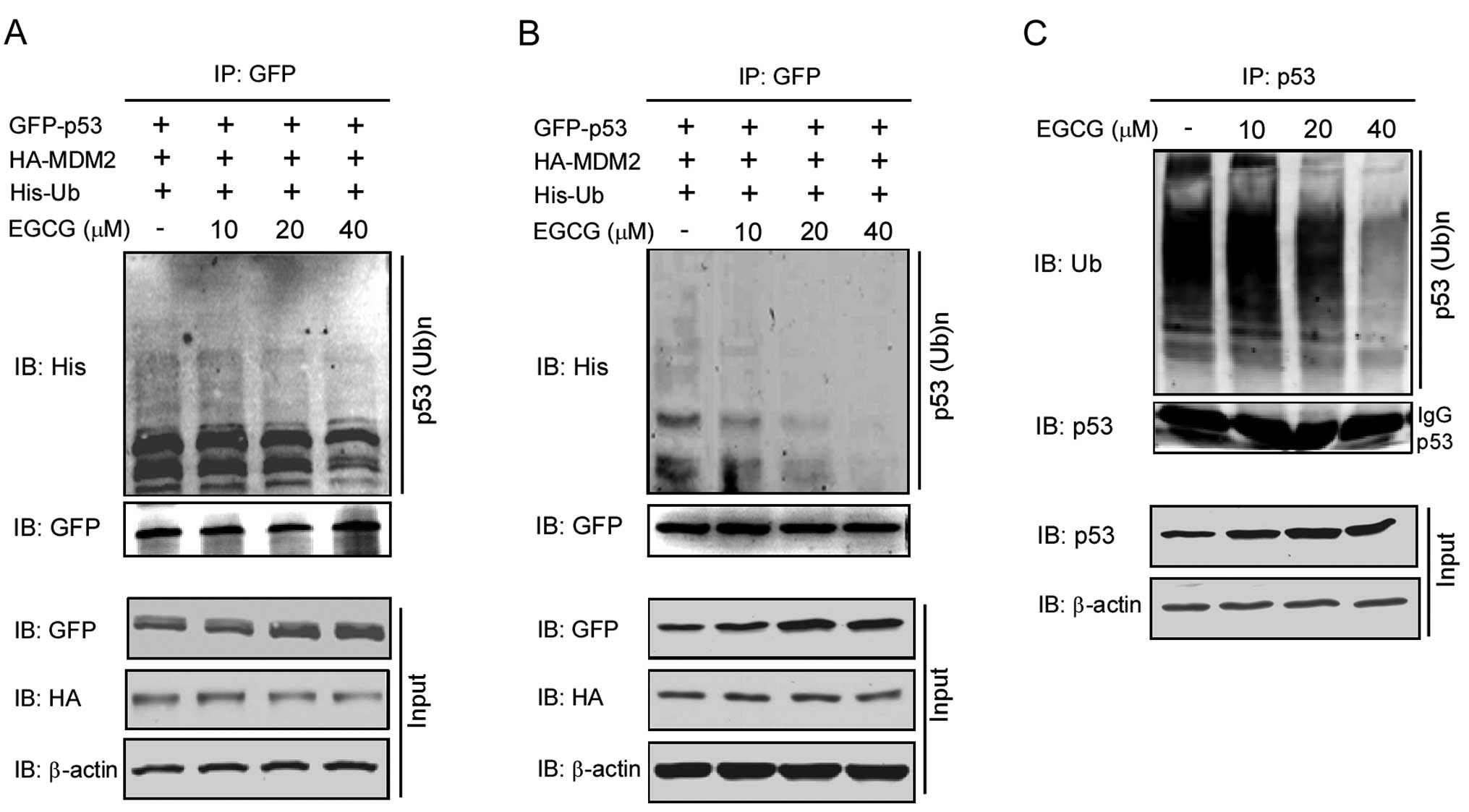
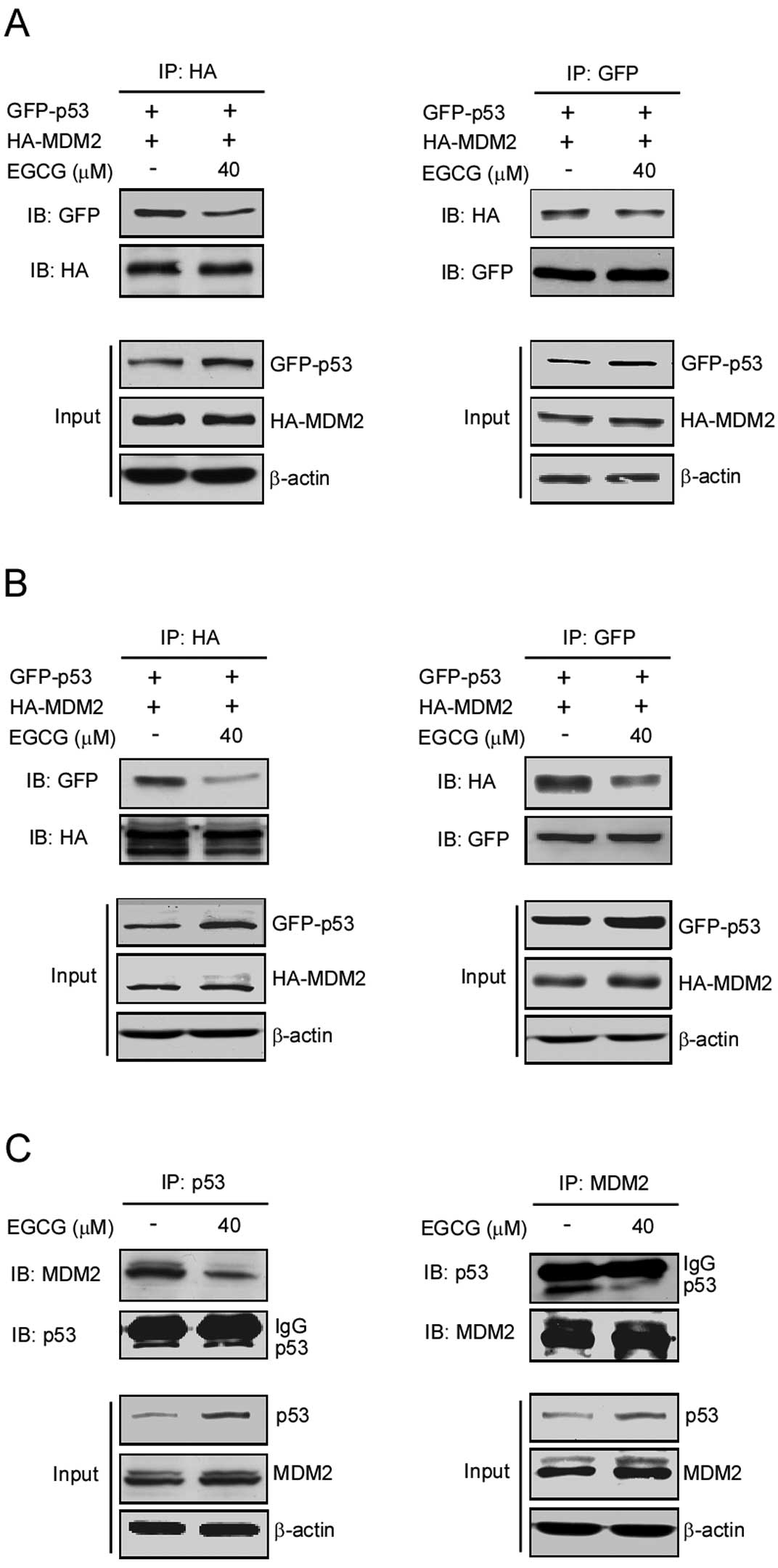
|
1
|
Chen L and Zhang HY: Cancer preventive
mechanisms of the green tea polyphenol
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Molecules. 12:946–957. 2007.
|
|
2
|
Johnson R, Bryant S and Huntley AL: Green
tea and green tea catechin extracts: an overview of the clinical
evidence. Maturitas. 73:280–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fujiki H and Suganuma M: Green tea: an
effective synergist with anticancer drugs for tertiary cancer
prevention. Cancer Lett. 324:119–125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujiki H, Imai K, Nakachi K, Shimizu M,
Moriwaki H and Suganuma M: Challenging the effectiveness of green
tea in primary and tertiary cancer prevention. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 138:1259–1270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Surh YJ: Cancer chemoprevention with
dietary phytochemicals. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:768–780. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang CS and Wang X: Green tea and cancer
prevention. Nutr Cancer. 62:931–937. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singh BN, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Green tea catechin, epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): mechanisms,
perspectives and clinical applications. Biochem Pharmacol.
82:1807–1821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Khan N, Afaq F, Saleem M, Ahmad N and
Mukhtar H: Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea
polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res.
66:2500–2505. 2006.
|
|
9
|
Shimizu M, Deguchi A, Lim JT, Moriwaki H,
Kopelovich L and Weinstein IB: (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate and
polyphenon E inhibit growth and activation of the epidermal growth
factor receptor and human epidermal growth factor receptor-2
signaling pathways in human colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
11:2735–2746. 2005.
|
|
10
|
Yang CS, Wang H, Li GX, Yang Z, Guan F and
Jin H: Cancer prevention by tea: evidence from laboratory studies.
Pharmacol Res. 64:113–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Levites Y, Amit T, Youdim MB and Mandel S:
Involvement of protein kinase C activation and cell survival/cell
cycle genes in green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin 3-gallate
neuroprotective action. J Biol Chem. 277:30574–30580.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Relat J, Blancafort A, Oliveras G, Cufi S,
Haro D, Marrero PF and Puig T: Different fatty acid metabolism
effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and C75 in adenocarcinoma
lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 12:2802012.
|
|
13
|
Sah JF, Balasubramanian S, Eckert RL and
Rorke EA: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits epidermal growth
factor receptor signaling pathway. Evidence for direct inhibition
of ERK1/2 and AKT kinases. J Biol Chem. 279:12755–12762. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanwar J, Taskeen M, Mohammad I, Huo C,
Chan TH and Dou QP: Recent advances on tea polyphenols. Front
Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:111–131. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pianetti S, Guo S, Kavanagh KT and
Sonenshein GE: Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3 gallate
inhibits Her-2/neu signaling, proliferation, and transformed
phenotype of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 62:652–655.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang F, Oz HS, Barve S, de Villiers WJ,
McClain CJ and Varilek GW: The green tea polyphenol
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks nuclear factor-kappa B
activation by inhibiting I kappa B kinase activity in the
intestinal epithelial cell line IEC-6. Mol Pharmacol. 60:528–533.
2001.
|
|
17
|
Ahmad N, Feyes DK, Nieminen AL, Agarwal R
and Mukhtar H: Green tea constituent epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human carcinoma
cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1881–1886. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saha A, Kuzuhara T, Echigo N, Suganuma M
and Fujiki H: New role of (−)-epicatechin in enhancing the
induction of growth inhibition and apoptosis in human lung cancer
cells by curcumin. Cancer Prev Res. 3:953–962. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Chang CM, Chang PY, Tu MG, et al:
Epigallocatechin gallate sensitizes CAL-27 human oral squamous cell
carcinoma cells to the anti-metastatic effects of gefitinib
(Iressa) via synergistic suppression of epidermal growth factor
receptor and matrix metalloproteinase-2. Oncol Rep. 28:1799–1807.
2012.
|
|
20
|
Deng YT and Lin JK: EGCG inhibits the
invasion of highly invasive CL1-5 lung cancer cells through
suppressing MMP-2 expression via JNK signaling and induces G2/M
arrest. J Agric Food Chem. 59:13318–13327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung YD and Ellis LM: Inhibition of tumour
invasion and angiogenesis by epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a
major component of green tea. Int J Exp Pathol. 82:309–316. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu LC, Tsao TC, Hsu SR, Wang HC, Tsai TC,
Kao J and Way TD: EGCG inhibits transforming growth
factor-β-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the
inhibition of Smad2 and Erk1/2 signaling pathways in nonsmall cell
lung cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 60:9863–9873. 2012.
|
|
23
|
Singh T and Katiyar SK: Green tea
catechins reduce invasive potential of human melanoma cells by
targeting COX-2, PGE2 receptors and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. PLoS One. 6:e252242011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Watanabe T, Kuramochi H, Takahashi A, et
al: Higher cell stiffness indicating lower metastatic potential in
B16 melanoma cell variants and in (−)-epigallocatechin
gallate-treated cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. Feb 2–2012.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Charvet C, Wissler M, Brauns-Schubert P,
et al: Phosphorylation of Tip60 by GSK-3 determines the induction
of PUMA and apoptosis by p53. Mol Cell. 42:584–596. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai C, Tang Y, Jung SY, Qin J, Aaronson SA
and Gu W: Differential effects on p53-mediated cell cycle arrest
vs. apoptosis by p90. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:18937–18942.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dai C and Gu W: p53 post-translational
modification: deregulated in tumorigenesis. Trends Mol Med.
16:528–536. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kruse JP and Gu W: SnapShot: p53
post-translational modifications. Cell. 133:930–930.e1. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kruse JP and Gu W: Modes of p53
regulation. Cell. 137:609–622. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Munoz-Fontela C, Gonzalez D, Marcos-Villar
L, et al: Acetylation is indispensable for p53 antiviral activity.
Cell Cycle. 10:3701–3705. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sakaguchi K, Herrera JE, Saito S, et al:
DNA damage activates p53 through a phosphorylation-acetylation
cascade. Genes Dev. 12:2831–2841. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jimenez GS, Khan SH, Stommel JM and Wahl
GM: p53 regulation by post-translational modification and nuclear
retention in response to diverse stresses. Oncogene. 18:7656–7665.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee JT and Gu W: The multiple levels of
regulation by p53 ubiquitination. Cell Death Differ. 17:86–92.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan J, Luo K, Zhang L, Cheville JC and
Lou Z: USP10 regulates p53 localization and stability by
deubiquitinating p53. Cell. 140:384–396. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Amin AR, Wang D, Zhang H, et al: Enhanced
anti-tumor activity by the combination of the natural compounds
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and luteolin: potential role of p53.
J Biol Chem. 285:34557–34565. 2010.
|
|
36
|
Hastak K, Gupta S, Ahmad N, Agarwal MK,
Agarwal ML and Mukhtar H: Role of p53 and NF-kappaB in
epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis of LNCaP cells.
Oncogene. 22:4851–4859. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee MH, Han DW, Hyon SH and Park JC:
Apoptosis of human fibrosarcoma HT-1080 cells by
epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate via induction of p53 and caspases as
well as suppression of Bcl-2 and phosphorylated nuclear
factor-kappaB. Apoptosis. 16:75–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qin J, Chen HG, Yan Q, et al: Protein
phosphatase-2A is a target of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and
modulates p53-Bak apoptotic pathway. Cancer Res. 68:4150–4162.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hastak K, Agarwal MK, Mukhtar H and
Agarwal ML: Ablation of either p21 or Bax prevents p53-dependent
apoptosis induced by green tea polyphenol
epigallocatechin-3-gallate. FASEB J. 19:789–791. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thakur VS, Ruhul Amin AR, Paul RK, et al:
p53-Dependent p21-mediated growth arrest pre-empts and protects
HCT116 cells from PUMA-mediated apoptosis induced by EGCG. Cancer
Lett. 296:225–232. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao BX, Chen HZ, Lei NZ, et al: p53
mediates the negative regulation of MDM2 by orphan receptor TR3.
EMBO J. 25:5703–5715. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chehab NH, Malikzay A, Stavridi ES and
Halazonetis TD: Phosphorylation of Ser-20 mediates stabilization of
human p53 in response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:13777–13782. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Unger T, Juven-Gershon T, Moallem E, et
al: Critical role for Ser20 of human p53 in the negative regulation
of p53 by Mdm2. EMBO J. 18:1805–1814. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|