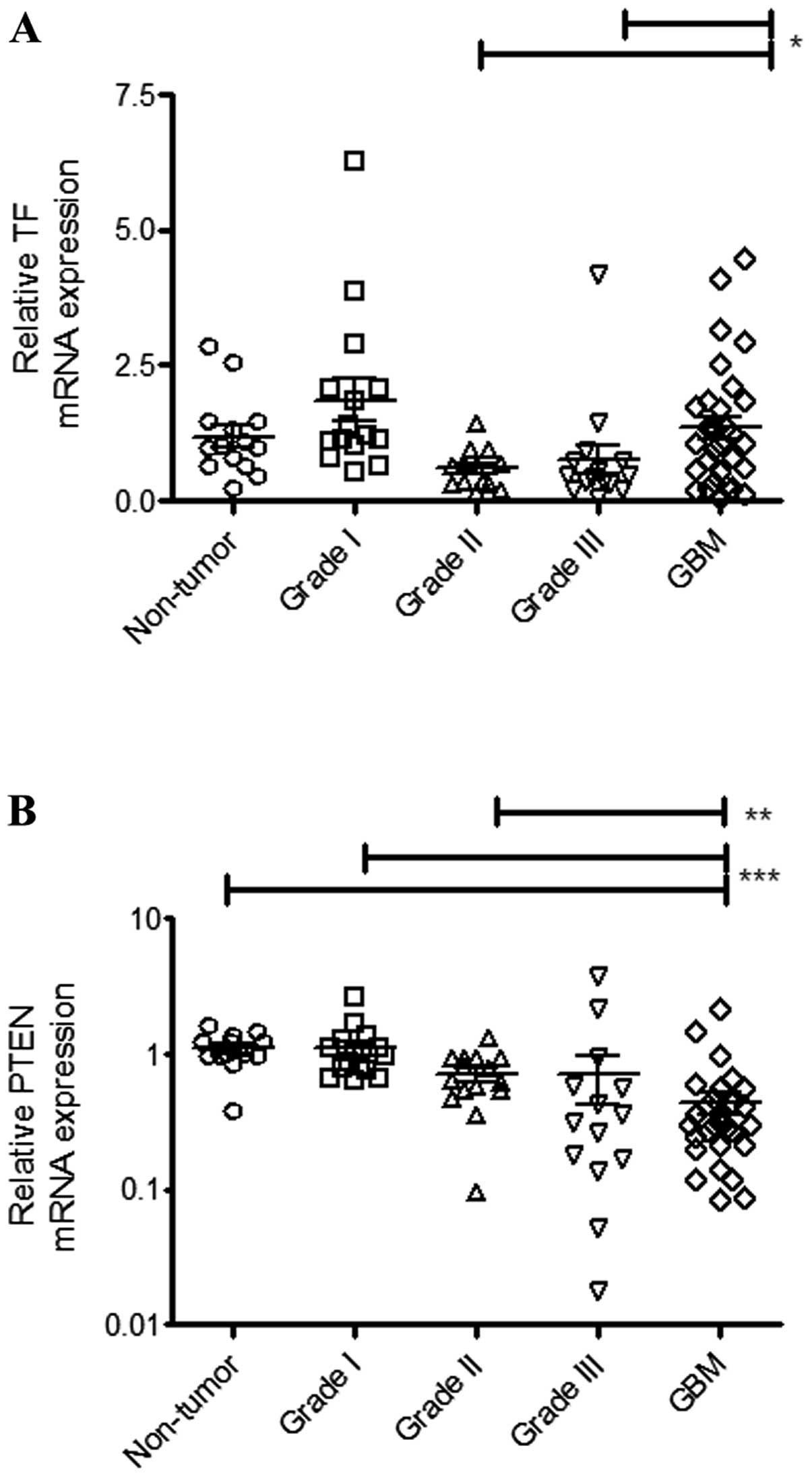
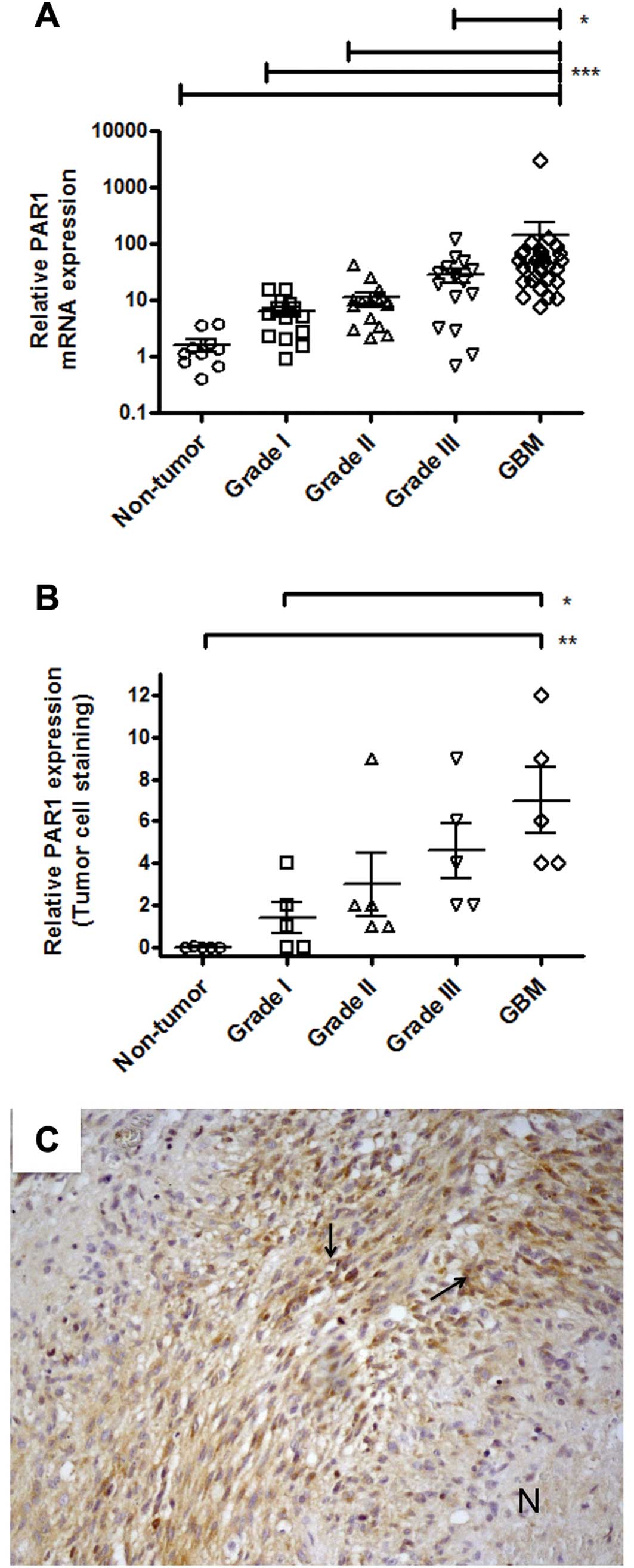
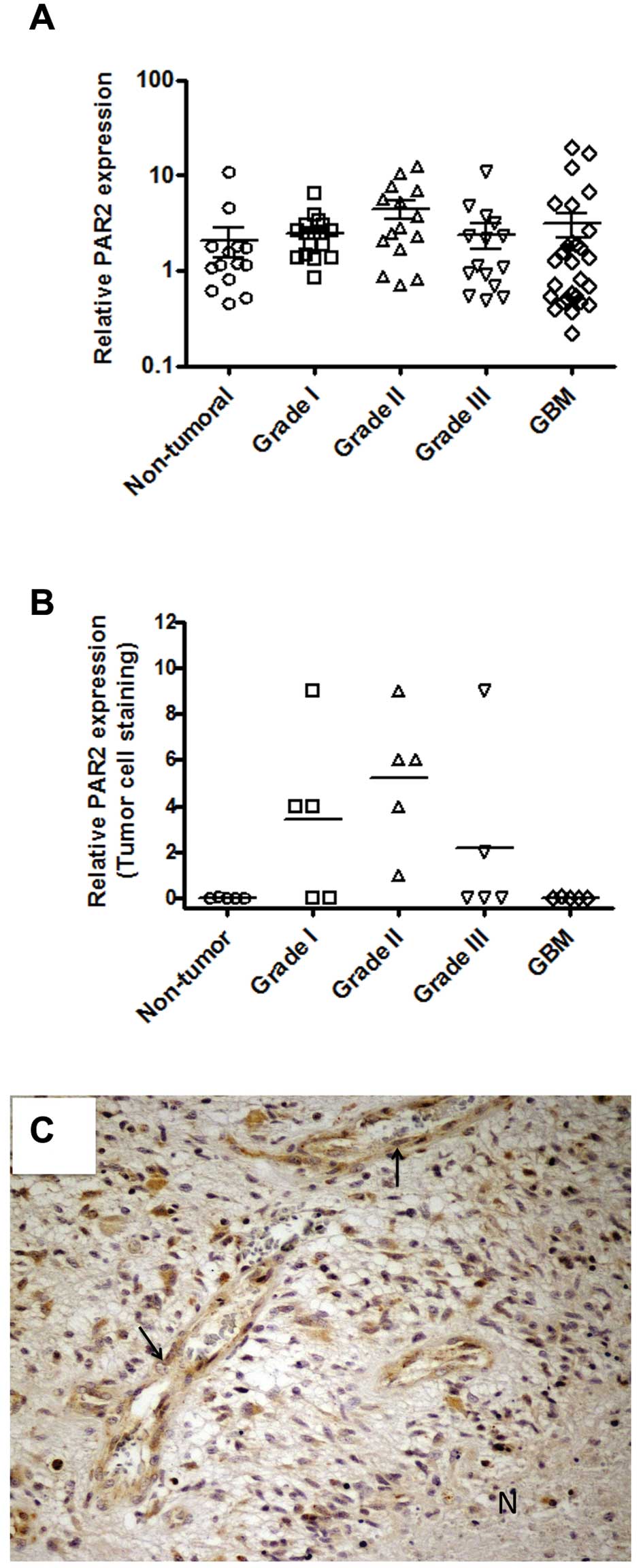
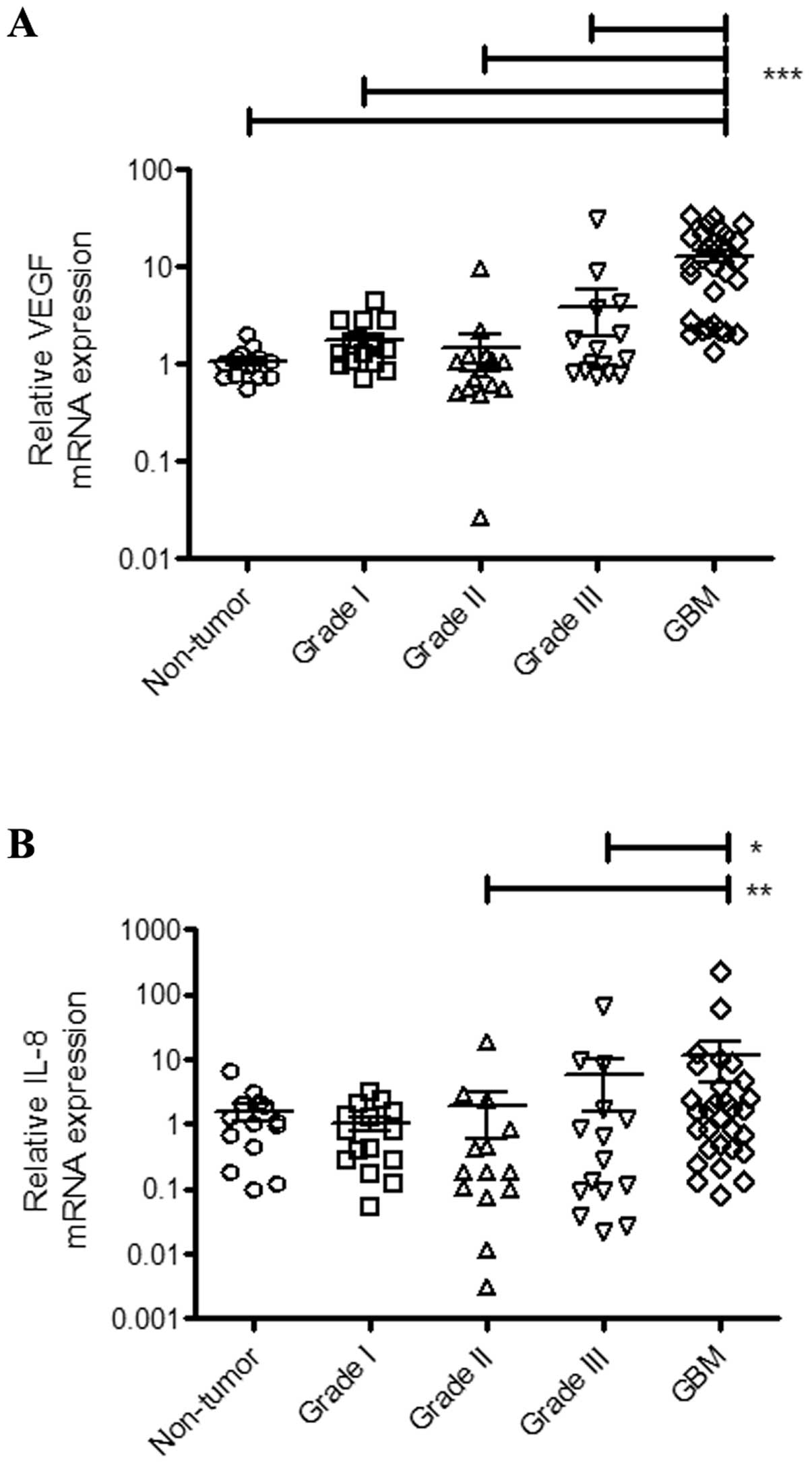
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Williams JC and Mackman N: Tissue factor
in health and disease. Front Biosci. 1:358–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Francischetti IM, Seydel KB and Monteiro
RQ: Blood coagulation, inflammation, and malaria. Microcirculation.
15:81–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rak J, Milsom C, Magnus N and Yu J: Tissue
factor in tumour progression. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol.
22:71–83. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruf W, Disse J, Carneiro-Lobo TC, Yokota N
and Schaffner F: Tissue factor and cell signalling in cancer
progression and thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 9(Suppl 1): 306–315.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lima LG and Monteiro RQ: Activation of
blood coagulation in cancer: implications for tumor progression.
Biosci Rep. 33:e000642013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tehrani M, Friedman TM, Olson JJ and Brat
DJ: Intravascular thrombosis in central nervous system
malignancies: a potential role in astrocytoma progression to
glioblastoma. Brain Pathol. 18:164–171. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brat DJ and Van Meir EG: Vaso-occlusive
and prothrombotic mechanisms associated with tumor hypoxia,
necrosis, and accelerated growth in glioblastoma. Lab Invest.
84:397–405. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Anand M and Brat DJ: Oncogenic regulation
of tissue factor and thrombosis in cancer. Thromb Res. 129(Suppl
1): S46–S49. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rong Y, Post DE, Pieper RO, Durden DL, Van
Meir EG and Brat DJ: PTEN and hypoxia regulate tissue factor
expression and plasma coagulation by glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
65:1406–1413. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kasthuri RS, Taubman MB and Mackman N:
Role of tissue factor in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:4834–4838. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Coughlin SR: Protease-activated receptors
in hemostasis, thrombosis and vascular biology. J Thromb Haemos.
3:1800–1814. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Elste AP and Petersen I: Expression of
proteinase-activated receptor 1–4 (PAR 1–4) in human cancer. J Mol
Histol. 41:89–99. 2010.
|
|
15
|
Albrektsen T, Sørensen BB, Hjortø GM,
Fleckner J, Rao LV and Petersen LC: Transcriptional program induced
by factor VIIa-tissue factor, PAR1 and PAR2 in MDA-MB-231 cells. J
Thromb Haemost. 5:1588–1597. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gessler F, Voss V, Dützmann S, Seifert V,
Gerlach R and Kögel D: Inhibition of tissue
factor/protease-activated receptor-2 signaling limits
proliferation, migration and invasion of malignant glioma cells.
Neuroscience. 165:1312–1322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oba-Shinjo SM, Bengtson MH, Winnischofer
SM, Colin C, Vedoy CG, de Mendonça Z, Marie SK and Sogayar MC:
Identification of novel differentially expressed genes in human
astrocytomas by cDNA representational difference analysis. Brain
Res Mol Brain Res. 140:25–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carneiro-Lobo TC, Konig S, Machado DE,
Nasciutti LE, Forni MF, Francischetti IM, Sogayar MC and Monteiro
RQ: Ixolaris, a tissue factor inhibitor, blocks primary tumor
growth and angiogenesis in a glioblastoma model. J Thromb Haemost.
7:1855–1864. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
De Groot CJ, Langeveld CH, Jongenelen CA,
Montagne L, Van Der Valk P and Dijkstra CD: Establishment of human
adult astrocyte cultures derived from postmortem multiple sclerosis
and control brain and spinal cord regions: immunophenotypical and
functional characterization. J Neurosci Res. 49:342–354. 1997.
|
|
21
|
Dutra-Oliveira A, Monteiro RQ and
Mariano-Oliveira A: Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) mediates
VEGF production through the ERK1/2 pathway in human glioblastoma
cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:221–227. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamada K, Kuratsu J, Saitoh Y, Takeshima
H, Nishi T and Ushio Y: Expression of tissue factor correlates with
grade of malignancy in human glioma. Cancer. 77:1877–1883. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guan M, Jin J, Su B, Liu WW and Lu Y:
Tissue factor expression and angiogenesis in human glioma. Clin
Biochem. 35:321–325. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA and Risau W:
Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour
angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature. 359:845–848.
1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koch AE, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL, Harlow
LA, DiPietro LA, Elner VM, Elner SG and Strieter RM: Interleukin-8
as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science.
258:1798–1801. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Brat DJ, Bellail AV and Van Meir EG: The
role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and
tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 7:122–133. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Magnus N, Garnier D and Rak J: Oncogenic
epidermal growth factor receptor up-regulates multiple elements of
the tissue factor signaling pathway in human glioma cells. Blood.
116:815–818. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lima FR, Kahn SA, Soletti RC, Biasoli D,
Alves T, da Fonseca AC, Garcia C, Romão J, Brito L, Holanda-Afonso
R, Faria J, Borges H and Moura-Neto V: Glioblastoma: therapeutic
challenges, what lies ahead. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1826:338–349.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fernandes RS, Kirszberg C, Rumjanek VM and
Monteiro RQ: On the molecular mechanisms for the highly
procoagulant pattern of C6 glioma cells. J Thromb Haemost.
4:1546–1552. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kirszberg C, Lima LG, Da Silva de Oliveira
A, Pickering W, Gray E, Barrowcliffe TW, Rumjanek VM and Monteiro
RQ: Simultaneous tissue factor expression and phosphatidylserine
exposure account for the highly procoagulant pattern of melanoma
cell lines. Melanoma Res. 19:301–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Zhan H, Xu W, Yuan Z, Lu P, Zhan
L and Li Q: Upregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and
proteinase-activated receptor-1 promotes the progression of human
gliomas. Pathol Res Pract. 207:24–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Boire A, Covic L, Agarwal A, Jacques S,
Sherifi S and Kuliopulos A: PAR1 is a matrix metalloprotease-1
receptor that promotes invasion and tumorigenesis of breast cancer
cells. Cell. 120:303–313. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin YJ, Salah Z, Maoz M, Even Ram SC,
Ochayon S, Neufeld G, Katzav S and Bar-Shavit R: Oncogenic
transformation induces tumor angiogenesis: a role for PAR1
activation. FASEB J. 17:163–174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu Y, Gu Y, Keep RF, Heth J, Muraszko KM,
Xi G and Hua Y: Thrombin up-regulates vascular endothelial growth
factor in experimental gliomas. Neurol Res. 31:759–765. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Versteeg HH, Schaffner F, Kerver M, Ellies
LG, Andrade-Gordon P, Mueller BM and Ruf W: Protease-activated
receptor (PAR) 2, but not PAR1, signaling promotes the development
of mammary adenocarcinoma in polyoma middle T mice. Cancer Res.
68:7219–7227. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schaffner F, Versteeg HH, Schillert A,
Yokota N, Petersen LC, Mueller BM and Ruf W: Cooperation of tissue
factor cytoplasmic domain and PAR2 signaling in breast cancer
development. Blood. 116:6106–6113. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Svensson KJ, Kucharzewska P, Christianson
HC, Sköld S, Löfstedt T, Johansson MC, Mörgelin M, Bengzon J, Ruf W
and Belting M: Hypoxia triggers a proangiogenic pathway involving
cancer cell microvesicles and PAR-2-mediated heparin-binding EGF
signaling in endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:13147–13152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Harter PN, Dützmann S, Drott U, Zachskorn
C, Hattingen E, Capper D, Gessler F, Senft C, Seifert V, Plate KH,
Kögel D and Mittelbronn M: Anti-tissue factor (TF9–10H10) treatment
reduces tumor cell invasiveness in a novel migratory glioma model.
Neuropathology. 33:515–525. 2013.
|
|
39
|
Ornstein DL, Meehan KR and Zacharski LR:
The coagulation system as a target for the treatment of human
gliomas. Semin Thromb Hemost. 28:19–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hua Y, Tang L, Keep RF, Schallert T, Fewel
ME, Muraszko KM, Hoff JT and Xi G: The role of thrombin in gliomas.
J Thromb Haemost. 3:1917–1923. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carneiro-Lobo TC, Schaffner F, Disse J,
Ostergaard H, Francischetti IM, Monteiro RQ and Ruf W: The
tick-derived inhibitor Ixolaris prevents tissue factor signaling on
tumor cells. J Thromb Haemost. 10:1849–1858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|