|
1
|
Dworkin AM, Huang TH and Toland AE:
Epigenetic alterations in the breast: implications for breast
cancer detection, prognosis and treatment. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:165–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hinshelwood RA and Clark SJ: Breast cancer
epigenetics: normal human mammary epithelial cells as a model
system. J Mol Med. 86:1315–1328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Widschwendter M and Jones PA: DNA
methylation and breast carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 21:5462–5482.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pogribny IP and Beland FA: DNA
hypomethylation in the origin and pathogenesis of human diseases.
Cell Mil Life Sci. 66:2249–2261. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balch C, Montgomery JS, Paik HI, et al:
New anti-cancer strategies: epigenetic therapies and biomarkers.
Front Biosci. 10:1897–1931. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wali A: FHIT: Doubts are clear now. Sci
World J. 10:1142–1151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ingvarsson S: FHIT alterations in breast
cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 11:361–366. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ingvarsson S, Sigbjornsdottir BI, Huiping
C, Jonasson JG and Agnarsson BA: Alterations of the FHIT gene in
breast cancer: association with tumour progression and patient
survival. Cancer Detect Prev. 25:292–298. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ahmadian M, Wistuba II, Fong KM, et al:
Analysis of the FHIT gene and FRA3B region in sporadic breast
cancer, preneoplastic lesions, and familial breast cancer probands.
Cancer Res. 57:3664–3668. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Negrini M, Monaco G, Vorchovsky I, et al:
The FHIT gene at 3p14.2 is abnormal in breast carcinomas. Cancer
Res. 56:3173–3179. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zöchbauer-Müller S, Fong KM, Maitra A, et
al: 5′ CpG island methylation of the FHIT gene is correlated
with loss of gene expression in lung and breast cancer. Cancer Res.
61:3581–3585. 2001.
|
|
12
|
Hayashi S, Tanimoto K, Hajiro-Nakanishi K,
et al: Abnormal FHIT transcripts in human breast carcinomas: a
clinicopathological and epidemiological analysis of 61 Japanese
cases. Cancer Res. 57:1981–1985. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ingvarsson S, Agnarsson BA,
Sigbjornsdottir BI, et al: Reduced Fhit expression in sporadic and
BRCA2-linked breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 59:2682–2689.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gatalica Z, Lele SM, Rampy BA and Norris
BA: The expression of Fhit protein is related inversely to disease
progression in patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer.
88:1378–1383. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Naqvi RA, Hussain A, Raish M, et al:
Specific 5′ CpG island methylation signatures of FHIT and
p16 genes and their potential diagnostic relevance in Indian
breast cancer patients. DNA Cell Biol. 27:517–525. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Maruyama R, Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, et al:
Aberrant promoter methylation profile of bladder cancer and its
relationship to clinicopathological features. Cancer Res.
61:8659–8663. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maruyama R, Toyooka S, Toyooka KO, et al:
Aberrant promoter methylation profile of prostate cancers and its
relationship to clinicopathological features. Clin Cancer Res.
8:514–519. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Virmani AK, Muller C, Rathi A,
Zoechbauer-Mueller S, Mathis M and Gazdar AF: Aberrant methylation
during cervical carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 7:584–589.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim H, Kwon YM, Kim JS, et al:
Tumor-specific methylation in bronchial lavage for early detection
on non-small cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:2363–2370. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raish M, Dhillon VS, Ahmad A, et al:
Promoter hypermethylation in tumor suppressing genes p16 and FHIT
and their relationship with estrogen receptor and progesterone
receptor status in breast cancer patients from Northern India.
Trans Oncol. 2:264–270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Syeed N, Husain SA, Sameer AS, Chowdhri NA
and Siddiqi MA: Mutational and promoter hypermethylation status of
FHIT gene in breast cancer patients of Kashmir. Mutation
Res. 707:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Q, Nakamura M, Nakamura Y, et al:
Two-hit inactivation of FHIT by loss of heterozygosity and
hypermethylation in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2890–2893.
2002.
|
|
23
|
Fiegl H, Millinger S, Goebel G, et al:
Breast cancer DNA methylation profiles in cancer cells and tumor
stroma: association with HER-2/neu status in primary breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:29–33. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bianchi F, Magnifico A, Olgiati C, et al:
FHIT-proteasome degradation caused by mitogenic stimulation of the
EGF receptor family in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:18981–18986. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, et al:
Strategies for subtypes - dealing with the diversity of breast
cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus
on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol.
22:1736–1747. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Menard S, Tagliabue E, Campiglio M and
Pupa SM: Role of HER2 gene overexpression in breast carcinoma. J
Cell Physiol. 182:150–162. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pekarsky Y, Garrison PN, Palamarchuk A, et
al: Fhit is a physiological target of the protein kinase Src. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:3775–3779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Campan M, Weisenberger DJ and Laird PW:
DNA methylation profiles of female steroid hormone-driven human
malignancies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 310:141–178.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bianchi F, Tagliabue E, Ménard S and
Campiglio M: Fhit expression protects against HER2-driven breast
tumor development. Cell Cycle. 6:643–646. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Campiglio M, Pekarsky Y, Menard S,
Tagliabue E, Pilotti S and Croce CM: FHIT loss of function in human
primary breast cancer correlates with advanced stage of the
disease. Cancer Res. 59:3866–3869. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang Q, Yoshimura G, Suzuma T, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of fragile histidine triad
transcription protein expression in breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer
Res. 7:3869–3873. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Arun B, Kilic G, Yen C, et al: Loss of
FHIT expression in breast cancer is correlated with poor prognostic
markers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:1681–1685. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Key TJ and Pike MC: The role of oestrogens
and progestagens in the epidemiology and prevention of breast
cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 24:29–43. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Creighton CJ, Kent Osborne C, van de
Vijver MJ, et al: Molecular profiles of progesterone receptor loss
in human breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 114:287–299. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li L, Lee KM, Ha W, et al: Estrogen and
progesterone receptor status affect genome-wide DNA methylation
profile in breast cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 19:4273–4277. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Widschwendter M, Siegmund KD, Muller HM,
et al: Association of breast cancer DNA methylation profiles with
hormone receptor status and response to tamoxifen. Cancer Res.
64:3807–3813. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
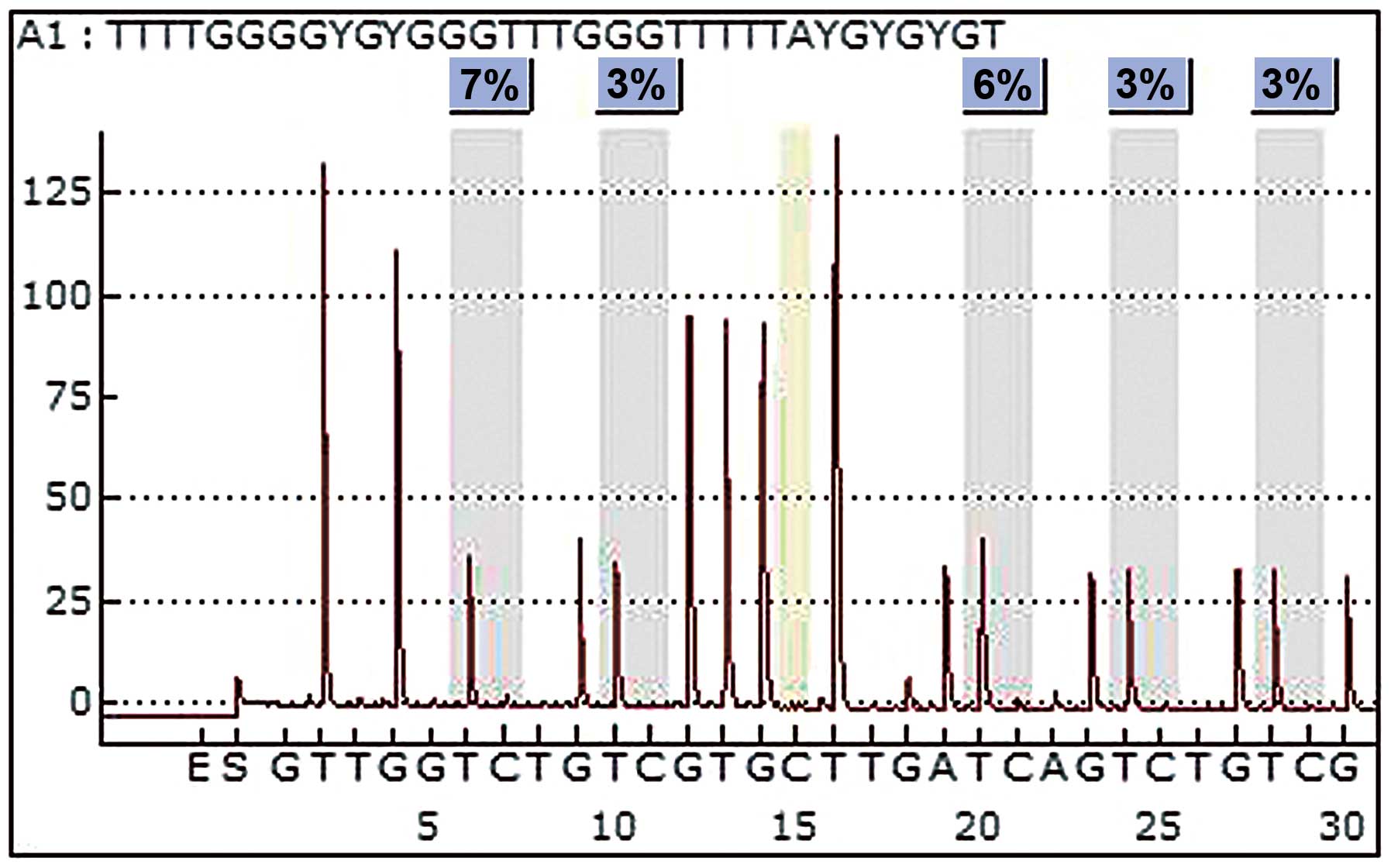
Tost J and Gut IG: Analysis of
gene-specific DNA methylation patterns by pyrosequencing
technology. Methods Mol Biol. 373:89–102. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|