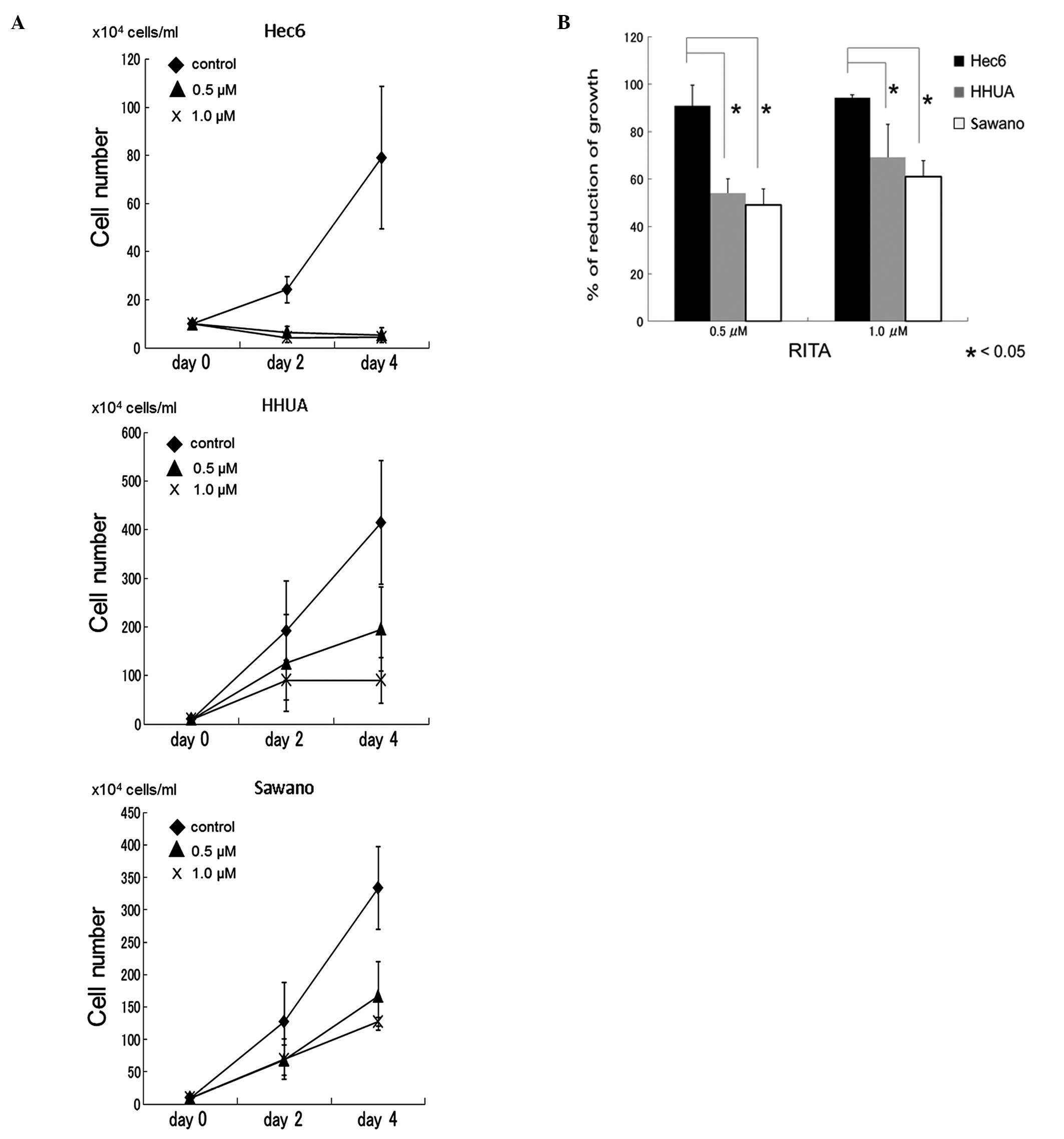
|
1
|
Bansal N, Yendluri V and Wenham RM: The
molecular biology of endometrial cancers and the implications for
pathogenesis, classification, and targeted therapies. Cancer
Control. 16:8–13. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Prat J, Gallardo A, Cuatrecasas M and
Catasus L: Endometrial carcinoma: pathology and genetics.
Pathology. 39:72–87. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Deb SP: Cell cycle regulatory functions of
the human oncoprotein MDM2. Mol Cancer Res. 1:1009–1016.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M: Mdm2
promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 387:296–299. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Honda R, Tanaka H and Yasuda H:
Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53.
FEBS Lett. 420:25–27. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH:
Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature. 387:299–303. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levav-Cohen Y, Haupt S and Haupt Y: Mdm2
in growth signaling and cancer. Growth Factors. 23:183–192. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gudas JM, Nguyen H, Klein RC, Katayose D,
Seth P and Cowan KH: Differential expression of multiple MDM2
messenger RNAs and proteins in normal and tumorigenic breast
epithelial cells. Clin Cancer Res. 1:71–80. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sheikh MS, Shao ZM, Hussain A and Fontana
JA: The p53-binding protein MDM2 gene is differentially expressed
in human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 53:3226–3228.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ries S, Biederer C, Woods D, et al:
Opposing effects of Ras on p53: transcriptional activation of mdm2
and induction of p19ARF. Cell. 103:321–330. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kato K, Ueoka Y, Hachiya T, Nishida J and
Wake N: Contribution of enhanced transcriptional activation by ER
to [12Val] K-Ras mediated NIH3T3 cell transformation. Oncogene.
15:3037–3046. 1997.
|
|
12
|
Kato K, Horiuchi S, Takahashi A, et al:
Contribution of estrogen receptor α to oncogenic K-Ras-mediated
NIH3T3 cell transformation and its implication for escape from
senescence by modulating the p53 pathway. J Biol Chem.
277:11217–11224. 2002.
|
|
13
|
Suga S, Kato K, Ohgami T, et al: An
inhibitory effect on cell proliferation by blockage of the
MAPK/estrogen receptor/MDM2 signal pathway in gynecologic cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 105:341–350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, et al: A single
nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the p53
tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans.
Cell. 119:591–602. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bond GL, Hirshfield KM, Kirchhoff T, et
al: MDM2 SNP309 accelerates tumor formation in a gender-specific
and hormone-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 66:5104–5110. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Campbell IG, Eccles DM and Choong DY: No
association of the MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism with risk of breast or
ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 240:195–197. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Petenkaya A, Bozkurt B, Akilli-Ozturk O,
Kaya HS, Gur-Dedeoglu B and Yulug IG: Lack of association between
the MDM2-SNP309 polymorphism and breast cancer risk. Anticancer
Res. 26:4975–4977. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krekac D, Brozkova K, Knoflickova D, et
al: MDM2SNP309 does not associate with elevated MDM2 protein
expression or breast cancer risk. Oncology. 74:84–87. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, et
al: WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell.
75:817–825. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roh J, Kim M, Kim J, et al: Polymorphisms
in codon 31 of p21 and cervical cancer susceptibility in Korean
women. Cancer Lett. 165:59–62. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roh JW, Kim JW, Park NH, et al: p53 and
p21 genetic polymorphisms and susceptibility to endometrial cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 93:499–505. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hachiya T, Kuriaki Y, Ueoka Y, Nishida J,
Kato K and Wake N: WAF1 genotype and endometrial cancer
susceptibility. Gynecol Oncol. 72:187–192. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Walsh CS, Miller CW, Karlan BY and
Koeffler HP: Association between a functional single nucleotide
polymorphism in the MDM2 gene and sporadic endometrial cancer risk.
Gynecol Oncol. 104:660–664. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Terry K, McGrath M, Lee IM, Buring J and
De Vivo I: MDM2 SNP309 is associated with endometrial cancer risk.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:983–986. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ueda M, Yamamoto M, Nunobiki O, et al:
Murine double-minute 2 homolog single nucleotide polymorphism 309
and the risk of gynecologic cancer. Hum Cell. 22:49–54. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ueda M, Terai Y, Kanda K, et al: Germline
polymorphism of p53 codon 72 in gynecological cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 100:173–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yaich L, Dupont WD, Cavener DR and Parl
FF: Analysis of the Pvu II restriction fragment-length
polymorphism and exon structure of the estrogen receptor gene in
breast cancer and peripheral blood. Cancer Res. 52:77–83. 1992.
|
|
29
|
Mizunuma H, Hosoi T, Okano H, et al:
Estrogen receptor gene polymorphism and bone mineral density at the
lumbar spine of pre- and postmenopausal women. Bone. 21:379–383.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun Y, Hildesheim A, Li H, et al: No point
mutation but a codon 31ser→arg polymorphism of the WAF-1/CIP-1/p21
tumor suppressor gene in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC): the
polymorphism distinguishes Caucasians from Chinese. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 4:261–267. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shih CM, Lin PT, Wang HC, Huang WC and
Wang YC: Lack of evidence of association of p21WAF1/CIP1
polymorphism with lung cancer susceptibility and prognosis in
Taiwan. Jpn J Cancer Res. 91:9–15. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Issaeva N, Bozko P, Enge M, et al: Small
molecule RITA binds to p53, blocks p53-HDM-2 interaction and
activates p53 function in tumors. Nat Med. 10:1321–1328. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ashton KA, Proietto A, Otton G, et al:
Polymorphisms in TP53 and MDM2 combined are associated with high
grade endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 113:109–114. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Niwa Y, Hirose K, Matsuo K, et al:
Association of p73 G4C14-to-A4T14 polymorphism at exon 2 and p53
Arg72Pro polymorphism with the risk of endometrial cancer in
Japanese subjects. Cancer Lett. 219:183–190. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nunobiki O, Ueda M, Yamamoto M, et al:
Polymorphisms of p53 codon 72 and MDM2 promoter 309 and the risk of
endometrial cancer. Hum Cell. 22:101–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Enomoto T, Fujita M, Inoue M, et al:
Alterations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene and its association
with activation of the c-K-ras-2 protooncogene in premalignant and
malignant lesions of the human uterine endometrium. Cancer Res.
53:1883–1888. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wilkening S, Bermejo JL and Hemminki K:
MDM2 SNP309 and cancer risk: a combined analysis. Carcinogenesis.
28:2262–2267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu Z, Jin G, Wang L, Chen F, Wang X and
Shen H: MDM2 promoter polymorphism SNP309 contributes to tumor
susceptibility: evidence from 21 case-control studies. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:2717–2723. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wan Y, Wu W, Yin Z, Guan P and Zhou B:
MDM2 SNP309, gene-gene interaction, and tumor susceptibility: an
updated meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 11:2082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wo X, Han D, Sun H, et al: MDM2 SNP309
contributes to tumor susceptibility: a meta-analysis. J Genet
Genomics. 38:341–350. 2011.
|
|
41
|
Li Y, Zhao H, Sun L, Huang L, Yang Q and
Kong B: MDM2 SNP309 is associated with endometrial cancer
susceptibility: a meta-analysis. Hum Cell. 24:57–64. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Arva NC, Gopen TR, Talbott KE, et al: A
chromatin-associated and transcriptionally inactive p53-Mdm2
complex occurs in mdm2 SNP309 homozygous cells. J Biol Chem.
280:26776–26787. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|