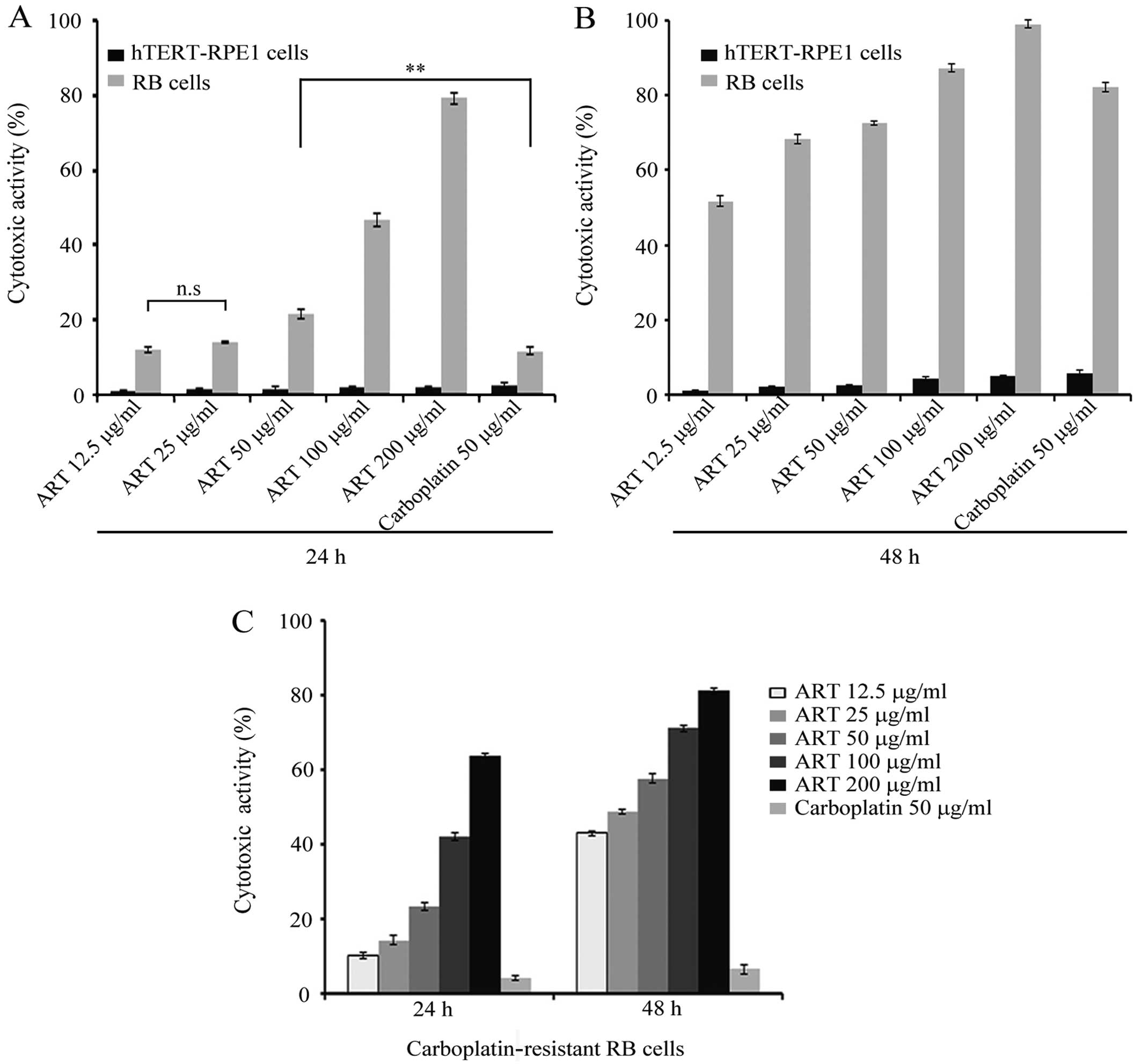
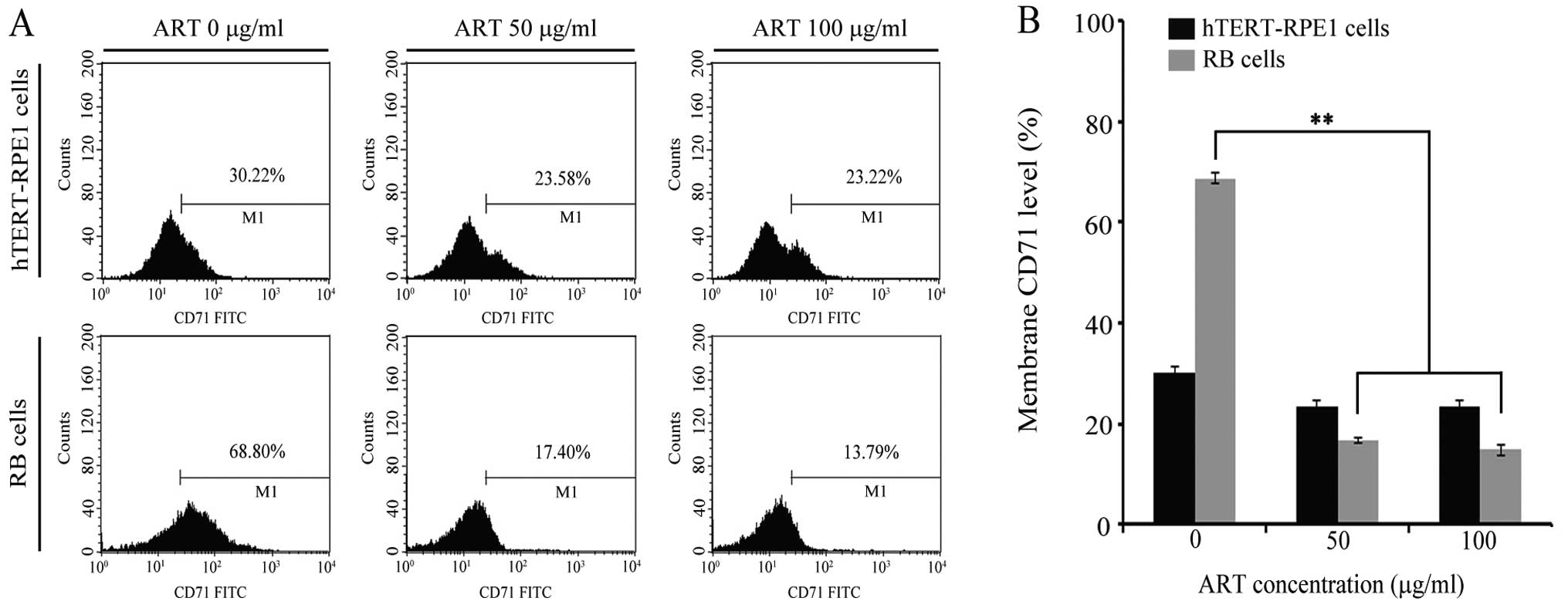
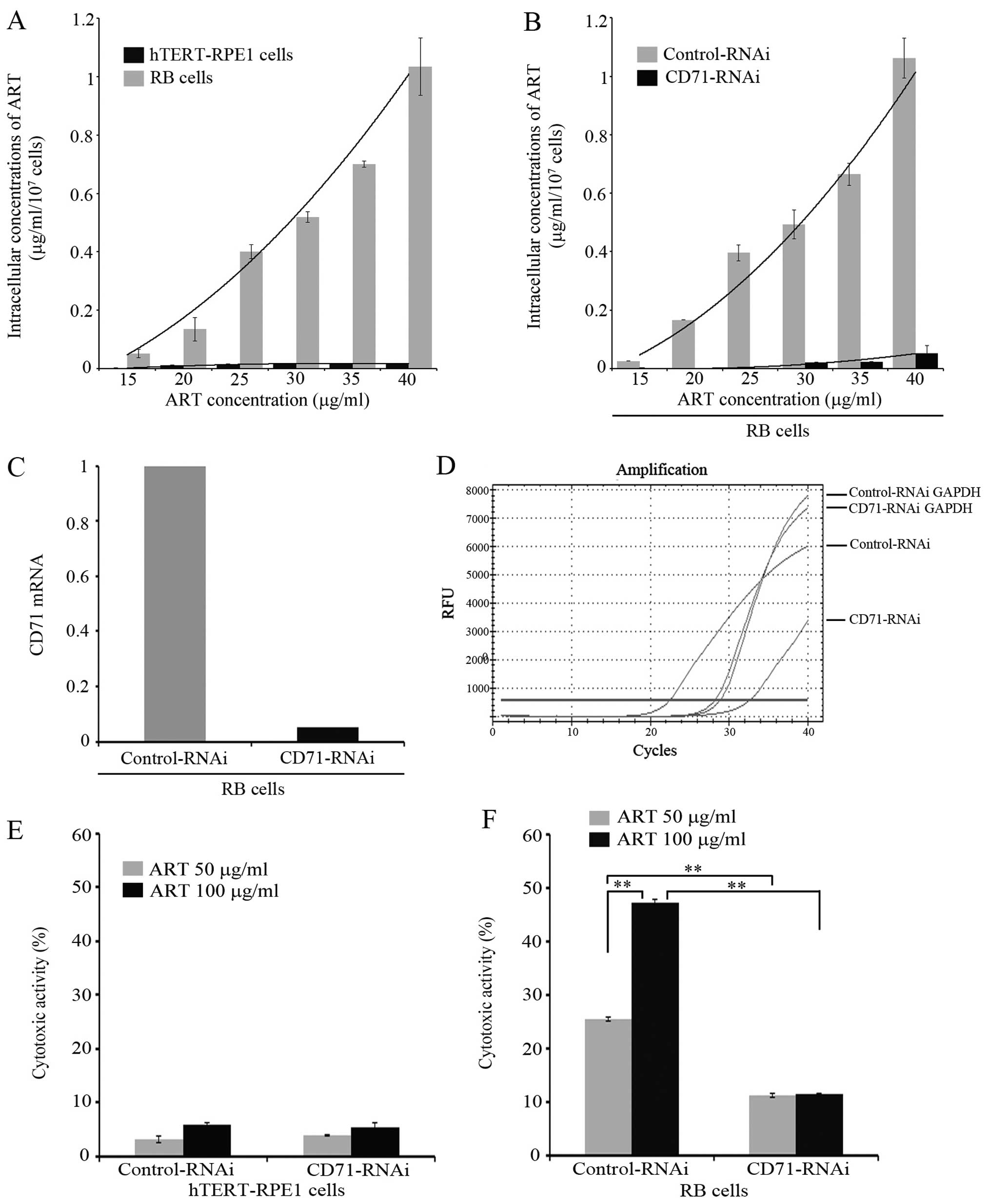
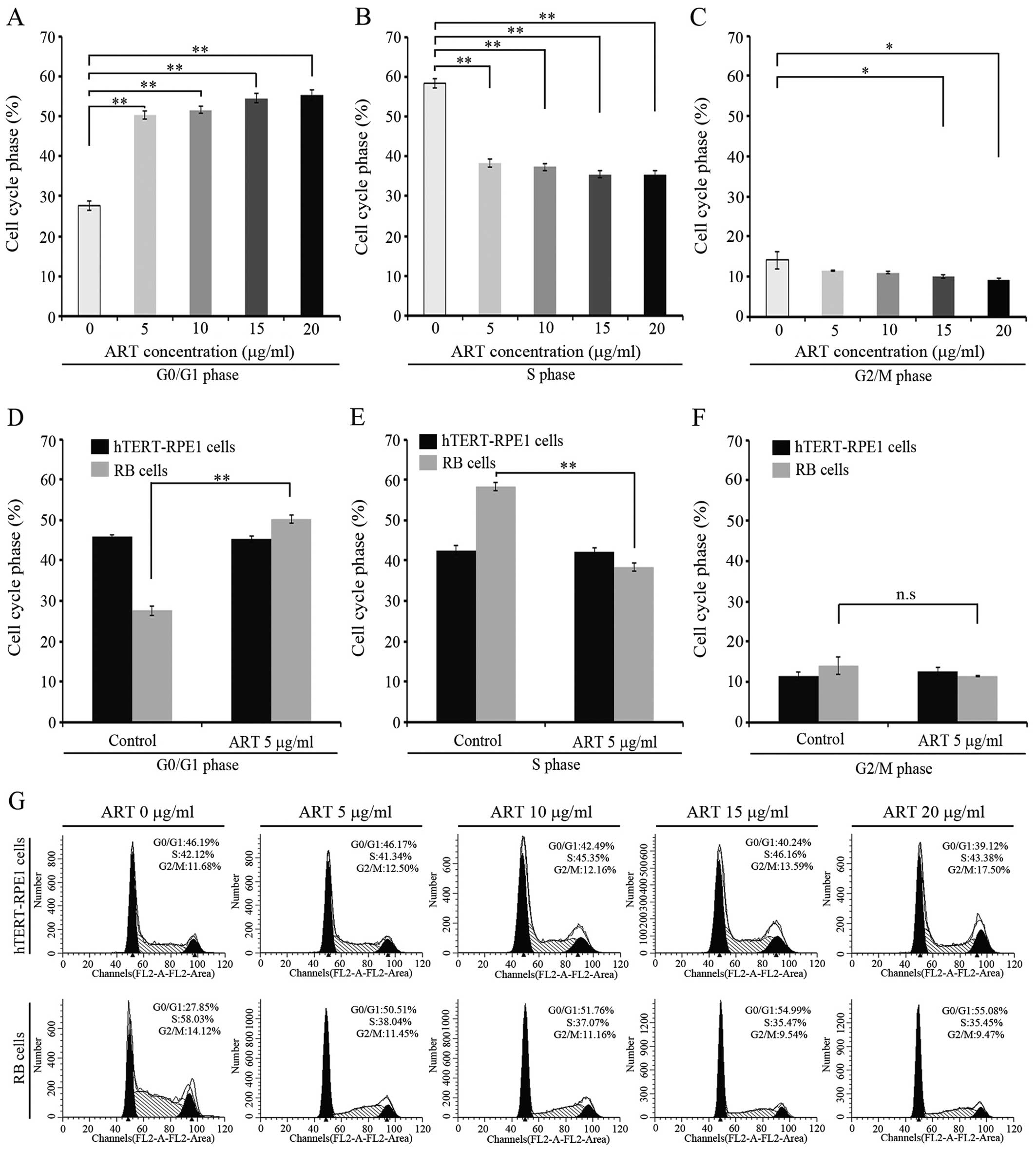
|
1
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Recent
developments in the management of retinoblastoma. J Pediatr
Ophthalmol Strabismus. 36:8–18; quiz 35–36. 1999.
|
|
2
|
Shields CL and Shields JA: Diagnosis and
management of retinoblastoma. Cancer Control. 11:317–327. 2004.
|
|
3
|
Dimaras H, Kahaki K, O’Dimba EA, et al:
Retinoblastoma. Lancet. 379:1436–1446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kivela T: The epidemiological challenge of
the most frequent eye cancer: retinoblastoma, an issue of birth and
death. Br J Ophthalmol. 93:1129–1131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bai S, Ren R, Shi J, et al: Retinoblastoma
in the Beijing Tongren Hospital from 1957 to 2006:
clinicopathological findings. Br J Ophthalmol. 95:1072–1076. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao J, Li S, Shi J and Wang N: Clinical
presentation and group classification of newly diagnosed
intraocular retinoblastoma in China. Br J Ophthalmol. 95:1372–1375.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Samaila MO: Malignant tumours of childhood
in Zaria. Afr J Paediatr Surg. 6:19–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
MacCarthy A, Draper GJ, Steliarova-Foucher
E and Kingston JE: Retinoblastoma incidence and survival in
European children (1978–1997). Report from the Automated Childhood
Cancer Information System project. Eur J Cancer. 42:2092–2102.
2006.
|
|
9
|
Broaddus E, Topham A and Singh AD:
Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. Br J Ophthalmol.
93:21–23. 2009.
|
|
10
|
Chantada G, Fandiño A, Manzitti J, Urrutia
L and Schvartzman E: Late diagnosis of retinoblastoma in a
developing country. Arch Dis Child. 80:171–174. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schipper J, Tan KE and van Peperzeel HA:
Treatment of retinoblastoma by precision megavoltage radiation
therapy. Radiother Oncol. 3:117–132. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gallie BL, Budning A, DeBoer G, et al:
Chemotherapy with focal therapy can cure intraocular retinoblastoma
without radiotherapy. Arch Ophthalmol. 114:1321–1328. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kingston JE, Hungerford JL, Madreperla SA
and Plowman PN: Results of combined chemotherapy and radiotherapy
for advanced intraocular retinoblastoma. Arch Ophthalmol.
114:1339–1343. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Veal GJ and Boddy AV: Carboplatin dosing
in infants with retinoblastoma: a case for therapeutic drug
monitoring. J Clin Oncol. 30:34242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rodriguez-Galindo C, Wilson MW, Haik BG,
et al: Treatment of intraocular retinoblastoma with vincristine and
carboplatin. J Clin Oncol. 21:2019–2025. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Varan A, Kiratli H, Aydin B, et al: The
treatment of retinoblastoma with four-drug regimen including
cisplatin, etoposide, vincristine, and cyclophosphamide. Pediatr
Hematol Oncol. 29:529–537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chantada G, Fandino A, Casak S, Manzitti
J, Raslawski E and Schvartzman E: Treatment of overt extraocular
retinoblastoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 40:158–161. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao YJ, Qian J, Yue H, Yuan YF, Xue K and
Yao YQ: Clinical characteristics and treatment outcome of children
with intraocular retinoblastoma: a report from a Chinese
cooperative group. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 57:1113–1116. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leahey A: A cautionary tale: dosing
chemotherapy in infants with retinoblastoma. J Clin Oncol.
30:1023–1024. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shields CL, Kaliki S, Shah SU, et al:
Minimal exposure (one or two cycles) of intra-arterial chemotherapy
in the management of retinoblastoma. Ophthalmology. 119:188–192.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan HS, Lu Y, Grogan TM, et al: Multidrug
resistance protein (MRP) expression in retinoblastoma correlates
with the rare failure of chemotherapy despite cyclosporine for
reversal of P-glycoprotein. Cancer Res. 57:2325–2330.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gobin YP, Dunkel IJ, Marr BP, Brodie SE
and Abramson DH: Intra-arterial chemotherapy for the management of
retinoblastoma: four-year experience. Arch Ophthalmol. 129:732–737.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qaddoumi I, Bass JK, Wu J, et al:
Carboplatin-associated ototoxicity in children with retinoblastoma.
J Clin Oncol. 30:1034–1041. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rizzuti AE, Dunkel IJ and Abramson DH: The
adverse events of chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: What are they?
Do we know? Arch Ophthalmol. 126:862–865. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Abramson DH, Lawrence SD, Beaverson KL,
Lee TC, Rollins IS and Dunkel IJ: Systemic carboplatin for
retinoblastoma: change in tumour size over time. Br J Ophthalmol.
89:1616–1619. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marees T, van Leeuwen FE, de Boer MR,
Imhof SM, Ringens PJ and Moll AC: Cancer mortality in long-term
survivors of retinoblastoma. Eur J Cancer. 45:3245–3253. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Araki Y, Matsuyama Y, Kobayashi Y, et al:
Secondary neoplasms after retinoblastoma treatment: retrospective
cohort study of 754 patients in Japan. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
41:373–379. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Turaka K, Shields CL, Meadows AT and
Leahey A: Second malignant neoplasms following chemoreduction with
carboplatin, etoposide, and vincristine in 245 patients with
intraocular retinoblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 59:121–125. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tu Y: The discovery of artemisinin
(qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat Med. 17:1217–1220.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Balint G: Artemisinin and its derivatives:
an important new class of antimalarial agents. Pharmacol Ther.
90:261–265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chaturvedi D, Goswami A, Saikia PP, Barua
NC and Rao PG: Artemisinin and its derivatives: a novel class of
anti-malarial and anti-cancer agents. Chem Soc Rev. 39:435–454.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Efferth T, Giaisi M, Merling A, Krammer PH
and Li-Weber M: artesunate induces ROS-mediated apoptosis in
doxorubicin-resistant T leukemia cells. PLoS One. 2:e6932007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lai HC, Singh NP and Sasaki T: Development
of artemisinin compounds for cancer treatment. Invest New Drugs.
31:230–246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gong Y, Gallis BM, Goodlett DR, et al:
Effects of transferrin conjugates of artemisinin and artemisinin
dimer on breast cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 33:123–132.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gong XM, Zhang Q, Torossian A, Cao JP and
Fu S: Selective radiosensitization of human cervical cancer cells
and normal cells by artemisinin through the abrogation of
radiation-induced G2 block. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:718–724. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kerb R, Fux R, Mörike K, Kremsner PG, Gil
JP, Gleiter CH and Schwab M: Pharmacogenetics of antimalarial
drugs: effect on metabolism and transport. Lancet Infect Dis.
9:760–774. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Efferth T, Benakis A, Romero MR, et al:
Enhancement of cytotoxicity of artemisinins toward cancer cells by
ferrous iron. Free Radic Biol Med. 37:998–1009. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Berdelle N, Nikolova T, Quiros S, Efferth
T and Kaina B: artesunate induces oxidative DNA damage, sustained
DNA double-strand breaks, and the ATM/ATR damage response in cancer
cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:2224–2233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li YSF, Wu JM, Wu GS, Ding J, Xiao D, Yang
WY, Atassi G, Léonce S, Caignard DH and Renard P: Novel antitumor
artemisinin derivatives targeting G1 phase of the cell cycle.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 11:5–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
O’Neill PM, Barton VE and Ward SA: The
molecular mechanism of action of artemisinin - the debate
continues. Molecules. 15:1705–1721. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU, Galy B and
Camaschella C: Two to tango: regulation of Mammalian iron
metabolism. Cell. 142:24–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shpyleva SI, Tryndyak VP, Kovalchuk O, et
al: Role of ferritin alterations in human breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:63–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Richardson DR, Kalinowski DS, Lau S,
Jansson PJ and Lovejoy DB: Cancer cell iron metabolism and the
development of potent iron chelators as anti-tumour agents. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1790:702–717. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Crespo-Ortiz MP and Wei MQ: Antitumor
activity of artemisinin and its derivatives: from a well-known
antimalarial agent to a potential anticancer drug. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2012:2475972012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang
J, Zhang Z, Miller W and Lipman DJ: Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a
new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids
Res. 25:3389–3402. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Green MD, Mount DL, Wirtz RA and White NJ:
A colorimetric field method to assess the authenticity of drugs
sold as the antimalarial artesunate. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 24:65–70.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Okwelogu C, Clark B, de Matas M, et al:
Design of a fixed-dose paediatric combination of artesunate and
amodiaquine hydrochloride. Int J Pharm. 387:19–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Calvert AH, Newell DR, Gumbrell LA, et al:
Carboplatin dosage: prospective evaluation of a simple formula
based on renal function. J Clin Oncol. 7:1748–1756. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shimokata T, Ando Y, Yasuda Y, et al:
Prospective evaluation of pharmacokinetically guided dosing of
carboplatin in Japanese patients with cancer. Cancer Sci.
101:2601–2605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Krishnakumar S, Mallikarjuna K, Desai N,
et al: Multidrug resistant proteins: P-glycoprotein and lung
resistance protein expression in retinoblastoma. Br J Ophthalmol.
88:1521–1526. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wilson MW, Fraga CH, Fuller CE, et al:
Immunohistochemical detection of multidrug-resistant protein
expression in retinoblastoma treated by primary enucleation. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 47:1269–1273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Deng DA, Xu CH and Cai JC: Derivatives of
arteannuin B with antileukemia activity. Yao Xue Xue Bao.
27:317–320. 1992.(In Chinese).
|
|
53
|
Sun WC, Han JX, Yang WY, Deng DA and Yue
XF: Antitumor activities of 4 derivatives of artemisic acid and
artemisinin B in vitro. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 13:541–543.
1992.(In Chinese).
|
|
54
|
Woerdenbag HJ, Moskal TA, Pras N, et al:
Cytotoxicity of artemisinin-related endoperoxides to Ehrlich
ascites tumor cells. J Nat Prod. 56:849–856. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang XP, Pan QC, Ling YJ, et al: Study on
antitumor effect of sodium artesunate. Cancer. 16:186–187. 1997.(In
Chinese).
|
|
56
|
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi
H and Chitambar CR: The anti-malarial artesunate is also active
against cancer. Int J Oncol. 18:767–773. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Buommino E, Baroni A, Canozo N, et al:
Artemisinin reduces human melanoma cell migration by
down-regulating alpha V beta 3 integrin and reducing
metalloproteinase 2 production. Invest New Drugs. 27:412–418. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Morrissey C, Gallis B, Solazzi JW, et al:
Effect of artemisinin derivatives on apoptosis and cell cycle in
prostate cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 21:423–432. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Du JH, Zhang HD, Ma ZJ and Ji KM:
Artesunate induces oncosis-like cell death in vitro and has
antitumor activity against pancreatic cancer xenografts in vivo.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 65:895–902. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Efferth TSA, Olbrich A, Gebhart E, Rauch
P, Weber HO, Hengstler JG, Halatsch ME, Volm M, Tew KD, Ross DD and
Funk JO: Molecular modes of action of artesunate in tumor cell
lines. Mol Pharmacol. 64:382–394. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Singh NP and Verma KB: Case report of a
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma treated with artesunate. Arch
Oncol. 10:279–280. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Torti SV and Torti FM: Ironing out cancer.
Cancer Res. 71:1511–1514. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Shterman N, Kupfer B and Moroz C:
Comparison of transferrin receptors, iron content and isoferritin
profile in normal and malignant human breast cell lines.
Pathobiology. 59:19–25. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Daniels TR, Delgado T, Rodriguez JA,
Helguera G and Penichet ML: The transferrin receptor part I:
biology and targeting with cytotoxic antibodies for the treatment
of cancer. Clin Immunol. 121:144–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Daniels TR, Delgado T, Helguera G and
Penichet ML: The transferrin receptor part II: targeted delivery of
therapeutic agents into cancer cells. Clin Immunol. 121:159–176.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ba Q, Zhou N, Duan J, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin exerts its anticancer activity through depleting
cellular iron via transferrin receptor-1. PLoS One. 7:e427032012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Eichhorn T, Schloissnig S, Hahn B, et al:
Bioinformatic and experimental fishing for artemisinin-interacting
proteins from human nasopharyngeal cancer cells. Mol Biosyst.
8:1311–1318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhao Y, Jiang W, Li B, et al: Artesunate
enhances radiosensitivity of human non-small cell lung cancer A549
cells via increasing NO production to induce cell cycle arrest at
G2/M phase. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:2039–2046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mercer AE, Maggs JL, Sun XM, et al:
Evidence for the involvement of carbon-centered radicals in the
induction of apoptotic cell death by artemisinin compounds. J Biol
Chem. 282:9372–9382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Mercer AE, Copple IM, Maggs JL, O’Neill PM
and Park BK: The role of heme and the mitochondrion in the chemical
and molecular mechanisms of mammalian cell death induced by the
artemisinin antimalarials. J Biol Chem. 286:987–996. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Selective cancer cell
cytotoxicity from exposure to dihydroartemisinin and
holotransferrin. Cancer Lett. 91:41–46. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lai H, Sasaki T and Singh NP: Targeted
treatment of cancer with artemisinin and artemisinin-tagged
iron-carrying compounds. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 9:995–1007.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Nakase I, Lai H, Singh NP and Sasaki T:
Anticancer properties of artemisinin derivatives and their targeted
delivery by transferrin conjugation. Int J Pharm. 354:28–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kwok JC and Richardson DR: The iron
metabolism of neoplastic cells: alterations that facilitate
proliferation? Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 42:65–78. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hamacher-Brady A, Stein HA, Turschner S,
et al: Artesunate activates mitochondrial apoptosis in breast
cancer cells via iron-catalyzed lysosomal reactive oxygen species
production. J Biol Chem. 286:6587–6601. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Krishna S, Bustamante L, Haynes RK and
Staines HM: Artemisinins: their growing importance in medicine.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 29:520–527. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Kelter G, Steinbach D, Konkimalla VB, et
al: Role of transferrin receptor and the ABC transporters ABCB6 and
ABCB7 for resistance and differentiation of tumor cells towards
artesunate. PLoS One. 2:e7982007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hartwig CL, Rosenthal AS, D’Angelo J,
Griffin CE, Posner GH and Cooper RA: Accumulation of artemisinin
trioxane derivatives within neutral lipids of Plasmodium
falciparum malaria parasites is endoperoxide-dependent. Biochem
Pharmacol. 77:322–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|