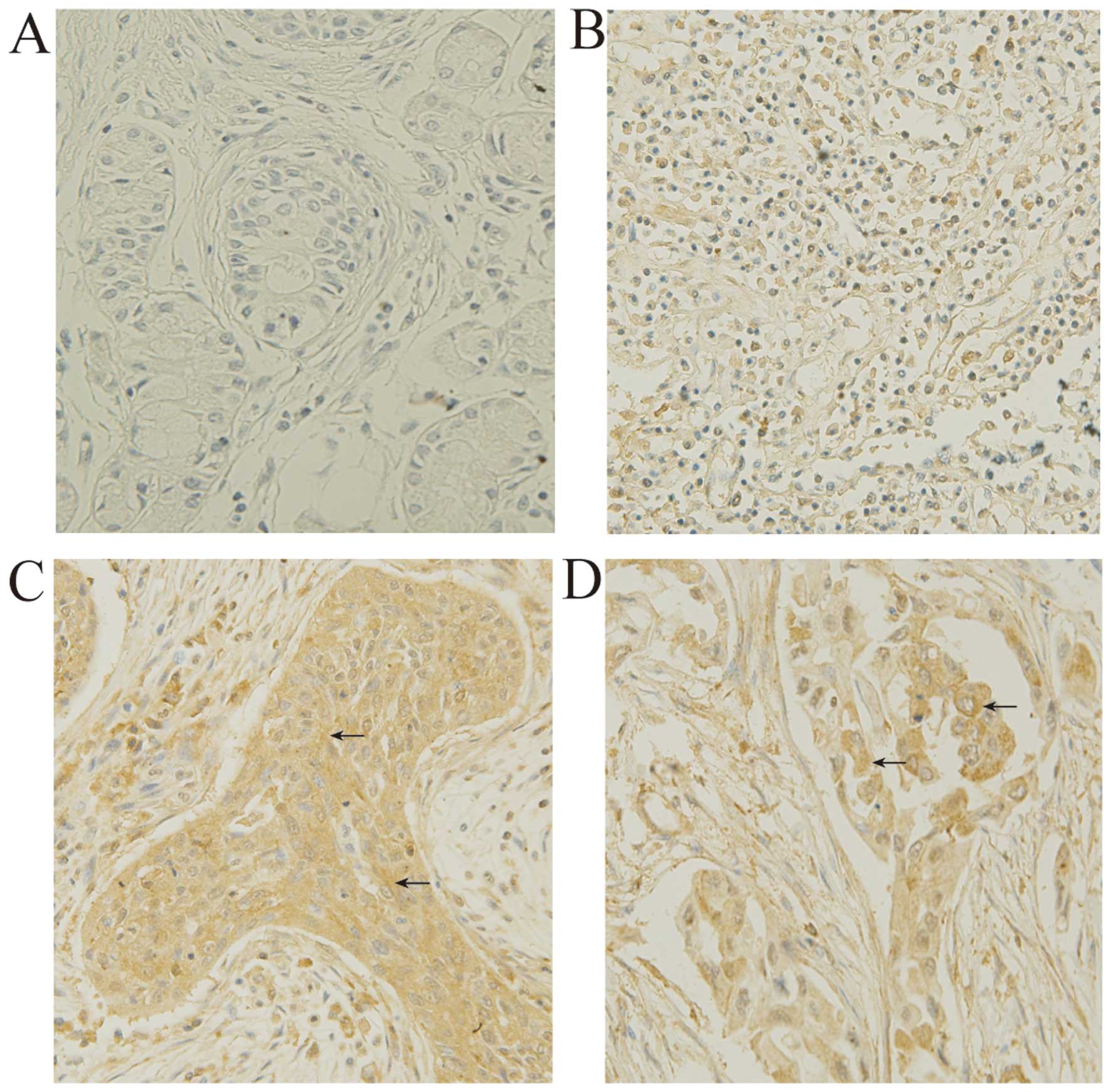
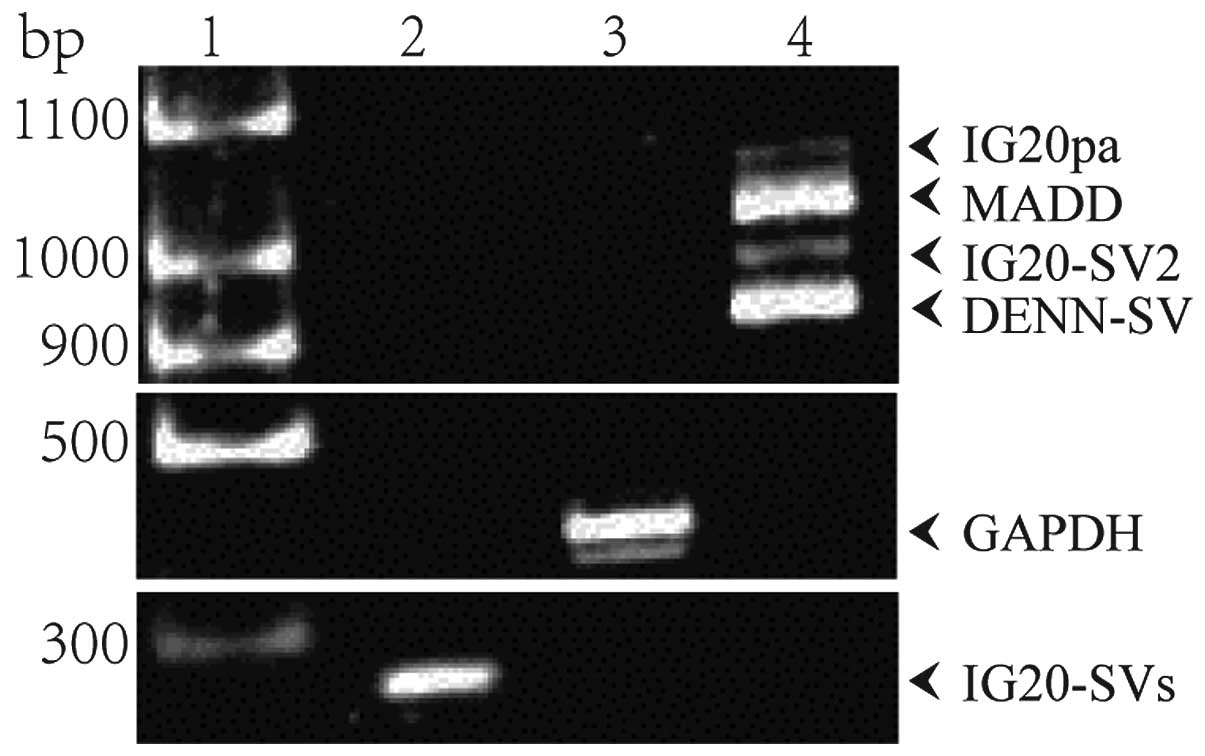
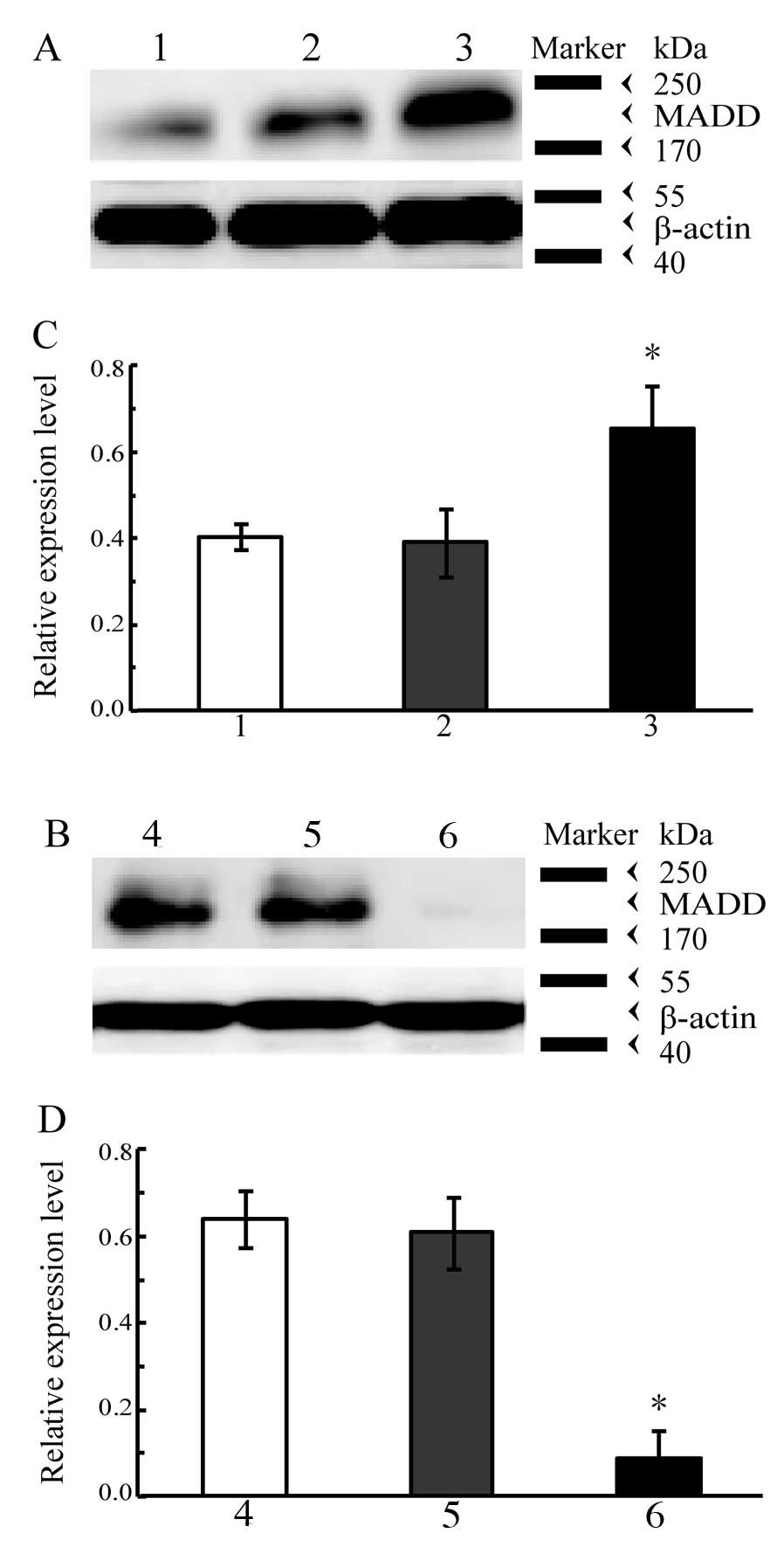
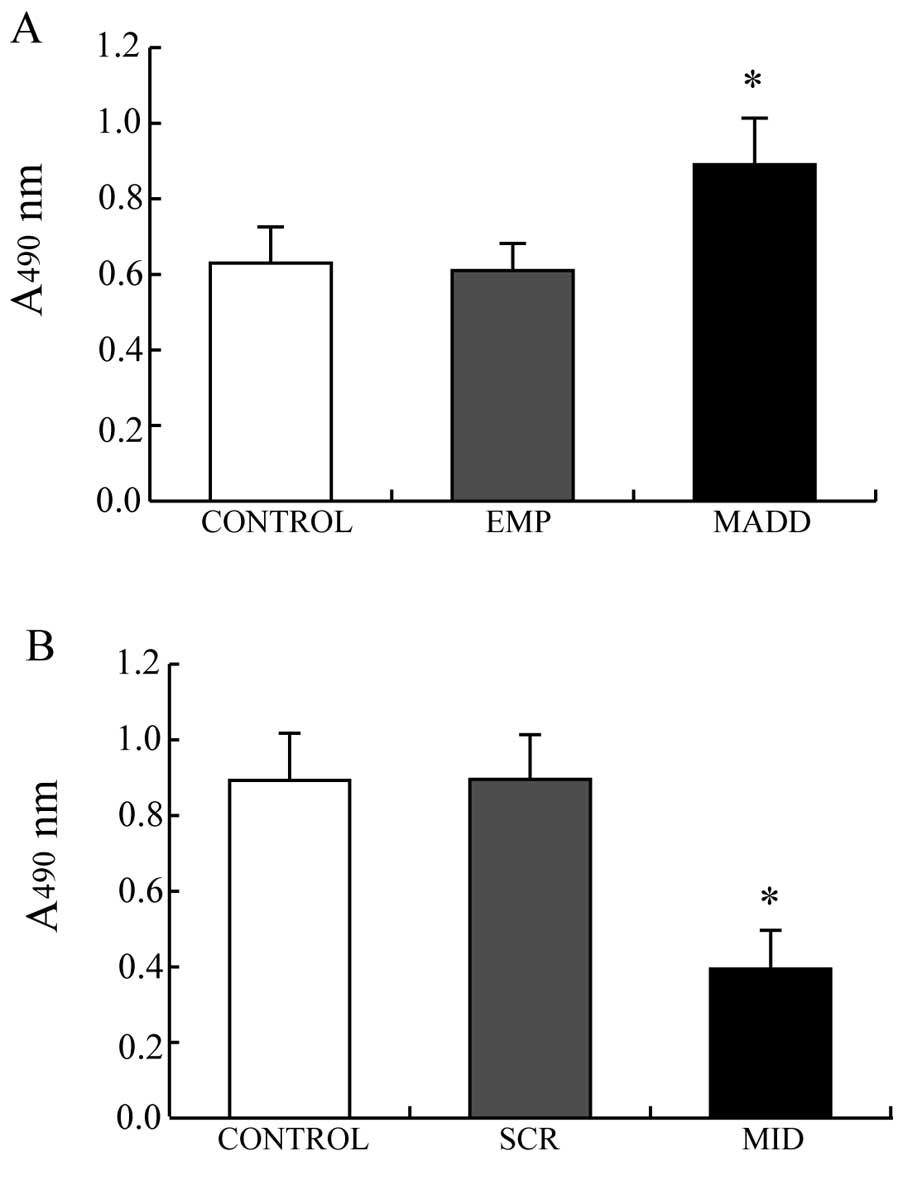
|
1
|
Niemoeller OM and Belka C: Radiotherapy
and TRAIL for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. July 12–2011.(Epub ahead
of print).
|
|
2
|
Johstone RW, Frew AJ and Smyth MJ: The
TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:782–798. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kruyt FA: TRAIL and cancer therapy. Cancer
Lett. 263:14–25. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Zoubi AM, Efimova EV, Kaithamana S,
Martinez O, El-Idrissi Mel-ADogan RE and Prabhakar BS: Contrasting
effects of IG20 and its splice isoforms, MADD and DENN-SV, on tumor
necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis and activation of caspase-8
and -3. J Biol Chem. 276:47202–47211. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li P, Jayarama S, Ganesh L, et al:
Akt-phosphorylated mitogen-activated kinase-activating death domain
protein (MADD) inhibits TRAIL-induced apoptosis by blocking
Fas-associated death domain (FADD) association with death receptor
4. J Biol Chem. 285:22713–22722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chow VT, Lim KM and Lim D: The human DENN
gene: genomic organization, alternative splicing, and localization
to chromosome 11p11.21–p11.22. Genome. 41:543–552. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Efimova EV, Al-Zoubi AM, Martinez O, et
al: IG20, in contrast to DENN-SV, (MADD splice variants) suppresses
tumor cell survival, and enhances their susceptibility to apoptosis
and cancer drugs. Oncogene. 23:1076–1087. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mulherkar N, Prasad KV and Prabhakar BS:
MADD/DENN splice variant of the IG20 gene is a negative regulator
of caspase-8 activation. Knockdown enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis
of cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 282:11715–11721. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mulherkar N, Ramaswamy M, Mordi DC and
Prabhakar BS: MADD/DENN splice variant of the IG20 gene is
necessary and sufficient for cancer cell survival. Oncogene.
25:6252–6261. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schievella AR, Chen JH, Graham JR and Lin
LL: MADD, a novel death domain protein that interacts with the type
1 tumor necrosis factor receptor and activates mitogen-activated
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 272:12069–12075. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lee MT, Coburn GA, McClure MO and Cullen
BR: Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication
in primary macrophages by using Tat- or CCR5-specific small
interfering RNAs expressed from a lentivirus vector. J Virol.
77:11964–11972. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Demirhan O, Tastemir D, Hastürk S, Kuleci
S and Hanta I: Alterations in p16 and p53 genes and chromosomal
findings in patients with lung cancer: fluorescence in situ
hybridization and cytogenetic studies. Cancer Epidemiol.
34:472–477. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee YL, Kuo WH, Lin CW, et al: Association
of genetic polymorphisms of CXCL12/SDF1 gene and its receptor,
CXCR4, to the susceptibility and prognosis of non-small cell lung
cancer. Lung Cancer. 73:147–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rosell R, Moran T, Queralt C, et al:
Screening for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 361:958–967. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R, et al:
HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody,
induces cell death in multiple tumor types in vitro and in vivo. Br
J Cancer. 92:1430–1441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
LeBlanc HN and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL
and its death and decoy receptors. Cell Death Differ. 10:66–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Riccioni R, Pasquini L, Mariani G, et al:
TRAIL decoy receptors mediate resistance of acute myeloid leukemia
cells to TRAIL. Haematologica. 90:612–624. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Morizot A, Mérino D, Lalaoui N, et al:
Chemotherapy overcomes TRAIL-R4-mediated TRAIL resistance at the
DISC level. Cell Death Differ. 18:700–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L and Fang B: Mechanisms of
resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther.
12:228–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hopkins-Donaldson S, Ziegler A, Kurtz S,
et al: Silencing of death receptor and caspase-8 expression in
small cell lung carcinoma cell lines and tumors by DNA methylation.
Cell Death Differ. 10:356–364. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ray S, Bucur O and Almasan A:
Sensitization of prostate carcinoma cells to Apo2L/TRAIL by a Bcl-2
family protein inhibitor. Apoptosis. 10:1411–1418. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Trauzold A, Siegmund D, Schniewind B, et
al: TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 25:7434–7439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cunningham SJ: Cloning and
characterization of a novel cDNA isolated from human β cells.
Doctoral dissertation. The University of Texas, Medical Branch;
1996
|
|
24
|
Chow VT and Lee SS: DENN, a novel human
gene differentially expressed in normal and neoplastic cells. DNA
Seq. 6:263–273. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li LC, Sheng JR, Mulherkar N, Prabhakar BS
and Meriggioli MN: Regulation of apoptosis and caspase-8 expression
in neuroblastoma cells by isoforms of the IG20 gene. Cancer Res.
68:7352–7361. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miyoshi J and Takai Y: Dual role of
DENN/MADD (Rab3GEP) in neurotransmission and neuroprotection.
Trends Mol Med. 10:476–480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Niwa S, Tanaka Y and Hirokawa N:
KIF1Bbeta- and KIF1A-mediated axonal transport of presynaptic
regulator Rab3 occurs in a GTP-dependent manner through DENN/MADD.
Nat Cell Biol. 10:1269–1279. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yamaguchi K, Tanaka M, Mizoguchi A, et al:
A GDP/GTP exchange protein for the Rab3 small G protein family
up-regulates a postdocking step of synaptic exocytosis in central
synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:14536–14541. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Del Villar K and Miller CA:
Down-regulation of DENN/MADD, a TNF receptor binding protein,
correlates with neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease brain
and hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:4210–4215.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kurada BR, Li LC, Mulherkar N, Subramanian
M, Prasad KV and Prabhakar BS: MADD, a splice variant of IG20, is
indispensable for MAPK activation and protection against apoptosis
upon tumor necrosis factor-alpha treatment. J Biol Chem.
284:13533–13541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Allaire PD, Marat AL, Dall’Armi C, Di
Paolo G, McPherson PS and Ritter B: The connecdenn DENN domain: a
GEF for Rab35 mediating cargo-specific exit from early endosomes.
Mol Cell. 37:370–382. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Prabhakar BS, Mulherkar N and Prasad KV:
Role of IG20 splice variants in TRAIL resistance. Clin Cancer Res.
14:347–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Coppola T, Perret-Menoud V, Gattesco S, et
al: The death domain of Rab3 guanine nucleotide exchange protein in
GDP/GTP exchange activity in living cells. Biochem J. 362:273–279.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lim KM, Yeo WS and Chow VT: Antisense
abrogation of DENN expression induces apoptosis of leukemia cells
in vitro, causes tumor regression in vivo and alters the
transcription of genes involved in apoptosis and the cell cycle.
Int J Cancer. 109:24–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Efimova E, Martinez O, Lokshin A, Arima T
and Prabhakar BS: IG20, a MADD splice variant, increases cell
susceptibility to gamma-irradiation and induces soluble mediators
that suppress tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 63:8768–8776.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|