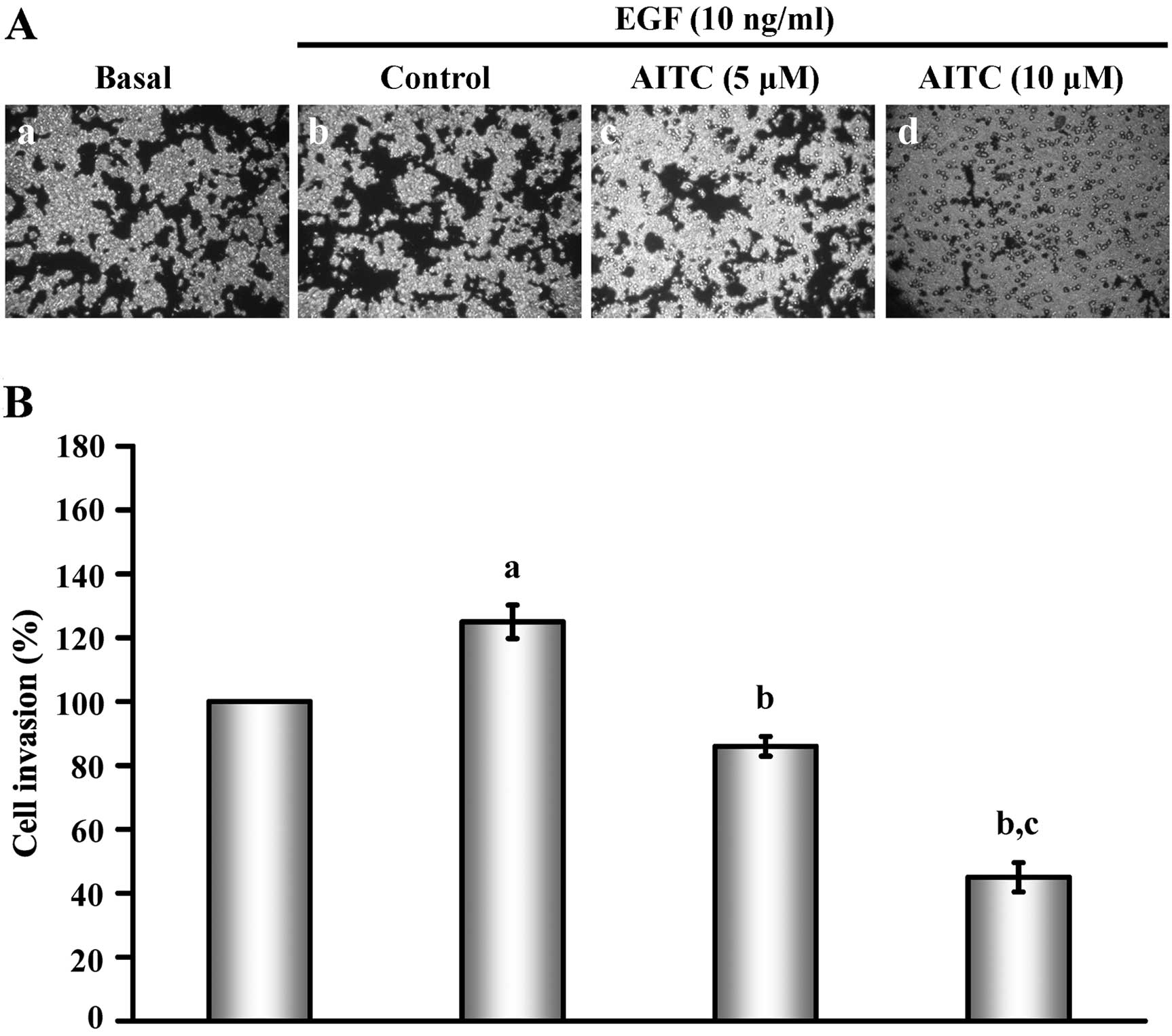
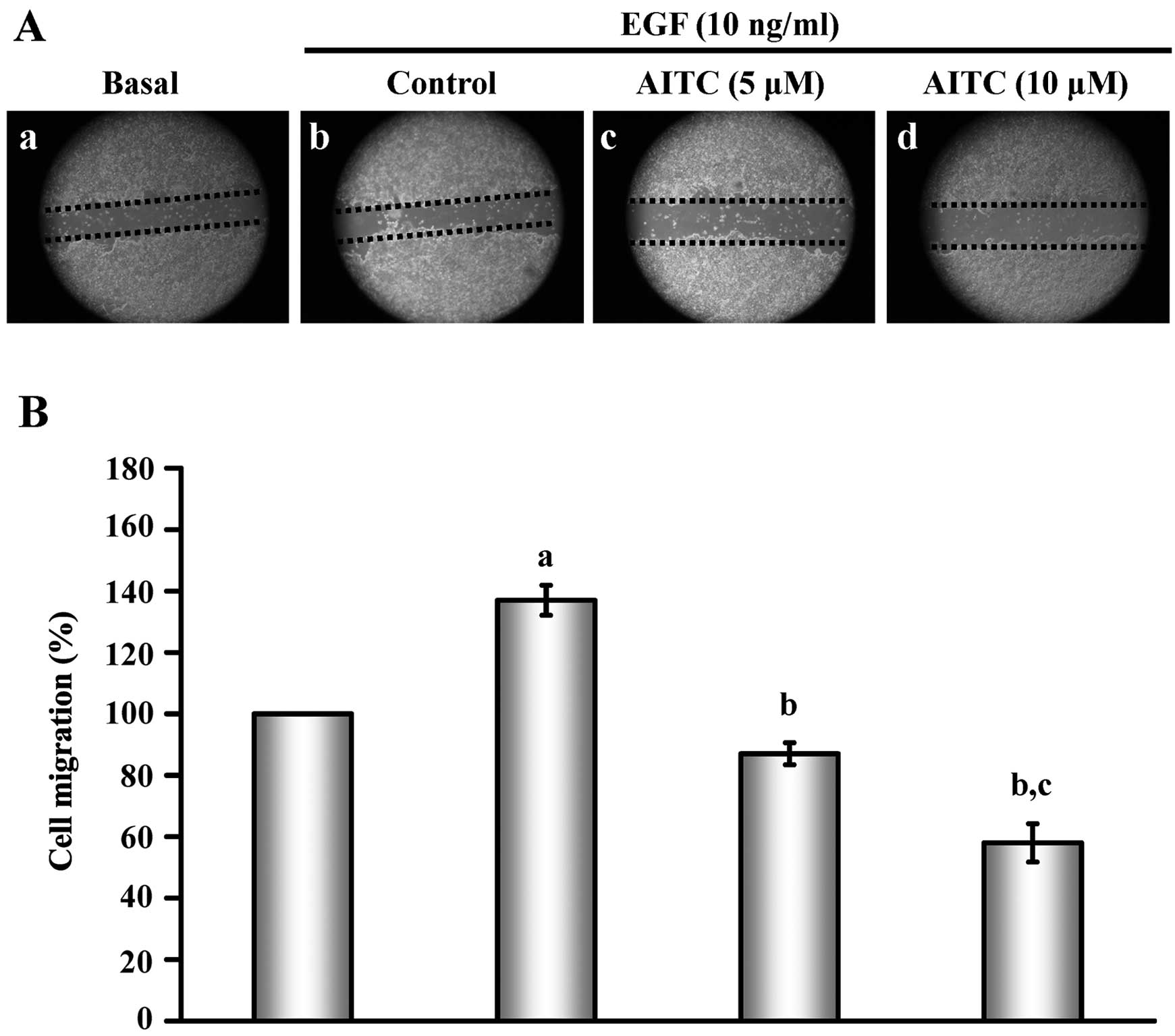
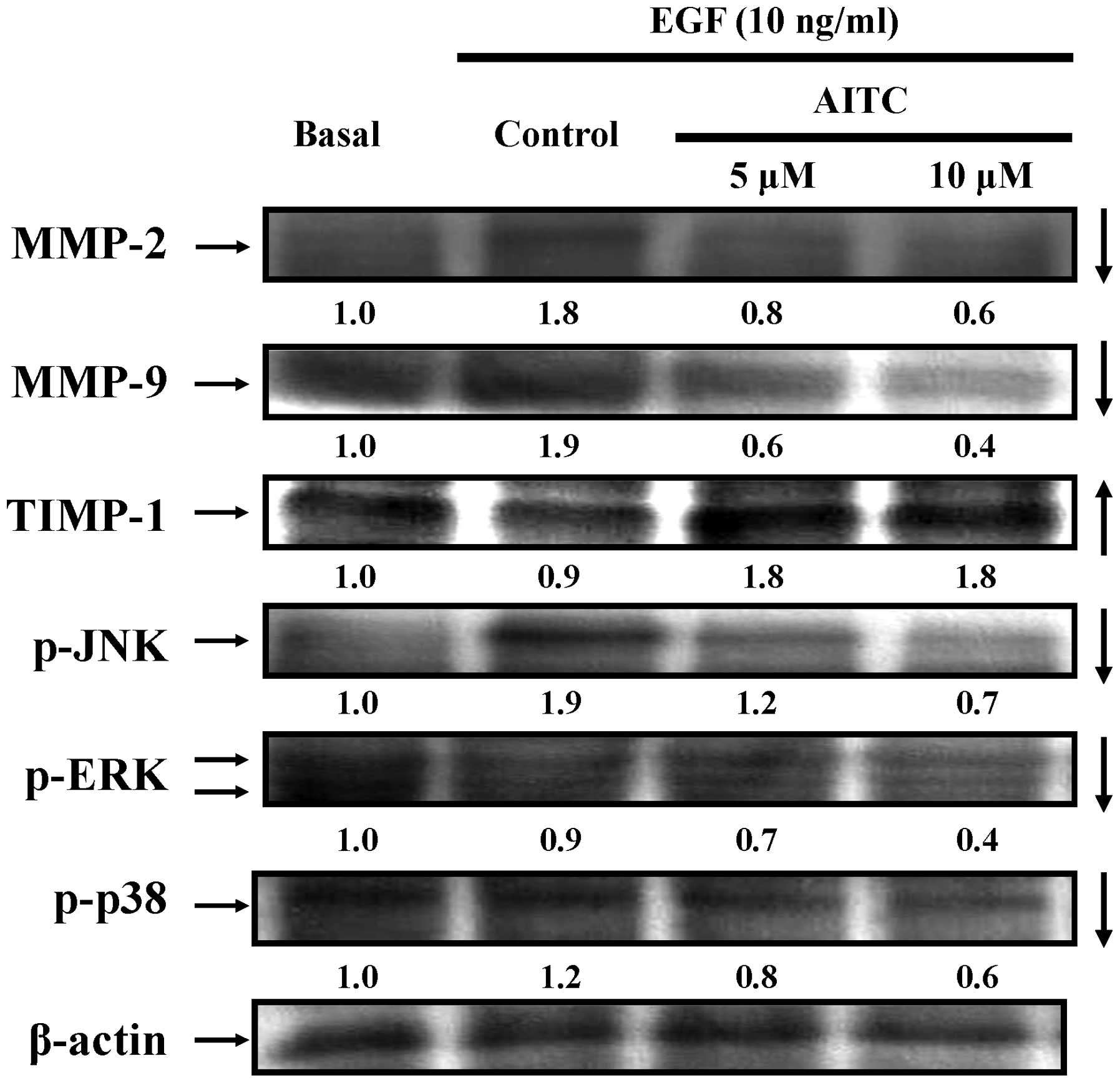
|
1
|
Geng F, Tang L, Li Y, et al: Allyl
isothiocyanate arrests cancer cells in mitosis, and mitotic arrest
in turn leads to apoptosis via Bcl-2 protein phosphorylation. J
Biol Chem. 286:32259–32267. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xiao D, Srivastava SK, Lew KL, et al:
Allyl isothiocyanate, a constituent of cruciferous vegetables,
inhibits proliferation of human prostate cancer cells by causing
G2/M arrest and inducing apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 24:891–897.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu CL, Huang AC, Yang JS, et al: Benzyl
isothiocyanate (BITC) and phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC)-mediated
generation of reactive oxygen species causes cell cycle arrest and
induces apoptosis via activation of caspase-3, mitochondria
dysfunction and nitric oxide (NO) in human osteogenic sarcoma U-2
OS cells. J Orthop Res. 29:1199–1209. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Xu K and Thornalley PJ: Studies on the
mechanism of the inhibition of human leukaemia cell growth by
dietary isothiocyanates and their cysteine adducts in vitro.
Biochem Pharmacol. 60:221–231. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bhattacharya A, Li Y, Wade KL, Paonessa
JD, Fahey JW and Zhang Y: Allyl isothiocyanate-rich mustard seed
powder inhibits bladder cancer growth and muscle invasion.
Carcinogenesis. 31:2105–2110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lau WS, Chen T and Wong YS: Allyl
isothiocyanate induces G2/M arrest in human colorectal
adenocarcinoma SW620 cells through down-regulation of Cdc25B and
Cdc25C. Mol Med Rep. 3:1023–1030. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schaefer EA, Stohr S, Meister M, Aigner A,
Gudermann T and Buech TR: Stimulation of the chemosensory TRPA1
cation channel by volatile toxic substances promotes cell survival
of small cell lung cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:426–438.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsai SC, Huang WW, Huang WC, et al:
ERK-modulated intrinsic signaling and G2/M phase arrest
contribute to the induction of apoptotic death by allyl
isothiocyanate in MDA-MB-468 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int
J Oncol. 41:2065–2072. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhattacharya A, Li Y, Geng F, Munday R and
Zhang Y: The principal urinary metabolite of allyl isothiocyanate,
N-acetyl-S-(N-allylthiocarbamoyl)cysteine, inhibits the growth and
muscle invasion of bladder cancer. Carcinogenesis. 33:394–398.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen NG, Chen KT, Lu CC, et al: Allyl
isothiocyanate triggers G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human
brain malignant glioma GBM 8401 cells through a
mitochondria-dependent pathway. Oncol Rep. 24:449–455. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Louhivuori LM, Bart G, Larsson KP, et al:
Differentiation dependent expression of TRPA1 and TRPM8 channels in
IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 221:67–74. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hwang ES and Kim GH: Allyl isothiocyanate
influences cell adhesion, migration and metalloproteinase gene
expression in SK-Hep1 cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 234:105–111.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Garcia A, Haza AI, Arranz N, Rafter J and
Morales P: Protective effects of isothiocyanates alone or in
combination with vitamin C towards N-nitrosodibutylamine or
N-nitrosopiperidine-induced oxidative DNA damage in the single-cell
gel electrophoresis (SCGE)/HepG2 assay. J Appl Toxicol. 28:196–204.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Srivastava SK, Xiao D, Lew KL, et al:
Allyl isothiocyanate, a constituent of cruciferous vegetables,
inhibits growth of PC-3 human prostate cancer xenografts in
vivo. Carcinogenesis. 24:1665–1670. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu C, Shen G, Yuan X, et al: ERK and JNK
signaling pathways are involved in the regulation of activator
protein 1 and cell death elicited by three isothiocyanates in human
prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Carcinogenesis. 27:437–445. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang ES and Lee HJ: Allyl isothiocyanate
and its N-acetylcysteine conjugate suppress metastasis via
inhibition of invasion, migration, and matrix
metalloproteinase-2/-9 activities in SK-Hep 1 human hepatoma cells.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 231:421–430. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Lai KC, Hsu SC, Kuo CL, et al: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate inhibited tumor migration and invasion via
suppressing multiple signal transduction pathways in human colon
cancer HT29 cells. J Agric Food Chem. 58:11148–11155. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lan YH, Wu YC, Wu KW, et al: Death
receptor 5-mediated TNFR family signaling pathways modulate
γ-humulene-induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HT29 cells.
Oncol Rep. 25:419–424. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin HJ, Su CC, Lu HF, et al: Curcumin
blocks migration and invasion of mouse-rat hybrid retina ganglion
cells (N18) through the inhibition of MMP-2, -9, FAK, Rho A and
Rock-1 gene expression. Oncol Rep. 23:665–670. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, et al:
Inhibition of invasion and migration by newly synthesized
quinazolinone MJ-29 in human oral cancer CAL 27 cells through
suppression of MMP-2/9 expression and combined down-regulation of
MAPK and AKT signaling. Anticancer Res. 32:2895–2903.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen YY, Chiang SY, Lin JG, et al: Emodin,
aloe-emodin and rhein inhibit migration and invasion in human
tongue cancer SCC-4 cells through the inhibition of gene expression
of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Int J Oncol. 36:1113–1120.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hong BH, Wu CH, Yeh CT and Yen GC:
Invadopodia-associated proteins blockade as a novel mechanism for
6-shogaol and pterostilbene to reduce breast cancer cell motility
and invasion. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:886–895. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Ma CY, et al:
Danthron, an anthraquinone derivative, induces DNA damage and
caspase cascades-mediated apoptosis in SNU-1 human gastric cancer
cells through mitochondrial permeability transition pores and
Bax-triggered pathways. Chem Res Toxicol. 24:20–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Lu CC, et al: Newly
synthesized quinazolinone HMJ-38 suppresses angiogenetic responses
and triggers human umbilical vein endothelial cell apoptosis
through p53-modulated Fas/death receptor signaling. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 269:150–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, et al: Novel
quinazolinone MJ-29 triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress and
intrinsic apoptosis in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells and inhibits
leukemic mice. PLoS One. 7:e368312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mozaffarieh M, Konieczka K, Hauenstein D,
Schoetzau A and Flammer J: Half a pack of cigarettes a day more
than doubles DNA breaks in circulating leukocytes. Tob Induc Dis.
8:142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jacobs AT and Marnett LJ: HSF1-mediated
BAG3 expression attenuates apoptosis in 4-hydroxynonenal-treated
colon cancer cells via stabilization of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2
proteins. J Biol Chem. 284:9176–9183. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu CY, Yang JS, Huang SM, et al: Smh-3
induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis through
calcium-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial
signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells. Oncol Rep.
29:751–762. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu RS, Yu CS, Liu KC, et al: Citosol
(thiamylal sodium) triggers apoptosis and affects gene expressions
of murine leukemia RAW 264.7 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 31:771–779.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang YJ, Yang JS, Lin CF, et al:
Houttuynia cordata Thunb extract induces apoptosis through
mitochondrial-dependent pathway in HT-29 human colon adenocarcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 22:1051–1056. 2009.
|
|
31
|
Chen HJ, Jiang YL, Lin CM, et al: Dual
inhibition of EGFR and c-Met kinase activation by MJ-56 reduces
metastasis of HT29 human colorectal cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
43:141–150. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friedmann B, Caplin M, Hartley JA and
Hochhauser D: Modulation of DNA repair in vitro after
treatment with chemotherapeutic agents by the epidermal growth
factor receptor inhibitor gefitinib (ZD1839). Clin Cancer Res.
10:6476–6486. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chu E: Clinical colorectal cancer: the
epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway as a
chemotherapeutic target. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2:202–203. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu Z, Jiang G, Blume-Jensen P and Hunter
T: Epidermal growth factor-induced tumor cell invasion and
metastasis initiated by dephosphorylation and downregulation of
focal adhesion kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4016–4031. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Toulany M, Baumann M and Rodemann HP:
Stimulated PI3K-AKT signaling mediated through ligand or
radiation-induced EGFR depends indirectly, but not directly, on
constitutive K-Ras activity. Mol Cancer Res. 5:863–872. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Z, Ahmad A, Li Y, Banerjee S, Kong D
and Sarkar FH: Forkhead box M1 transcription factor: a novel target
for cancer therapy. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:151–156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dong J, Ramachandiran S, Tikoo K, Jia Z,
Lau SS and Monks TJ: EGFR-independent activation of p38 MAPK and
EGFR-dependent activation of ERK1/2 are required for ROS-induced
renal cell death. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 287:F1049–F1058.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu P, Weaver VM and Werb Z: The
extracellular matrix: a dynamic niche in cancer progression. J Cell
Biol. 196:395–406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hidalgo M and Eckhardt SG: Development of
matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 93:178–193. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murray D, Morrin M and McDonnell S:
Increased invasion and expression of MMP-9 in human colorectal cell
lines by a CD44-dependent mechanism. Anticancer Res. 24:489–494.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kapral M, Wawszczyk J, Jurzak M, Dymitruk
D and Weglarz L: Evaluation of the expression of metalloproteinases
2 and 9 and their tissue inhibitors in colon cancer cells treated
with phytic acid. Acta Pol Pharm. 67:625–629. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jeong WS, Kim IW, Hu R and Kong AN:
Modulation of AP-1 by natural chemopreventive compounds in human
colon HT-29 cancer cell line. Pharm Res. 21:649–660. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|