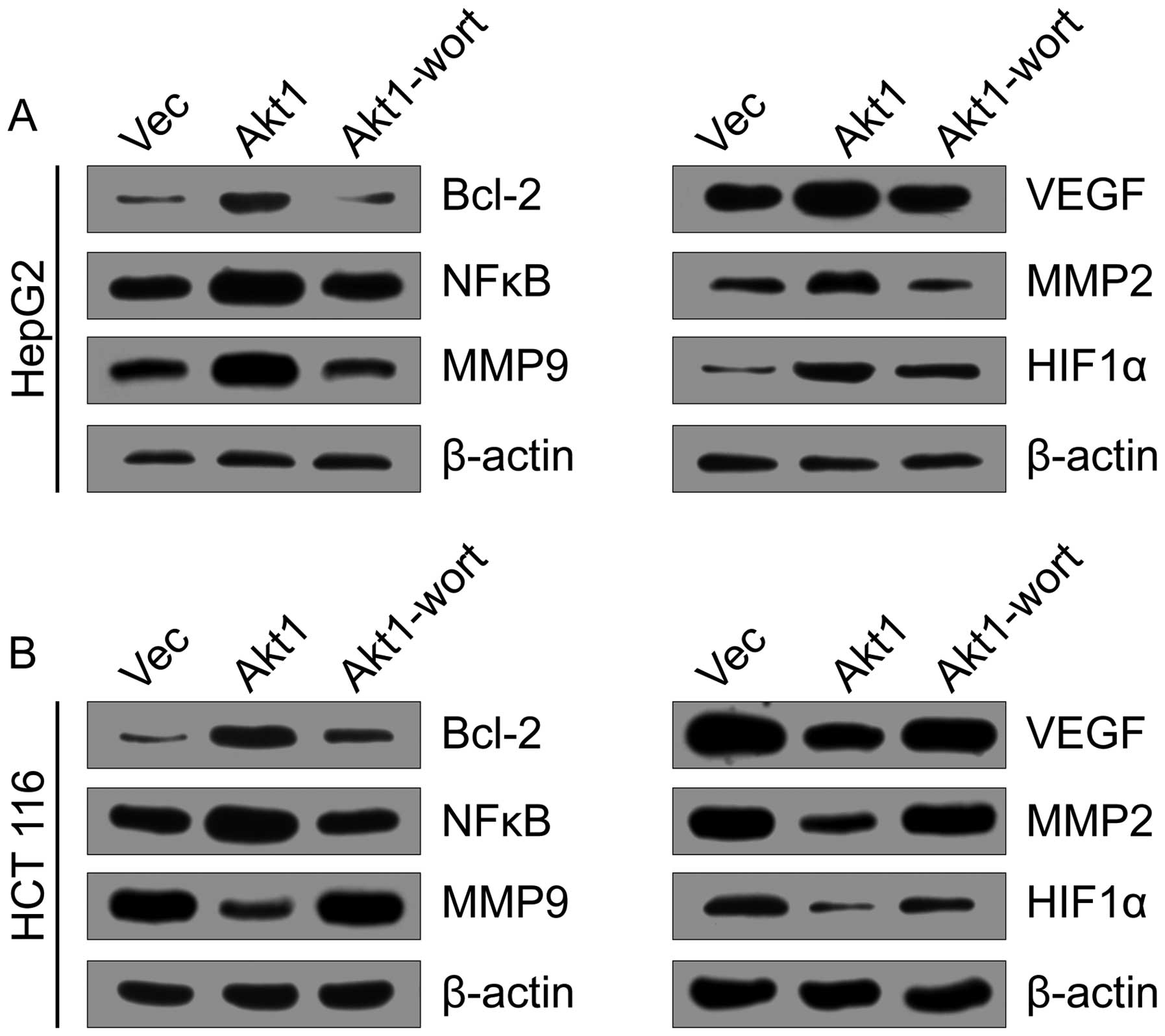
|
1
|
Staal SP: Molecular cloning of the akt
oncogene and its human homologues AKT1 and AKT2: amplification of
AKT1 in a primary human gastric adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 84:5034–5037. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang BH, Aoki M, Zheng JZ, Li J and Vogt
PK: Myogenic signaling of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase requires
the serine-threonine kinase Akt/protein kinase B. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:2077–2081. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fernandez-Hernando C, Jozsef L, Jenkins D,
Di Lorenzo A and Sessa WC: Absence of Akt1 reduces vascular smooth
muscle cell migration and survival and induces features of plaque
vulnerability and cardiac dysfunction during atherosclerosis.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:2033–2040. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Menges CW, Sementino E, Talarchek J, et
al: Group I p21-activated kinases (PAKs) promote tumor cell
proliferation and survival through the AKT1 and Raf-MAPK pathways.
Mol Cancer Res. 10:1178–1188. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Okumura N, Yoshida H, Nishimura Y,
Kitagishi Y and Matsuda S: Terpinolene, a component of herbal sage,
downregulates AKT1 expression in K562 cells. Oncol Lett. 3:321–324.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Young CD, Nolte EC, Lewis A, Serkova NJ
and Anderson SM: Activated Akt1 accelerates MMTV-c-ErbB2 mammary
tumourigenesis in mice without activation of ErbB3. Breast Cancer
Res. 10:R702008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pierau M, Na SY, Simma N, et al:
Constitutive Akt1 signals attenuate B-cell receptor signaling and
proliferation, but enhance B-cell migration and effector function.
Eur J Immunol. 42:3381–3393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sporn MB: The war on cancer. Lancet.
347:1377–1381. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim EK, Yun SJ, Ha JM, et al: Selective
activation of Akt1 by mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2
regulates cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis.
Oncogene. 30:2954–2963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chin YR and Toker A: The actin-bundling
protein palladin is an Akt1-specific substrate that regulates
breast cancer cell migration. Mol Cell. 38:333–344. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yoeli-Lerner M, Yiu GK, Rabinovitz I,
Erhardt P, Jauliac S and Toker A: Akt blocks breast cancer cell
motility and invasion through the transcription factor NFAT. Mol
Cell. 20:539–550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Irie HY, Pearline RV, Grueneberg D, et al:
Distinct roles of Akt1 and Akt2 in regulating cell migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 171:1023–1034.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Virtakoivu R, Pellinen T, Rantala JK,
Perala M and Ivaska J: Distinct roles of AKT isoforms in regulating
β1-integrin activity, migration, and invasion in prostate cancer.
Mol Biol Cell. 23:3357–3369. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Hutchinson JN, Jin J, Cardiff RD, Woodgett
JR and Muller WJ: Activation of Akt-1 (PKB-α) can accelerate
ErbB-2-mediated mammary tumorigenesis but suppresses tumor
invasion. Cancer Res. 64:3171–3178. 2004.
|
|
16
|
Maroulakou IG, Oemler W, Naber SP and
Tsichlis PN: Akt1 ablation inhibits, whereas Akt2 ablation
accelerates, the development of mammary adenocarcinomas in mouse
mammary tumor virus (MMTV)-ErbB2/neu and MMTV-polyoma middle T
transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 67:167–177. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie SQ, Li Q, Zhang YH, et al: NPC-16, a
novel naphthalimide-polyamine conjugate, induced apoptosis and
autophagy in human hepatoma HepG2 cells and Bel-7402 cells.
Apoptosis. 16:27–34. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP and
Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates
G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Hepatology. 50:113–121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koomoa DL, Geerts D, Lange I, et al:
DFMO/eflornithine inhibits migration and invasion downstream of
MYCN and involves p27Kip1 activity in neuroblastoma. Int
J Oncol. 42:1219–1228. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, et al:
MicroRNA-29b suppresses tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and
metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression.
Hepatology. 54:1729–1740. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie SQ, Zhang YH, Li Q, et al:
3-Nitro-naphthalimide and nitrogen mustard conjugate NNM-25 induces
hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis via PARP-1/p53 pathway.
Apoptosis. 17:725–734. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Lau GK, Chen L, et al: Interleukin
17A promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via NF-κB induced
matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 expression. PLoS One.
6:e218162011.
|
|
23
|
Yang P, Yuan W, He J, et al:
Overexpression of EphA2, MMP-9, and MVD-CD34 in hepatocellular
carcinoma: implications for tumor progression and prognosis.
Hepatol Res. 39:1169–1177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chandarlapaty S, Sawai A, Scaltriti M, et
al: AKT inhibition relieves feedback suppression of receptor
tyrosine kinase expression and activity. Cancer Cell. 19:58–71.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dillon RL and Muller WJ: Distinct
biological roles for the akt family in mammary tumor progression.
Cancer Res. 70:4260–4264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cariaga-Martinez AE, Lopez-Ruiz P,
Nombela-Blanco MP, et al: Distinct and specific roles of AKT1 and
AKT2 in androgen-sensitive and androgen-independent prostate cancer
cells. Cell Signal. 25:1586–1597. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saji M, Narahara K, McCarty SK, et al:
Akt1 deficiency delays tumor progression, vascular invasion, and
distant metastasis in a murine model of thyroid cancer. Oncogene.
30:4307–4315. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Imanishi Y, Hu B, Xiao G, Yao X and Cheng
SY: Angiopoietin-2, an angiogenic regulator, promotes initial
growth and survival of breast cancer metastases to the lung through
the integrin-linked kinase (ILK)-AKT-B cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2)
pathway. J Biol Chem. 286:29249–29260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Xiao L, Ma X, et al: Effect of
DNAzymes targeting Akt1 on cell proliferation and apoptosis in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:366–371. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Basseres DS and Baldwin AS: Nuclear
factor-κB and inhibitor of κB kinase pathways in oncogenic
initiation and progression. Oncogene. 25:6817–6830. 2006.
|
|
31
|
Han SS, Yun H, Son DJ, et al:
NF-κB/STAT3/PI3K signaling crosstalk in iMycEμ B
lymphoma. Mol Cancer. 9:972010.
|
|
32
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rundhaug JE: Matrix metalloproteinases and
angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 9:267–285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Zhang QY, Fu YC, et al:
Expression of p-Akt and COX-2 in gastric adenocarcinomas and
adenovirus mediated Akt1 and COX-2 ShRNA suppresses SGC-7901
gastric adenocarcinoma and U251 glioma cell growth in vitro and in
vivo. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 8:467–478. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Karar J and Maity A: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 4:512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pore N, Jiang Z, Shu HK, Bernhard E, Kao
GD and Maity A: Akt1 activation can augment hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α expression by increasing protein translation through a
mammalian target of rapamycin-independent pathway. Mol Cancer Res.
4:471–479. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee YC, Lin HH, Hsu CH, Wang CJ, Chiang TA
and Chen JH: Inhibitory effects of andrographolide on migration and
invasion in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via
down-regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
632:23–32. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee MW, Kim DS, Lee JH, et al: Roles of
AKT1 and AKT2 in non-small cell lung cancer cell survival, growth,
and migration. Cancer Sci. 102:1822–1828. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li R, Dai H, Wheeler TM, et al: Prognostic
value of Akt-1 in human prostate cancer: a computerized
quantitative assessment with quantum dot technology. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:3568–3573. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|