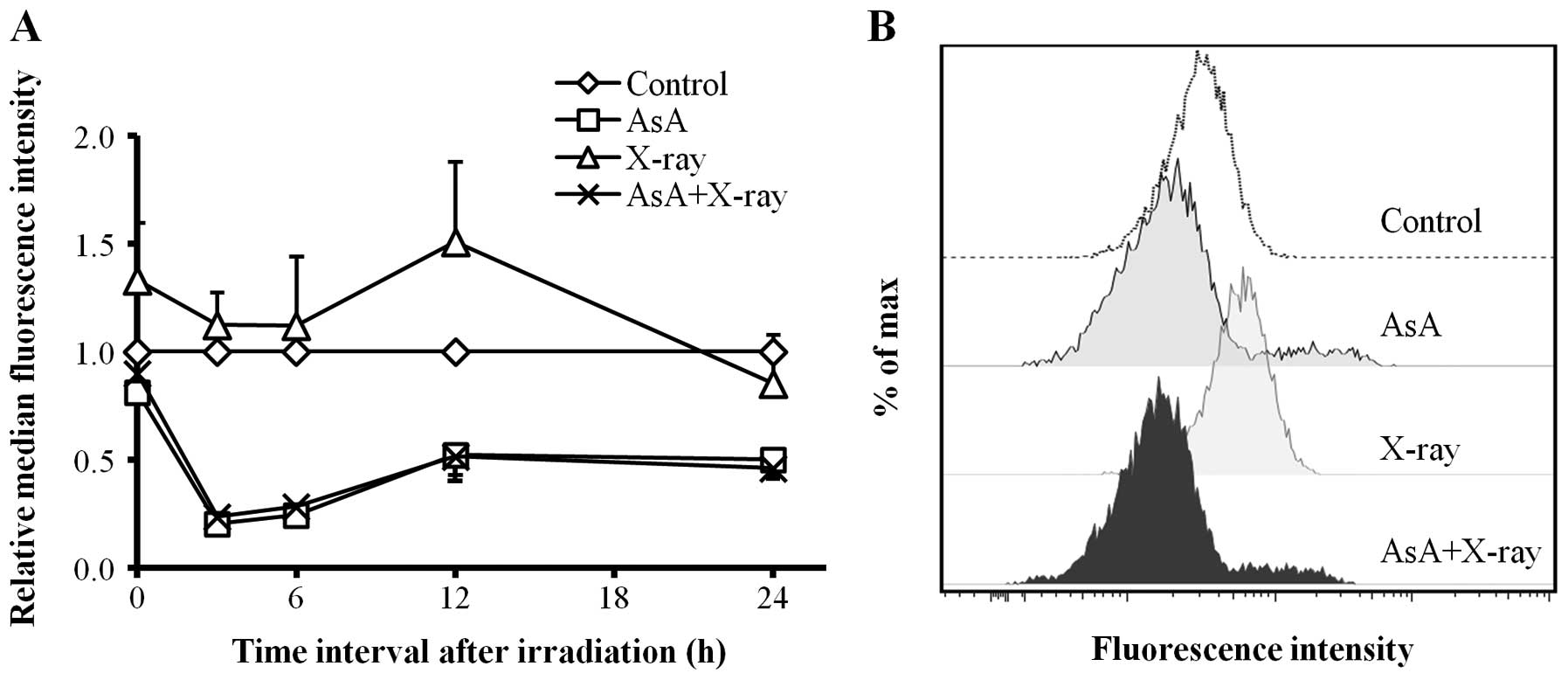
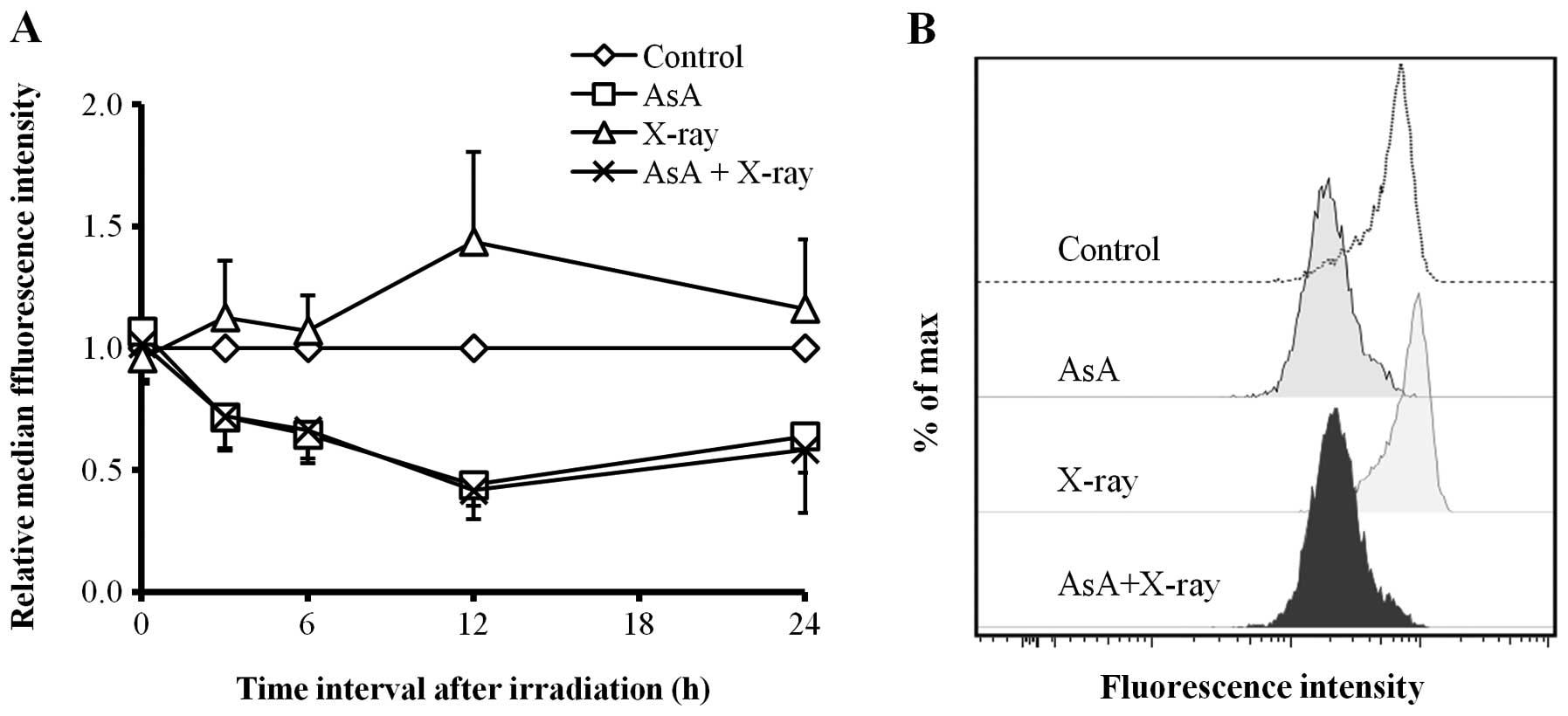
|
1
|
Padayatty SJ, Sun AY, Chen Q, Espey MG,
Drisko J and Levine M: Vitamin C: intravenous use by complementary
and alternative medicine practitioners and adverse effects. PLoS
One. 5:e114142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Krishna MC, et al:
Pharmacologic ascorbic acid concentrations selectively kill cancer
cells: action as a pro-drug to deliver hydrogen peroxide to
tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:13604–13609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Q, Espey MG, Sun AY, et al: Ascorbate
in pharmacologic concentrations selectively generates ascorbate
radical and hydrogen peroxide in extracellular fluid in vivo. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:8749–8787. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takemura Y, Satoh M, Satoh K, Hamada H,
Sekido Y and Kubota S: High dose of ascorbic acid induces cell
death in mesothelioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
394:249–253. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hsieh BS, Huang LW, Su SJ, et al: Combined
arginine and ascorbic acid treatment induces apoptosis in the
hepatoma cell line HA22T/VGH and changes in redox status involving
the pentose phosphate pathway and reactive oxygen and nitrogen
species. J Nutr Biochem. 22:234–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hampton MB and Orrenius S: Dual regulation
of caspase activity by hydrogen peroxide: implications for
apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 414:552–556. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hyslop PA, Hinshaw DB, Halsey WA Jr, et
al: Mechanisms of oxidant-mediated cell injury. The glycolytic and
mitochondrial pathways of ADP phosphorylation are major
intracellular targets inactivated by hydrogen peroxide. J Biol
Chem. 263:1665–1675. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lamson DW and Brignall MS: Antioxidants in
cancer therapy; their actions and interactions with oncologic
therapies. Altern Med Rev. 4:304–329. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Padayatty SJ, Riordan HD, Hewitt SM, Katz
A, Hoffer LJ and Levine M: Intravenously administered vitamin C as
cancer therapy: three cases. CMAJ. 174:937–942. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Riordan HD, Casciari JJ, González MJ, et
al: A pilot clinical study of continuous intravenous ascorbate in
terminal cancer patients. PR Health Sci J. 24:269–276.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Monti DA, Mitchell E, Bazzan AJ, et al:
Phase I evaluation of intravenous ascorbic acid in combination with
gemcitabine and erlotinib in patients with metastatic pancreatic
cancer. PLoS One. 7:e297942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shinozaki K, Hosokawa Y, Hazawa M, et al:
Ascorbic acid enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in an HL60 human
leukemia cell line. J Radiat Res. 52:229–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Herst PM, Broadley KW, Harper JL and
McConnell MJ: Pharmacological concentrations of ascorbate
radiosensitize glioblastoma multiforme primary cells by increasing
oxidative DNA damage and inhibiting G2/M arrest. Free Radic Biol
Med. 52:1486–1493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rose RC and Bode AM: Biology of free
radical scavengers: an evaluation of ascorbate. FASEB J.
7:1135–1142. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Y and Schellhorn HE: New developments
and novel therapeutic perspectives for vitamin C. J Nutr.
137:2171–2184. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reth M: Antioxidant defenses - endogenous
and diet derived. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. Halliwell
B and Gutteridge JMC: 4th edition. Oxford University Press; New
York: pp. 160–166. 2007
|
|
17
|
Lawenda BD, Kelly KM, Ladas EJ, Sagar SM,
Vickers A and Blumberg JB: Should supplemental antioxidant
administration be avoided during chemotherapy and radiation
therapy? J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:773–783. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heaney ML, Gardner JR, Karasavvas N, et
al: Vitamin C antagonizes the cytotoxic effects of antineoplastic
drugs. Cancer Res. 68:8031–8038. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto T, Kinoshita M, Shinomiya N, et
al: Pretreatment with ascorbic acid prevents lethal
gastrointestinal syndrome in mice receiving a massive amount of
radiation. J Radiat Res. 51:145–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Witenberg B, Kalir HH, Raviv Z, Kletter Y,
Kravtsov V and Fabian I: Inhibition by ascorbic acid of apoptosis
induced by oxidative stress in HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 57:823–832. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Witenberg B, Kletter Y, Kalir HH, et al:
Ascorbic acid inhibits apoptosis induced by X irradiation in HL60
myeloid leukemia cells. Radiat Res. 152:468–478. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee YJ, Lee DH, Cho CK, et al: HSP25
inhibits radiation-induced apoptosis through reduction of
PKCδ-mediated ROS production. Oncogene. 24:3715–3725.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ni Y, Gong XG, Lu M, Chen HM and Wang Y:
Mitochondrial ROS burst as an early sign in sarsasapogenin-induced
apoptosis in HepG2 cells. Cell Biol Int. 32:337–343. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogura A, Oowada S, Kon Y, et al: Redox
regulation in radiation-induced cytochrome c release from
mitochondria of human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Cancer Lett.
277:64–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grad JM, Cepero E and Boise LH:
Mitochondria as targets for established and novel anti-cancer
agents. Drug Resist Updat. 4:85–91. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoshino H, Kiminarita T, Matsushita Y and
Kashiwakura I: Response of the Nrf2 protection system in human
monocytic cells after ionising irradiation. Radiat Prot Dosimetry.
152:104–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hachiya M and Akashi M: Catalase regulates
cell growth in HL60 human promyelocytic cells: evidence for growth
regulation by H2O2. Radiat Res. 163:271–282.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yanai H: Statcel-The Useful Add-in
Software Forms on Excel. 2nd edition. OMS; Tokyo: 2006
|
|
30
|
Koyama S, Kodama S, Suzuki K, Matsumoto T,
Miyazaki T and Watanabe M: Radiation-induced long-lived radicals
which cause mutation and transformation. Mutat Res. 421:45–54.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frömberg A, Gutsch D, Schulze D, et al:
Ascorbate exerts anti-proliferative effects through cell cycle
inhibition and sensitizes tumor cells towards cytostatic drugs.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 67:1157–1166. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang XH, Jia DZ, Liang YJ, et al: Lgf-YL-9
induces apoptosis in human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells and
multidrug resistant KBv200 cells via reactive oxygen
species-independent mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Lett.
249:256–270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang JY, Wu HY, Xia XK, et al:
Anthracenedione derivative 1403P-3 induces apoptosis in KB and
KBv200 cells via reactive oxygen species-independent mitochondrial
pathway and death receptor pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:1413–1421.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lin KT, Xue JY, Sun FF and Wong PY:
Reactive oxygen species participate in peroxynitrite-induced
apoptosis in HL-60 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 230:115–119.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Antunes F and Cadenas E: Estimation of
H2O2 gradients across biomembranes. FEBS
Lett. 475:121–126. 2000.
|
|
36
|
Griffiths EJ: Mitochondria-potential role
in cell life and death. Cardiovasc Res. 46:24–27. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hara K, Kasahara E, Takahashi N, et al:
Mitochondria determine the efficacy of anticancer agents that
interact with DNA but not the cytoskeleton. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
337:838–845. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hou DX, Uto T, Tong X, et al: Involvement
of reactive oxygen species-independent mitochondrial pathway in
gossypol-induced apoptosis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 428:179–187.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ko CH, Shen SC, Hsu CS and Chen YC:
Mitochondrial-dependent, reactive oxygen species-independent
apoptosis by myricetin: roles of protein kinase C, cytochrome c,
and caspase cascade. Biochem Pharmacol. 69:913–927. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yamamori T, Yasui H, Yamazumi M, et al:
Ionizing radiation induces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species
production accompanied by upregulation of mitochondrial electron
transport chain function and mitochondrial content under control of
the cell cycle checkpoint. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:260–270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|