|
1
|
Marsh Rde W, Alonzo M, Bajaj S, et al:
Comprehensive review of the diagnosis and treatment of biliary
tract cancer 2012. Part I: diagnosis-clinical staging and
pathology. J Surg Oncol. 106:332–338. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blechacz B, Komuta M, Roskams T and Gores
GJ: Clinical diagnosis and staging of cholangiocarcinoma. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:512–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Romiti A, D’Antonio C, Zullo A, et al:
Chemotherapy for the biliary tract cancers: moving toward improved
survival time. J Gastrointest Cancer. 43:396–404. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, et al:
Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor.
Nature. 342:440–443. 1989. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Date K, Matsumoto K, Shimura H, Tanaka M
and Nakamura T: HGF/NK4 is a specific antagonist for pleiotrophic
actions of hepatocyte growth factor. FEBS Lett. 420:1–6. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Comoglio PM, Giordano S and Trusolino L:
Drug development of MET inhibitors: targeting oncogene addiction
and expedience. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:504–516. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sattler M and Salgia R: The MET axis as a
therapeutic target. Update Cancer Ther. 3:109–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, et
al: MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer
by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 316:1039–1043. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Murakami M, et al:
Radiation to stromal fibroblasts increases invasiveness of
pancreatic cancer cells through tumor-stromal interactions. Cancer
Res. 64:3215–3222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yano S, Wang W, Li Q, et al: Hepatocyte
growth factor induces gefitinib resistance of lung adenocarcinoma
with epidermal growth factor receptor-activating mutations. Cancer
Res. 68:9479–9487. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Onimaru M, Ohuchida K, Egami T, et al:
Gemcitabine synergistically enhances the effect of adenovirus gene
therapy through activation of the CMV promoter in pancreatic cancer
cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:541–549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
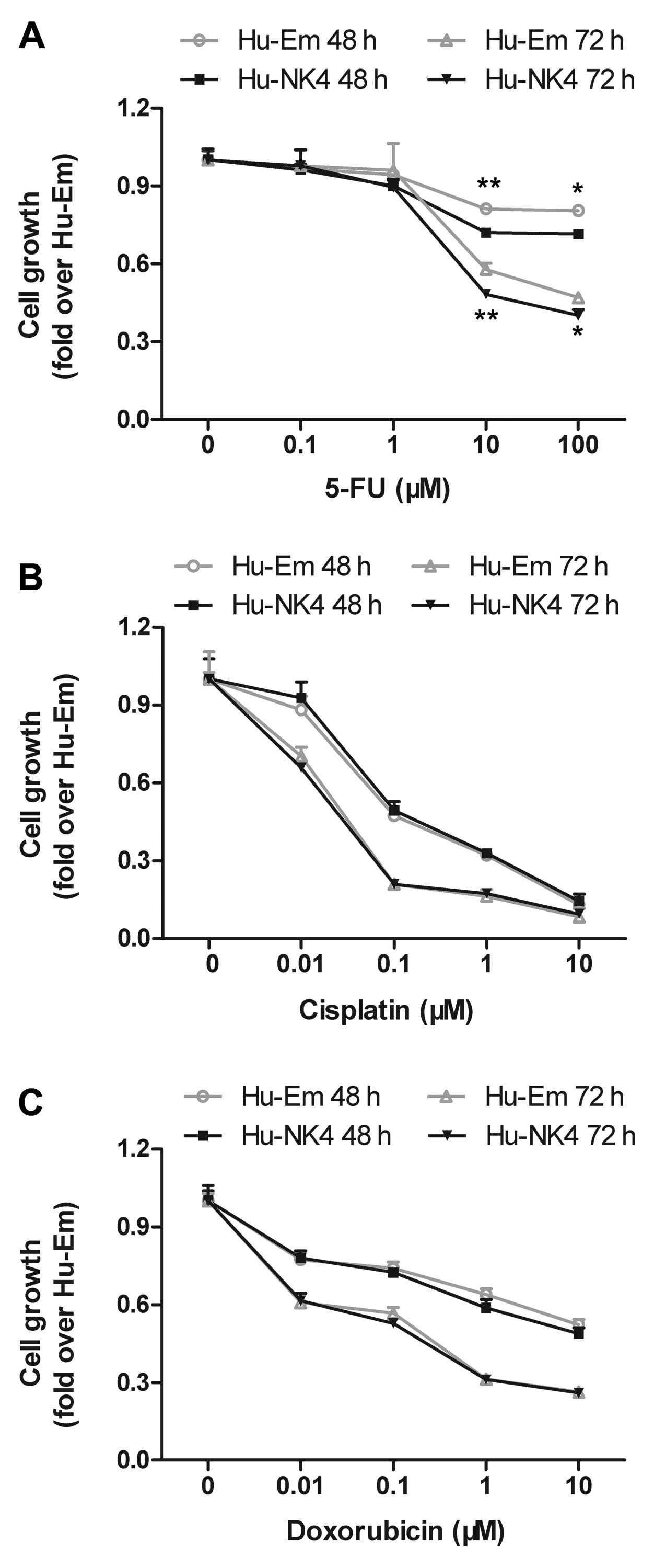
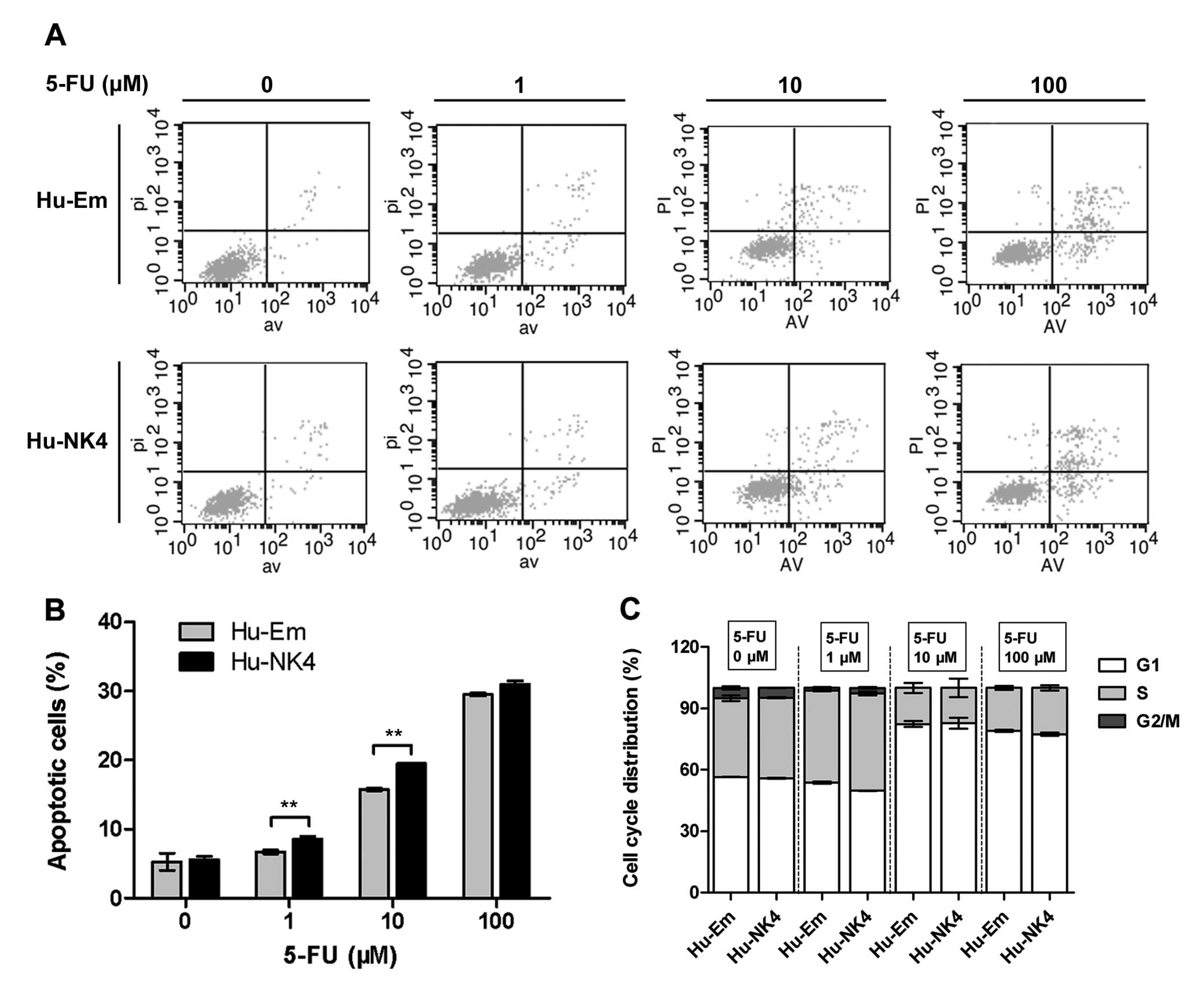
Taiyoh H, Kubota T, Fujiwara H, et al: NK4
gene expression enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis of murine
colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 31:2217–2224. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Crea F, Nobili S, Paolicchi E, et al:
Epigenetics and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer: an
opportunity for treatment tailoring and novel therapeutic
strategies. Drug Resist Updat. 14:280–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Banerjee D, Mayer-Kuckuk P, Capiaux G,
Budak-Alpdogan T, Gorlick R and Bertino JR: Novel aspects of
resistance to drugs targeted to dihydrofolate reductase and
thymidylate synthase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1587:164–173. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Longley DB, Allen WL and Johnston PG: Drug
resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:184–196. 2006.
|
|
16
|
Leichman CG, Lenz HJ, Leichman L, et al:
Quantitation of intratumoral thymidylate synthase expression
predicts for disseminated colorectal cancer response and resistance
to protracted-infusion fluorouracil and weekly leucovorin. J Clin
Oncol. 15:3223–3229. 1997.
|
|
17
|
Metzger R, Danenberg K, Leichman CG, et
al: High basal level gene expression of thymidine phosphorylase
(platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor) in colorectal
tumors is associated with nonresponse to 5-fluorouracil. Clin
Cancer Res. 4:2371–2376. 1998.
|
|
18
|
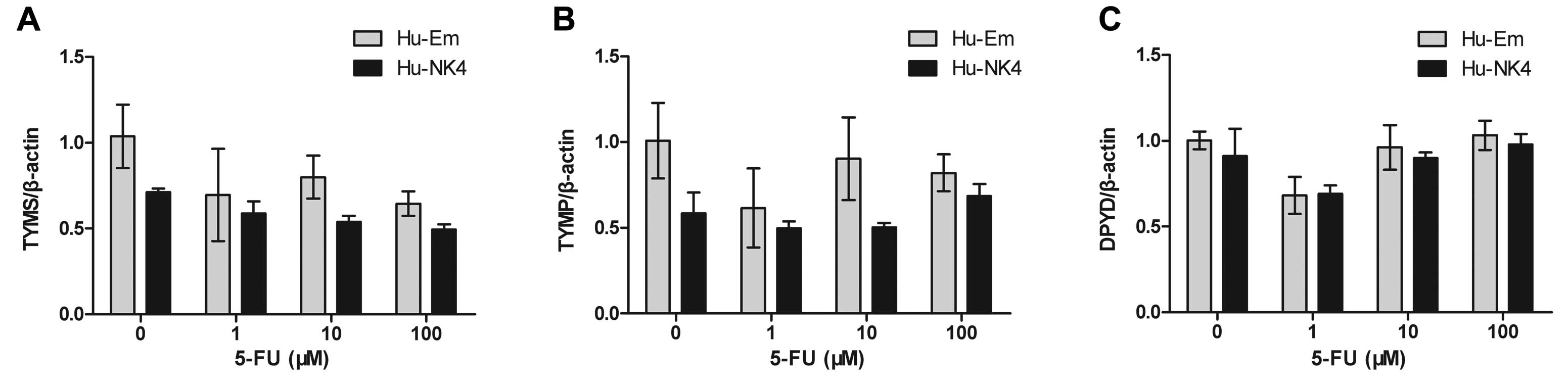
Nishi M, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, et al:
Role of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase and thymidylate synthase
expression in immunohistochemistry of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatol Res. 41:64–70. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morine Y, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, et al:
Role of thymidylate synthase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
mRNA in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Today. 42:135–140.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wilson TR, Johnston PG and Longley DB:
Anti-apoptotic mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 9:307–319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang L, Wong YP, Cai YJ, Lung I, Leung CS
and Burd A: Low-dose 5-fluorouracil induces cell cycle G2 arrest
and apoptosis in keloid fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol. 163:1181–1185.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okamoto S, Sakai M, Uchida J and Saito H:
5-Fluorouracil induces apoptotic cell death with G2 phase arrest in
human breast cancer grafted in nude mice. Anticancer Res.
16:2699–2704. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Naus PJ, Henson R, Bleeker G, Wehbe H,
Meng F and Patel T: Tannic acid synergizes the cytotoxicity of
chemotherapeutic drugs in human cholangiocarcinoma by modulating
drug efflux pathways. J Hepatol. 46:222–229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ikeguchi M, Hirooka Y, Makino M and
Kaibara N: Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity of cancerous
and non-cancerous tissues in liver and large intestine. Oncol Rep.
8:621–625. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Salonga D, Danenberg KD, Johnson M, et al:
Colorectal tumors responding to 5-fluorouracil have low gene
expression levels of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase, thymidylate
synthase, and thymidine phosphorylase. Clin Cancer Res.
6:1322–1327. 2000.
|
|
26
|
Namwat N, Amimanan P, Loilome W, et al:
Characterization of 5-fluorouracil-resistant cholangiocarcinoma
cell lines. Chemotherapy. 54:343–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
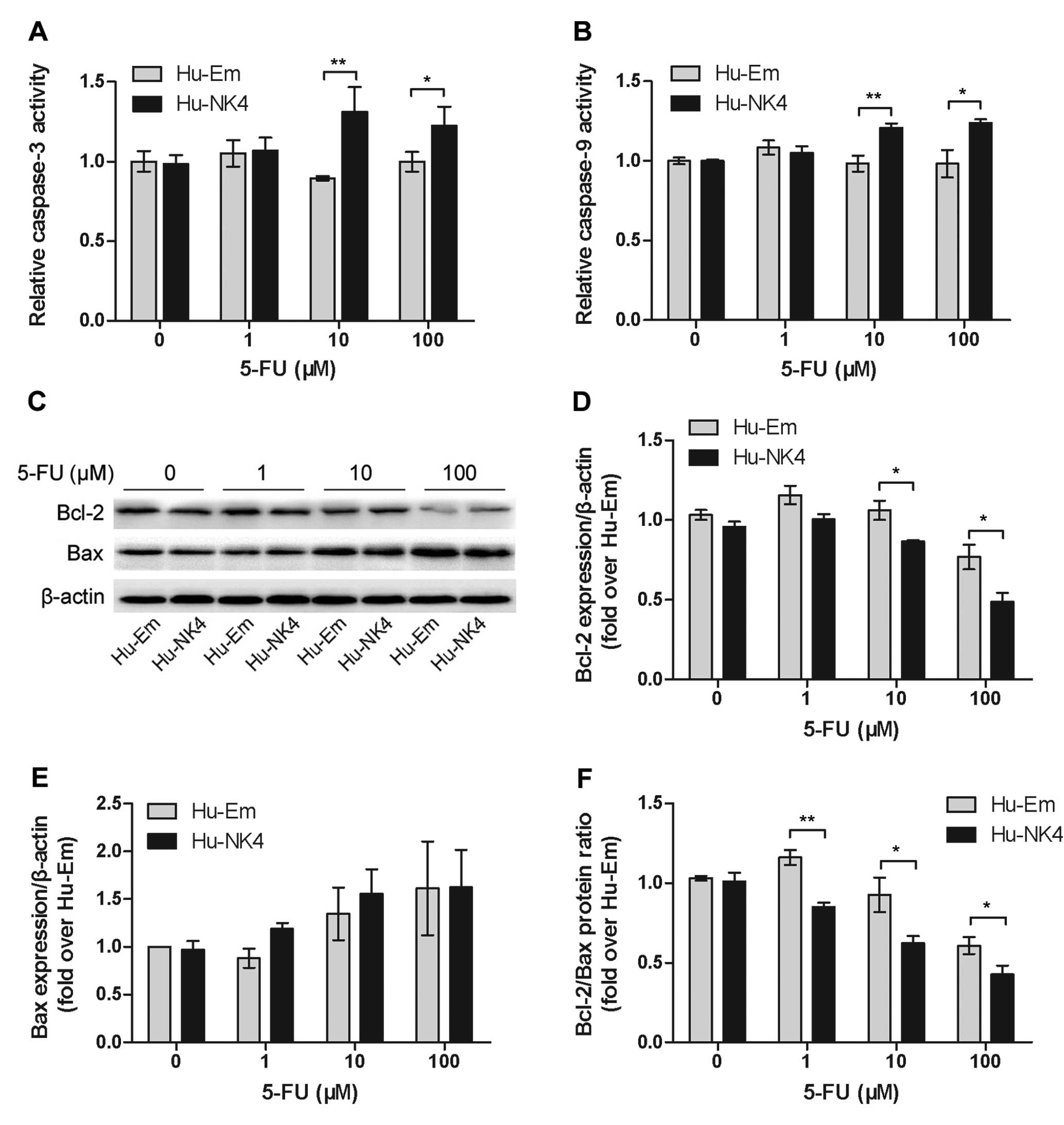
Danial NN: BCL-2 family proteins: critical
checkpoints of apoptotic cell death. Clin Cancer Res. 13:7254–7263.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Yu J, Park BH, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: Role of BAX in the apoptotic response to anticancer
agents. Science. 290:989–992. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heiser D, Labi V, Erlacher M and Villunger
A: The Bcl-2 protein family and its role in the development of
neoplastic disease. Exp Gerontol. 39:1125–1135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yin XM, Oltvai ZN and Korsmeyer SJ: BH1
and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis
and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature. 369:321–323. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zou H, Li Y, Liu X and Wang X: An APAF-1.
cytochrome c multimeric complex is a functional apoptosome that
activates procaspase-9. J Biol Chem. 274:11549–11556. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nachmias B, Ashhab Y and Ben-Yehuda D: The
inhibitor of apoptosis protein family (IAPs): an emerging
therapeutic target in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 14:231–243. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|