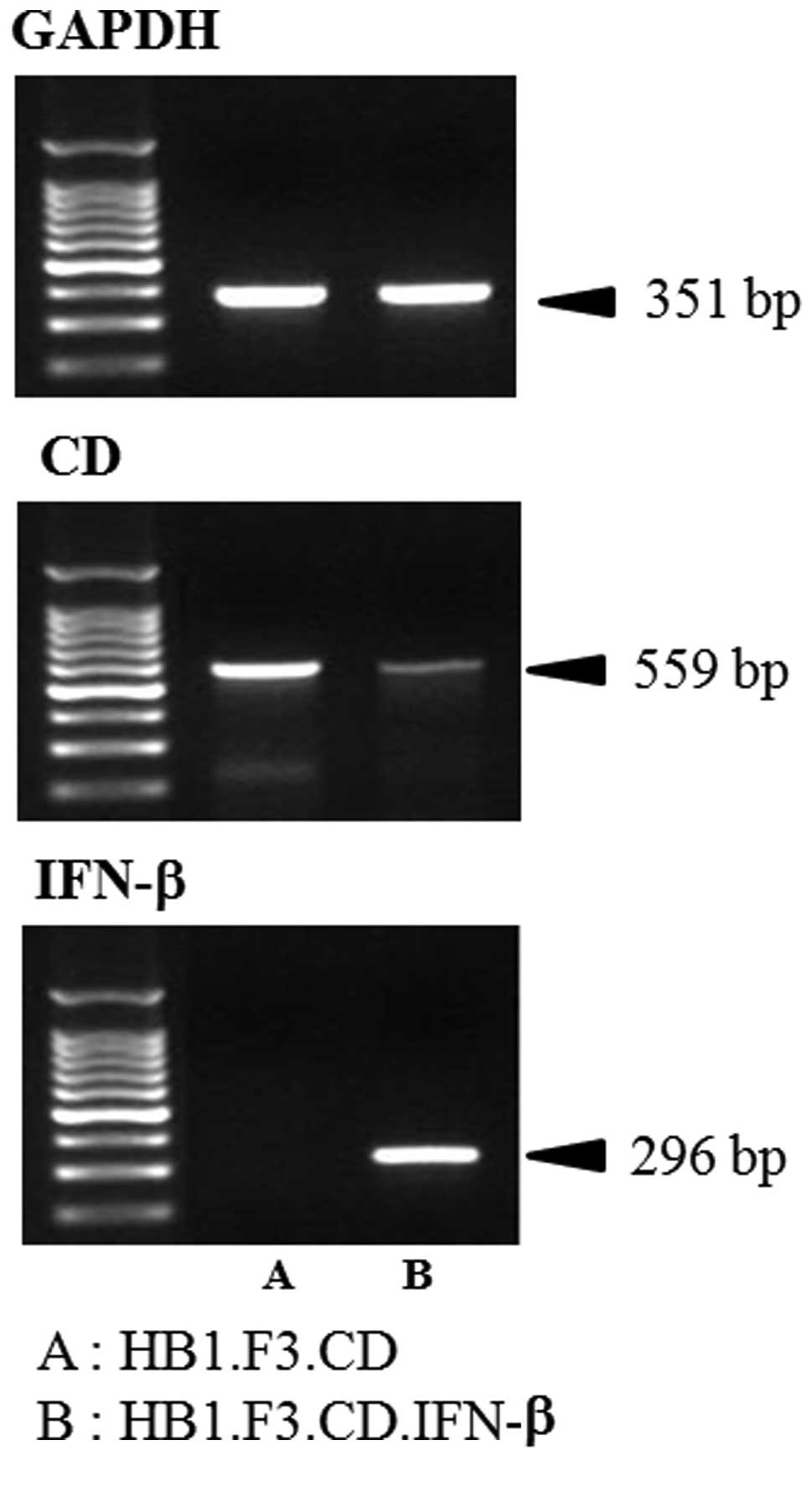
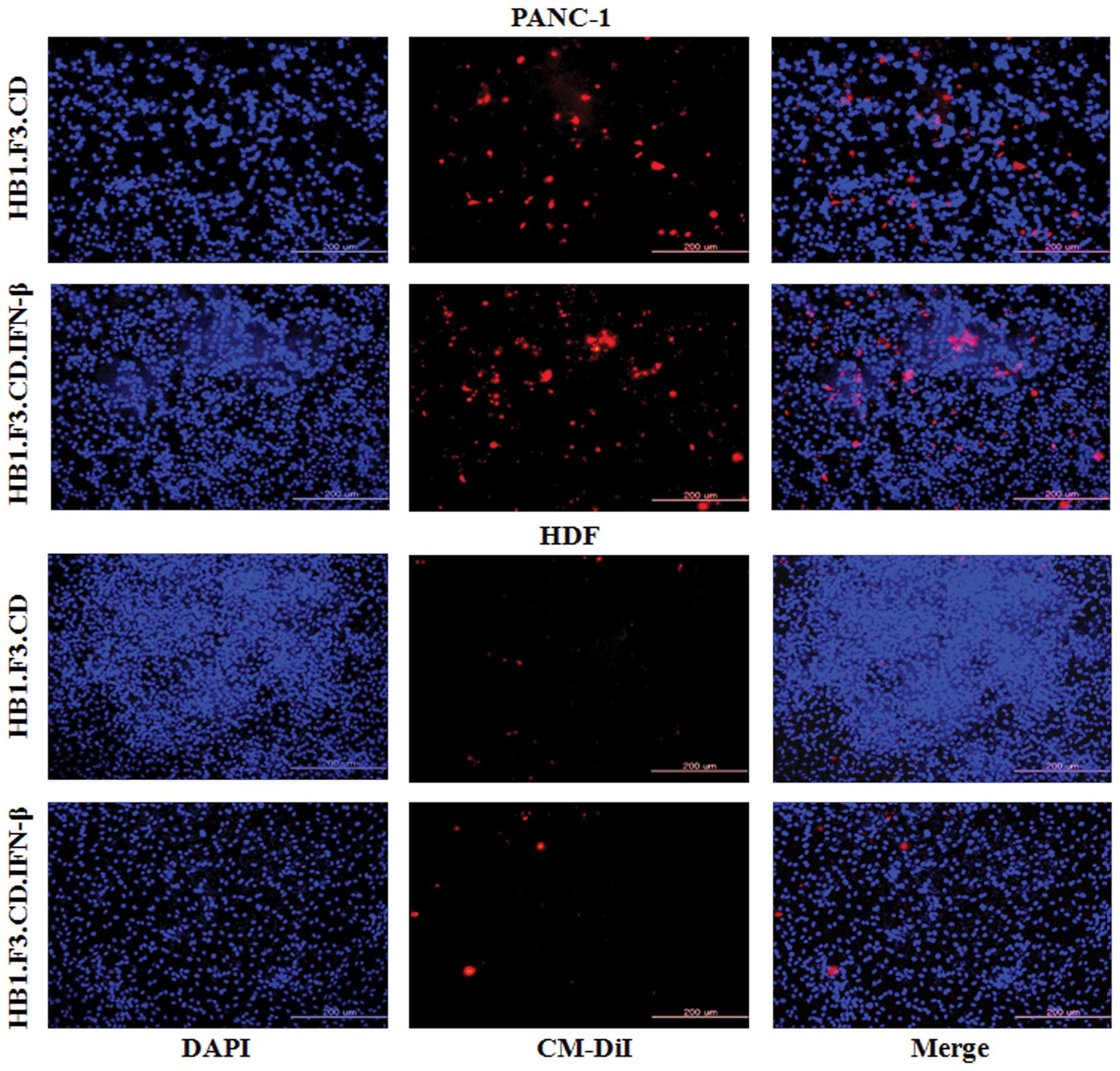
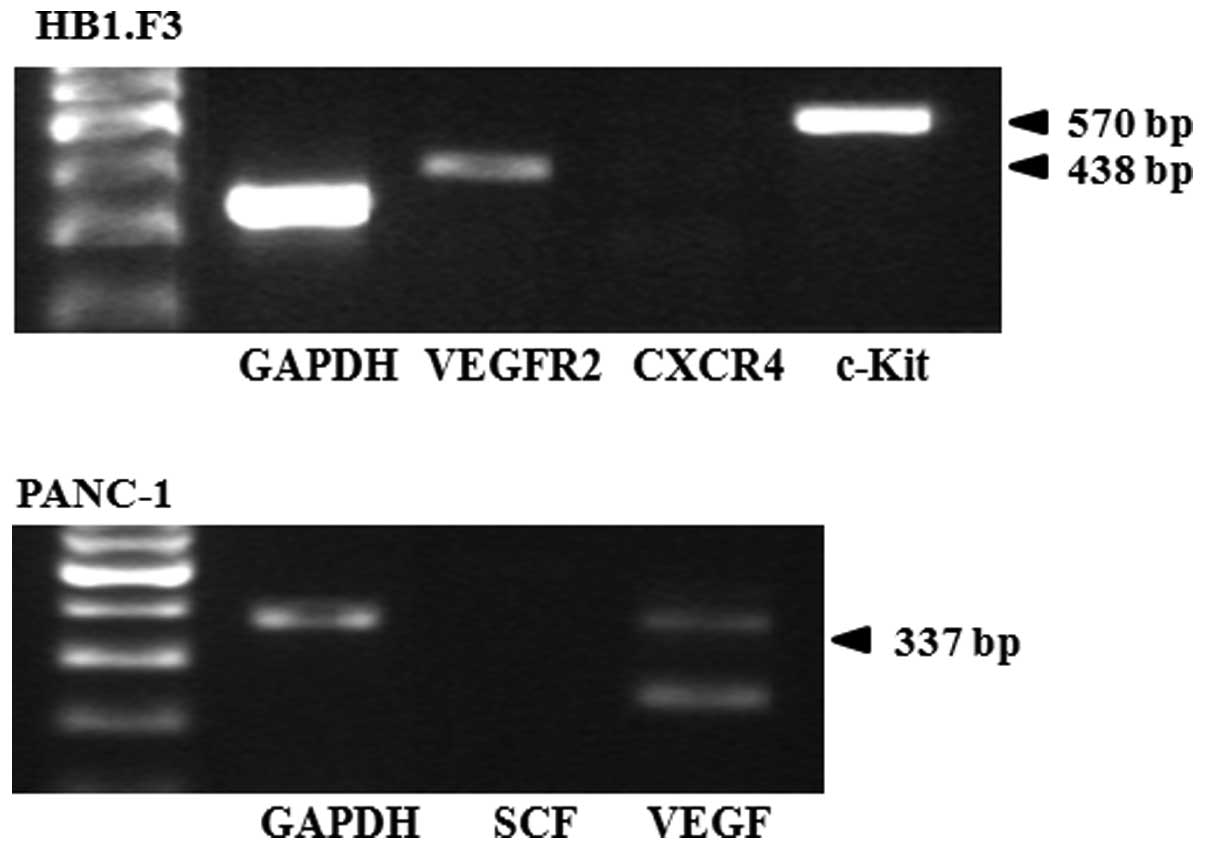
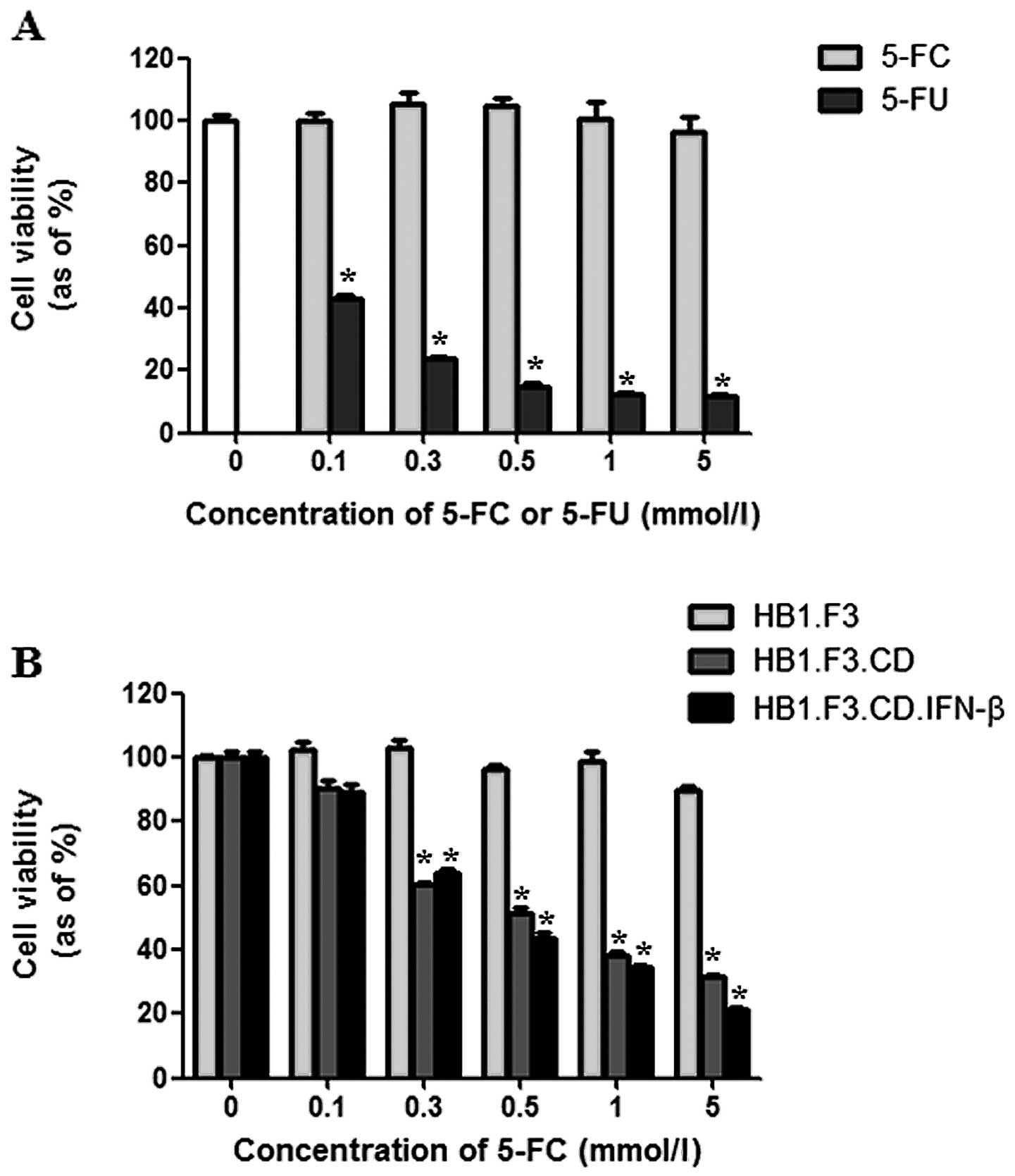
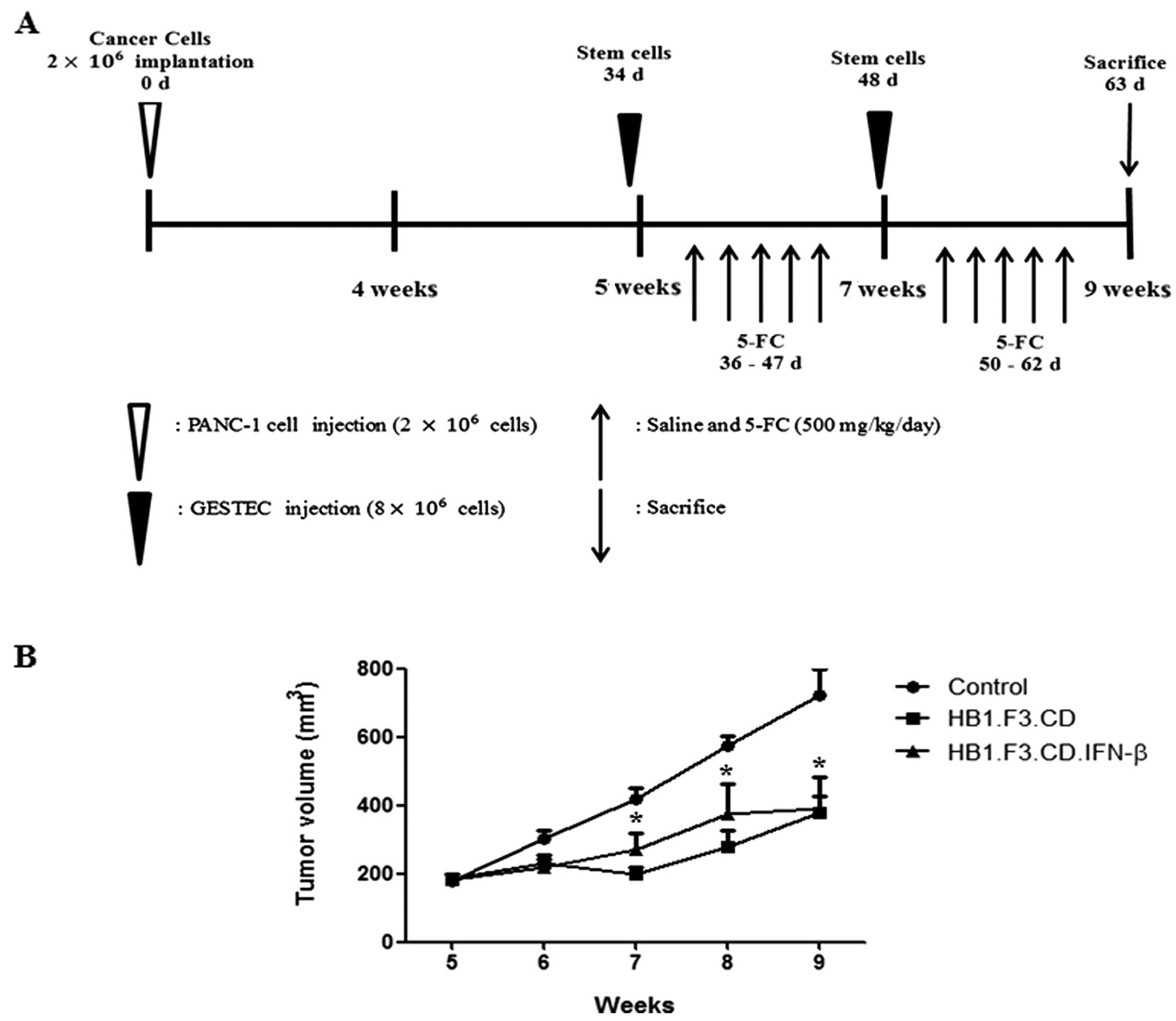
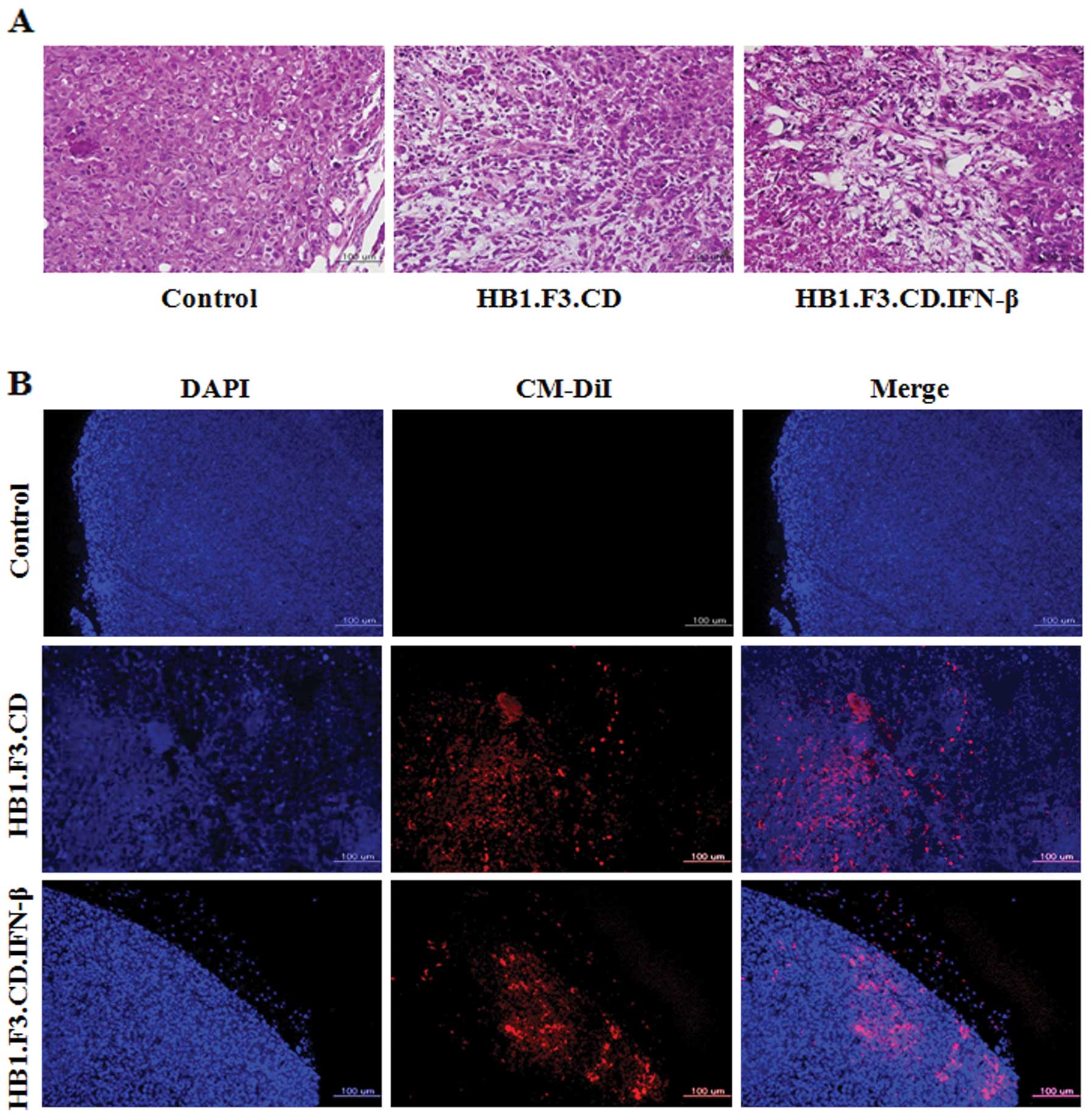
|
1
|
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R and Abbruzzese JL:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 363:1049–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kang NH, Yi BR, Lim SY, Hwang KA, Baek YS,
Kang KS and Choi KC: Human amniotic membrane-derived epithelial
stem cells display anticancer activity in BALB/c female nude mice
bearing disseminated breast cancer xenografts. Int J Oncol.
40:2022–2028. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Yi BR, Choi KJ, Kim SU and Choi KC:
Therapeutic potential of stem cells expressing suicide genes that
selectively target human breast cancer cells: Evidence that they
exert tumoricidal effects via tumor tropism (Review). Int J Oncol.
41:798–804. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Yi BR, Kim SU, Kim YB, Lee HJ, Cho MH and
Choi KC: Antitumor effects of genetically engineered stem cells
expressing yeast cytosine deaminase in lung cancer brain metastases
via their tumor-tropic properties. Oncol Rep. 27:1823–1828.
2012.
|
|
5
|
Studeny M, Marini FC, Champlin RE,
Zompetta C, Fidler IJ and Andreeff M: Bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells as vehicles for interferon-β delivery into
tumors. Cancer Res. 62:3603–3608. 2002.
|
|
6
|
Zhang JF, Wei F, Wang HP, Li HM, Qiu W,
Ren PK, Chen XF and Huang Q: Potent anti-tumor activity of
telomerase-dependent and HSV-TK armed oncolytic adenovirus for
non-small cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yi BR, Kang NH, Hwang KA, Kim SU, Jeung EB
and Choi KC: Antitumor therapeutic effects of cytosine deaminase
and interferon-β against endometrial cancer cells using genetically
engineered stem cells in vitro. Anticancer Res. 31:2853–2861.
2011.
|
|
8
|
Aboody KS, Brown A, Rainov NG, Bower KA,
Liu S, Yang W, Small JE, Herrlinger U, Ourednik V, Black PM,
Breakefield XO and Snyder EY: Neural stem cells display extensive
tropism for pathology in adult brain: evidence from intracranial
gliomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:12846–12851. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aboody KS, Bush RA, Garcia E, Metz MZ,
Najbauer J, Justus KA, Phelps DA, Remack JS, Yoon KJ, Gillespie S,
Kim SU, Glackin CA, Potter PM and Danks MK: Development of a
tumor-selective approach to treat metastatic cancer. PLoS One.
1:e232006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SK, Kim SU, Park IH, Bang JH, Aboody
KS, Wang KC, Cho BK, Kim M, Menon LG, Black PM and Carroll RS:
Human neural stem cells target experimental intracranial
medulloblastoma and deliver a therapeutic gene leading to tumor
regression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:5550–5556. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim KY, Kim SU, Leung PC, Jeung EB and
Choi KC: Influence of the prodrugs 5-fluorocytosine and CPT-11 on
ovarian cancer cells using genetically engineered stem cells:
tumor-tropic potential and inhibition of ovarian cancer cell
growth. Cancer Sci. 101:955–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim SU: Human neural stem cells
genetically modified for brain repair in neurological disorders.
Neuropathology. 24:159–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim SU, Nakagawa E, Hatori K, Nagai A, Lee
MA and Bang JH: Production of immortalized human neural crest stem
cells. Methods Mol Biol. 198:55–65. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Evoy D, Hirschowitz EA, Naama HA, Li XK,
Crystal RG, Daly JM and Lieberman MD: In vivo adenoviral-mediated
gene transfer in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. J Surg Res.
69:226–231. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hirschowitz EA, Ohwada A, Pascal WR, Russi
TJ and Crystal RG: In vivo adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the
Escherichia coli cytosine deaminase gene to human colon
carcinoma-derived tumors induces chemosensitivity to
5-fluorocytosine. Hum Gene Ther. 6:1055–1063. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanai F, Lan KH, Shiratori Y, Tanaka T,
Ohashi M, Okudaira T, Yoshida Y, Wakimoto H, Hamada H, Nakabayashi
H, Tamaoki T and Omata M: In vivo gene therapy for
α-fetoprotein-producing hepatocellular carcinoma by
adenovirus-mediated transfer of cytosine deaminase gene. Cancer
Res. 57:461–465. 1997.
|
|
17
|
Lan KH, Kanai F, Shiratori Y, Okabe S,
Yoshida Y, Wakimoto H, Hamada H, Tanaka T, Ohashi M and Omata M:
Tumor-specific gene expression in carcinoembryonic antigen -
producing gastric cancer cells using adenovirus vectors.
Gastroenterology. 111:1241–1251. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Shanmugam N, Katayose D, Huber B,
Srivastava S, Cowan K and Seth P: Enzyme/prodrug gene therapy
approach for breast cancer using a recombinant adenovirus
expressing Escherichia coli cytosine deaminase. Cancer Gene
Ther. 4:113–117. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Austin EA and Huber BE: A first step in
the development of gene therapy for colorectal carcinoma: cloning,
sequencing, and expression of Escherichia coli cytosine
deaminase. Mol Pharmacol. 43:380–387. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mullen CA, Kilstrup M and Blaese RM:
Transfer of the bacterial gene for cytosine deaminase to mammalian
cells confers lethal sensitivity to 5-fluorocytosine: a negative
selection system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:33–37. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Etienne MC, Cheradame S, Fischel JL,
Formento P, Dassonville O, Renée N, Schneider M, Thyss A, Demard F
and Milano G: Response to fluorouracil therapy in cancer patients:
the role of tumoral dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity. J
Clin Oncol. 13:1663–1670. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pinedo HM and Peters GF: Fluorouracil:
biochemistry and pharmacology. J Clin Oncol. 6:1653–1664.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chung-Faye GA, Chen MJ, Green NK, Burton
A, Anderson D, Mautner V, Searle PF and Kerr DJ: In vivo gene
therapy for colon cancer using adenovirus-mediated, transfer of the
fusion gene cytosine deaminase and uracil
phosphoribosyltransferase. Gene Ther. 8:1547–1554. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Crystal RG, Hirschowitz E, Lieberman M,
Daly J, Kazam E, Henschke C, Yankelevitz D, Kemeny N, Silverstein
R, Ohwada A, Russi T, Mastrangeli A, Sanders A, Cooke J and Harvey
BG: Phase I study of direct administration of a replication
deficient adenovirus vector containing the E. coli cytosine
deaminase gene to metastatic colon carcinoma of the liver in
association with the oral administration of the pro-drug
5-fluorocytosine. Hum Gene Ther. 8:985–1001. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Freytag SO, Khil M, Stricker H, Peabody J,
Menon M, DePeralta-Venturina M, Nafziger D, Pegg J, Paielli D,
Brown S, Barton K, Lu M, Aguilar-Cordova E and Kim JH: Phase I
study of replication-competent adenovirus-mediated double suicide
gene therapy for the treatment of locally recurrent prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 62:4968–4976. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yi BR, Hwang KA, Kang NH, Kim SU, Jeung
EB, Kim HC and Choi KC: Synergistic effects of genetically
engineered stem cells expressing cytosine deaminase and
interferon-β via their tumor tropism to selectively target human
hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 19:644–651. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Kang NH, Hwang KA, Yi BR, Lee HJ, Jeung
EB, Kim SU and Choi KC: Human amniotic fluid-derived stem cells
expressing cytosine deaminase and thymidine kinase inhibits the
growth of breast cancer cells in cellular and xenograft mouse
models. Cancer Gene Ther. 19:412–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim KY, Yi BR, Lee HR, Kang NH, Jeung EB,
Kim SU and Choi KC: Stem cells with fused gene expression of
cytosine deaminase and interferon-β migrate to human gastric cancer
cells and result in synergistic growth inhibition for potential
therapeutic use. Int J Oncol. 40:1097–1104. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schmidt NO, Przylecki W, Yang W, Ziu M,
Teng Y, Kim SU, Black PM, Aboody KS and Carroll RS: Brain tumor
tropism of transplanted human neural stem cells is induced by
vascular endothelial growth factor. Neoplasia. 7:623–629. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nawa A, Tanino T, Luo C, Iwaki M, Kajiyama
H, Shibata K, Yamamoto E, Ino K, Nishiyama Y and Kikkawa F: Gene
directed enzyme prodrug therapy for ovarian cancer: could GDEPT
become a promising treatment against ovarian cancer? Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 8:232–239. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lee DH, Ahn Y, Kim SU, Wang KC, Cho BK,
Phi JH, Park IH, Black PM, Carroll RS, Lee J and Kim SK: Targeting
rat brainstem glioma using human neural stem cells and human
mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4925–4934. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yi BR, OSN, Kang NH, Hwang KA, Kim SU,
Jeung EB, Kim YB, Heo GJ and Choi KC: Genetically engineered stem
cells expressing cytosine deaminase and interferon-β migrate to
human lung cancer cells and have potentially therapeutic anti-tumor
effects. Int J Oncol. 39:833–839. 2011.
|
|
33
|
Saidi RF, Williams F, Ng J, Danquah G,
Mittal VK, ReMine SG and Jacobs MJ: Interferon receptors and the
caspase cascade regulate the antitumor effects of interferons on
human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Am J Surg. 191:358–363. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|