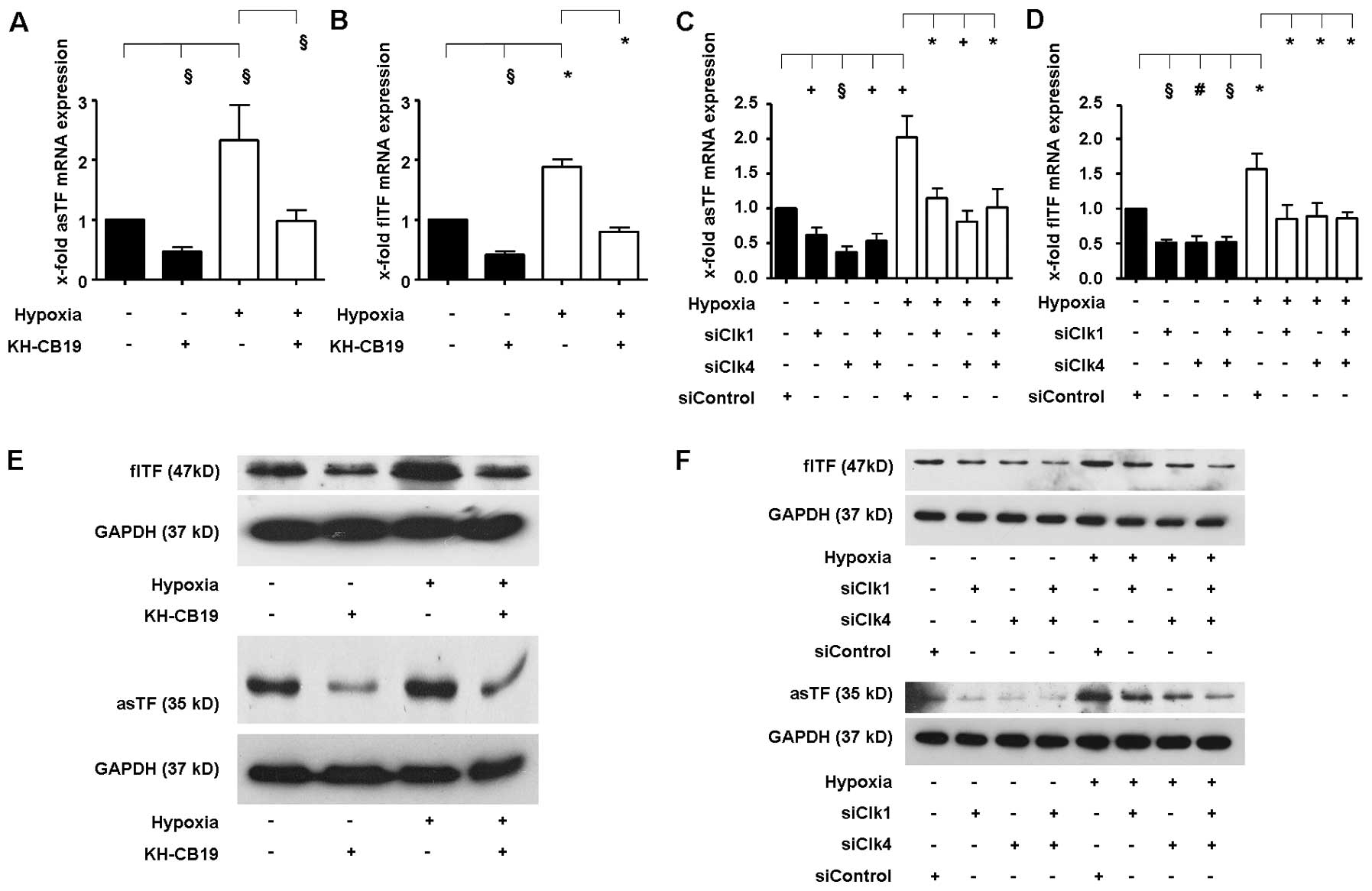
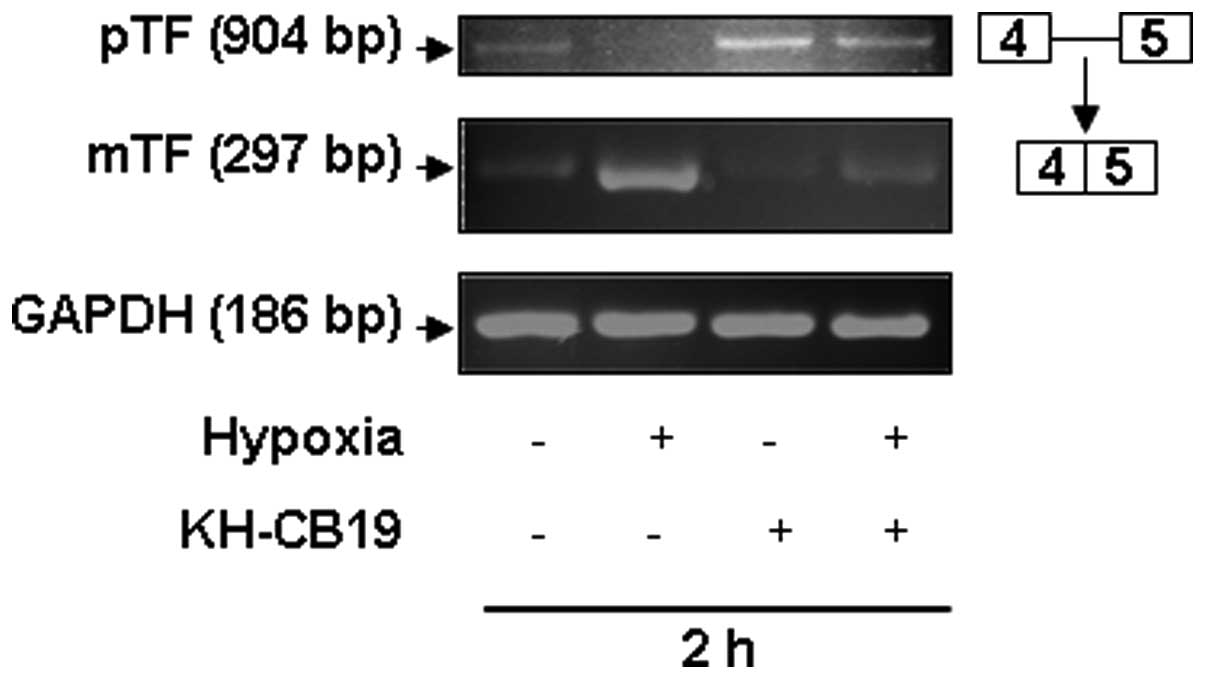
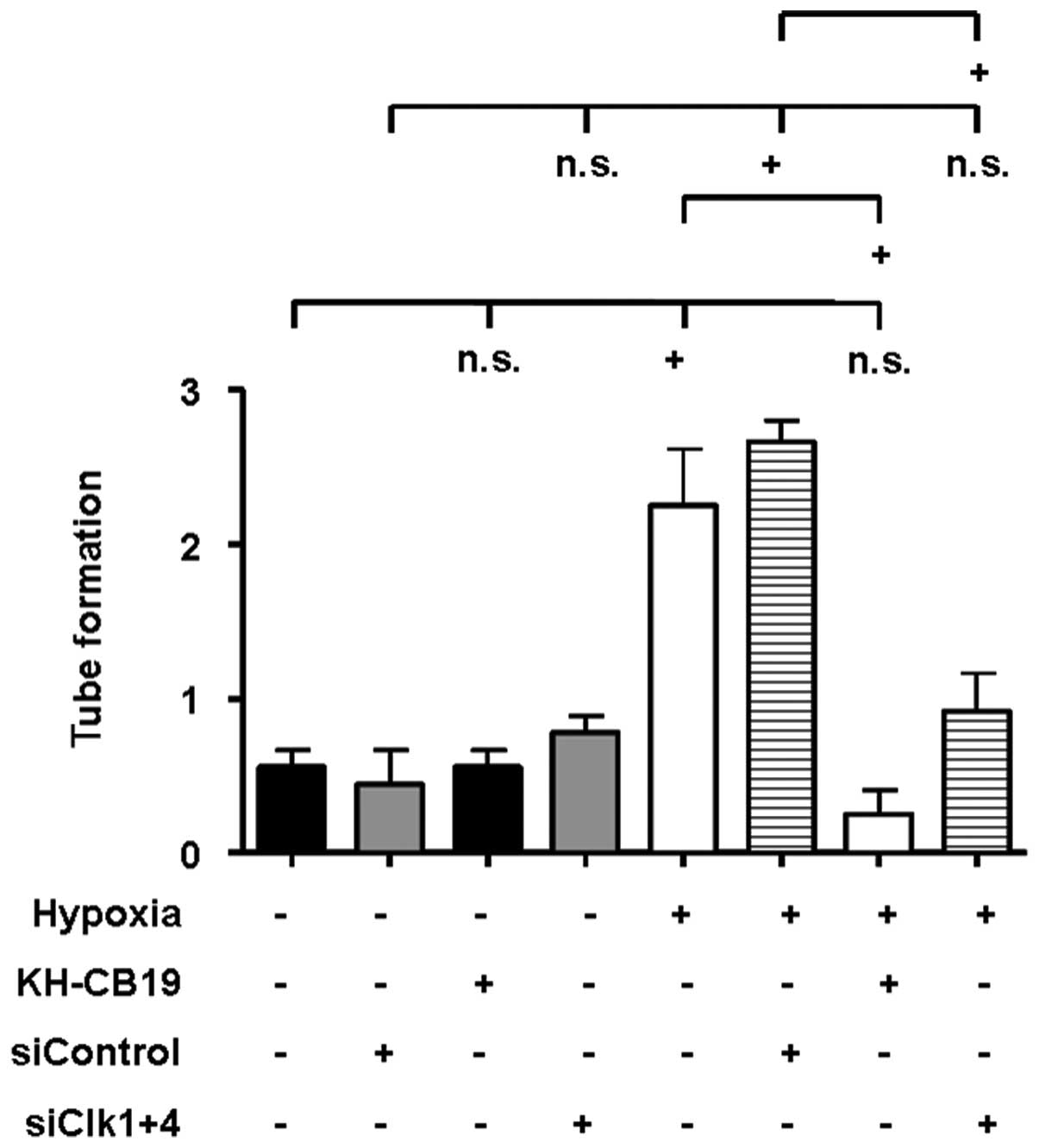
|
1
|
Eisenreich A, Celebi O, Goldin-Lang P,
Schultheiss HP and Rauch U: Upregulation of tissue factor
expression and thrombogenic activity in human aortic smooth muscle
cells by irradiation, rapamycin and paclitaxel. Int
Immunopharmacol. 8:307–311. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Giesen PL, Rauch U, Bohrman B, et al:
Blood-borne tissue factor: another view of thrombosis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 96:2311–2315. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rauch U, Antoniak S, Boots M, et al:
Association of tissue-factor upregulation in squamous-cell
carcinoma of the lung with increased tissue factor in circulating
blood. Lancet Oncol. 6:2542005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Szotowski B, Antoniak S, Poller W,
Schultheiss HP and Rauch U: Procoagulant soluble tissue factor is
released from endothelial cells in response to inflammatory
cytokines. Circ Res. 96:1233–1239. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bogdanov VY, Balasubramanian V, Hathcock
J, Vele O, Lieb M and Nemerson Y: Alternatively spliced human
tissue factor: a circulating, soluble, thrombogenic protein. Nat
Med. 9:458–462. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eisenreich A, Bogdanov VY, Zakrzewicz A,
et al: Cdc2-like kinases and DNA topoisomerase I regulate
alternative splicing of tissue factor in human endothelial cells.
Circ Res. 104:589–599. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eisenreich A, Malz R, Pepke W, Ayral Y,
Poller W, Schultheiss HP and Rauch U: Role of the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway in
regulating alternative splicing of tissue factor mRNA in human
endothelial cells. Circ J. 73:1746–1752. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tardos JG, Eisenreich A, Deikus G, et al:
SR proteins ASF/SF2 and SRp55 participate in tissue factor
biosynthesis in human monocytic cells. J Thromb Haemost. 6:877–884.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rauch U and Antoniak S: Tissue
factor-positive microparticles in blood associated with
coagulopathy in cancer. Thromb Haemost. 97:9–10. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eisenreich A, Boltzen U, Malz R,
Schultheiss HP and Rauch U: Overexpression of alternatively spliced
tissue factor induces the pro-angiogenic properties of murine
cardiomyocytic HL-1 cells. Circ J. 75:1235–1242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eisenreich A and Rauch U: Regulation and
differential role of the tissue factor isoforms in cardiovascular
biology. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 20:199–203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hobbs JE, Zakarija A, Cundiff DL, et al:
Alternatively spliced human tissue factor promotes tumor growth and
angiogenesis in a pancreatic cancer tumor model. Thromb Res.
120(Suppl 2): S13–S21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van den Berg YW, van den Hengel LG, Myers
HR, et al: Alternatively spliced tissue factor induces angiogenesis
through integrin ligation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:19497–19502.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goldin-Lang P, Tran QV, Fichtner I, et al:
Tissue factor expression pattern in human non-small cell lung
cancer tissues indicate increased blood thrombogenicity and tumor
metastasis. Oncol Rep. 20:123–128. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Zhang T, Koide N, Wada Y, et al:
Significance of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and thymidine
phosphorylase in angiogenesis of human cardiac myxoma. Circ J.
67:54–60. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Han J, Yang X, et al: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor inhibits angiogenesis and growth of
gastric carcinoma by down-regulation of VEGF. Oncol Rep.
26:681–686. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shimizu T, Okayama A, Inoue T and Takeda
K: Analysis of gene expression during staurosporine-induced
neuronal differentiation of human prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
14:441–448. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen N, Leu SJ, Todorovic V, Lam SC and
Lau LF: Identification of a novel integrin
αvβ3 binding site in CCN1 (CYR61) critical
for pro-angiogenic activities in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 279:44166–44176. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Hutchings H, Ortega N and Plouët J:
Extracellular matrix-bound vascular endothelial growth factor
promotes endothelial cell adhesion, migration, and survival through
integrin ligation. FASEB J. 17:1520–1522. 2003.
|
|
20
|
Löbel M, Bauer S, Meisel C, et al: CCN1:
CCN1: a novel inflammation-regulated biphasic immune cell migration
modulator. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3101–3113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schaffner F, Versteeg HH, Schillert A,
Yokota N, Petersen LC, Mueller BM and Ruf W: Cooperation of tissue
factor cytoplasmic domain and PAR2 signaling in breast cancer
development. Blood. 116:6106–6113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fedorov O, Huber K, Eisenreich A, et al:
Specific CLK inhibitors from a novel chemotype for regulation of
alternative splicing. Chem Biol. 18:67–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schwertz H, Tolley ND, Foulks JM, et al:
Signal-dependent splicing of tissue factor pre-mRNA modulates the
thrombogenicity of human platelets. J Exp Med. 203:2433–2440. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SH, Kim KW and Jeong JW: Inhibition of
hypoxia-induced angiogenesis by sodium butyrate, a histone
deacetylase inhibitor, through hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
suppression. Oncol Rep. 17:793–797. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Łuczak MW, Roszak A, Pawlik P, Kędzia H,
Lianeri M and Jagodziński PP: Increased expression of HIF-1A and
its implication in the hypoxia pathway in primary advanced uterine
cervical carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 26:1259–1264. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gang H, Hai Y, Dhingra R, et al: A novel
hypoxia-inducible spliced variant of mitochondrial death gene Bnip3
promotes survival of ventricular myocytes. Circ Res. 108:1084–1092.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hirschfeld M, zur Hausen A, Bettendorf H,
Jäger M and Stickeler E: Alternative splicing of Cyr61 is regulated
by hypoxia and significantly changed in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
69:2082–2090. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tazi J, Bakkour N and Stamm S: Alternative
splicing and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:14–26. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu F, Shi J, Yu B, Ni W, Wu X and Gu Z:
Chemokines mediate mesenchymal stem cell migration toward gliomas
in vitro. Oncol Rep. 23:1561–1567. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao X, Li DC, Zhao H, et al: A study of
the suppressive effect on human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell
proliferation and angiogenesis by stable plasmid-based siRNA
silencing of c-Src gene expression. Oncol Rep. 27:628–636.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arderiu G, Peña E, Aledo R, Juan-Babot O
and Badimon L: Tissue factor regulates microvessel formation and
stabilization by induction of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2
expression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:2607–2615. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ollivier V, Bentolila S, Chabbat J, Hakim
J and de Prost D: Tissue factor-dependent vascular endothelial
growth factor production by human fibroblasts in response to
activated factor VII. Blood. 91:2698–2703. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Roberts JR, Perkins GD, Fujisawa T,
Pettigrew KA, Gao F, Ahmed A and Trickett DR: Vascular endothelial
growth factor promotes physical wound repair and is anti-apoptotic
in primary distal lung epithelial and A549 cells. Crit Care Med.
35:2164–2170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Loges S, Butzal M, Otten J, et al:
Cilengitide inhibits proliferation and differentiation of human
endothelial progenitor cells in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
357:1016–1020. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cirillo P, Calì G, Golino P, et al: Tissue
factor binding of activated factor VII triggers smooth muscle cell
proliferation via extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation.
Circulation. 109:2911–2916. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bourgeois CF, Lejeune F and Stévenin J:
Broad specificity of SR (serine/arginine) proteins in the
regulation of alternative splicing of pre-messenger RNA. Prog
Nucleic Acids Res Mol Biol. 78:37–88. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eisenreich A, Boltzen U, Poller W,
Schultheiss HP and Rauch U: Effects of the Cdc2-like kinase-family
and DNA topoisomerase I on the alternative splicing of eNOS in
TNF-α-stimulated human endothelial cells. Biol Chem. 389:1333–1338.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Eisenreich A and Rauch U: PI3K inhibitors
in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Ther. 29:29–36. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Prasad J, Colwill K, Pawson T and Manley
JL: The protein kinase Clk/Sty directly modulates SR protein
activity: both hyper- and hypophosphorylation inhibit splicing. Mol
Cell Biol. 19:6991–7000. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|