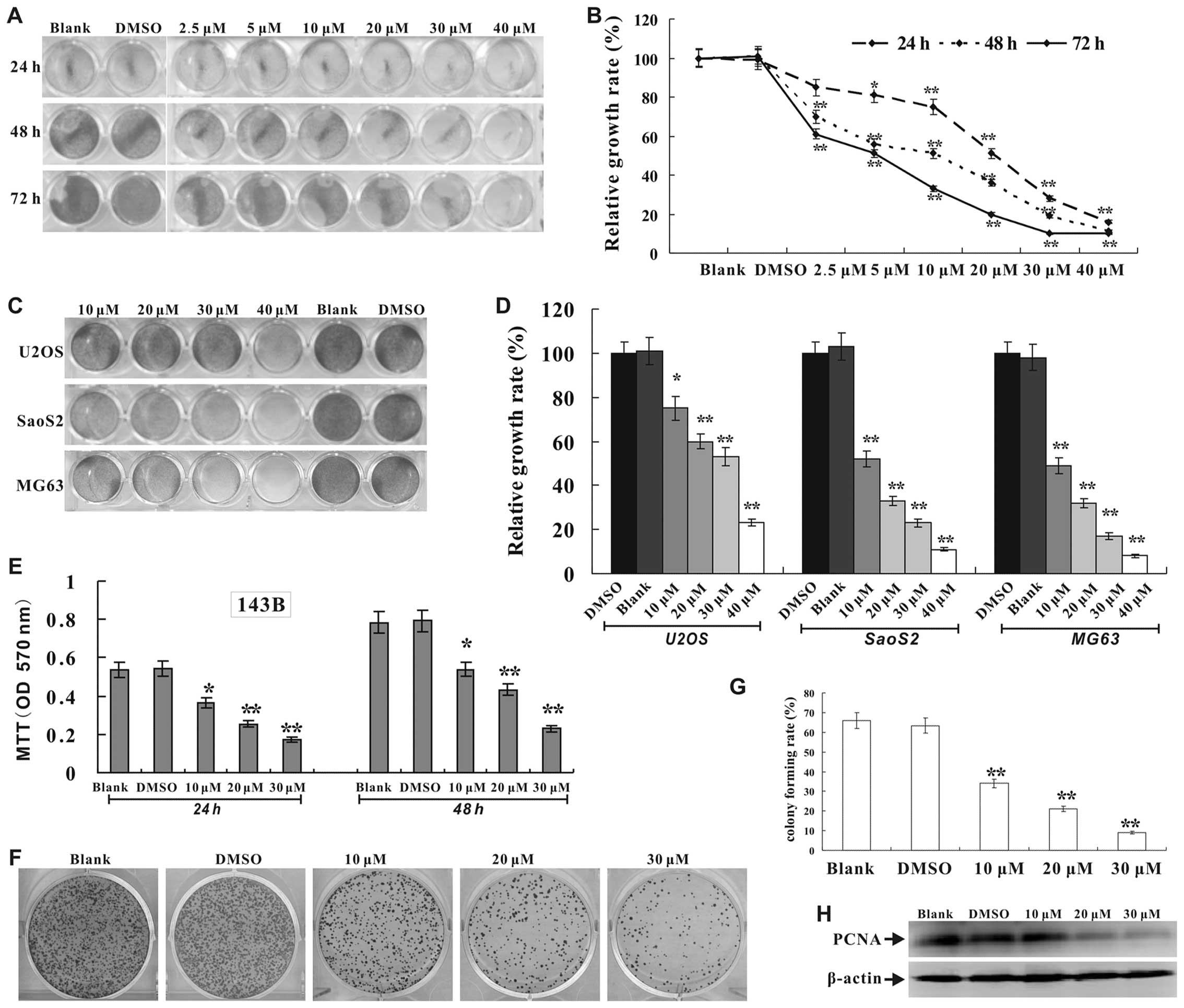
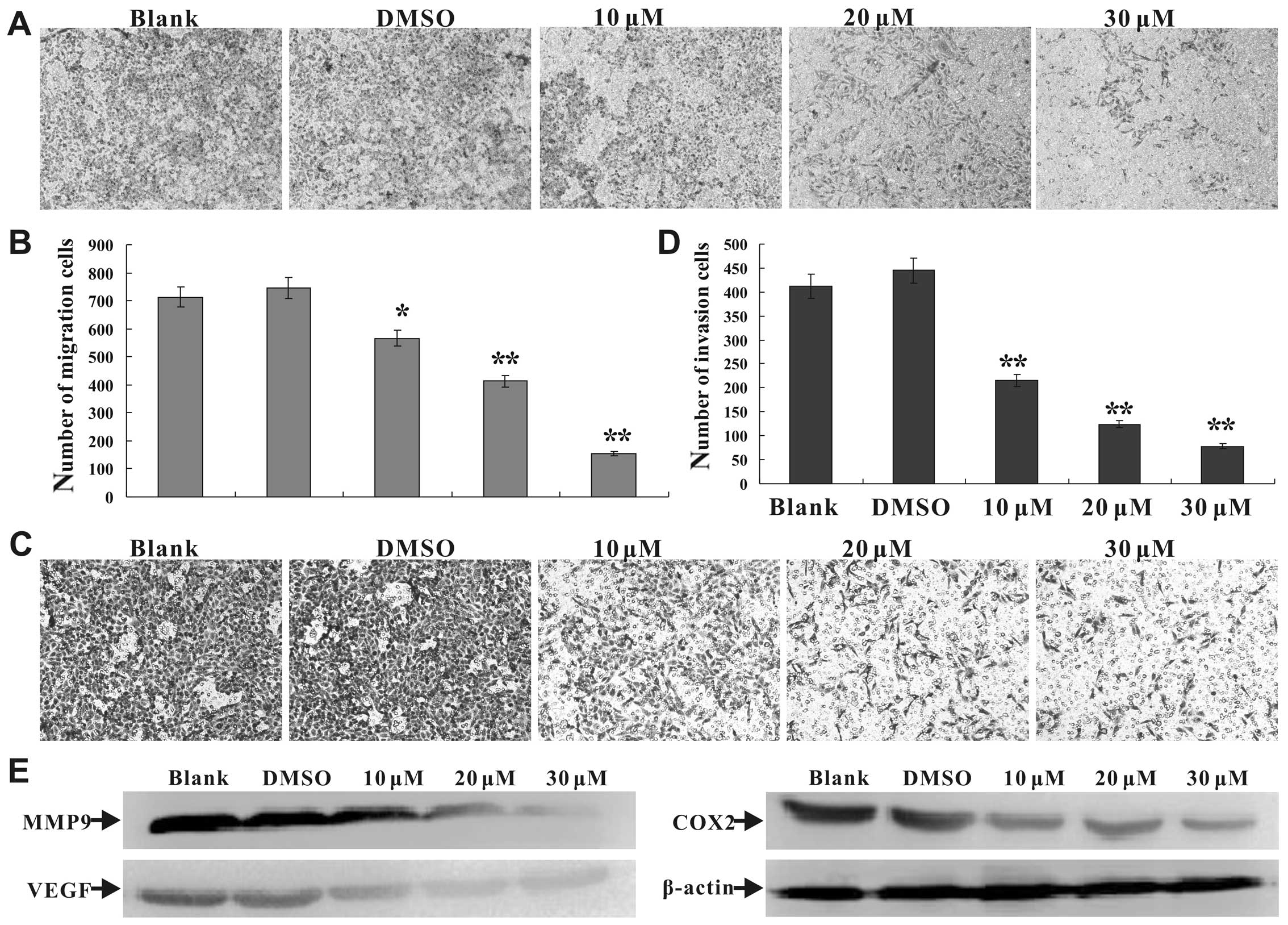
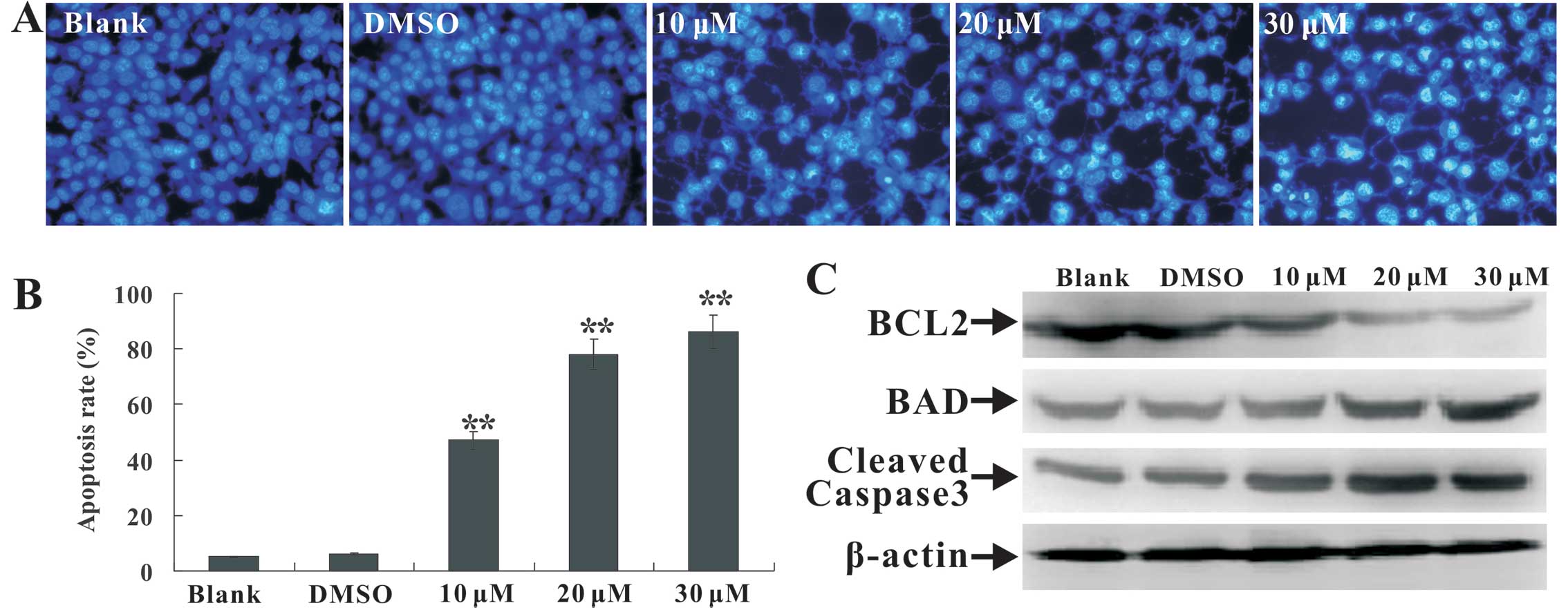
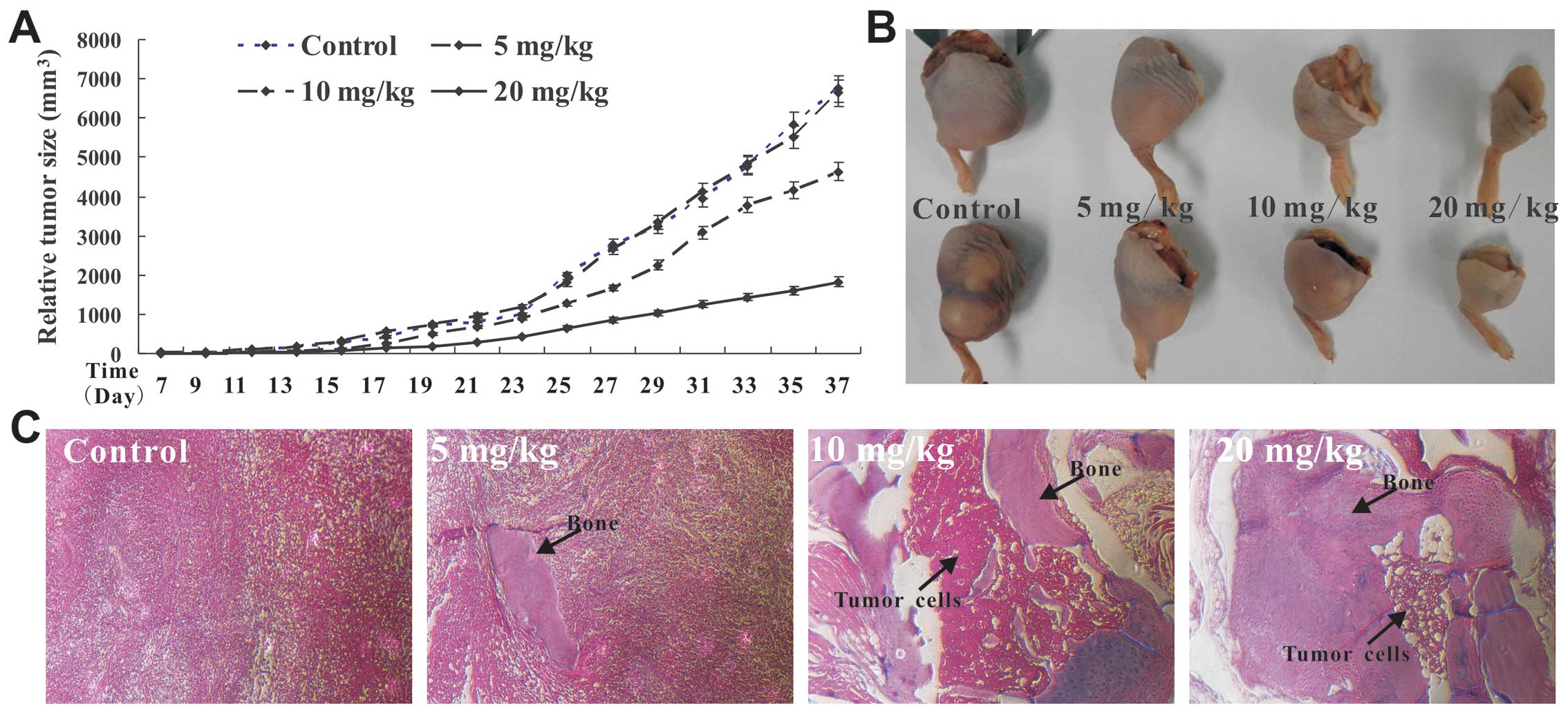
|
1
|
Tang N, Song WX, Luo J, Haydon RC and He
TC: Osteosarcoma development and stem cell differentiation. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 466:2114–2130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whelan JS: Osteosarcoma. Eur J Cancer.
33:1618–1619. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kager L, Zoubek A, Kastner U, et al: Skip
metastases in osteosarcoma: experience of the Cooperative
Osteosarcoma Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 24:1535–1541. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kager L, Zoubek A, Pötschger U, et al:
Primary metastatic osteosarcoma: presentation and outcome of
patients treated on neoadjuvant Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study
Group protocols. J Clin Oncol. 21:2011–2018. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Geller DS and Gorlick R: Osteosarcoma: a
review of diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies. Clin Adv
Hematol Oncol. 8:705–718. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ferrari S and Palmerini E: Adjuvant and
neoadjuvant combination chemotherapy for osteogenic sarcoma. Curr
Opin Oncol. 19:341–346. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ayerza MA, Farfalli GL, Aponte-Tinao L and
Muscolo DL: Does increased rate of limb-sparing surgery affect
survival in osteosarcoma? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 468:2854–2859.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Link MP, Goorin AM, Horowitz M, et al:
Adjuvant chemotherapy of high-grade osteosarcoma of the extremity.
Updated results of the Multi-Institutional Osteosarcoma Study. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 270:8–14. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bruland OS, Høifødt H, Saeter G, Smeland S
and Fodstad O: Hematogenous micrometastases in osteosarcoma
patients. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4666–4673. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cragg GM, Grothaus PG and Newman DJ:
Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents.
Chem Rev. 109:3012–3043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ji HF, Li XJ and Zhang HY: Natural
products and drug discovery. Can thousands of years of ancient
medical knowledge lead us to new and powerful drug combinations in
the fight against cancer and dementia? EMBO Rep. 10:194–200.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klayman DL: Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an
antimalarial drug from China. Science. 228:1049–1055. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
O’Neill PM and Posner GH: A medicinal
chemistry perspective on artemisinin and related endoperoxides. J
Med Chem. 47:2945–2964. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh NP and Lai H: Selective toxicity of
dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin toward human breast cancer
cells. Life Sci. 70:49–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen H, Sun B, Wang S, et al: Growth
inhibitory effects of dihydroartemisinin on pancreatic cancer
cells: involvement of cell cycle arrest and inactivation of nuclear
factor-κB. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:897–903. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He Q, Shi J, Shen XL, An J, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin upregulates death receptor 5 expression and
cooperates with TRAIL to induce apoptosis in human prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:819–824. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kanno S, Kurauchi K, Tomizawa A, Yomogida
S and Ishikawa M: Albumin modulates docosahexaenoic acid-induced
cytotoxicity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Toxicol
Lett. 200:154–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Efferth T: Molecular pharmacology and
pharmacogenomics of artemisinin and its derivatives in cancer
cells. Curr Drug Targets. 7:407–421. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ishiyama M, Tominaga H, Shiga M, Sasamoto
K, Ohkura Y and Ueno K: A combined assay of cell viability and in
vitro cytotoxicity with a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt,
neutral red and crystal violet. Biol Pharm Bull. 19:1518–1520.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Su Y, Luo X, He BC, et al: Establishment
and characterization of a new highly metastatic human osteosarcoma
cell line. Clin Exp Metastasis. 26:599–610. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu K, Yang Q, Mu Y, et al: Berberine
inhibits the proliferation of colon cancer cells by inactivating
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Oncol. 41:292–298. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haydon RC, Zhou L, Feng T, et al: Nuclear
receptor agonists as potential differentiation therapy agents for
human osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1288–1294. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park HR and Park YK: Expression of p53
protein, PCNA, and Ki-67 in osteosarcomas of bone. J Korean Med
Sci. 10:360–367. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Avnet S, Longhi A, Salerno M, et al:
Increased osteoclast activity is associated with aggressiveness of
osteosarcoma. Int J Oncol. 33:1231–1238. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee EJ, Choi EM, Kim SR, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes cell proliferation, migration and
invasion in U2OS human osteosarcoma cells. Exp Mol Med. 39:469–476.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kaya M, Wada T, Nagoya S, Sasaki M,
Matsumura T and Yamashita T: The level of vascular endothelial
growth factor as a predictor of a poor prognosis in osteosarcoma. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 91:784–788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu Y and Yagi T: Apoptosis of human tumor
cells by chemotherapeutic anthracyclines is enhanced by Bax
overexpression. J Radiat Res. 40:263–272. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seki K, Yoshikawa H, Shiiki K, Hamada Y,
Akamatsu N and Tasaka K: Cisplatin (CDDP) specifically induces
apoptosis via sequential activation of caspase-8, -3 and -6 in
osteosarcoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 45:199–206. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lamoureux F, Richard P, Wittrant Y, et al:
Therapeutic relevance of osteoprotegerin gene therapy in
osteosarcoma: blockade of the vicious cycle between tumor cell
proliferation and bone resorption. Cancer Res. 67:7308–7318. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Noori S, Hassan ZM, Taghikhani M, Rezaei B
and Habibi Z: Dihydroartemisinin can inhibit calmodulin,
calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase activity and stimulate
cellular immune responses. Int Immunopharmacol. 10:213–217. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhao YG, Wang Y, Guo Z, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin ameliorates inflammatory disease by its
reciprocal effects on Th and regulatory T cell function via
modulating the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Immunol.
189:4417–4425. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Finaurini S, Basilico N, Corbett Y, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the human erythroid cell
differentiation by altering the cell cycle. Toxicology. 300:57–66.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ba Q, Zhou N, Duan J, et al:
Dihydroartemisinin exerts its anticancer activity through depleting
cellular iron via transferrin receptor-1. PLoS One. 7:e427032012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Firestone GL and Sundar SN: Anticancer
activities of artemisinin and its bioactive derivatives. Expert Rev
Mol Med. 11:e322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Kempen LC and Coussens LM: MMP9
potentiates pulmonary metastasis formation. Cancer Cell. 2:251–252.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B and
Szmitkowski M: The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and
their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 50:12–19. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Claesson-Welsh L and Welsh M: VEGFA and
tumour angiogenesis. J Intern Med. 273:114–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin M, Lin HZ, Ma SP, Ji P, Xie D and Yu
JX: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A and -C: expression and
correlations with lymphatic metastasis and prognosis in colorectal
cancer. Med Oncol. 28:151–158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nathanson SD: Insights into the mechanisms
of lymph node metastasis. Cancer. 98:413–423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69:4–10. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Robles Irizarry L, Hambardzumyan D, Nakano
I, Gladson CL and Ahluwalia MS: Therapeutic targeting of VEGF in
the treatment of glioblastoma. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
16:973–984. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mao XY, Wang XG, Lv XJ, Xu L and Han CB:
COX-2 expression in gastric cancer and its relationship with
angiogenesis using tissue microarray. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3466–3471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Soumaoro LT, Uetake H, Takagi Y, et al:
Coexpression of VEGF-C and Cox-2 in human colorectal cancer and its
association with lymph node metastasis. Dis Colon Rectum.
49:392–398. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rodriguez NI, Hoots WK, Koshkina NV, et
al: COX-2 expression correlates with survival in patients with
osteosarcoma lung metastases. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 30:507–512.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006.
|
|
47
|
Luu HH, Zhang R, Haydon RC, et al:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway as a novel cancer drug target. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 4:653–671. 2004.
|
|
48
|
Haydon RC, Deyrup A, Ishikawa A, et al:
Cytoplasmic and/or nuclear accumulation of the β-catenin protein is
a frequent event in human osteosarcoma. Int J Cancer. 102:338–342.
2002.
|
|
49
|
Iwaya K, Ogawa H, Kuroda M, Izumi M,
Ishida T and Mukai K: Cytoplasmic and/or nuclear staining of
beta-catenin is associated with lung metastasis. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 20:525–529. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luo J, Chen J, Deng ZL, et al: Wnt
signaling and human diseases: what are the therapeutic
implications? Lab Invest. 87:97–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jope RS, Yuskaitis CJ and Beurel E:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): inflammation, diseases, and
therapeutics. Neurochem Res. 32:577–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao Y, Yang ZQ, Wang Y, et al:
Dishevelled-1 and dishevelled-3 affect cell invasion mainly through
canonical and noncanonical Wnt pathway, respectively, and associate
with poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Mol Carcinog.
49:760–770. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wei Q, Zhao Y, Yang ZQ, et al: Dishevelled
family proteins are expressed in non-small cell lung cancer and
function differentially on tumor progression. Lung Cancer.
62:181–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kwan HT, Chan DW, Cai PC, et al: AMPK
activators suppress cervical cancer cell growth through inhibition
of DVL3 mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling activity. PLoS One.
8:e535972013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Uematsu K, Seki N, Seto T, et al:
Targeting the Wnt signaling pathway with dishevelled and cisplatin
synergistically suppresses mesothelioma cell growth. Anticancer
Res. 27:4239–4242. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Uematsu K, He B, You L, Xu Z, McCormick F
and Jablons DM: Activation of the Wnt pathway in non small cell
lung cancer: evidence of dishevelled overexpression. Oncogene.
22:7218–7221. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|