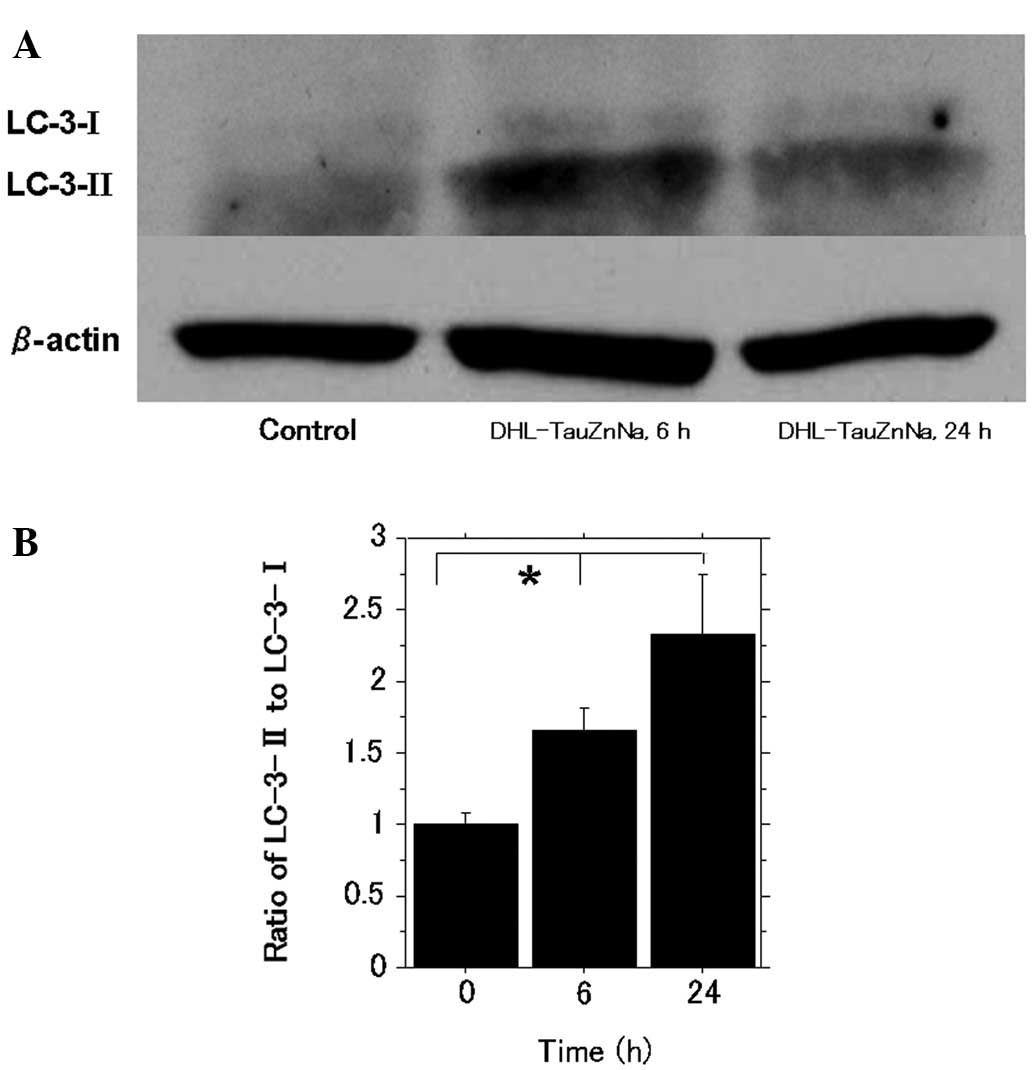
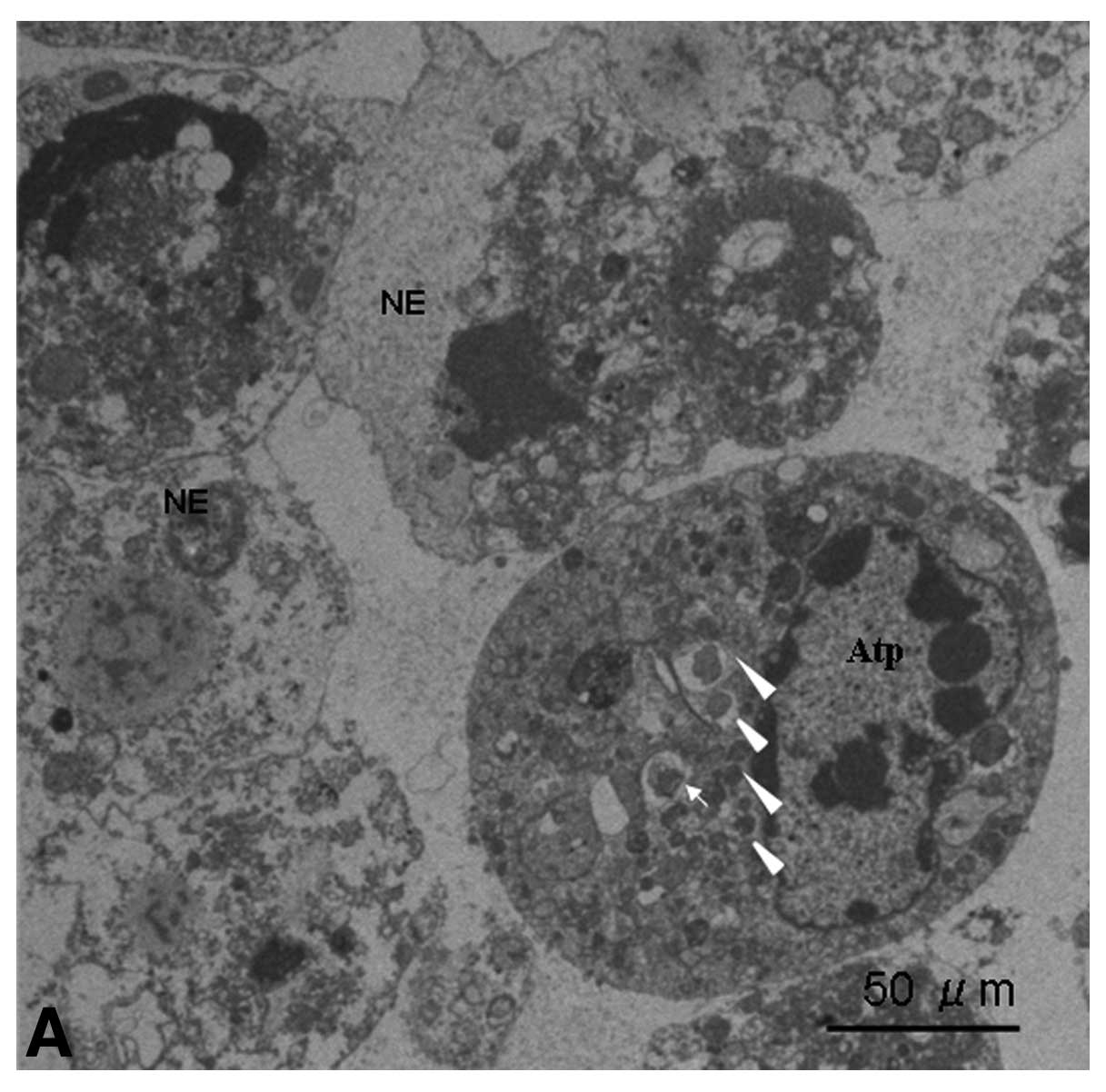
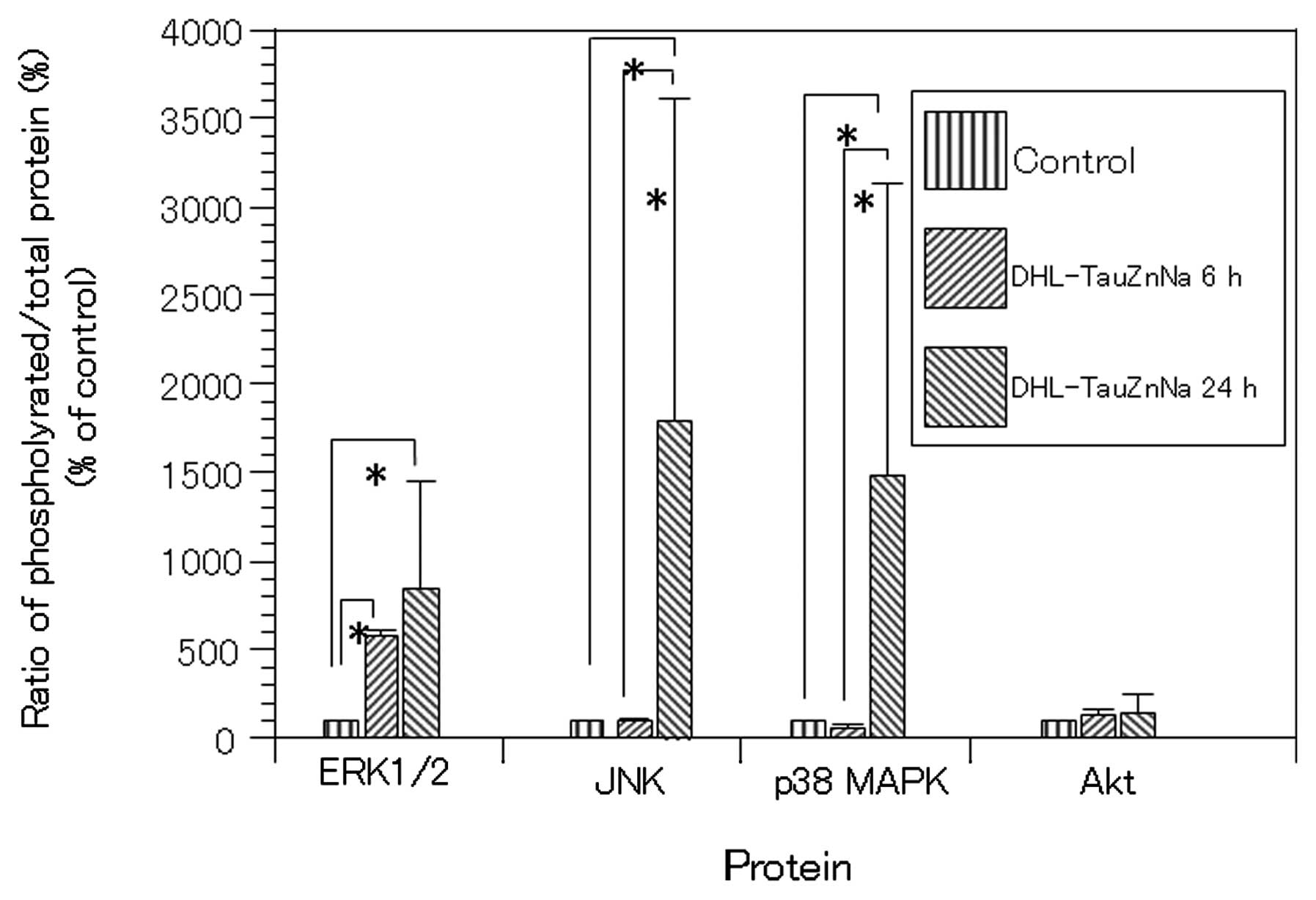
|
1
|
Bretthauer M: Colorectal cancer screening.
J Intern Med. 270:87–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hind D, Tappenden P, Tumur I, et al: The
use of irinotecan, oxaliplatin and raltitrexed for the treatment of
advanced colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic
evaluation. Health Technol Assess. 12:iii–ix. xi–162.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wolpin BM and Mayer RJ: Systemic treatment
of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 134:1296–1310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Inokuma T, Haraguchi M, Fujita F, et al:
Oxidative stress and tumor progression in colorectal cancer.
Hepatogastroenterology. 56:343–347. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Novotny L, Rauko P and Cojocel C:
alpha-Lipoic acid: the potential for use in cancer therapy.
Neoplasma. 55:81–86. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao P, Zhang H, Dinavahi R, et al:
HIF-dependent antitumorigenic effect of antioxidants in vivo.
Cancer Cell. 12:230–238. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Anand P and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin inhibits proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis and
metastasis of different cancers through interaction with multiple
cell signaling proteins. Cancer Lett. 269:199–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shi DY, Liu HL, Stern JS, et al:
Alpha-lipoic acid induces apoptosis in hepatoma cells via the
PTEN/Akt pathway. FEBS Lett. 582:1667–1671. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wenzel U, Nickel A and Daniel H:
alpha-Lipoic acid induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cells by
increasing mitochondrial respiration with a concomitant
O2-·-generation. Apoptosis. 10:359–368. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du J, Martin SM, Levine M, et al:
Mechanisms of ascorbate-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:509–520. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Altman SA, Randers L and Rao G: Comparison
of trypan blue dye exclusion and fluorometric assays for mammalian
cell viability determinations. Biotechnol Prog. 9:671–674. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kalejta RF, Shenk T and Beavis AJ: Use of
a membrane-localized green fluorescent protein allows simultaneous
identification of transfected cells and cell cycle analysis by flow
cytometry. Cytometry. 29:286–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Makhov P, Kutikov A, Golovine K, et al:
Docetaxel-mediated apoptosis in myeloid progenitor TF-1 cells is
mitigated by zinc: potential implication for prostate cancer
therapy. Prostate. 71:1413–1419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li M, Zhang Y, Zhai Q, et al: Thymosin
beta-10 is aberrantly expressed in pancreatic cancer and induces
JNK activation. Cancer Invest. 27:251–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsuchihara K, Fujii S and Esumi H:
Autophagy and cancer: dynamism of the metabolism of tumor cells and
tissues. Cancer Lett. 278:130–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang KY, Tsai SY, Wu CM, et al: Novel
phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mTOR dual inhibitor, NVP-BGT226, displays
potent growth-inhibitory activity against human head and neck
cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7116–7126.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lefranc F, Facchini V and Kiss R:
Proautophagic drugs: a novel means to combat apoptosis-resistant
cancers, with a special emphasis on glioblastomas. Oncologist.
12:1395–1403. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ullman E, Fan Y, Stawowczyk M, et al:
Autophagy promotes necrosis in apoptosis-deficient cells in
response to ER stress. Cell Death Differ. 15:422–425. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gamrekelashvili J, Krüger C, von
Wasielewski R, et al: Necrotic tumor cell death in vivo impairs
tumor-specific immune responses. J Immunol. 178:1573–1580. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Yuan J, Zhang HY, et al: Natural
resistance to apoptosis correlates with resistance to chemotherapy
in colorectal cancer cells. Clin Exp Med. 12:97–103. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim KW, Mutter RW, Cao C, et al: Autophagy
for cancer therapy through inhibition of pro-apoptotic proteins and
mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. J Biol Chem.
281:36883–36890. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shinojima N, Yokoyama T, Kondo U, et al:
Roles of the Akt/mTOR/p70S6K and ERK1/2 signaling pathways in
curcumin-induced autophagy. Autophagy. 3:635–637. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Nishida Y, et al:
Involvement of JNK in the regulation of autophagic cell death.
Oncogene. 29:2070–2082. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Duan WJ, Li QS, Xia MY, et al: Silibinin
activated p53 and induced autophagic death in human fibrosarcoma
HT1080 cells via reactive oxygen species-p38 and c-Jun N-terminal
kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:47–53. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Böck BC, Tagscherer KE, Fassl A, et al:
The PEA-15 protein regulates autophagy via activation of JNK. J
Biol Chem. 285:21644–21654. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen SY, Chiu LY, Maa MC, et al:
zVAD-induced autophagic cell death requires c-Src-dependent ERK and
JNK activation and reactive oxygen species generation. Autophagy.
7:217–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ogier-Denis E, Pattingre S, El Benna J, et
al: Erk1/2-dependent phosphorylation of Galpha-interacting protein
stimulates its GTPase accelerating activity and autophagy in human
colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 275:39090–39095. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xie CM, Chan WY, Yu S, et al: Bufalin
induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon cancer cells
through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK activation. Free
Radic Biol Med. 51:1365–1375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Majewski N, Nogueira V, Robey RB, et al:
Akt inhibits apoptosis downstream of BID cleavage via a
glucose-dependent mechanism involving mitochondrial hexokinases.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:730–740. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Viola G, Bortolozzi R, Hamel E, et al:
MG-2477, a new tubulin inhibitor, induces autophagy through
inhibition of the Akt/mTOR pathway and delayed apoptosis in A549
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 83:16–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|