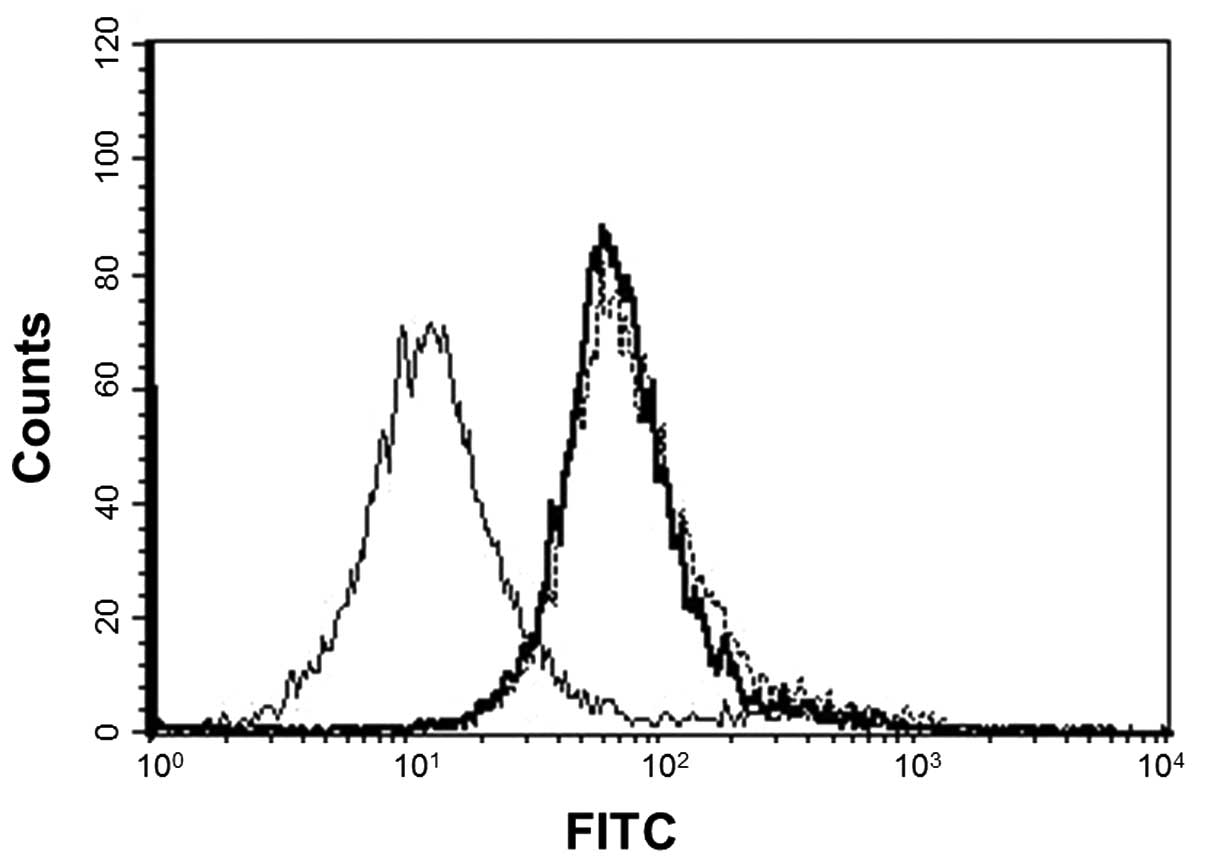
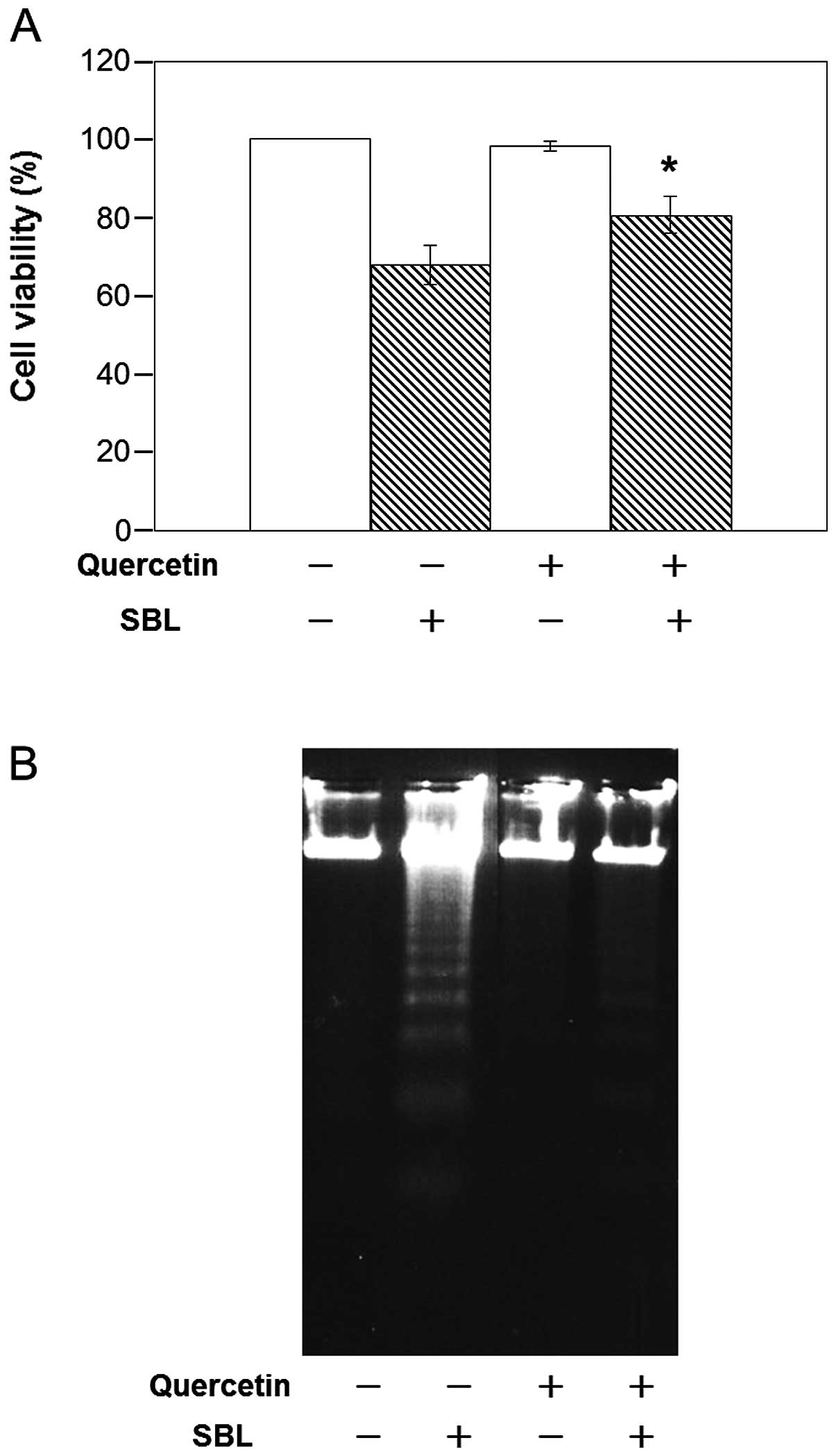
|
1
|
Snoeckx LH, Cornelussen RN, Van
Nieuwenhoven FA, Reneman RS and Van Der Vusse GJ: Heat shock
proteins and cardiovascular pathophysiology. Physiol Rev.
81:1461–1497. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mosser DD, Caron AW, Bourget L,
Denis-Larose C and Massie B: Role of the human heat shock protein
hsp70 in protection against stress-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell
Biol. 17:5317–5327. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Beere HM, Wolf BB, Cain K, Mosser DD,
Mahboubi A, Kuwana T, Tailor P, et al: Heat-shock protein 70
inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the
Apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat Cell Biol. 2:469–475. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liossis SN, Ding XZ, Kiang JG and Tsokos
GC: Overexpression of the heat shock protein 70 enhances the
TCR/CD3- and Fas/Apo-1/CD95-mediated apoptotic cell death in Jurkat
T cells. J Immunol. 158:5668–5675. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Welch WJ: Mammalian stress response: cell
physiology, structure/function of stress proteins, and implications
for medicine and disease. Physiol Rev. 72:1063–1081.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bausero MA, Page DT, Osinaga E and Asea A:
Surface expression of Hsp25 and Hsp72 differentially regulates
tumor growth and metastasis. Tumour Biol. 25:243–251. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calderwood SK, Mambula SS, Gray PJ Jr and
Theriault JR: Extracellular heat shock proteins in cell signaling.
FEBS Lett. 581:3689–3694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sugawara S, Kawano T, Omoto T, Hosono M,
Tatsuta T and Nitta K: Binding of Silurus asotus lectin to
Gb3 on Raji cells causes disappearance of membrane-bound form of
HSP70. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1790:101–109. 2009.
|
|
9
|
Chen S, Bawa D, Besshoh S, Gurd JW and
Brown IR: Association of heat shock proteins and neuronal membrane
components with lipid rafts from the rat brain. J Neurosci Res.
81:522–529. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Broquet AH, Thomas G, Masliah J, Trugnan G
and Bachelet M: Expression of the molecular chaperone Hsp70 in
detergent-resistant microdomains correlates with its membrane
delivery and release. J Biol Chem. 278:21601–21606. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawauchi H, Sakakibara F and Watanabe K:
Agglutinins of frog eggs: a new class of proteins causing
preferential agglutination of tumor cells. Experientia. 31:364–365.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sakakibara F, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi G and
Ise H: Egg lectin of Rana japonica and its receptor
glycoprotein of Ehrlich tumor cells. Cancer Res. 39:1347–1352.
1979.
|
|
13
|
Nitta K, Takayanagi G, Kawauchi H and
Hakomori S: Isolation and characterization of Rana
catesbeiana lectin and demonstration of the lectin-binding
glycoprotein of rodent and human tumor cell membranes. Cancer Res.
47:4877–4883. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Titani K, Takio K, Kuwada M, Nitta K,
Sakakibara F, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi G and Hakomori S: Amino acid
sequence of sialic acid binding lectin from frog (Rana
catesbeiana) eggs. Biochemistry. 26:2189–2194. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kamiya Y, Oyama F, Oyama R, Sakakibara F,
Nitta K, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y and Titani K: Amino acid sequence
of a lectin from Japanese frog (Rana japonica) eggs. J
Biochem. 108:139–143. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nitta K, Oyama F, Oyama R, Sekiguchi K,
Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y, Hakomori S and Titani K: Ribonuclease
activity of sialic acid-binding lectin from Rana catesbeiana
eggs. Glycobiology. 3:37–45. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okabe Y, Katayama N, Iwama M, Watanabe H,
Ohgi K, Irie M, Nitta K, et al: Comparative base specificity,
stability, and lectin activity of two lectins from eggs of Rana
catesbeiana and R. japonica and liver ribonuclease from
R. catesbeiana. J Biochem. 109:786–790. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nitta K, Ozaki K, Ishikawa M, Furusawa S,
Hosono M, Kawauchi H, Sasaki K, et al: Inhibition of cell
proliferation by Rana catesbeiana and Rana japonica
lectins belonging to the ribonuclease superfamily. Cancer Res.
54:920–927. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nitta K, Ozaki K, Tsukamoto Y, Furusawa S,
Ohkubo Y, Takimoto H, Murata R, et al: Characterization of a
Rana catesbeiana lectin-resistant mutant of leukemia P388
cells. Cancer Res. 54:928–934. 1994.
|
|
20
|
Nitta K, Ozaki K, Tsukamoto Y, Hosono M,
Ogawakonno Y, Kawauchi H, Takayanagi Y, et al: Catalytic lectin
(leczyme) from bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana) eggs: Mechanism
of tumoricidal activity. Int J Oncol. 9:19–23. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tatsuta T, Hosono M, Sugawara S, et al:
Sialic acid-binding lectin (leczyme) induces caspase-dependent
apoptosis-mediated mitochondrial perturbation in Jurkat cells. Int
J Oncol. 43:1402–1412. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Haigis MC, Kurten EL and Raines RT:
Ribonuclease inhibitor as an intracellular sentry. Nucleic Acids
Res. 31:1024–1032. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hosokawa N, Hirayoshi K, Kudo H, Takechi
H, Aoike A, Kawai K and Nagata K: Inhibition of the activation of
heat shock factor in vivo and in vitro by flavonoids. Mol Cell
Biol. 12:3490–3498. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Asea A, Kraeft SK, Kurt-Jones EA,
Stevenson MA, Chen LB, Finberg RW, Koo GC and Calderwood SK: HSP70
stimulates cytokine production through a CD14-dependant pathway,
demonstrating its dual role as a chaperone and cytokine. Nat Med.
6:435–442. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Becker T, Hartl FU and Wieland F: CD40, an
extracellular receptor for binding and uptake of Hsp70-peptide
complexes. J Cell Biol. 158:1277–1285. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Asea A, Rehli M, Kabingu E, Boch JA, Bare
O, Auron PE, Stevenson MA and Calderwood SK: Novel signal
transduction pathway utilized by extracellular HSP70: role of
toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4. J Biol Chem. 277:15028–15034.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guerrero CA and Moreno LP: Rotavirus
receptor proteins Hsc70 and integrin αvβ3 are located in the lipid
microdomains of animal intestinal cells. Acta Virol. 56:63–70.
2012.
|