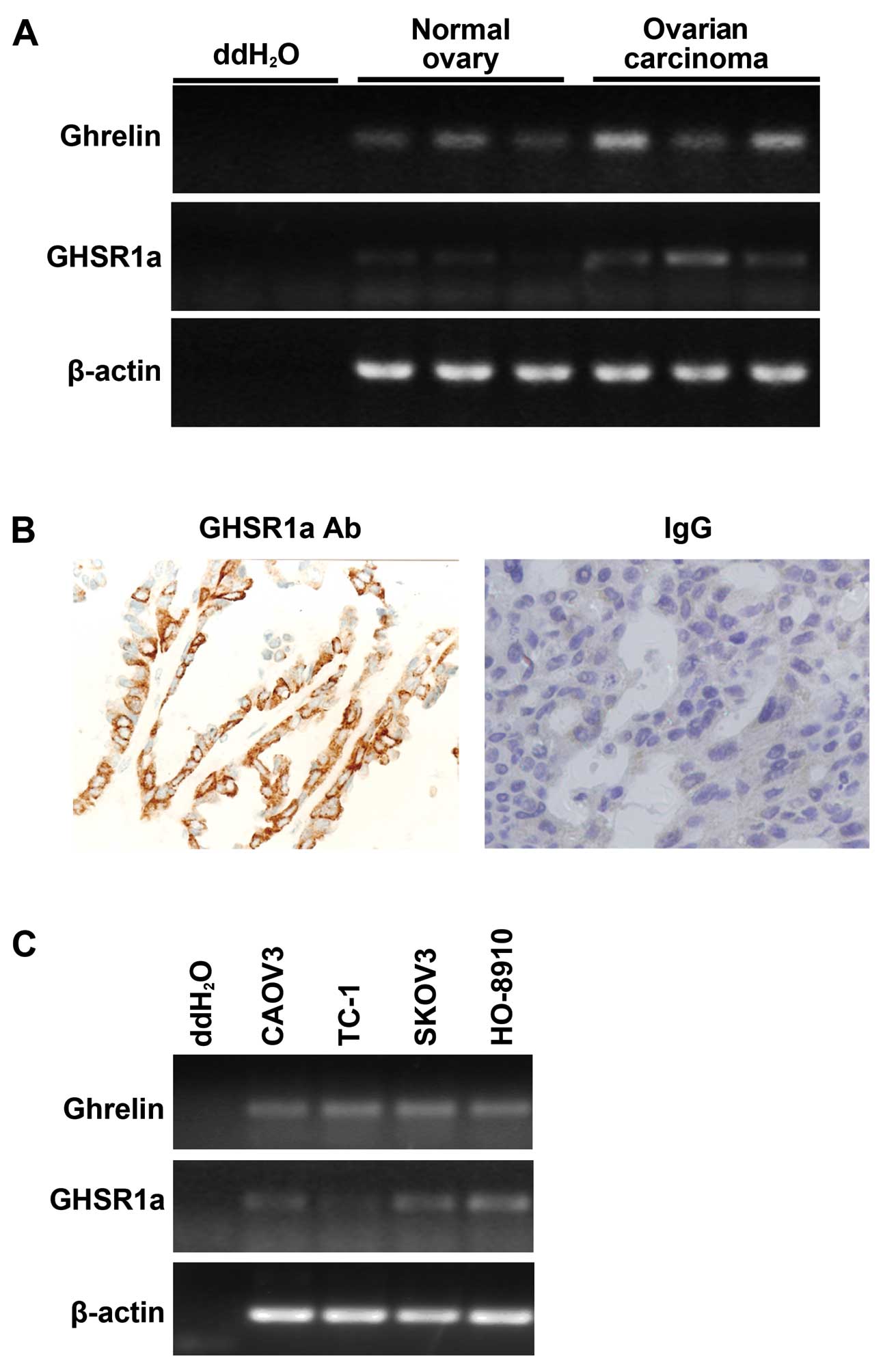
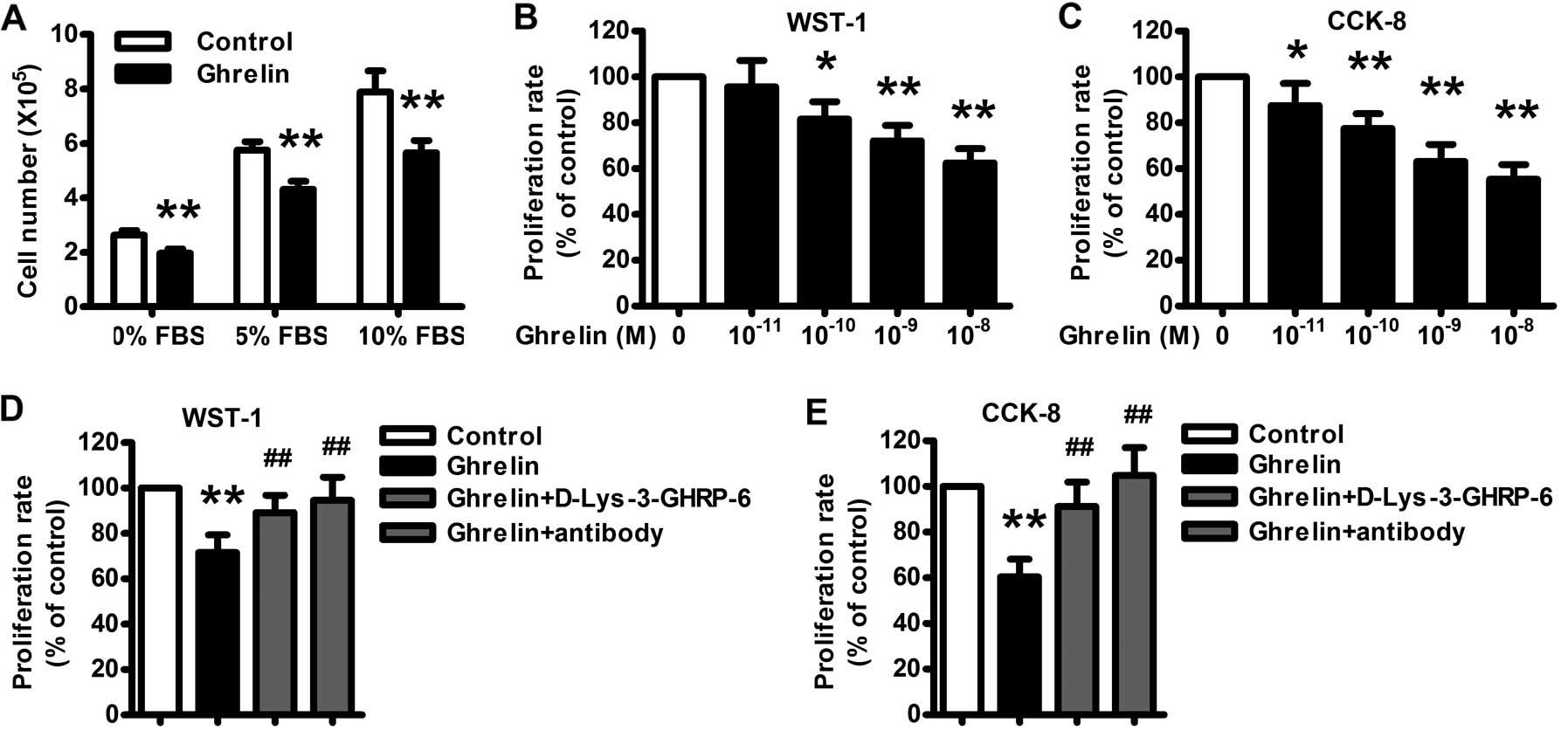
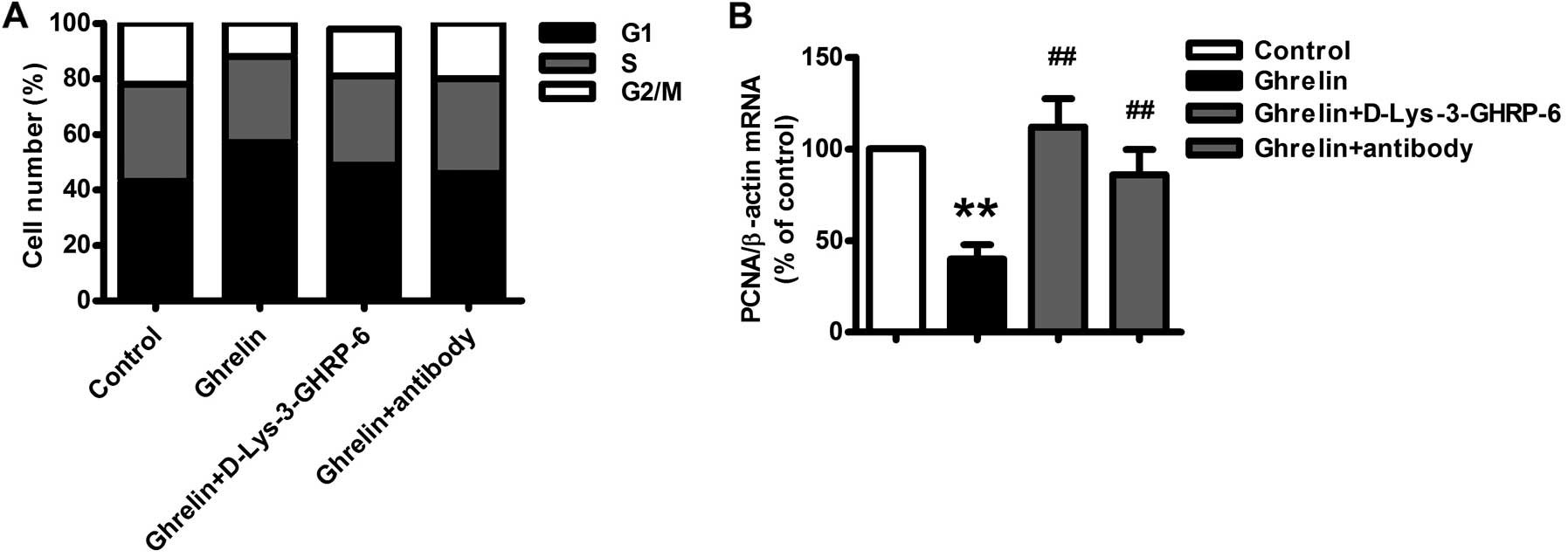
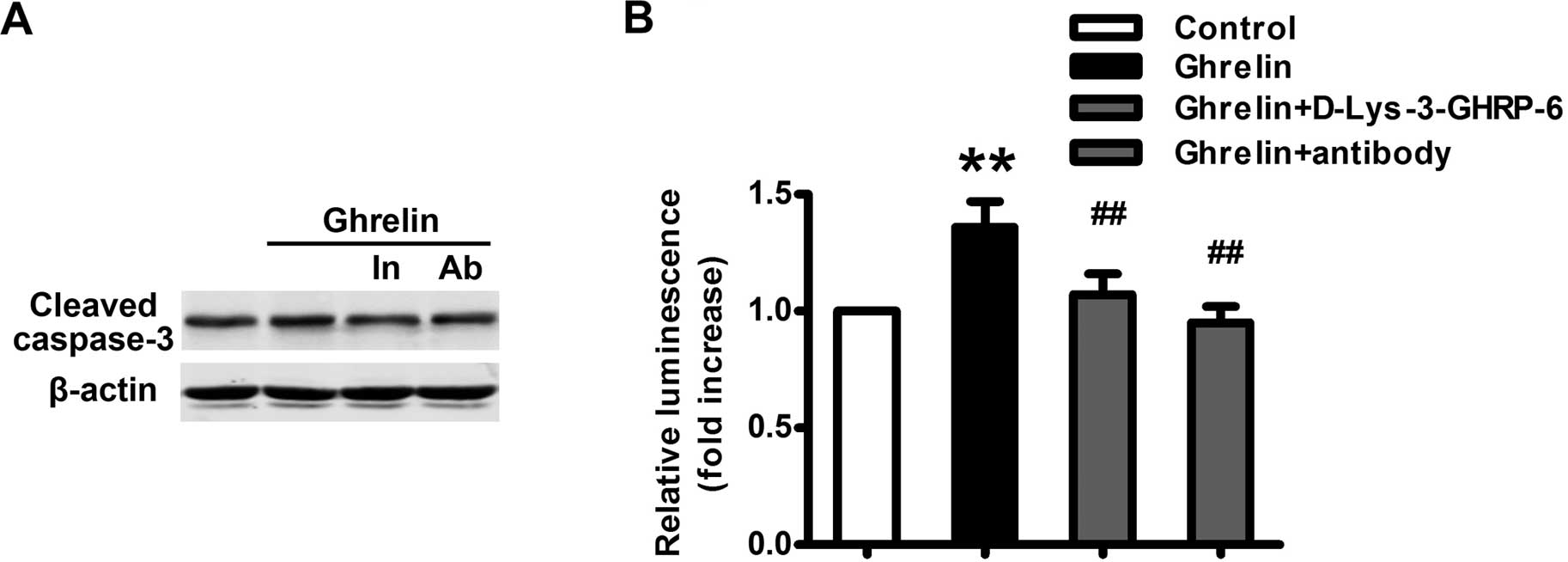
|
1
|
Billottet C, Janji B, Thiery JP and
Jouanneau J: Rapid tumor development and potent vascularization are
independent events in carcinoma producing FGF-1 or FGF-2. Oncogene.
21:8128–8139. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Di Blasio AM, Cremonesi L, Viganó P, et
al: Basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptor messenger
ribonucleic acids are expressed in human ovarian epithelial
neoplasms. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 169:1517–1523. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chopin L, Walpole C, Seim I, et al:
Ghrelin and cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 340:65–69. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M,
Matsuo H and Kangawa K: Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing
acylated peptide from stomach. Nature. 402:656–660. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kojima M and Kangawa K: Ghrelin: structure
and function. Physiol Rev. 85:495–522. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Smith RG, Leonard R, Bailey AR, et al:
Growth hormone secretagogue receptor family members and ligands.
Endocrine. 14:9–14. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Majchrzak K, Szyszko K, Pawlowski KM,
Motyl T and Król M: A role of ghrelin in cancerogenesis. Pol J Vet
Sci. 15:189–197. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang W, Lin TR, Hu Y, et al: Ghrelin
stimulates neurogenesis in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. J
Physiol. 559:729–737. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SW, Her SJ, Park SJ, et al: Ghrelin
stimulates proliferation and differentiation and inhibits apoptosis
in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Bone. 37:359–369. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Vriese C and Delporte C: Autocrine
proliferative effect of ghrelin on leukemic HL-60 and THP-1 cells.
J Endocrinol. 192:199–205. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Waseem T, Javaid-Ur-Rehman, Ahmad F, Azam
M and Qureshi MA: Role of ghrelin axis in colorectal cancer: a
novel association. Peptides. 29:1369–1376. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ghè C, Cassoni P, Catapano F, et al: The
antiproliferative effect of synthetic peptidyl GH secretagogues in
human CALU-1 lung carcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 143:484–491.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, et al:
The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its
receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 87:29882002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gomez-Pinillos A and Ferrari AC: mTOR
signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. Hematol
Oncol Clin North Am. 26:483–505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lynch CJ: Role of leucine in the
regulation of mTOR by amino acids: revelations from
structure-activity studies. J Nutr. 131:861S–865S. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rosenfeldt MT and Ryan KM: The multiple
roles of autophagy in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:955–963. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mah LY and Ryan KM: Autophagy and cancer.
Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:a0088212012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gaytan F, Morales C, Barreiro ML, et al:
Expression of growth hormone secretagogue receptor type 1a, the
functional ghrelin receptor, in human ovarian surface epithelium,
mullerian duct derivatives, and ovarian tumors. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 90:1798–1804. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Markowska A, Ziółkowska A,
Jaszczyńska-Nowinka K, Madry R and Malendowicz LK: Elevated blood
plasma concentrations of active ghrelin and obestatin in benign
ovarian neoplasms and ovarian cancers. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
30:518–522. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gutierrez JA, Solenberg PJ, Perkins DR, et
al: Ghrelin octanoylation mediated by an orphan lipid transferase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:6320–6325. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang J, Brown MS, Liang G, Grishin NV and
Goldstein JL: Identification of the acyltransferase that
octanoylates ghrelin, an appetite-stimulating peptide hormone.
Cell. 132:387–396. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lim CT, Kola B, Grossman A and Korbonits
M: The expression of ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) in human
tissues. Endocr J. 58:707–710. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang W, Chai B, Li JY, Wang H and
Mulholland MW: Effect of des-acyl ghrelin on adiposity and glucose
metabolism. Endocrinology. 149:4710–4716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H and Kangawa
K: Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: two major forms of rat ghrelin
peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
279:909–913. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Inoki K, Corradetti MN and Guan KL:
Dysregulation of the TSC-mTOR pathway in human disease. Nat Genet.
37:19–24. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang Q and Guan KL: Expanding mTOR
signaling. Cell Res. 17:666–681. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
LoRusso PM: Mammalian target of rapamycin
as a rational therapeutic target for breast cancer treatment.
Oncology. 84:43–56. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bergmann A and Steller H: Apoptosis, stem
cells, and tissue regeneration. Sci Signal. 3:re82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Meijer AJ: Amino acids as regulators and
components of nonproteinogenic pathways. J Nutr. 133:2057S–2062S.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crighton D, Wilkinson S, O’Prey J, et al:
DRAM, a p53-induced modulator of autophagy, is critical for
apoptosis. Cell. 126:121–134. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang H, Bosch-Marce M, Shimoda LA, et al:
Mitochondrial autophagy is an HIF-1-dependent adaptive metabolic
response to hypoxia. J Biol Chem. 283:10892–10903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM and Kim DH:
mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett. 584:1287–1295. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang YY, Juhász G, Goraksha-Hicks P, et
al: Nutrient-dependent regulation of autophagy through the target
of rapamycin pathway. Biochem Soc Trans. 37:232–236. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|