts in vitro are partially
mediated by inhibition of Akt/protein kinase B. Mol Med Rep.
5:788–792. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Wei LH, Chen YQ, Lin JM, et al:
Scutellaria barbata D. Don induces apoptosis of human colon
carcinoma cell through activation of the mitochondrion-dependent
pathway. J Med Plants Res. 5:1962–1970. 2011.
|
|
44
|
Wei LH, Lin JM, Xu W, Hong ZF, Liu XX and
Peng J: Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by Scutellaria
barbata D. Don via suppressing proliferation, migration and
tube formation of endothelial cells and downregulation of the
expression of VEGF-A in cancer cells. J Med Plants Res.
5:3260–3268. 2011.
|
|
45
|
Wei LH, Lin JM, Xu W, et al:
Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits tumor angiogenesis via
suppression of Hedgehog pathway in a mouse model of colorectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:9419–9430. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|