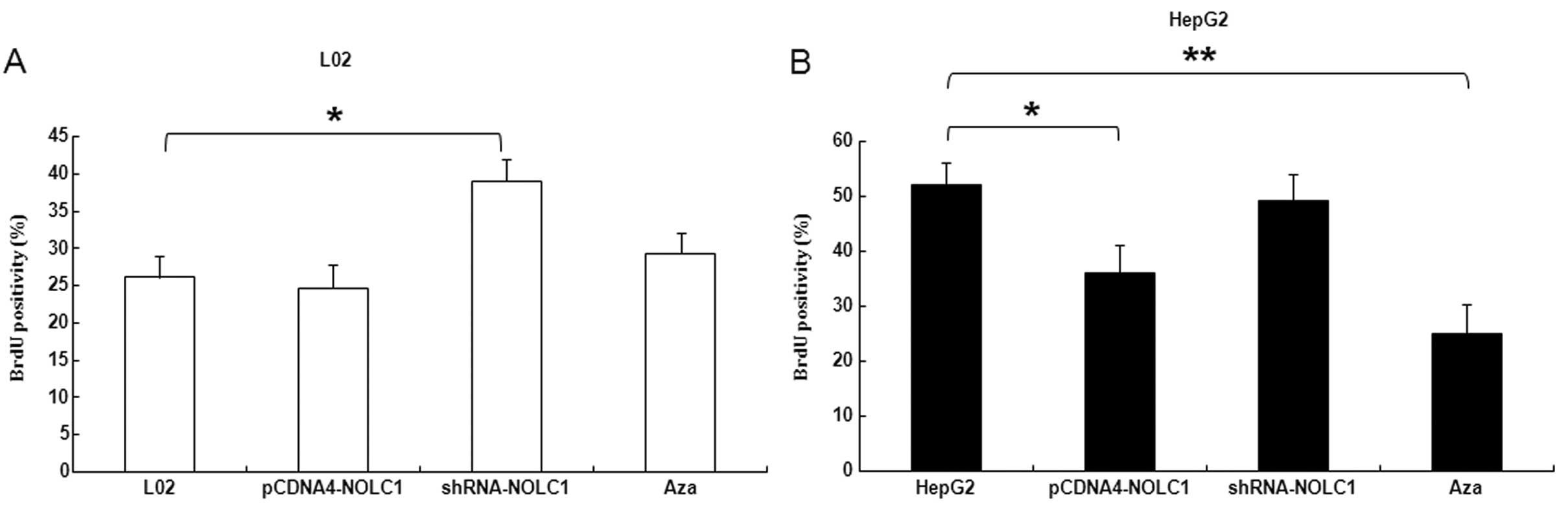
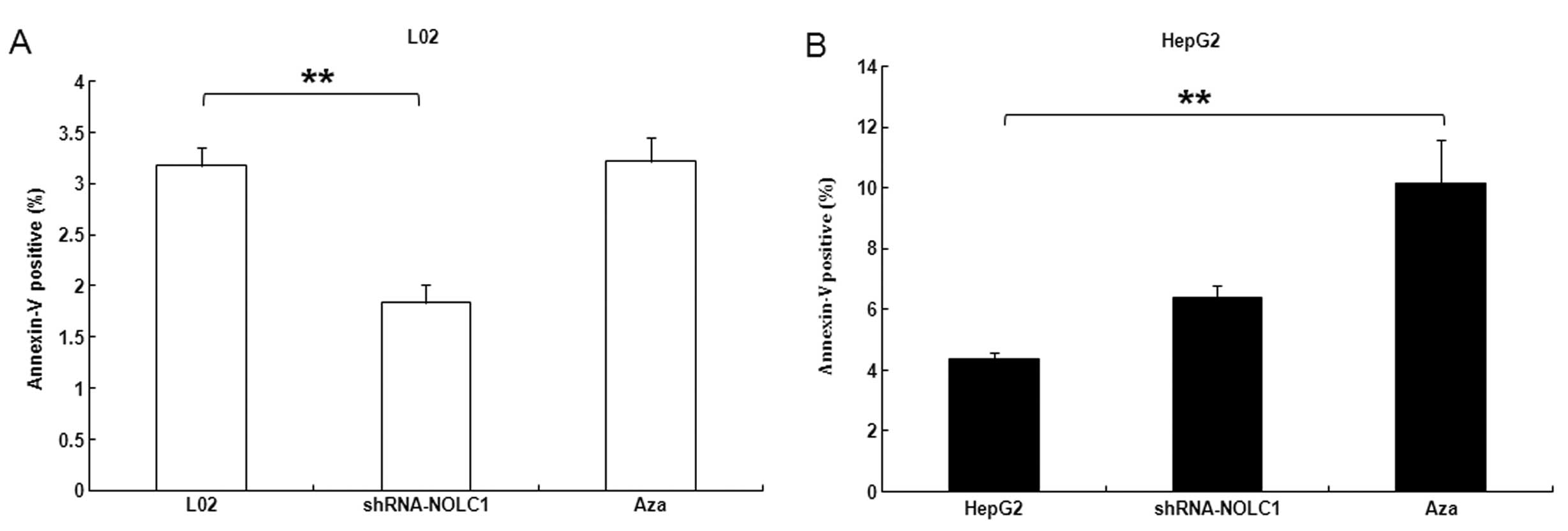
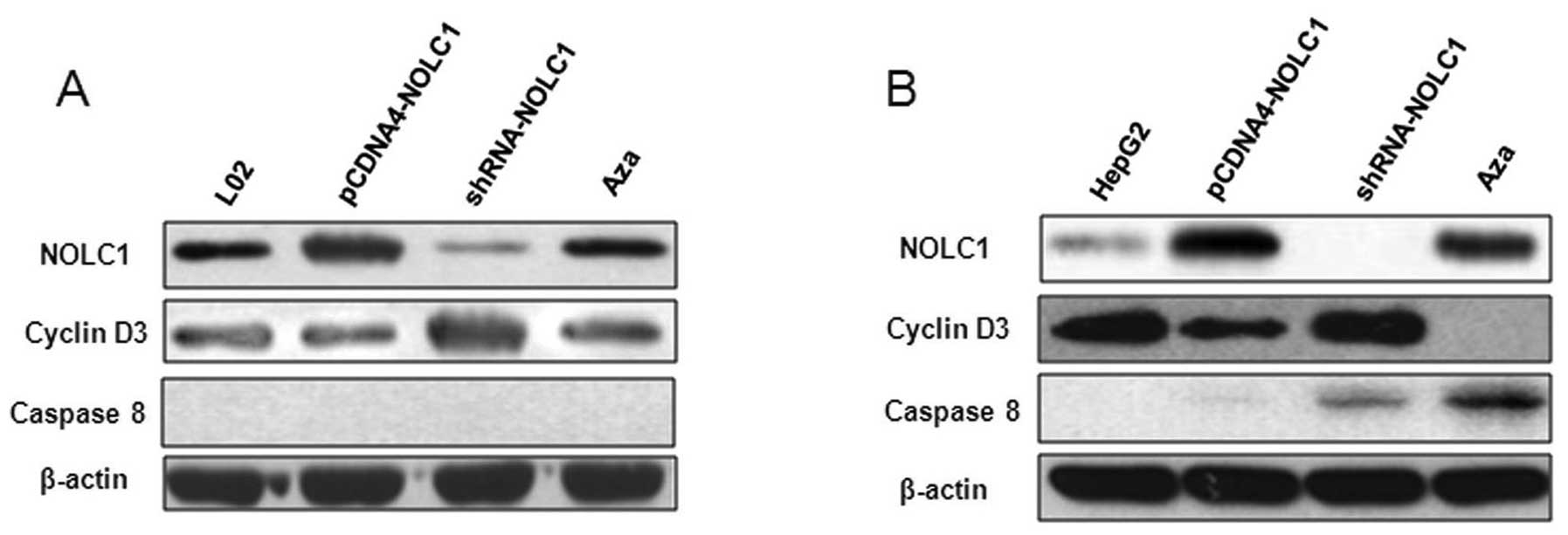
|
1
|
Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC and Chien CS:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study
of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 2:1129–1133. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Estimating the world cancer burden: Globocan 2000. Int J Cancer.
94:153–156. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tischoff I and Tannapfe A: DNA methylation
in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 14:1741–1748.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baylin SB and Herman JG: DNA
hypermethylation in tumorigenesis: epigenetics joins genetics.
Trends Genet. 16:168–174. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Riggs AD and Pfeifer GP: X-chromosome
inactivation and cell memory. Trends Genet. 8:169–174. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang Q, Cheng J, Liu Y, Hong Y, Wang JJ
and Zhang SL: Cloning and identification of NS5ATP2 gene and
its spliced variant transactivated by hepatitis C virus
non-structural protein 5A. World J Gastroenterol. 10:1735–1739.
2004.
|
|
7
|
Meier UT: Comparison of the rat nucleolar
protein nopp140 with its yeast homolog SRP40. Differential
phosphorylation in vertebrates and yeast. J Biol Chem.
271:19376–19384. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meier UT and Blobel G: Nopp140 shuttles on
tracks between nucleolus and cytoplasm. Cell. 70:127–138. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao XS, Wang Q, Li W, Yang B, Song H, Ju
W, Liu SA and Cheng J: Identification of nucleolar and coiled-body
phosphoprotein 1 (NOLC1) minimal promoter regulated by NF-κB and
CREB. BMB Rep. 44:70–75. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meier UT and Blobel G: A nuclear
localization signal binding protein in the nucleolus. J Cell Biol.
111:2235–2245. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miau LH, Chang CJ, Tsai WH and Lee SC:
Identification and characterization of a nucleolar phosphoprotein.
Nopp140, as a transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 17:230–239.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hwang YC, Lu TY, Huang DY, Kuo YS, Kao CF,
Yeh NH, Wu HC and Lin CT: NOLC1, an enhancer of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma progression, is essential for TP53 to regulate MDM2
expression. Am J Pathol. 175:342–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pai CY, Chen HK, Sheu HL and Yeh NH:
Cell-cycle-dependent alterations of a highly phosphorylated
nucleolar protein p130 are associated with nucleologenesis. J Cell
Sci. 108:1911–1920. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin CT, Lin CR, Tan GK, Chen W, Dee AN and
Chan WY: The mechanism of Epstein-Barr virus infection in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol. 150:1745–1756.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu HC and Lin CT: Association of
heterotrimeric GTP binding regulatory protein (Go) with mitosis.
Lab Invest. 71:175–181. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang M and Milner J: Bcl-2 constitutively
suppresses p53-dependent apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells.
Genes Dev. 17:832–837. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jiang M, Rubbi CP and Milner J: Gel-based
application of siRNA to human epithelial cancer cells induces
RNAi-dependent apoptosis. Oligonucleotides. 14:239–248. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim YK, Lee WK, Jin YN, Lee KJ, Jeon HS
and Yu YG: Doxorubicin binds to un-phosphorylated form of hNopp140
and reduces protein kinase CK2-dependent phosphorylation of
hNopp140. J Biochem Mol Biol. 39:774–781. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamamoto R, Furukawa Y, Morita M, Iimura
Y, Silva FP, Li M, Yagyu R and Nakamura Y: SMYD3 encodes a histone
methyltransferase involved in the proliferation of cancer cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 6:731–740. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ford J, Jiang M and Milner J:
Cancer-specific functions of SIRT1 enable human epithelial cancer
cell growth and survival. Cancer Res. 65:10457–10463. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li H, Bergeron L, Cryns V, Pasternack MS,
Zhu H, Shi L, Greenberg A and Yuan J: Activation of caspase-2 in
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 272:21010–21017. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Zhao LJ, Tan YX, Ren H and Qi ZT:
MiR-138 induces cell cycle arrest by targeting cyclin D3 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 33:1113–1120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu HY, Dong HJ, Robertson K and Liu C:
DNA methylation suppresses expression of the urea cycle enzyme
carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 178:652–661. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Herath NI, Leggett BA and MacDonald GA:
Review of genetic and epigenetic alterations in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:15–21. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li HP, Leu YW and Chang YS: Epigenetic
changes in virus-associated human cancers. Cell Res. 15:262–271.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Herceg Z: Epigenetics and cancer: towards
an evaluation of the impact of environmental and dietary factors.
Mutagenesis. 22:91–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Adrien LR, Schlecht NF, Kawachi N, Smith
RV, Brandwein-Gensler M, Massimi A, Chen S, Prystowsky MB, Childs G
and Belbin TJ: Classification of DNA methylation patterns in tumor
cell genomes using a CpG island microarray. Cytogenet Genome Res.
114:16–23. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lund AH and van Lohuizen M: Epigenetics
and cancer. Genes Dev. 18:2315–2335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sparmann A and van Lohuizen M: Polycomb
silencers control cell fate, development and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 6:846–856. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lo SJ, Lee CC and Lai HJ: The nucleolus:
reviewing oldies to have new understandings. Cell Res. 16:530–538.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Esteller M, Corn PG, Baylin SB and Herman
JG: A gene hypermethylation profile of human cancer. Cancer Res.
61:3225–3229. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin J, Jinno S and Okayama H: Cdk6-cyclin
D3 complex evades inhibition by inhibitor proteins and uniquely
controls cell’s proliferation competence. Oncogene. 20:2000–2009.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rao CN, Liu YY, Peavey CL and Woodley DT:
Novel extracellular matrix-associated serine proteinase inhibitors
from human skin fibroblasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 317:311–314.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sprecher CA, Kisiel W, Mathewes S and
Foster DC: Molecular cloning, expression, and partial
characterization of a second human tissue-factor-pathway inhibitor.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:3353–3357. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Rao CN, Cook B, Liu Y, Chilukuri K, Stack
MS, Foster DC, Kisiel W and Woodley DT: HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell
matrix degradation and invasion are inhibited by the
matrix-associated serine protease inhibitor TFPI-2/33 kDa MSPI. Int
J Cancer. 76:749–756. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rao CN, Mohanam S, Puppala A and Rao JS:
Regulation of ProMMP-1 and ProMMP-3 activation by tissue factor
pathway inhibitor-2/matrix-associated serine protease inhibitor.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 255:94–98. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wong CM, Ng YL, Lee JM, Wong CC, Cheung
OF, Chan CY, Tung EK, Ching YP and Ng IO: Tissue factor pathway
inhibitor-2 as a frequently silenced tumor suppressor gene in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 45:1129–1138. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim H, Jen J, Vogelstein B and Hamilton
SR: Clinical and pathological characteristics of sporadic
colorectal carcinomas with DNA replication errors in microsatellite
sequences. Am J Pathol. 145:148–156. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oliveira C, Seruca R, Seixas M and
Sobrinho-Simões M: The clinicopathological features of gastric
carcinomas with microsatellite instability may be mediated by
mutations of different ‘target genes’: a study of the TGFβ
RII, IGFII R, and BAX genes. Am J Pathol.
153:1211–1219. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Park JH, Cho SB, Lee WS, Park CH, Joo YE,
Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS, Lee JH and Kim SJ: Methylation pattern of
DNA repair genes and microsatellite instability in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Korean J Gastroenterol. 48:327–336. 2006.(In
Korean).
|
|
41
|
Matsukura S, Soejima H, Nakagawachi T,
Yakushiji H, Ogawa A, Fukuhara M, Miyazaki K, Nakabeppu Y,
Sekiguchi M and Mukai T: CpG methylation of MGMT and hMLH1 promoter
in hepatocellular carcinoma associated with hepatitis viral
infection. Br J Cancer. 88:521–529. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang L, Bani-Hani A, Montoya DP, Roche PC,
Thibodeau SN, Burgart LJ and Roberts LR: hMLH1 and hMSH2 expression
in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 19:567–570.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|