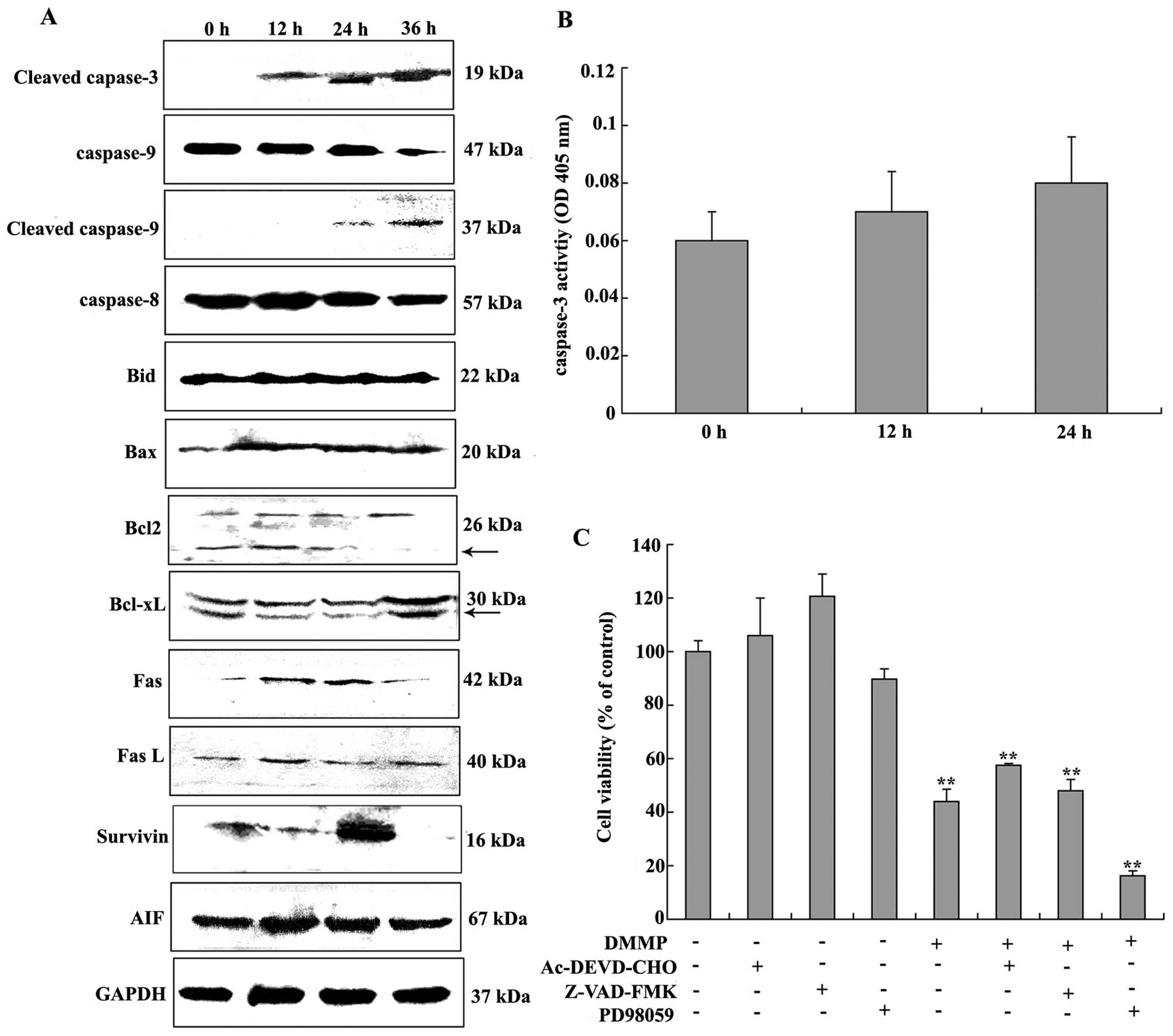
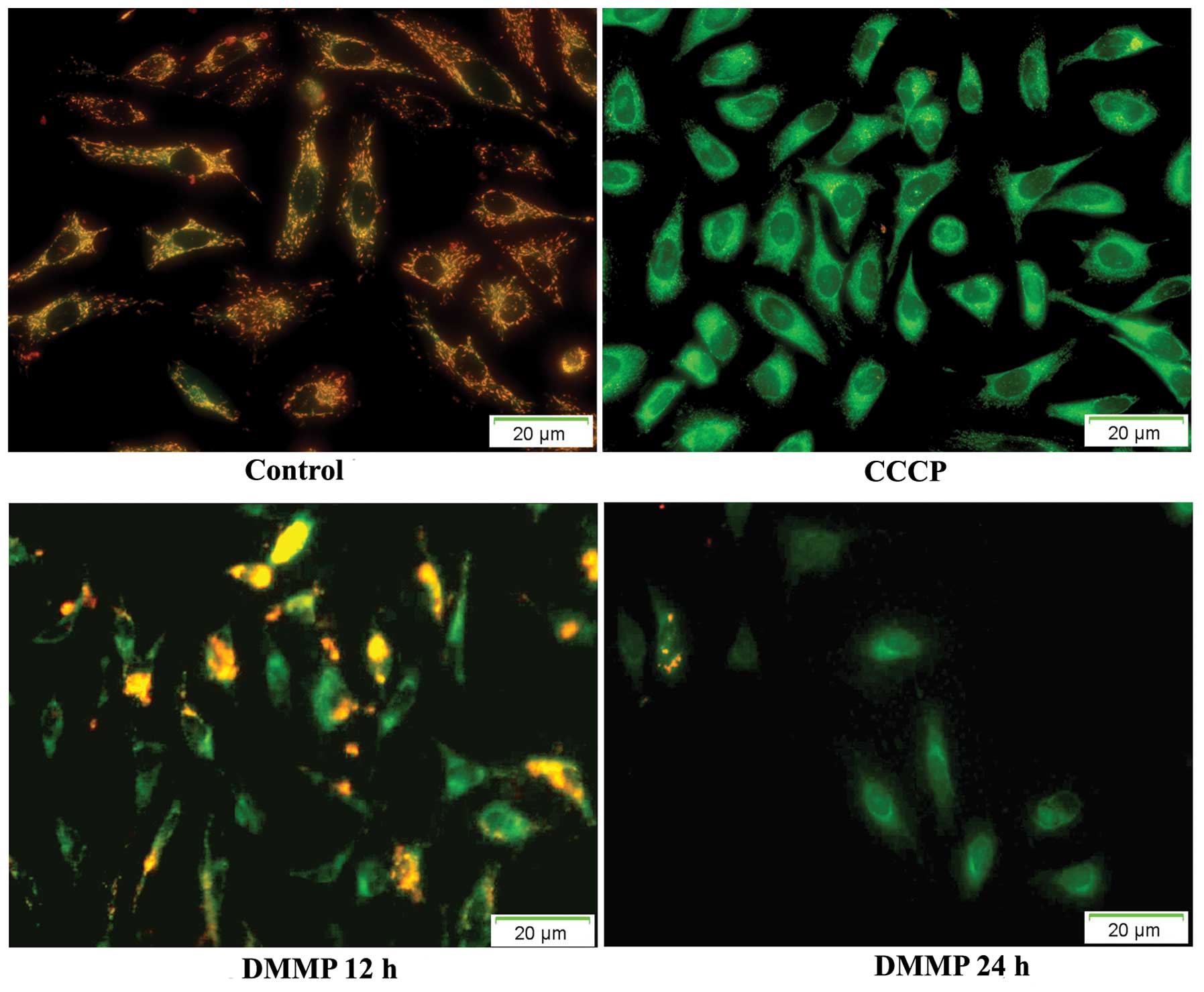
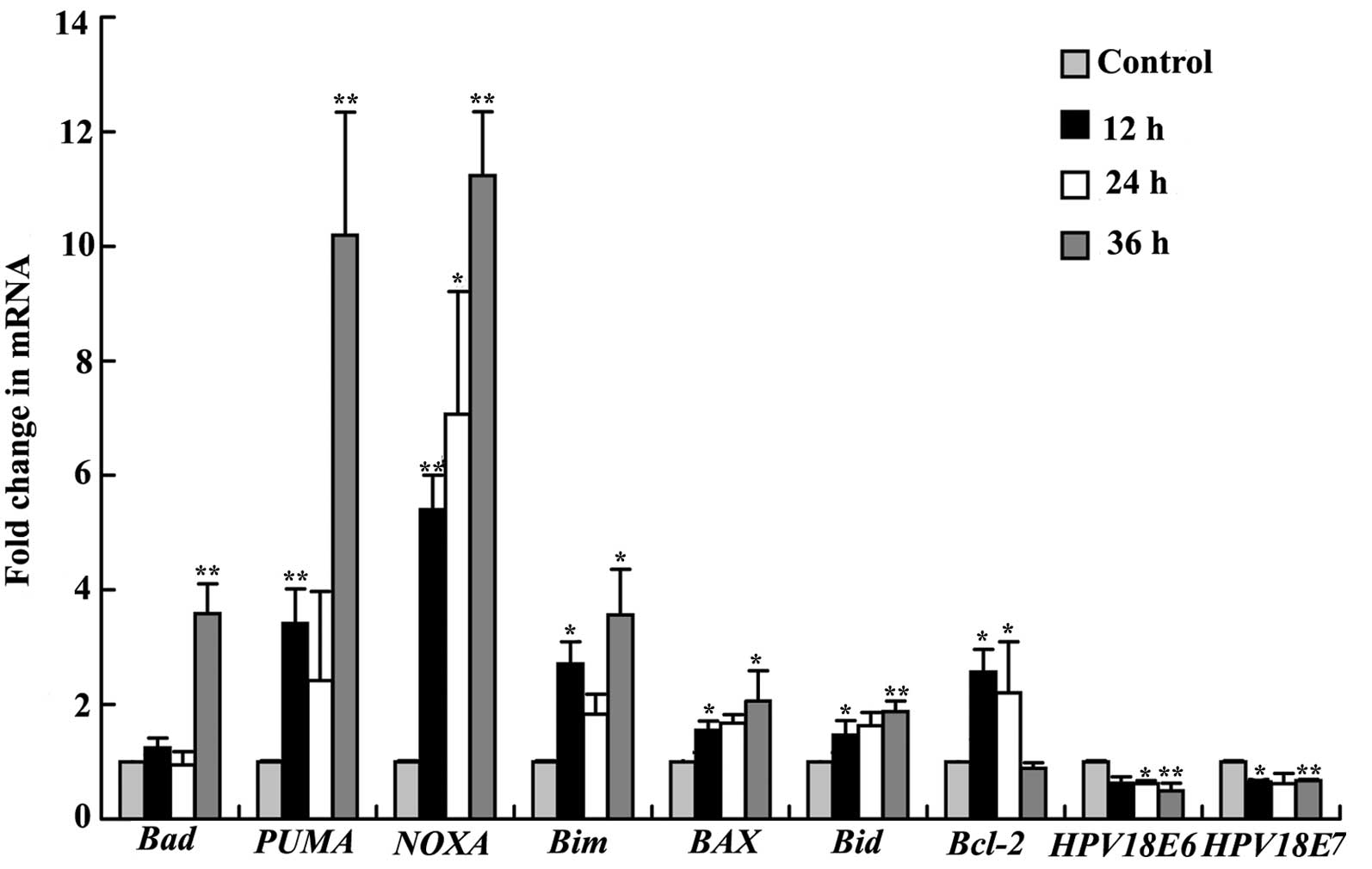
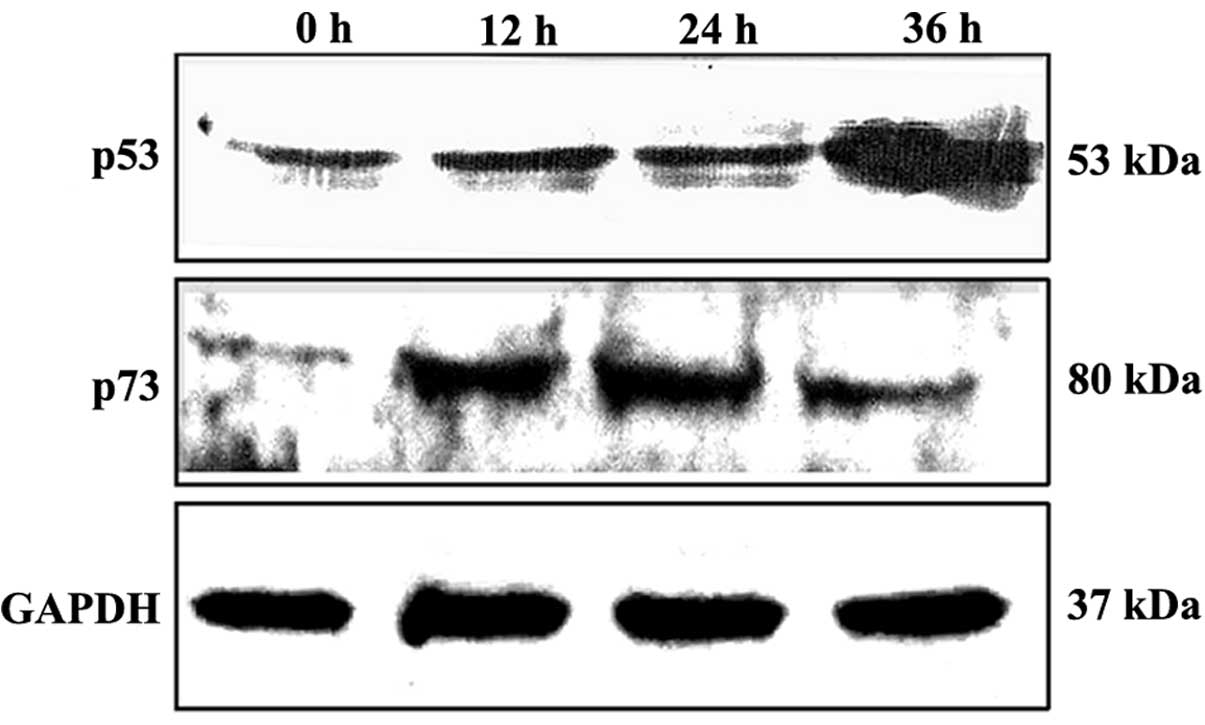
|
1
|
Koehn FE and Carter GT: The evolving role
of natural products in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
4:206–220. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KI, Qing C, Sze DM and Neilan BA:
Investigation of the biosynthetic potential of endophytes in
traditional Chinese anticancer herbs. PLoS One. 7:e359532012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan RX and Zou WX: Endophytes: a rich
source of functional metabolites. Nat Prod Rep. 18:448–459.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reed JC: Drug insight: cancer therapy
strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death
mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 3:388–398. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frankfurt OS and Krishan A:
Apoptosis-based drug screening and detection of selective toxicity
to cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 14:555–561. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen F, Wang W and El-Deiry WS: Current
strategies to target p53 in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:724–730.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Collavin L, Lunardi A and Del Sal G:
p53-family proteins and their regulators: hubs and spokes in tumor
suppression. Cell Death Differ. 17:901–911. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ferreira CG, Tolis C and Giaccone G: p53
and chemosensitivity. Ann Oncol. 10:1011–1021. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lunghi P, Costanzo A, Mazzera L, Rizzoli
V, Levrero M and Bonati A: The p53 family protein p73 provides new
insights into cancer chemosensitivity and targeting. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:6495–6502. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bisso A, Collavin L and Del Sal G: p73 as
a pharmaceutical target for cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des.
17:578–590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Slade N and Horvat A: Targeting p73 - a
potential approach in cancer treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 17:591–602.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lain S, Hollick JJ, Campbell J, et al:
Discovery, in vivo activity, and mechanism of action of a
small-molecule p53 activator. Cancer Cell. 13:454–463. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, et al: In
vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of
MDM2. Science. 303:844–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peirce SK and Findley HW: The MDM2
antagonist nutlin-3 sensitizes p53-null neuroblastoma cells to
doxorubicin via E2F1 and TAp73. Int J Oncol. 34:1395–1402.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sampath D, Calin GA, Puduvalli VK, et al:
Specific activation of microRNA106b enables the p73 apoptotic
response in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by targeting the ubiquitin
ligase Itch for degradation. Blood. 113:3744–3753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Phuwapraisirisan P, Rangsan J, Siripong P
and Tip-Pyang S: New antitumour fungal metabolites from
Alternaria porri. Nat Prod Res. 23:1063–1071. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suemitsu R, Ohnishi K, Morikawa Y and
Nagatomo S: Zinnimidine and
5-(3′,3′-dimethylallyloxy)-7-methoxy-6-methylphthalide from
Alternaria porri. Phytochemistry. 38:495–497.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang XL, Zhang S, Hu QB, Luo DQ and Zhang
Y: Phthalide derivatives with antifungal activities against the
plant pathogens isolated from the liquid culture of
Pestalotiopsis photiniae. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 64:723–727.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: To cycle or
not to cycle: a critical decision in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
1:222–231. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hengst L and Reed SI: Translational
control of p27KIP1 accumulation during the cell cycle.
Science. 271:1861–1864. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, et al:
Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of
the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science. 269:682–685.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vervoorts J and Lüscher B:
Post-translational regulation of the tumor suppressor p27(KIP1).
Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3255–3264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harbour JW and Dean DC: The Rb/E2F
pathway: expanding roles and emerging paradigms. Genes Dev.
14:2393–2409. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: How do BCL-2
proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization?
Trends Cell Biol. 18:157–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: Do inducers of
apoptosis trigger caspase-independent cell death? Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 6:268–275. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brooks CL and Gu W: p53 ubiquitination:
Mdm2 and beyond. Mol Cell. 21:307–315. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sullivan KD, Gallant-Behm CL, Henry RE,
Fraikin JL and Espinosa JM: The p53 circuit board. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1825:229–244. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Diaz D, Santander MA and Chavez JA: HPV-16
E6 and E7 oncogene expression is downregulated as a
result of Mdm2 knockdown. Int J Oncol. 41:141–146. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: Dissecting
p53-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 13:994–1002. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hemann MT and Lowe SW: The p53-Bcl-2
connection. Cell Death Differ. 13:1256–1259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Villunger A, Michalak EM, Coultas L, et
al: p53- and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only
proteins puma and noxa. Science. 302:1036–1038. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu Z, Zheng S and Yu Q: The E2F family and
the role of E2F1 in apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:2389–2397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stiewe T and Pützer BM: Role of the
p53-homologue p73 in E2F1-induced apoptosis. Nat Genet. 26:464–469.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Amin AR, Paul RK, Thakur VS and Agarwal
ML: A novel role for p73 in the regulation of Akt-Foxo1a-Bim
signaling and apoptosis induced by the plant lectin, Concanavalin
A. Cancer Res. 67:5617–5621. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|