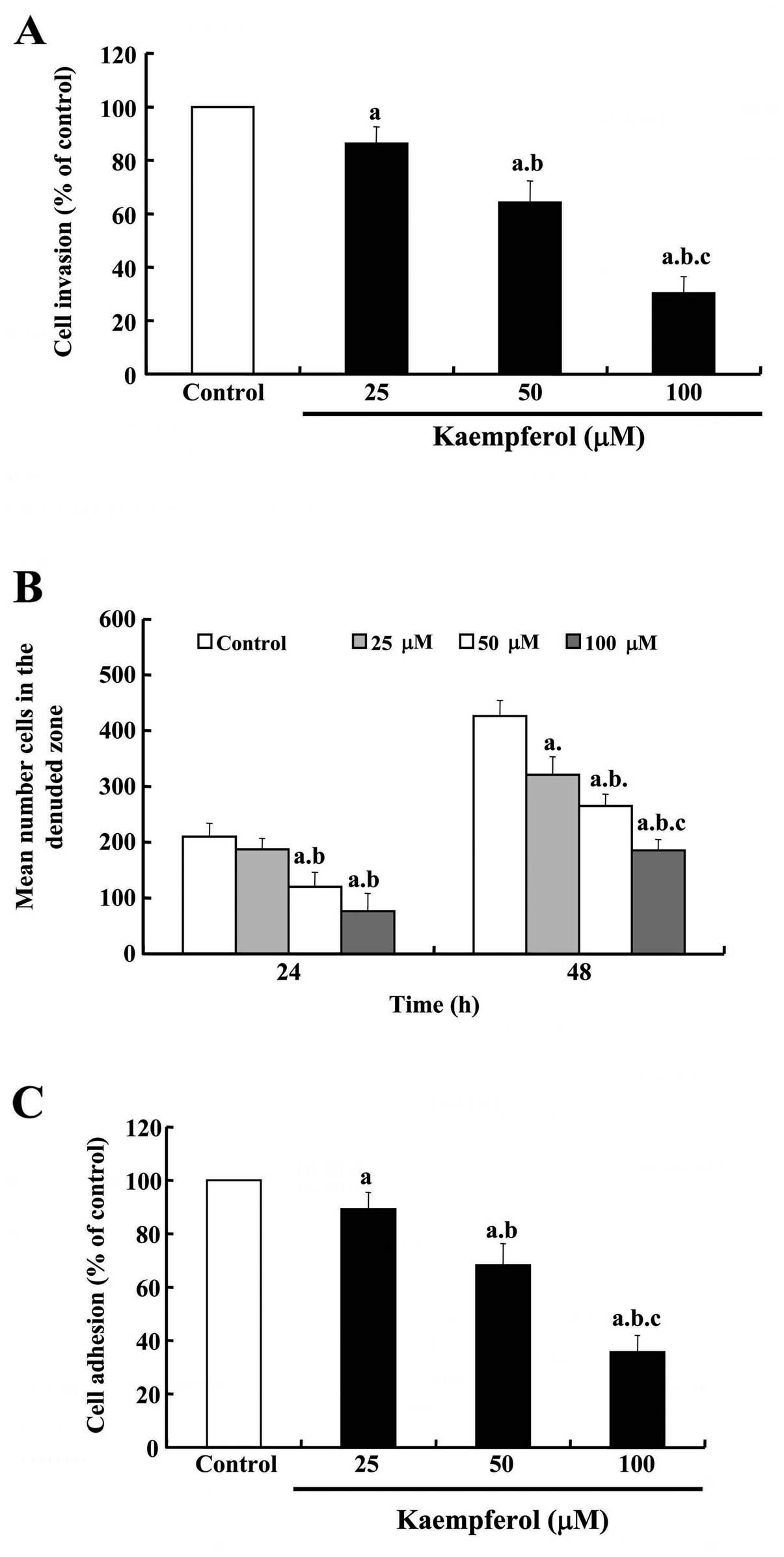
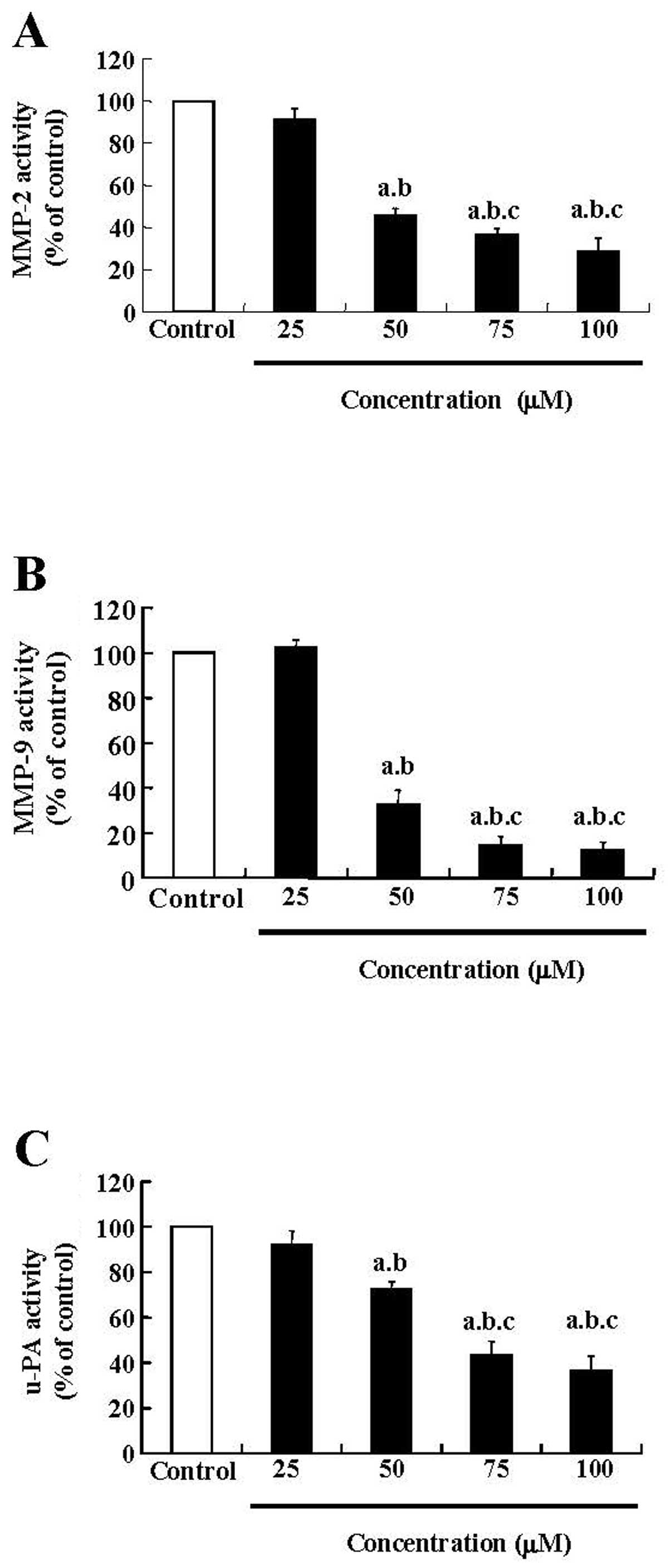
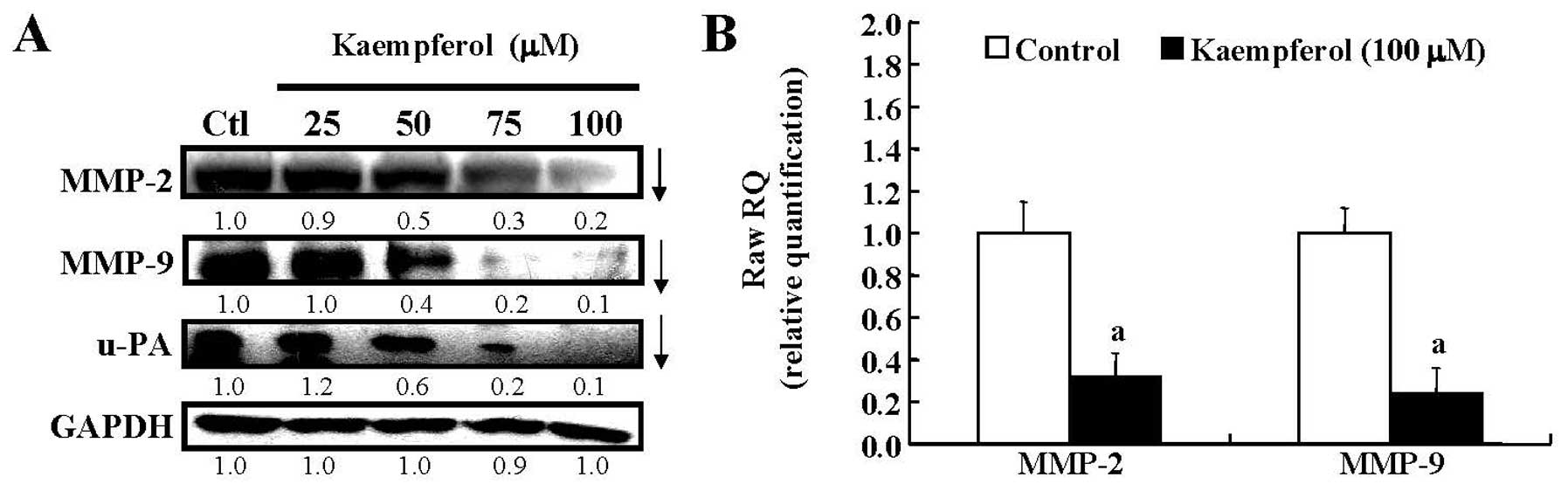
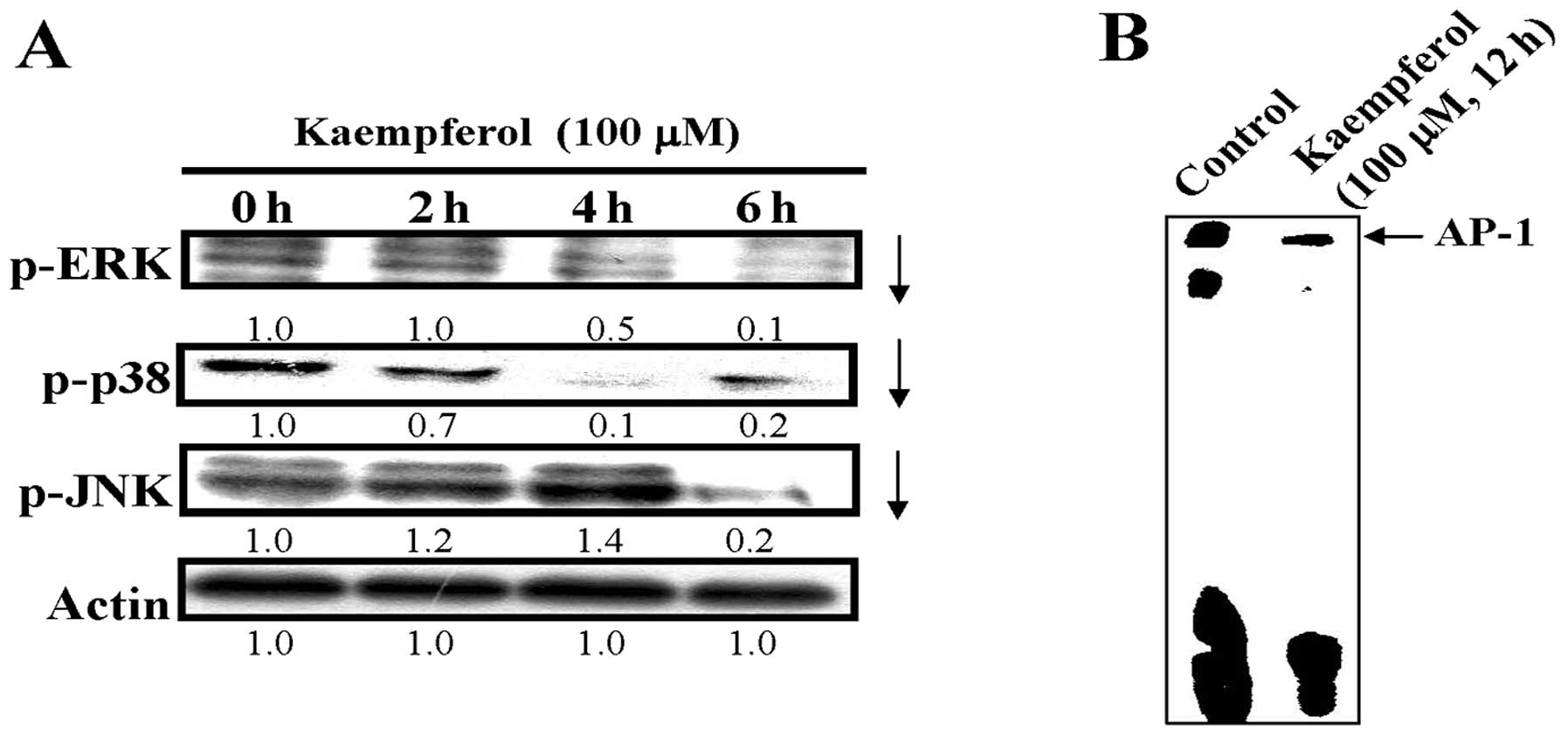
|
1
|
Kansara M and Thomas DM: Molecular
pathogenesis of osteosarcoma. DNA Cell Biol. 26:1–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Whelan JS: Osteosarcoma. Eur J Cancer.
33:1611–1618. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Krishnan K, Khanna C and Helman LJ: The
biology of metastases in pediatric sarcomas. Cancer J. 11:306–313.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hayden JB and Hoang BH: Osteosarcoma:
basic science and clinical implications. Orthop Clin North Am.
37:1–7. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo M, et al:
Osteosarcoma: a randomized, prospective trial of the addition of
ifosfamide and/or muramyl tripeptide to cisplatin, doxorubicin, and
high-dose methotrexate. J Clin Oncol. 23:2004–2011. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meyers PA: Muramyl tripeptide
(mifamurtide) for the treatment of osteosarcoma. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 9:1035–1049. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hodek P, Trefil P and Stiborová M:
Flavonoids-potent and versatile biologically active compounds
interacting with cytochromes P450. Chem Biol Interact. 139:1–21.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pietta PG: Flavonoids as antioxidants. J
Nat Prod. 63:1035–1042. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Weng CJ and Yen GC: Flavonoids, a
ubiquitous dietary phenolic subclass, exert extensive in vitro
anti-invasive and in vivo anti-metastatic activities. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 31:323–351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Middleton E Jr, Kandaswami C and
Theoharides TC: The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells:
implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol
Rev. 52:673–751. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo Q, Zhao L, You Q, et al:
Anti-hepatitis B virus activity of wogonin in vitro and in vivo.
Antiviral Res. 74:16–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cárdenas M, Marder M, Blank VC and Roguin
LP: Antitumor activity of some natural flavonoids and synthetic
derivatives on various human and murine cancer cell lines. Bioorg
Med Chem. 14:2966–2971. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burda S and Oleszek W: Antioxidant and
antiradical activities of flavonoids. J Agric Food Chem.
49:2774–2779. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Crespo I, García-Mediavilla MV, Gutiérrez
B, Sánchez-Campos S, Tuñón MJ and González-Gallego J: A comparison
of the effects of kaempferol and quercetin on cytokine-induced
pro-inflammatory status of cultured human endothelial cells. Br J
Nutr. 100:968–976. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: Therapeutic
potential of inhibition of the NF-κB pathway in the treatment of
inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 107:135–142. 2001.
|
|
17
|
Cushnie TP and Lamb AJ: Antimicrobial
activity of flavonoids. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 26:343–356. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu SF, Shun CT, Chen TM and Chen YH:
3-O-β-D-glucosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucosyl-kaempferol isolated from
Sauropus androgenus reduces body weight gain in Wistar rats.
Biol Pharm Bull. 29:2510–2513. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Yao P, Nussler A, Liu L, et al: Quercetin
protects human hepatocytes from ethanol-derived oxidative stress by
inducing heme oxygenase-1 via the MAPK/Nrf2 pathways. J Hepatol.
47:253–261. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tijburg LB, Mattern T, Folts JD,
Weisgerber UM and Katan MB: Tea flavonoids and cardiovascular
disease: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 37:771–785. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park JS, Rho HS, Kim DH and Chang IS:
Enzymatic preparation of kaempferol from green tea seed and its
antioxidant activity. J Agric Food Chem. 54:2951–2956. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stewart AJ, Bozonnet S, Mullen W, Jenkins
GI, Lean ME and Crozier A: Occurrence of flavonols in tomatoes and
tomato-based products. J Agric Food Chem. 48:2663–2669. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jaganathan SK and Mandal M:
Antiproliferative effects of honey and of its polyphenols: a
review. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2009:8306162009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Seeram NP, Lee R, Feng L and
Heber D: Isolation and identification of strawberry phenolics with
antioxidant and human cancer cell antiproliferative properties. J
Agric Food Chem. 56:670–675. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kang JW, Kim JH, Song K, Kim SH, Yoon JH
and Kim KS: Kaempferol and quercetin, components of Ginkgo
biloba extract (EGb 761), induce caspase-3-dependent apoptosis
in oral cavity cancer cells. Phytother Res. 24(Suppl 1): S77–S82.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bajpai M, Pande A, Tewari SK and Prakash
D: Phenolic contents and antioxidant activity of some food and
medicinal plants. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 56:287–291. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Calderón-Montaño JM, Burgos-Morón E,
Pérez-Guerrero C and López-Lázaro M: A review on the dietary
flavonoid kaempferol. Mini Rev Med Chem. 11:298–344.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leung HW, Lin CJ, Hour MJ, Yang WH, Wang
MY and Lee HZ: Kaempferol induces apoptosis in human lung non-small
carcinoma cells accompanied by an induction of antioxidant enzymes.
Food Chem Toxicol. 45:2005–2013. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Q, Zhao XH and Wang ZJ: Flavones and
flavonols exert cytotoxic effects on a human oesophageal
adenocarcinoma cell line (OE33) by causing G2/M arrest and inducing
apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:2042–2053. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marfe G, Tafani M, Indelicato M, et al:
Kaempferol induces apoptosis in two different cell lines via Akt
inactivation, Bax and SIRT3 activation, and mitochondrial
dysfunction. J Cell Biochem. 106:643–650. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim KS, Rhee KH, Yoon JH, Lee JG, Lee JH
and Yoo JB: Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) induces
apoptosis by the activation of caspase-3 in oral cavity cancer
cells. Oral Oncol. 41:383–389. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
De Leo M, Braca A, Sanogo R, Cardile V,
DeTommasi N and Russo A: Antiproliferative activity of
Pteleopsis suberosa leaf extract and its flavonoid
components in human prostate carcinoma cells. Planta Med.
72:604–610. 2006.
|
|
33
|
Mutoh M, Takahashi M, Fukuda K, et al:
Suppression of cyclooxygenase-2 promoter-dependent transcriptional
activity in colon cancer cells by chemopreventive agents with a
resorcin-type structure. Carcinogenesis. 21:959–963. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, et al:
Kaempferol induced apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondria-dependent pathway in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sliva D: Suppression of cancer
invasiveness by dietary compounds. Mini Rev Med Chem. 8:677–688.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Phromnoi K, Yodkeeree S, Anuchapreeda S
and Limtrakul P: Inhibition of MMP-3 activity and invasion of the
MDA-MB-231 human invasive breast carcinoma cell line by
bioflavonoids. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1169–1176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Labbé D, Provençal M, Lamy S, Boivin D,
Gingras D and Béliveau R: The flavonols quercetin, kaempferol, and
myricetin inhibit hepatocyte growth factor-induced medulloblastoma
cell migration. J Nutr. 139:646–652. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin CW, Shen SC, Chien CC, Yang LY, Shia
LT and Chen YC: 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced
invasion/migration of glioblastoma cells through activating
PKCα/ERK/NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression. J Cell Physiol.
225:472–481. 2010.
|
|
39
|
Chiu YJ, Hour MJ, Lu CC, et al: Novel
quinazoline HMJ-30 induces U-2 OS human osteogenic sarcoma cell
apoptosis through induction of oxidative stress and up-regulation
of ATM/p53 signaling pathway. J Orthop Res. 29:1448–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chen KT, Hour MJ, Tsai SC, et al: The
novel synthesized
6-fluoro-(3-fluorophenyl)-4-(3-methoxyanilino)quinazoline (LJJ-10)
compound exhibits anti-metastatic effects in human osteosarcoma U-2
OS cells through targeting insulin-like growth factor-I receptor.
Int J Oncol. 39:611–619. 2011.
|
|
41
|
Hour MJ, Tsai SC, Wu HC, et al: Antitumor
effects of the novel quinazolinone MJ-33: Inhibition of metastasis
through the MAPK, AKT, NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways in DU145
human prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:1513–1519.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lai KC, Huang AC, Hsu SC, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate (BITC) inhibits migration and invasion of human
colon cancer HT29 cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9
and urokinase plasminogen (uPA) through PKC and MAPK signaling
pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 58:2935–2942. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kao WT, Lin CY, Lee LT, et al:
Investigation of MMP-2 and -9 in a highly invasive A431 tumor cell
sub-line selected from a Boyden chamber assay. Anticancer Res.
28:2109–2120. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mazar AP: The urokinase plasminogen
activator receptor (uPAR) as a target for the diagnosis and therapy
of cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 12:387–400. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kawabata K, Murakami A and Ohigashi H:
Citrus auraptene targets translation of MMP-7 (matrilysin) via
ERK1/2-dependent and mTOR-independent mechanism. FEBS Lett.
580:5288–5294. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mook OR, Frederiks WM and Van Noorden CJ:
The role of gelatinases in colorectal cancer progression and
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1705:69–89. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ried S, Jäger C, Jeffers M, et al:
Activation mechanisms of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator
promoter by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor. J Biol Chem.
274:16377–16386. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lengyel E, Stepp E, Gum R and Boyd D:
Involvement of a mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway
in the regulation of urokinase promoter activity by c-Ha-ras. J
Biol Chem. 270:23007–23012. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Peng PL, Hsieh YS, Wang CJ, Hsu JL and
Chou FP: Inhibitory effect of berberine on the invasion of human
lung cancer cells via decreased productions of
urokinase-plasminogen activator and matrix metalloproteinase-2.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 214:8–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Denys H, De Wever O, Nusgens B, et al:
Invasion and MMP expression profile in desmoid tumours. Br J
Cancer. 90:1443–1449. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Masson V, de la Ballina LR, Munaut C, et
al: Contribution of host MMP-2 and MMP-9 to promote tumor
vascularization and invasion of malignant keratinocytes. FASEB J.
19:234–236. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Duffy MJ, Maguire TM, Hill A, McDermott E
and O’Higgins N: Metalloproteinases: role in breast carcinogenesis,
invasion and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2:252–257. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hanemaaijer R, Verheijen JH, Maguire TM,
et al: Increased gelatinase-A and gelatinase-B activities in
malignant vs. benign breast tumors. Int J Cancer. 86:204–207. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chambers AF and Matrisian LM: Changing
views of the role of matrix metalloproteinases in metastasis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1260–1270. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ferrari C, Benassi S, Ponticelli F, et al:
Role of MMP-9 and its tissue inhibitor TIMP-1 in human
osteosarcoma: findings in 42 patients followed for 1–16 years. Acta
Orthop Scand. 75:487–491. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Bjornland K, Flatmark K, Pettersen S,
Aaasen AO, Fodstad O and Maelandsmo GM: Matrix metalloproteinases
participate in osteosarcoma invasion. J Surg Res. 127:151–156.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Uchibori M, Nishida Y, Nagasaka T, Yamada
Y, Nakanishi K and Ishiguro N: Increased expression of
membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 is correlated with poor
prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 28:33–42.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Foukas AF, Deshmukh NS, Grimer RJ, Mangham
DC, Mangos EG and Taylor S: Stage-IIB osteosarcomas around the
knee. A study of MMP-9 in surviving tumour cells. J Bone Joint Surg
Br. 84:706–711. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sliva D, English D, Lyons D and Lloyd FP
Jr: Protein kinase C induces motility of breast cancers by
upregulating secretion of urokinase-type plasminogen activator
through activation of AP-1 and NF-κB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
290:552–557. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Choong PF and Nadesapillai AP: Urokinase
plasminogen activator system: a multifunctional role in tumor
progression and metastasis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (Suppl 415):
S46–S58. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Choong PF, Fernö M, Akerman M, et al:
Urokinase-plasminogen-activator levels and prognosis in 69
soft-tissue sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 69:268–272. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Dass CR, Nadesapillai AP, Robin D, et al:
Downregulation of uPAR confirms link in growth and metastasis of
osteosarcoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 22:643–652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gondi CS and Rao JS: Therapeutic potential
of siRNA-mediated targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator, its
receptor, and matrix metalloproteinases. Methods Mol Biol.
487:267–281. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen PN, Hsieh YS, Chiou HL and Chu SC:
Silibinin inhibits cell invasion through inactivation of both
PI3K-Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Chem Biol Interact.
156:141–150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Westermarck J and Kähäri VM: Regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. FASEB J.
13:781–792. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Aguirre Ghiso JA, Alonso DF, Farías EF,
Gomez DE and de Kier Joffè EB: Deregulation of the signaling
pathways controlling urokinase production. Its relationship with
the invasive phenotype. Eur J Biochem. 263:295–304. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wu JX, Carpenter PM, Gresens C, et al: The
proto-oncogene c-fos is over-expressed in the majority of human
osteosarcomas. Oncogene. 5:989–1000. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Franchi A, Calzolari A and Zampi G:
Immunohistochemical detection of c-fos and c-jun expression in
osseous and cartilaginous tumours of the skeleton. Virchows Arch.
432:515–519. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gamberi G, Benassi MS, Bohling T, et al:
C-myc and c-fos in human osteosarcoma: prognostic value of mRNA and
protein expression. Oncology. 55:556–563. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Leaner VD, Chick JF, Donninger H, et al:
Inhibition of AP-1 transcriptional activity blocks the migration,
invasion, and experimental metastasis of murine osteosarcoma. Am J
Pathol. 174:265–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tan ML, Choong PF and Dass CR: Direct
anti-metastatic efficacy by the DNA enzyme Dz13 and downregulated
MMP-2, MMP-9 and MT1-MMP in tumours. Cancer Cell Int. 10:92010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|