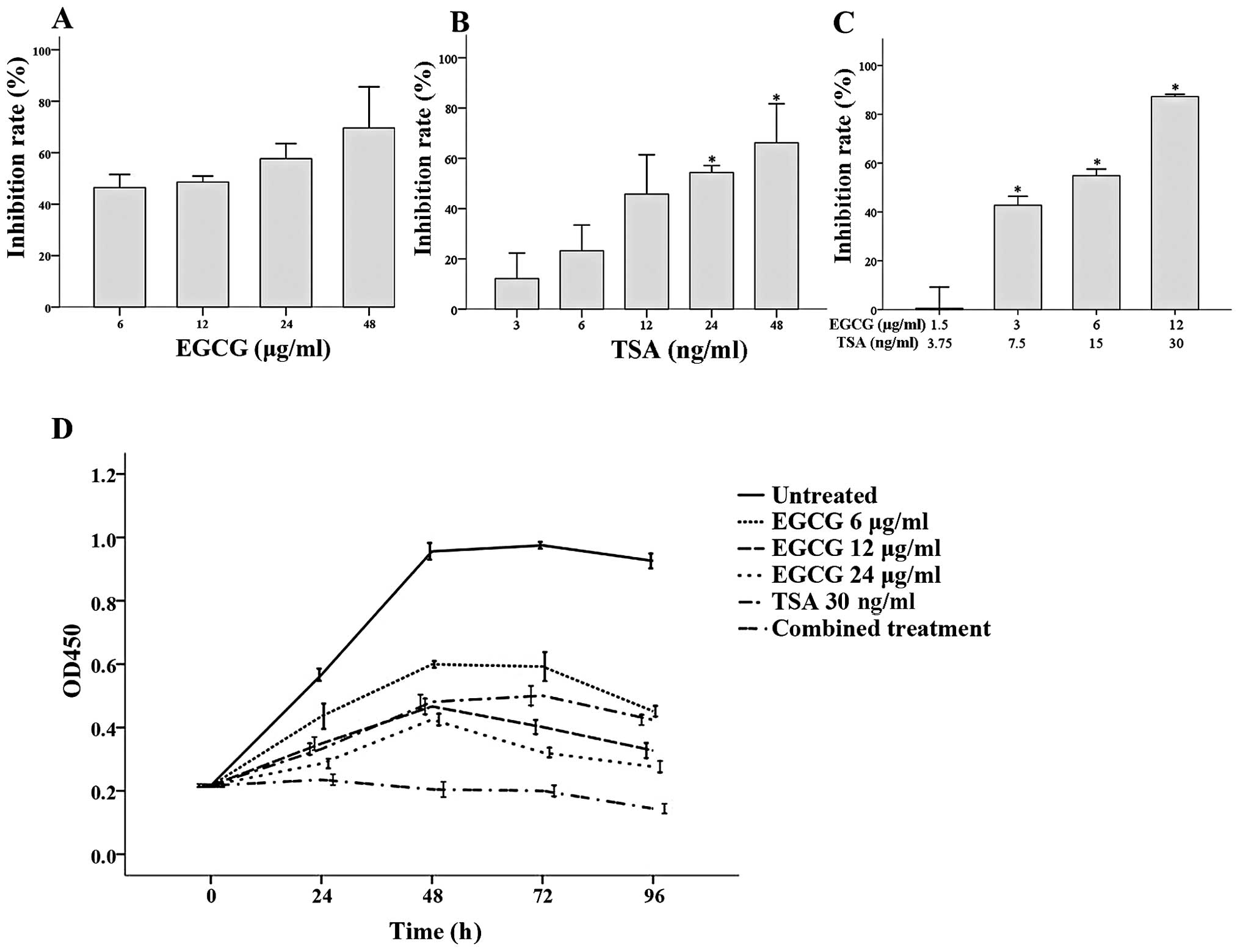
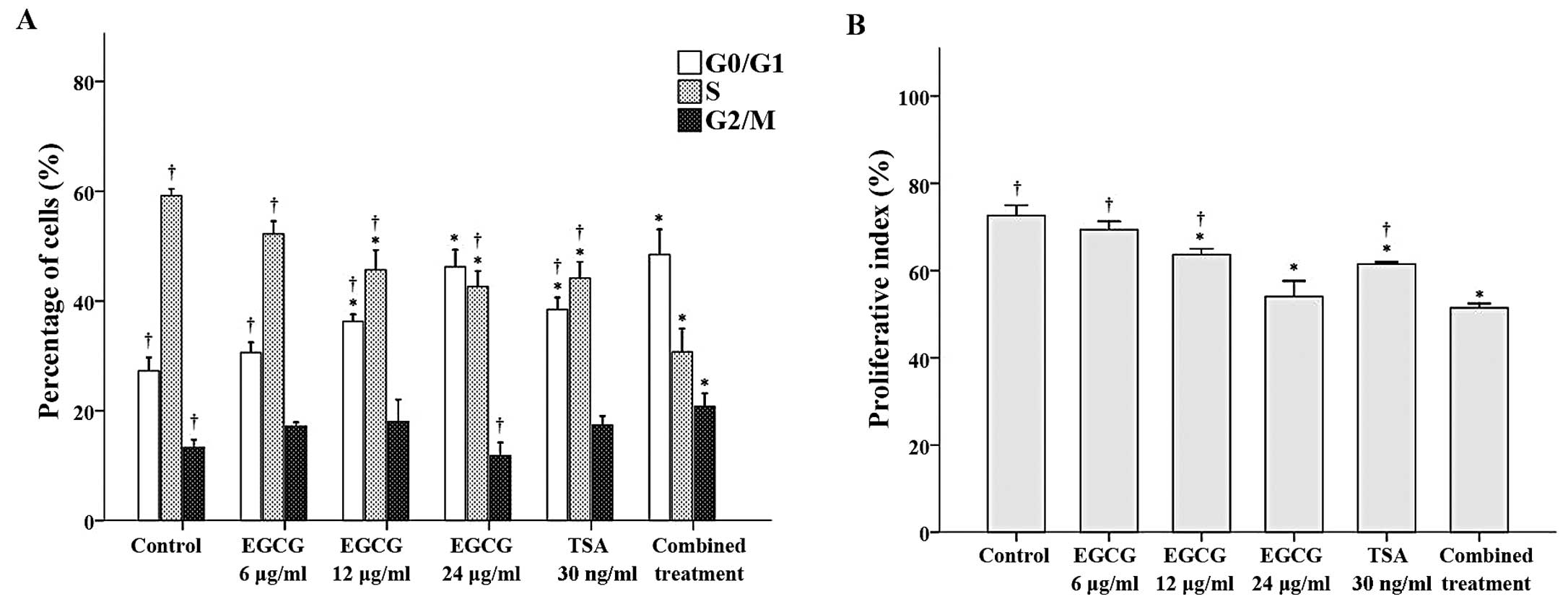
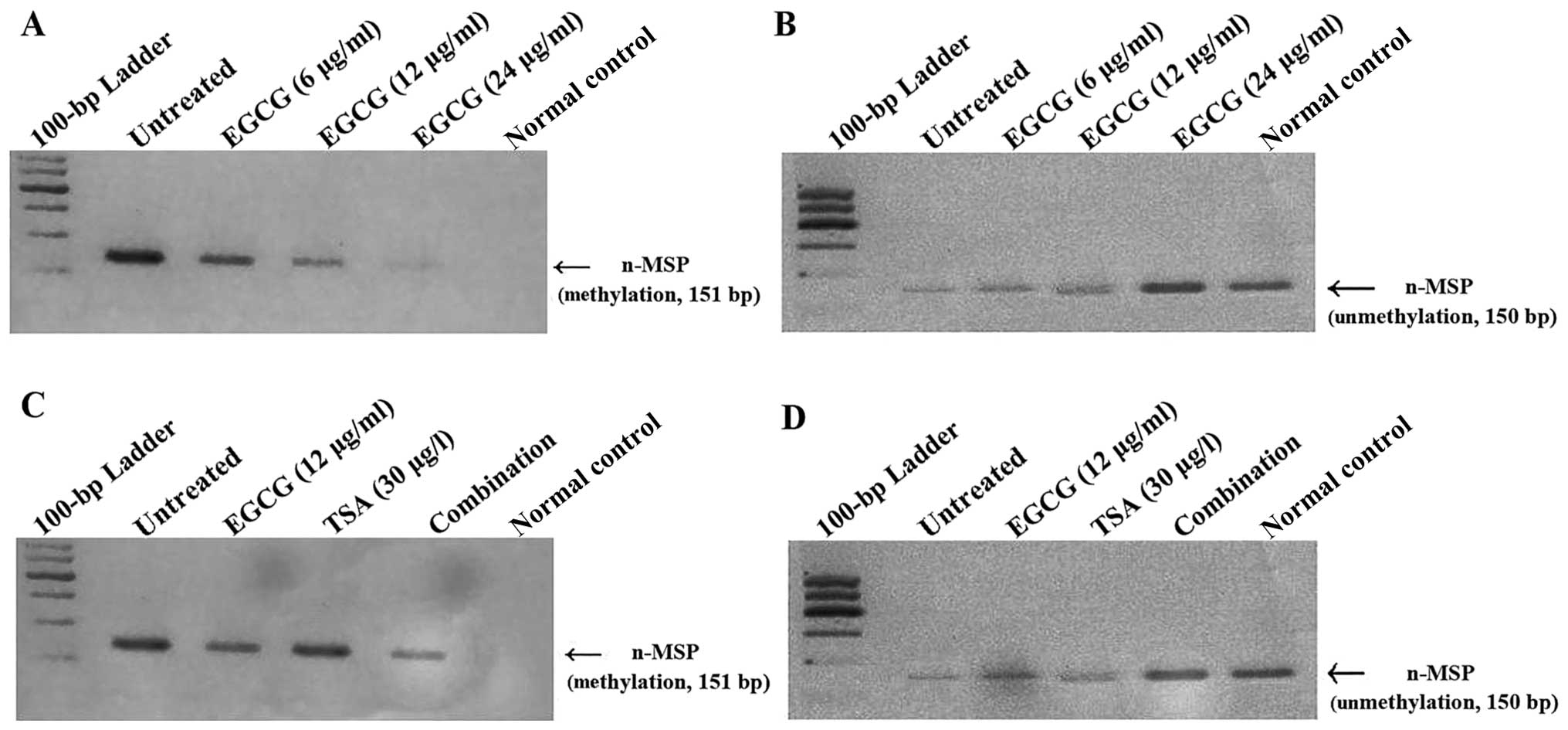
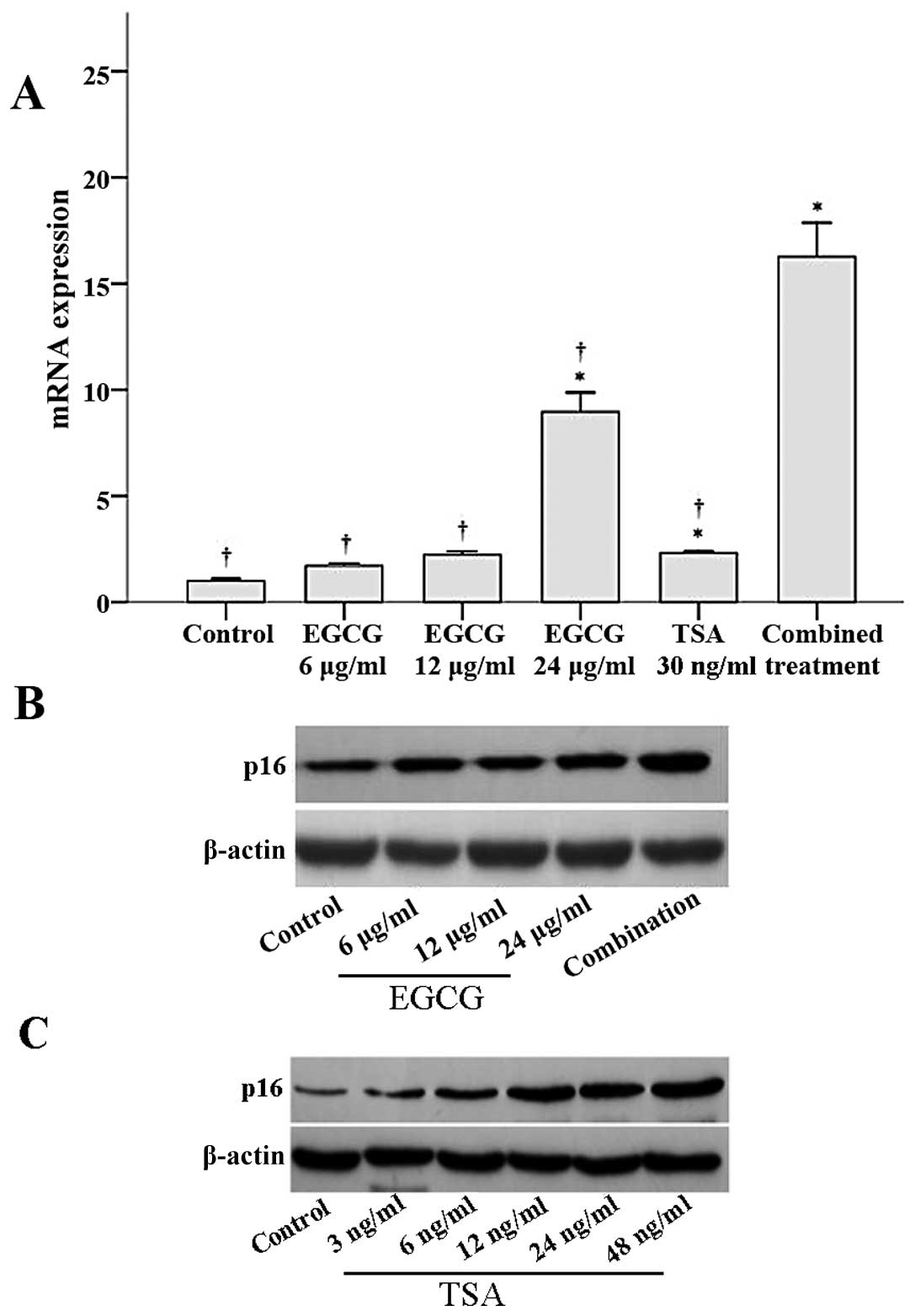
|
1
|
Li G, Ji Y, Liu C, Li J and Zhou Y:
Reduced levels of p15INK4b, p16INK4a, p21cip1 and p27kip1 in
pancreatic carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 5:1106–1110. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Herman JG, Merlo A, Mao L, et al:
Inactivation of the CDKN2/p16/MTS1 gene is frequently
associated with aberrant DNA methylation in all common human
cancers. Cancer Res. 55:4525–4530. 1995.
|
|
3
|
Sherr CJ: Cancer cell cycles. Science.
274:1672–1677. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee MH, Choi BY, Cho YY, et al: Tumor
suppressor p16INK4a inhibits cancer cell growth by
down-regulating eEF1A2 through a direct interaction. J Cell Sci.
126:1744–1752. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takeuchi S, Takahashi A, Motoi N, et al:
Intrinsic cooperation between p16INK4a and
p21Waf1/Cip1 in the onset of cellular senescence and
tumor suppression in vivo. Cancer Res. 70:9381–9390.
2010.
|
|
6
|
Fang K, Chiu CC, Li CH, Chang YT and Hwang
HT: Cisplatin-induced senescence and growth inhibition in human
non-small cell lung cancer cells with ectopic transfer of p16INK4a.
Oncol Res. 16:479–488. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee JJ, Ko E, Cho J, et al: Methylation
and immunoexpression of p16INK4a tumor
suppressor gene in primary breast cancer tissue and their
quantitative p16INK4a hypermethylation in
plasma by real-time PCR. Korean J Pathol. 46:554–561.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ameri A, Alidoosti A, Hosseini SY, et al:
Prognostic value of promoter hypermethylation of retinoic acid
receptor beta (RARB) and CDKN2 (p16/MTS1) in prostate
cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 23:306–311. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu Z, Wang Y, Liu Z, Wang F and Zhao Q:
Inhibitory effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on cell
proliferation and the expression of HIF-1α and P-gp in the human
pancreatic carcinoma cell line PANC-1. Oncol Rep. 27:1567–1572.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nandakumar V, Vaid M and Katiyar SK:
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reactivates silenced tumor
suppressor genes, Cip1/p21 and
p16INK4a, by reducing DNA methylation and
increasing histones acetylation in human skin cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 32:537–544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang W, Pan K, Chen Y, Huang C and Zhang
X: The acetylation of transcription factor HBP1 by p300/CBP
enhances p16INK4A expression. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:981–995. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zanders ED: Overview of chemical genomics
and proteomics. Methods Mol Biol. 800:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sandoval J and Esteller M: Cancer
epigenomics: beyond genomics. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 22:50–55. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Palmisano WA, Divine KK, Saccomanno G, et
al: Predicting lung cancer by detecting aberrant promoter
methylation in sputum. Cancer Res. 60:5954–5958. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choung HK, Kim YA, Lee MJ, Kim N and
Khwarg SI: Multigene methylation analysis of ocular adnexal MALT
lymphoma and their relationship to Chlamydophila psittaci
infection and clinical characteristics in South Korea. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:1928–1935. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zainuddin N, Kanduri M, Berglund M, et al:
Quantitative evaluation of p16INK4a
promoter methylation using pyrosequencing in de novo diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia Res. 35:438–443. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Sato H, Oka T, Shinnou Y, et al:
Multi-step aberrant CpG island hyper-methylation is associated with
the progression of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Am J Pathol.
176:402–415. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kondo T, Oka T, Sato H, et al:
Accumulation of aberrant CpG hypermethylation by Helicobacter
pylori infection promotes development and progression of
gastric MALT lymphoma. Int J Oncol. 35:547–557. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim SO and Kim MR: (-)-Epigallocatechin
3-gallate inhibits invasion by inducing the expression of Raf
kinase inhibitor protein in AsPC 1 human pancreatic adenocarcinoma
cells through the modulation of histone deacetylase activity. Int J
Oncol. 42:349–358. 2013.
|
|
20
|
Rajarajacholan UK, Thalappilly S and
Riabowol K: The ING1a tumor suppressor regulates endocytosis to
induce cellular senescence via the Rb-E2F pathway. PLoS Biol.
11:e10015022013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nakagawa H, Hasumi K, Woo JT, Nagai K and
Wachi M: Generation of hydrogen peroxide primarily contributes to
the induction of Fe(II)-dependent apoptosis in Jurkat cells by
(-)-epigallocatechin gallate. Carcinogenesis. 25:1567–1574. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Satoh A, Toyota M, Itoh F, et al: DNA
methylation and histone deacetylation associated with silencing DAP
kinase gene expression in colorectal and gastric cancers. Br J
Cancer. 86:1817–1823. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Steele N, Finn P, Brown R and Plumb JA:
Combined inhibition of DNA methylation and histone acetylation
enhances gene re-expression and drug sensitivity in vivo. Br J
Cancer. 100:758–763. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dannenberg LO and Edenberg HJ: Epigenetics
of gene expression in human hepatoma cells: expression profiling
the response to inhibition of DNA methylation and histone
deacetylation. BMC Genomics. 7:1812006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oh HJ, Lee TH, Lee JH and Lee BC:
Trichostatin A improves preimplantation development of bovine
cloned embryos and alters expression of epigenetic and pluripotency
genes in cloned blastocysts. J Vet Med Sci. 74:1409–1415. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu X, Li Y, Li GP, et al: Trichostatin A
improved epigenetic modifications of transfected cells but did not
improve subsequent cloned embryo development. Anim Biotechnol.
19:211–224. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Klisovic MI, Maghraby EA, Parthun MR, et
al: Depsipeptide (FR 901228) promotes histone acetylation, gene
transcription, apoptosis and its activity is enhanced by DNA
methyltransferase inhibitors in AML1/ETO-positive leukemic cells.
Leukemia. 17:350–358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shaker S, Bernstein M, Momparler LF and
Momparler RL: Preclinical evaluation of antineoplastic activity of
inhibitors of DNA methylation (5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine) and histone
deacetylation (trichostatin A, depsipeptide) in combination against
myeloid leukemic cells. Leuk Res. 27:437–444. 2003.
|
|
29
|
Beltz LA, Bayer DK, Moss AL and Simet IM:
Mechanisms of cancer prevention by green and black tea polyphenols.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 6:389–406. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Navarro-Martínez MD, García-Cánovas F and
Rodríguez-López JN: Tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate
inhibits ergosterol synthesis by disturbing folic acid metabolism
in Candida albicans. J Antimicrob Chemother. 57:1083–1092.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fang M, Chen D and Yang CS: Dietary
polyphenols may affect DNA methylation. J Nutr. 137:223S–228S.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fang MZ, Wang Y, Ai N, et al: Tea
polyphenol (-)-epigallo-catechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA
methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in
cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 63:7563–7570. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y and Tollefsbol TO: Impact on DNA
methylation in cancer prevention and treatment by bioactive dietary
components. Curr Med Chem. 17:2141–2151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee WJ, Shim JY and Zhu BT: Mechanisms for
the inhibition of DNA methyltransferases by tea catechins and
bioflavonoids. Mol Pharmacol. 68:1018–1030. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peurala E, Koivunen P, Haapasaari KM,
Bloigu R and Jukkola-Vuorinen A: The prognostic significance and
value of cyclin D1, CDK4 and p16 in human breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 15:R52013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|