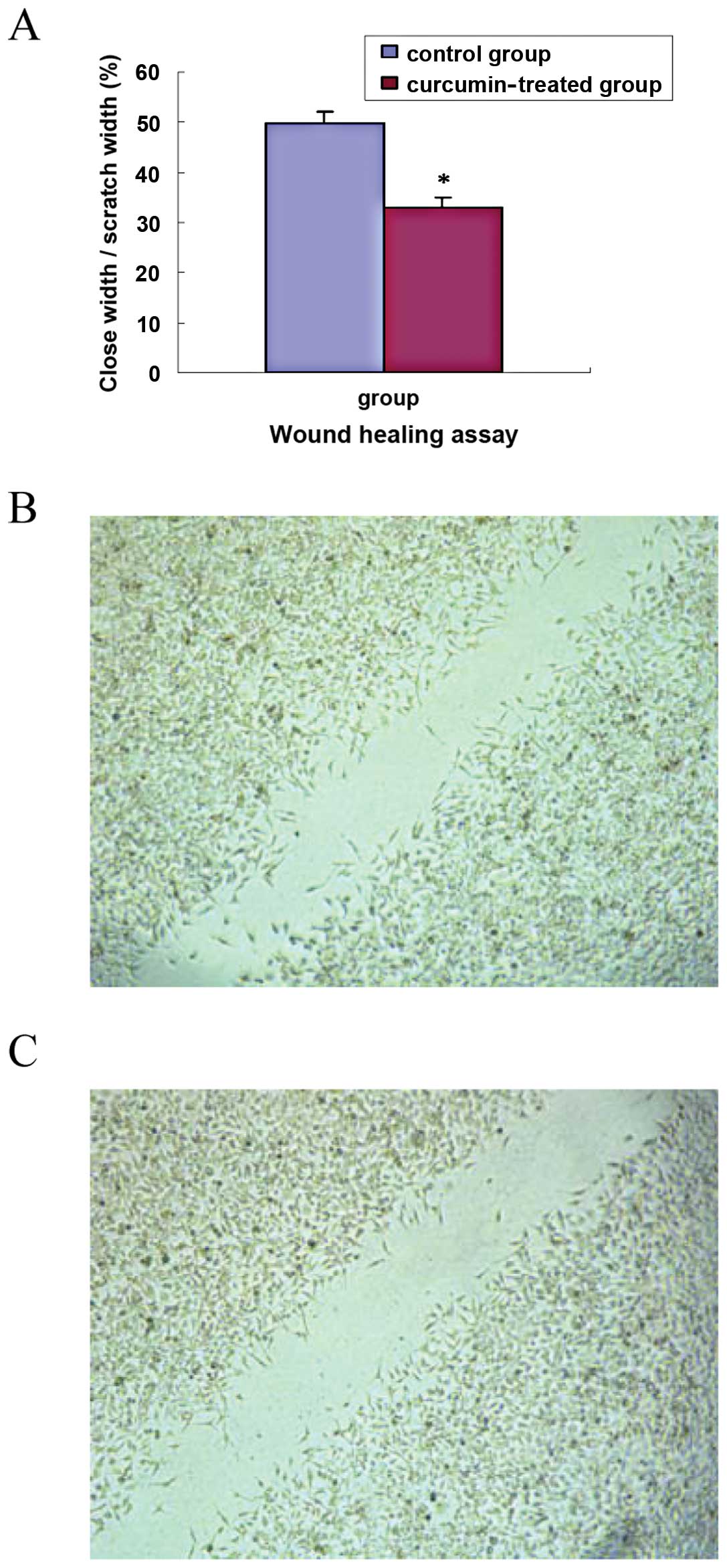
|
1
|
Goel A and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin, the
golden spice from Indian saffron, is a chemosensitizer and
radiosensitizer for tumors and chemoprotector and radioprotector
for normal organs. Nutr Cancer. 62:919–930. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Basnet P and Skalko-Basnet N: Curcumin: an
anti-inflammatory molecule from a curry spice on the path to cancer
treatment. Molecules. 16:4567–4598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pirozzi G, Tirino V and Camerlingo R:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition by TGF-β1 induction increases
stemness characteristics in primary non small cell lung cancer
line. PLoS One. 6:e215482011.
|
|
4
|
Maitah YM, Ali S, Ahmad A, Gadgeel S and
Sarkar FH: Up-regulation of sonic hedgehog contributes to
TGF-β1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in NSCLC cells.
PLoS One. 6:e160682011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thomson S, Petti F, Sujka-Kwok I, Mercado
P, Bean J, Monaghan M, Seymour SL, Argast GM, Epstein DM and Haley
JD: A systems view of epithelial-mesenchymal transition signaling
states. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:137–155. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Uramoto H, Iwata T, Onitsuka T, Shimokawa
H, Hanagiri T and Oyama T: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
EGFR-TKI acquired resistant lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res.
30:2513–2517. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wells A, Yates C and Shepard CR:
E-cadherin as an indicator of mesenchymal to epithelial reverting
transitions during the metastatic seeding of disseminated
carcinomas. Clin Exp Metastasis. 25:621–628. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hotz HG, Hotz B and Buhr HJ: Genes
associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition: possible
therapeutic targets in ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma? Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 11:448–454. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dai J, Ai K, Du Y and Chen G: Sonic
hedgehog expression correlates with distant metastasis in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 40:233–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kelleher FC: Hedgehog signaling and
therapeutics in pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:445–451.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Katoh Y and Katoh M: Hedgehog target
genes: mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog
signaling activation. Curr Mol Med. 9:873–886. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Potential
application of curcumin and its novel synthetic analogs and
nanotechnology-based formulations in cancer prevention and therapy.
Chin Med. 23:312011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nautiyal J, Banerjee S, Kanwar SS, Yu Y,
Patel BB, Sarkar FH and Majumdar AP: Curcumin enhances
dasatinib-induced inhibition of growth and transformation of colon
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 128:951–961. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Teiten MH, Gaascht F, Cronauer M, Henry E,
Dicato M and Diederich M: Anti-proliferative potential of curcumin
in androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells occurs through
modulation of the Wingless signaling pathway. Int J Oncol.
38:603–611. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yallapu MM, Maher DM, Sundram V, Bell MC,
Jaggi M and Chauhan SC: Curcumin induces chemo/radio-sensitization
in ovarian cancer cells and curcumin nanoparticles inhibit ovarian
cancer cell growth. J Ovarian Res. 3:112010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aggarwal BB, Banerjee S, Bharadwaj U, Sung
B, Shishodia S and Sethi G: Curcumin induces the degradation of
cyclin E expression through ubiquitin- dependent pathway and
up-regulates cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27 in
multiple human tumor cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:1024–1032.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Guha S, Krishnan S,
Diagaradjane P, Gelovani J and Aggarwal BB: Curcumin potentiates
antitumor activity of gemcitabine in an orthotopic model of
pancreatic cancer through suppression of proliferation,
angiogenesis, and inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB regulated
gene products. Cancer Res. 67:3853–3861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ali S, Ahmad A, Banerjee S, Padhye S,
Dominiak K, Schaffert JM, Wang Z, Philip PA and Sarkar FH:
Gemcitabine sensitivity can be induced in pancreatic cancer cells
through modulation of miR-200 and miR-21 expression by curcumin or
its analogue CDF. Cancer Res. 70:3606–3617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jutooru I, Chadalapaka G, Lei P and Safe
S: Inhibition of NFkappaB and pancreatic cancer cell and tumor
growth by curcumin is dependent on specificity protein
down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 285:25332–25344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ramachandran C, Resek AP, Escalon E,
Aviram A and Melnick SJ: Potentiation of gemcitabine by Turmeric
Force™ in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 23:1529–1535.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Frequent
deregulations in the hedgehog signaling network and cross-talks
with the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway involved in
cancer progression and targeted therapies. Pharmacol Rev.
62:497–524. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Morton JP, Mongeau ME, Klimstra DS, Morris
JP, Lee YC, Kawaguchi Y, Wright CV, Hebrok M and Lewis BC: Sonic
hedgehog acts at multiple stages during pancreatic tumorigenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:5103–5108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nolan-Stevaux O, Lau J, Truitt ML, Chu GC,
Hebrok M, Fernandez-Zapico ME and Hanahan D: GLI1 is
regulated through Smoothened-independent mechanisms in neoplastic
pancreatic ducts and mediates PDAC cell survival and
transformation. Genes Dev. 23:24–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cao M, Seike M, Soeno C, Mizutani H,
Kitamurak, Minegishi Y, Noro R, Yoshimura A, Cai L and Gemma A:
MiR-23a regulates TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
by targeting E-cadherin in lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
41:865–875. 2012.
|