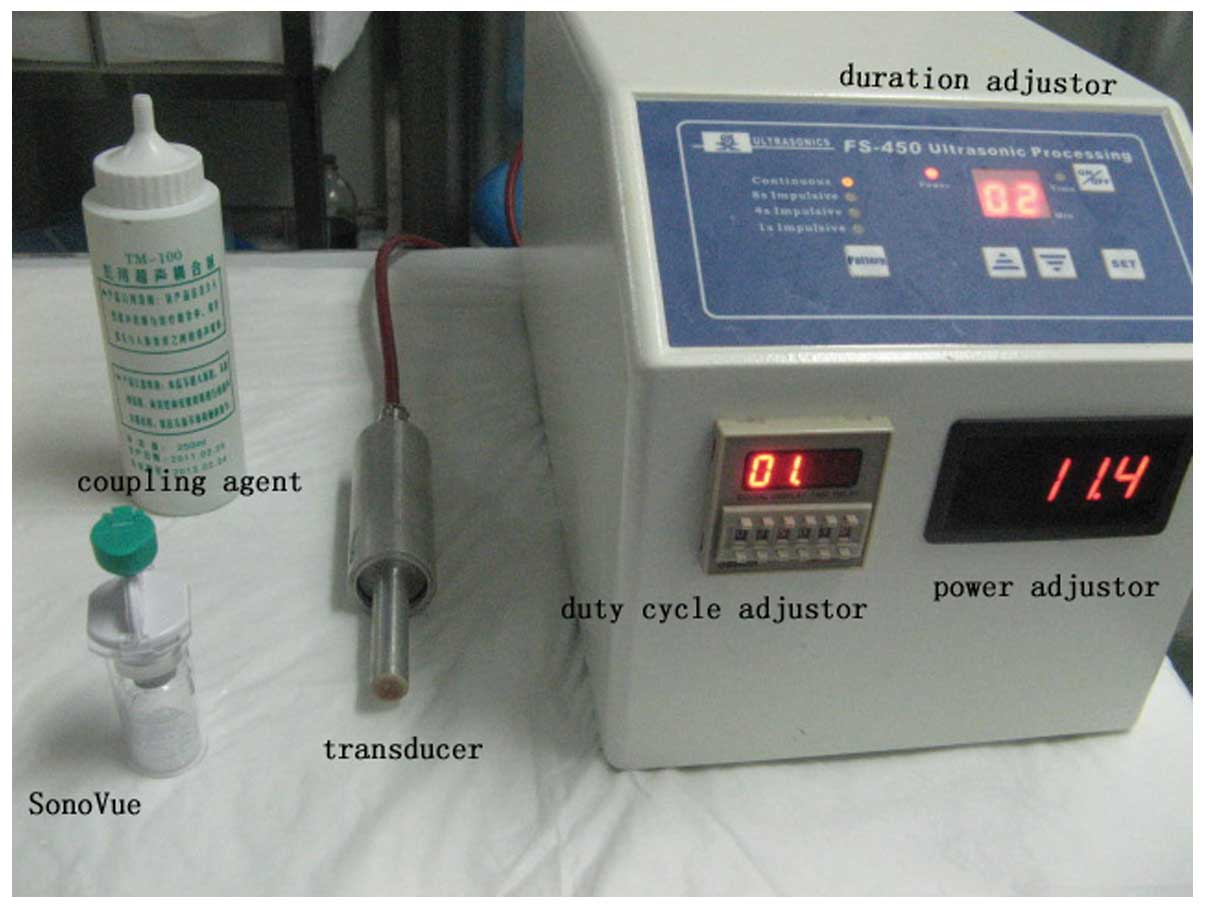
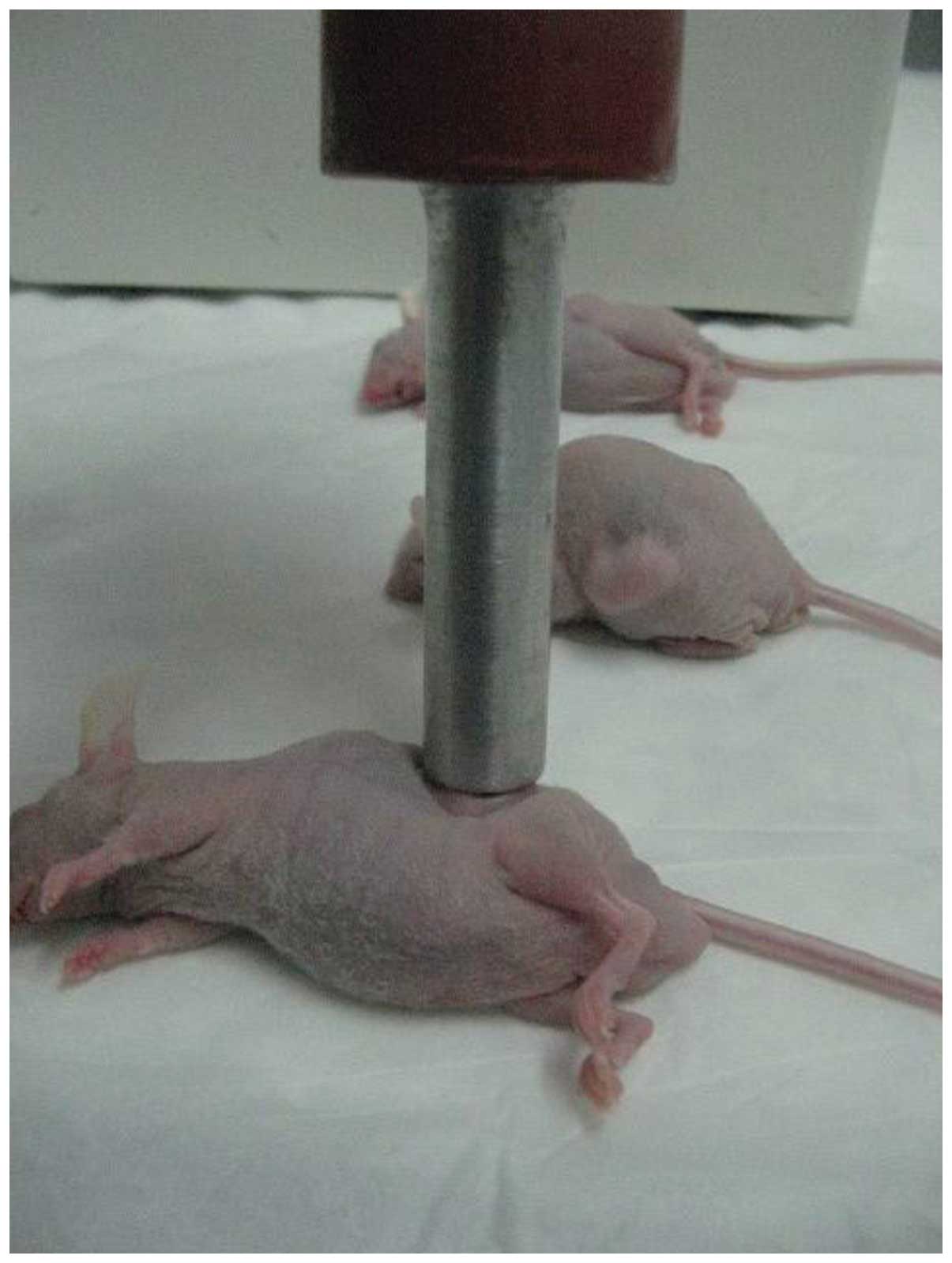
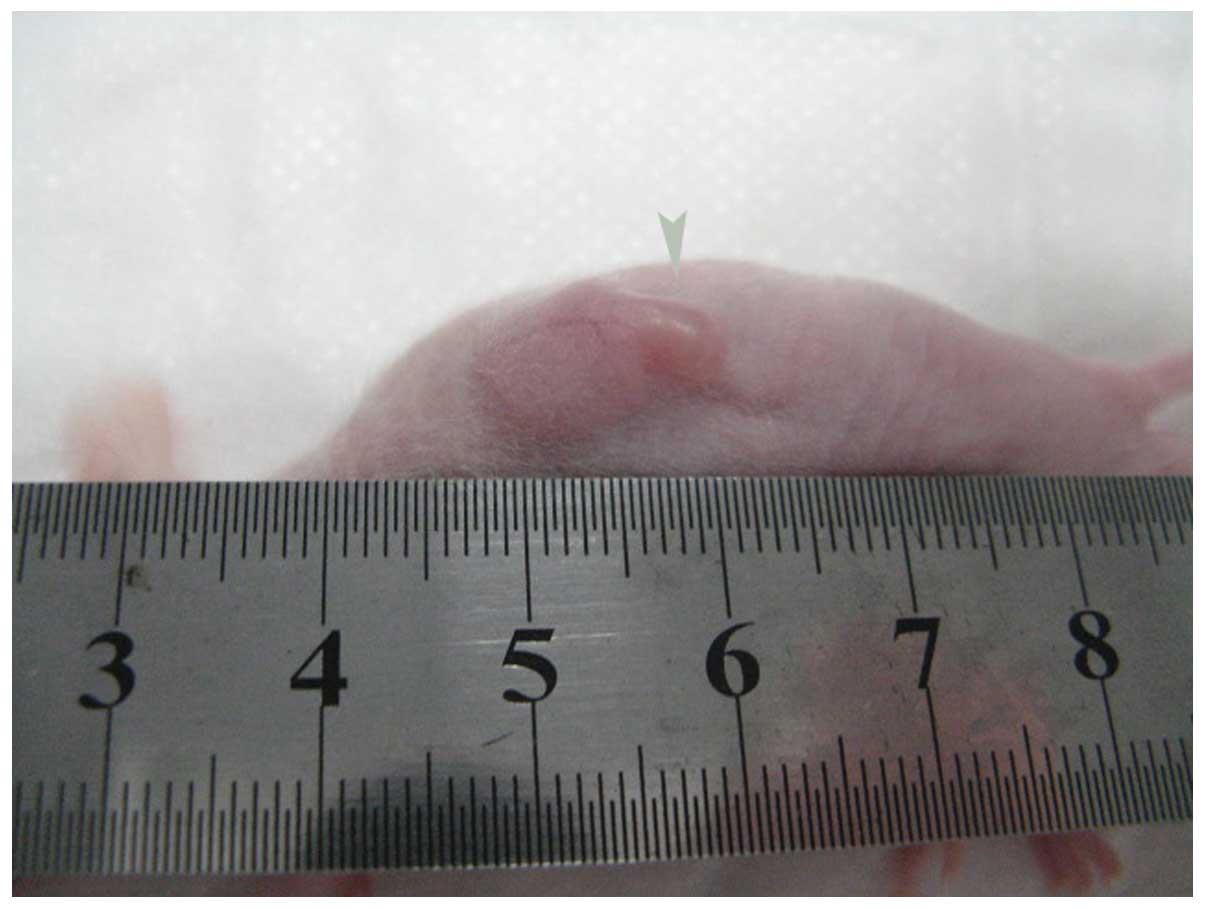
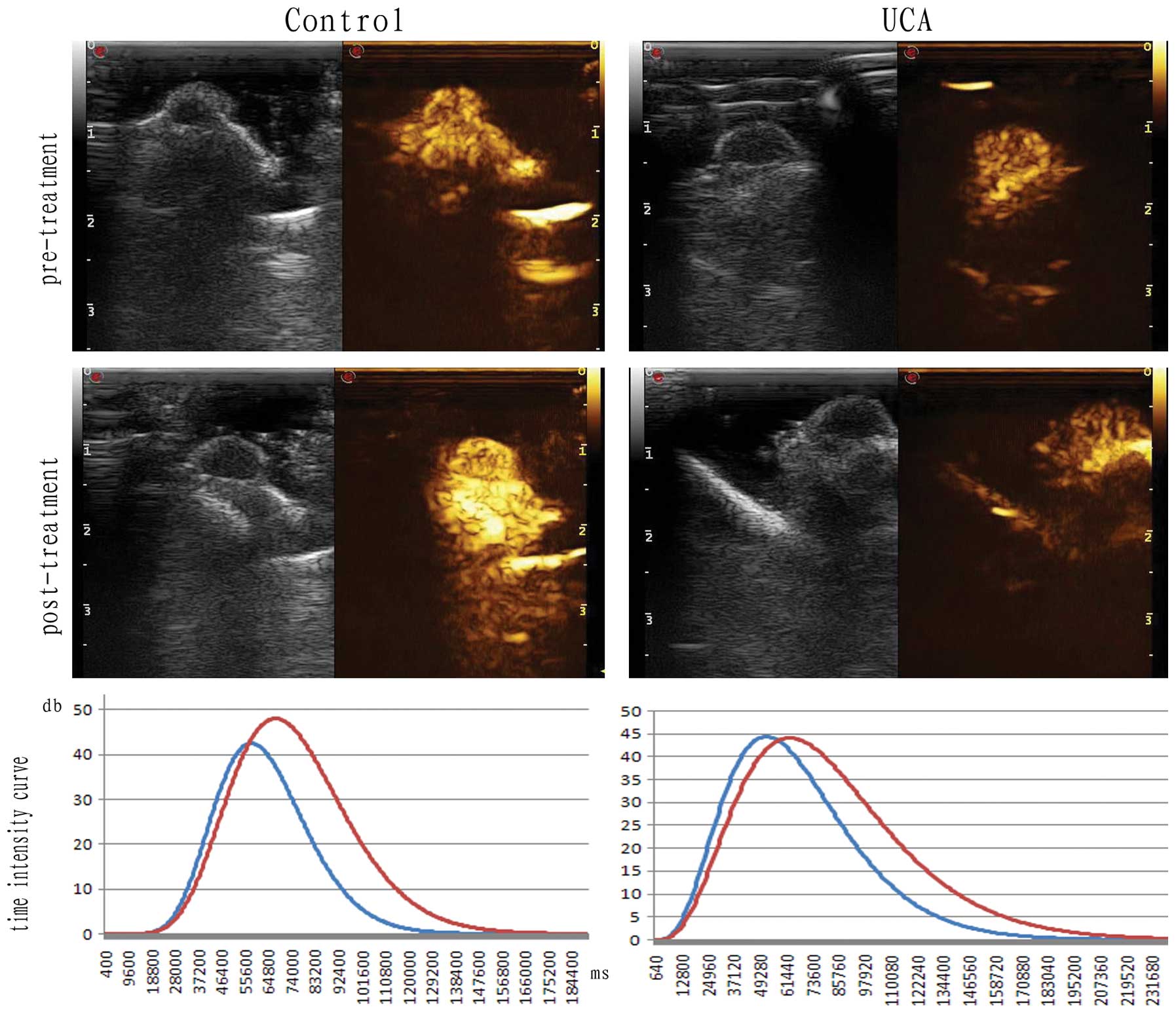
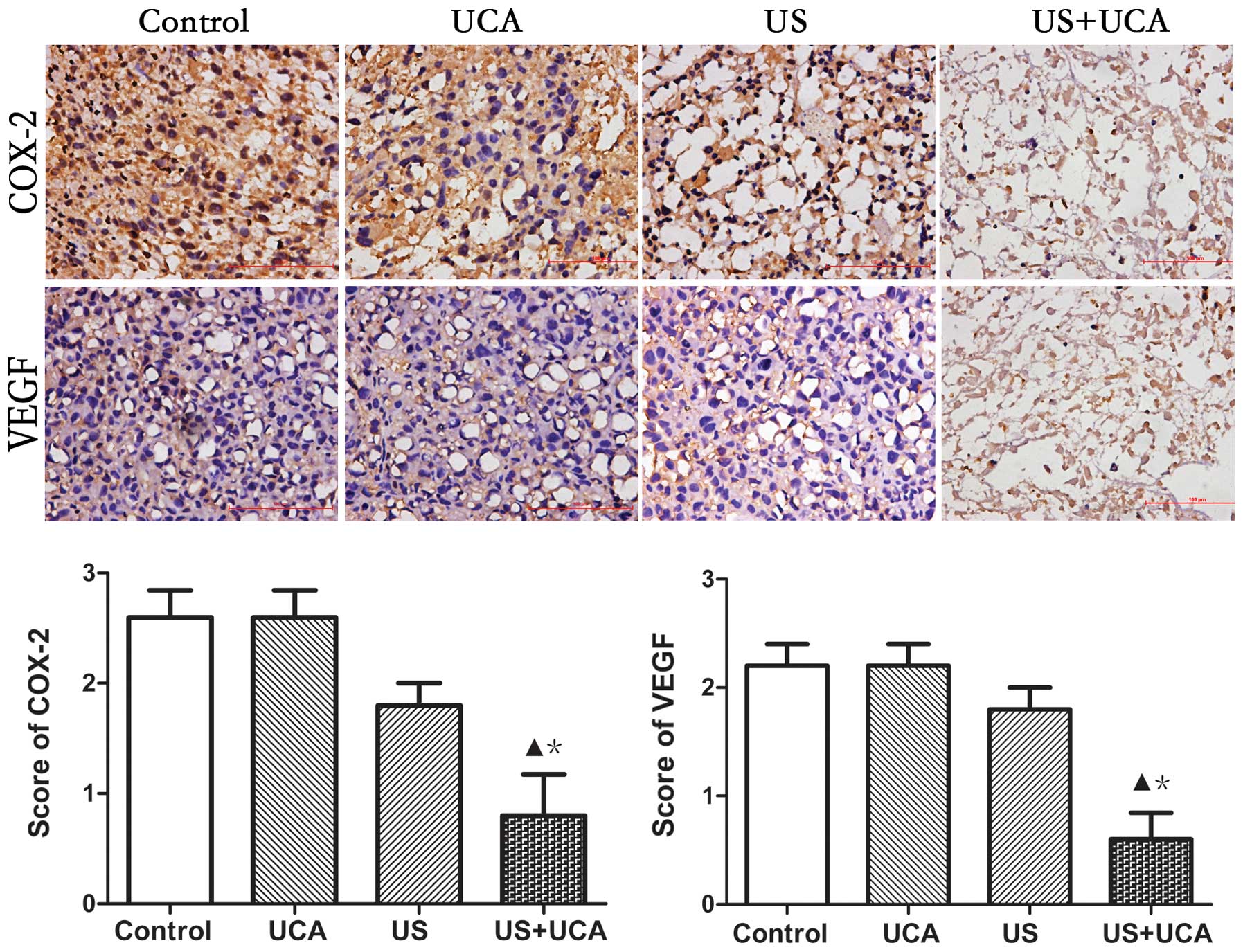
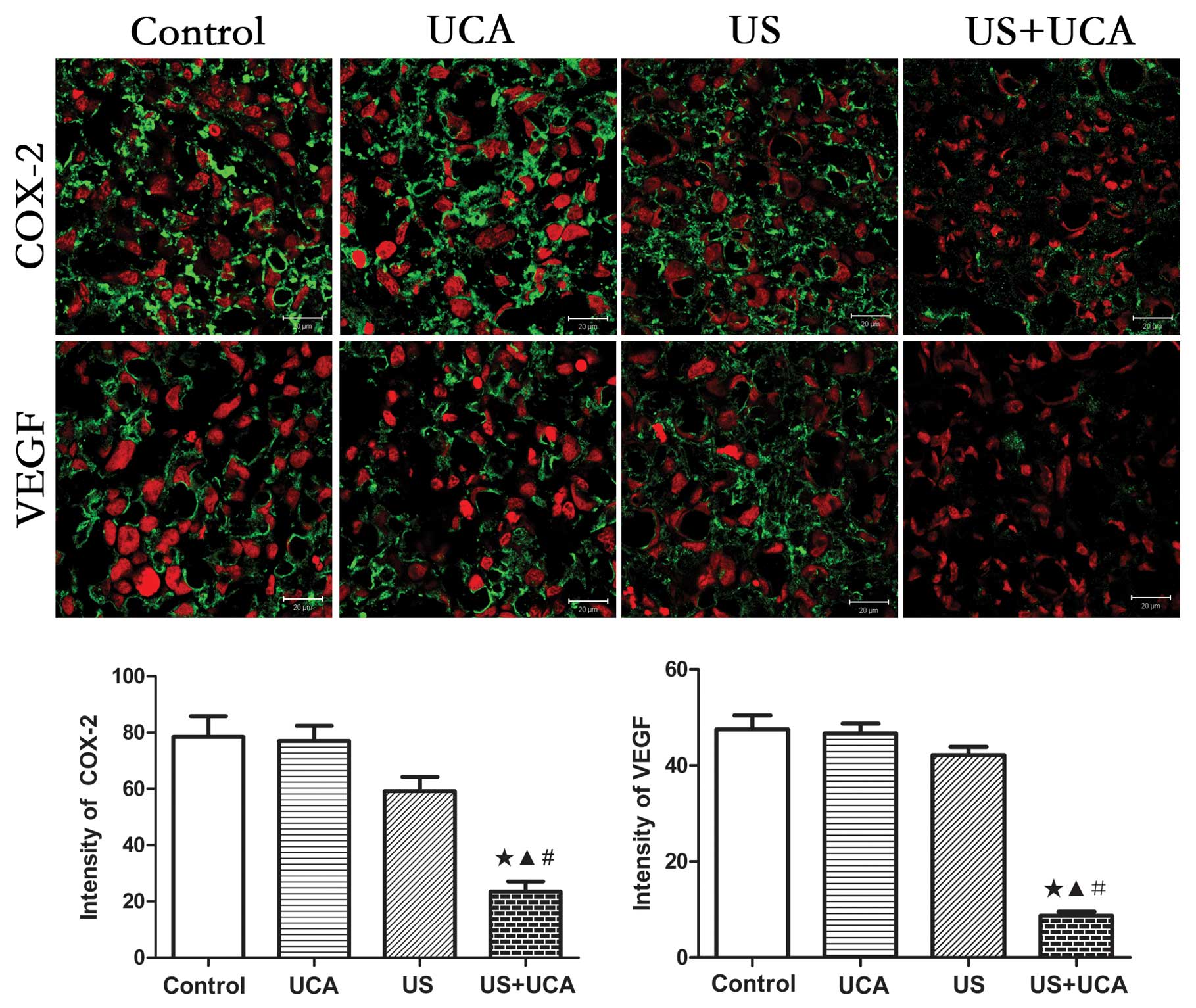
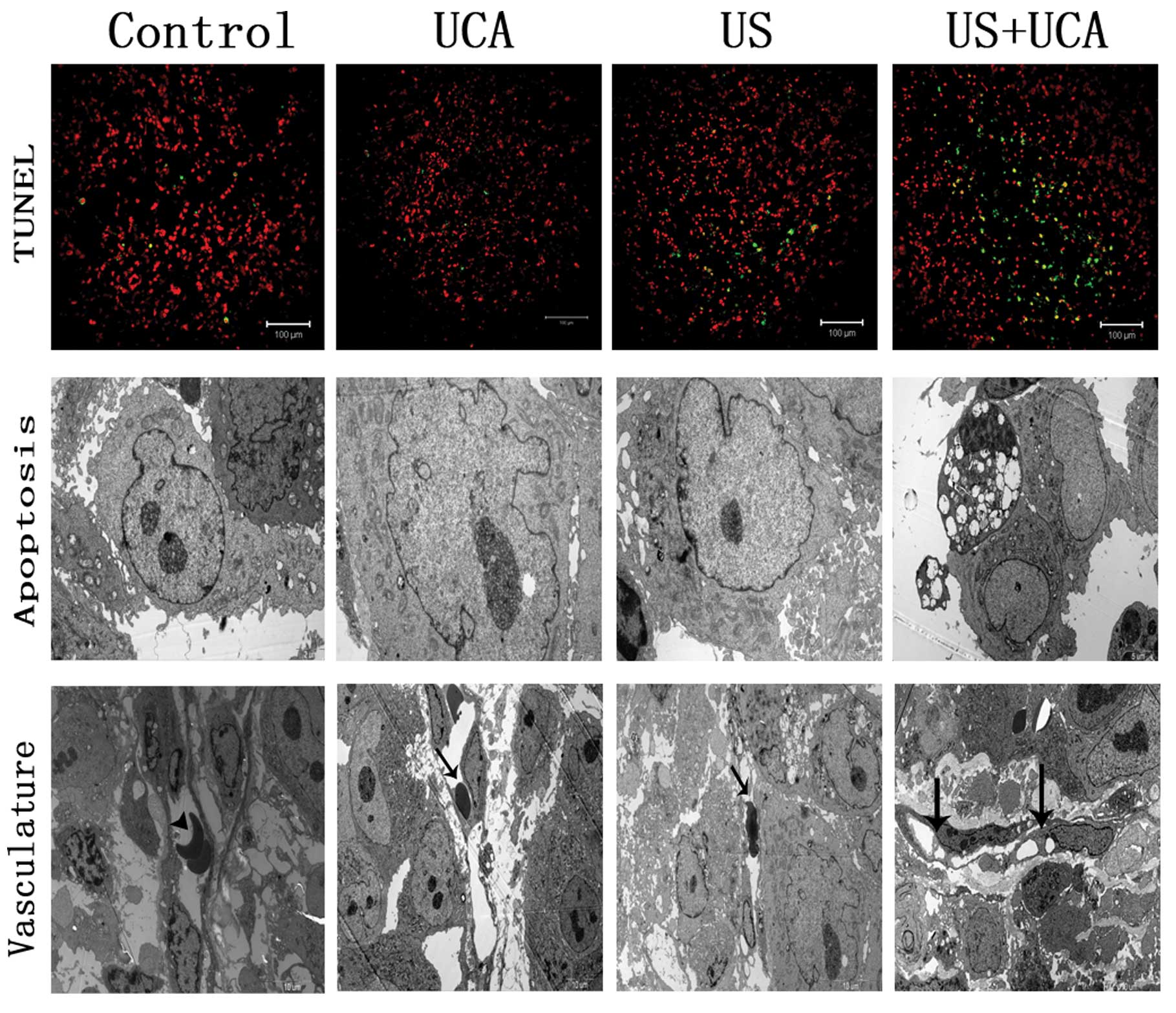
|
1
|
Samant RS and Shevde LA: Recent advances
in anti-angiogenic therapy of cancer. Oncotarget. 2:122–134.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sherwood LM, Parris EE and Folkman J:
Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med.
285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hwang JH, Brayman AA, Reidy MA, Matula TJ,
Kimmey MB and Crum LA: Vascular effects induced by combined 1-MHz
ultrasound and microbubble contrast agent treatments in vivo.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 31:553–564. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Skyba DM, Price RJ, Linka AZ, Skalak TC
and Kaul S: Direct in vivo visualization of intravascular
destruction of microbubbles by ultrasound and its local effects on
tissue. Circulation. 98:290–293. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wood AKW, Ansaloni S, Ziemer LS, Lee WMF,
Feldman MD and Sehgal CM: The antivascular action of physiotherapy
ultrasound on murine tumors. Ultrasound Med Biol. 31:1403–1410.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wood AKW, Bunte RM, Price HE, et al: The
disruption of murine tumor neovasculature by low-intensity
ultrasound-comparison between 1- and 3-MHz sonication frequencies.
Acad Radiol. 15:1133–1141. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wollina U, Heinig B, Naumann G, Scheibe A,
Schmidt WD and Neugebauer R: Effects of low-frequency ultrasound on
microcirculation in venous leg ulcers. Indian J Dermatol.
56:174–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barnett SB, Rott HD, ter Haar GR, Ziskin
MC and Maeda K: The sensitivity of biological tissue to ultrasound.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 23:805–812. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Johnson CA, Sarwate S, Miller RJ and
O’Brien WD Jr: A temporal study of ultrasound contrast
agent-induced changes in capillary density. J Ultrasound Med.
29:1267–1275. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang X and Church CC: A model for the
dynamics of gas bubbles in soft tissue. J Acoust Soc Am.
118:3595–3606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hutcheson J, Schlicher R, Hicks H and
Prausnitz M: Saving cells from ultrasound-induced apoptosis:
quantification of cell death and uptake following sonication and
effects of targeted calcium chelation. Ultrasound Med Biol.
36:1008–1021. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lassau N, Chami L, Benatsou B, Peronneau P
and Roche A: Dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (DCE-US)
with quantification of tumor perfusion: a new diagnostic tool to
evaluate the early effects of antiangiogenic treatment. Eur Radiol.
17:F89–F98. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Paprottka P, Cyran C, Zengel P, et al:
Non-invasive contrast enhanced ultrasound for quantitative
assessment of tumor microcirculation. Contrast mixed mode
examination vs only contrast enhanced ultrasound examination. Clin
Hemorheol Microcirc. 46:149–158. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Yu SM and Kim SJ: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress (ER-stress) by 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) reduces
cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression and N-glycosylation and induces
a loss of COX-2 activity via a Src kinase-dependent pathway in
rabbit articular chondrocytes. Exp Mol Med. 42:777–786. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Forsberg F, Dicker AP, Thakur ML, et al:
Comparing contrast-enhanced ultrasound to immunohistochemical
markers of angiogenesis in a human melanoma xenograft model:
preliminary results. Ultrasound Med Biol. 28:445–451. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kotturi H, Li J, Branham-O’Connor M, et
al: Tumor cells expressing a fusion protein of MULT1 and Fas are
rejected in vivo by apoptosis and NK cell activation. Gene Ther.
15:1302–1310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Feril LB Jr and Kondo T: Biological
effects of low intensity ultrasound: the mechanism involved, and
its implications on therapy and on biosafety of ultrasound. J
Radiat Res. 45:479–489. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miller DL and Dou C: Induction of
apoptosis in sonoporation and ultrasonic gene transfer. Ultrasound
Med Biol. 35:144–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Forsberg F, Ro RJ, Fox TB, et al: Contrast
enhanced maximum intensity projection ultrasound imaging for
assessing angiogenesis in murine glioma and breast tumor models: a
comparative study. Ultrasonics. 51:382–389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Lv F, Fei X, et al: Study on the
characteristics of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and its utility in
assessing the microvessel density in ovarian tumors or tumor-like
lesions. Int J Biol Sci. 7:600–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang LY, et al: BAY
43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets
the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in
tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64:7099–7109. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lavisse S, Lejeune P, Rouffiac V, et al:
Early quantitative evaluation of a tumor vasculature disruptive
agent AVE8062 using dynamic contrast-enhanced ultrasonography.
Invest Radiol. 43:100–111. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chan TA: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs, apoptosis, and colon-cancer chemoprevention. Lancet Oncol.
3:166–174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu J, Min W, Conchello JA, Xie XS and
Lichtman JW: Super-resolution laser scanning microscopy through
spatiotemporal modulation. Nano Lett. 9:3883–3889. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ashush H, Rozenszajn LA, Blass M, et al:
Apoptosis induction of human myeloid leukemic cells by ultrasound
exposure. Cancer Res. 60:1014–1020. 2000.
|
|
26
|
Honda H, Zhao QL and Kondo T: Effects of
dissolved gases and an echo contrast agent on apoptosis induced by
ultrasound and its mechanism via the mitochondria-caspase pathway.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 28:673–682. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feril LB, Kondo T, Zhao QL, et al:
Enhancement of ultrasound-induced apoptosis and cell lysis by
echo-contrast agents. Ultrasound Med Biol. 29:331–337. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen H, Brayman AA, Bailey MR and Matula
TJ: Blood vessel rupture by cavitation. Urol Res. 38:321–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tian ZM, Wan MX, Lu MZ, Wang XD and Wang
L: The alteration of protein profile of Walker 256 carinosarcoma
cells during the apoptotic process induced by ultrasound.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 31:121–128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|