|
1
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang
SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC and Wu KJ: Direct regulation of TWIST by HIF-1α
promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:295–305. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Gjerdrum C, Tiron C, Hoiby T, Stefansson
I, Haugen H, Sandal T, Collett K, Li S, McCormack E, Gjertsen BT,
Micklem DR, Akslen LA, Glackin C and Lorens JB: Axl is an essential
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced regulator of breast
cancer metastasis and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:1124–1129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Skvortsova I, Skvortsov S, Raju U, Stasyk
T, Riesterer O, Schottdorf EM, Popper BA, Schiestl B, Eichberger P,
Debbage P, Neher A, Bonn GK, Huber LA, Milas L and Lukas P:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and c-myc expression are the
determinants of cetuximab-induced enhancement of squamous cell
carcinoma radioresponse. Radiother Oncol. 96:108–115. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bandyopadhyay A, Wang L, Agyin J, Tang Y,
Lin S, Yeh IT, De K and Sun LZ: Doxorubicin in combination with a
small TGFβ inhibitor: a potential novel therapy for metastatic
breast cancer in mouse models. PLoS One. 5:e103652010.
|
|
8
|
Lobo NA, Shimono Y, Qian D and Clarke MF:
The biology of cancer stem cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
23:675–699. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu Z, Pestell TG, Lisanti MP and Pestell
RG: Cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:2144–2151. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kong D, Banerjee S, Ahmad A, Li Y, Wang Z,
Sethi S and Sarkar FH: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is
mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer
cells. PLoS One. 5:e124452010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Turner C and Kohandel M: Investigating the
link between epithelial-mesenchymal transition and the cancer stem
cell phenotype: a mathematical approach. J Theor Biol. 265:329–335.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
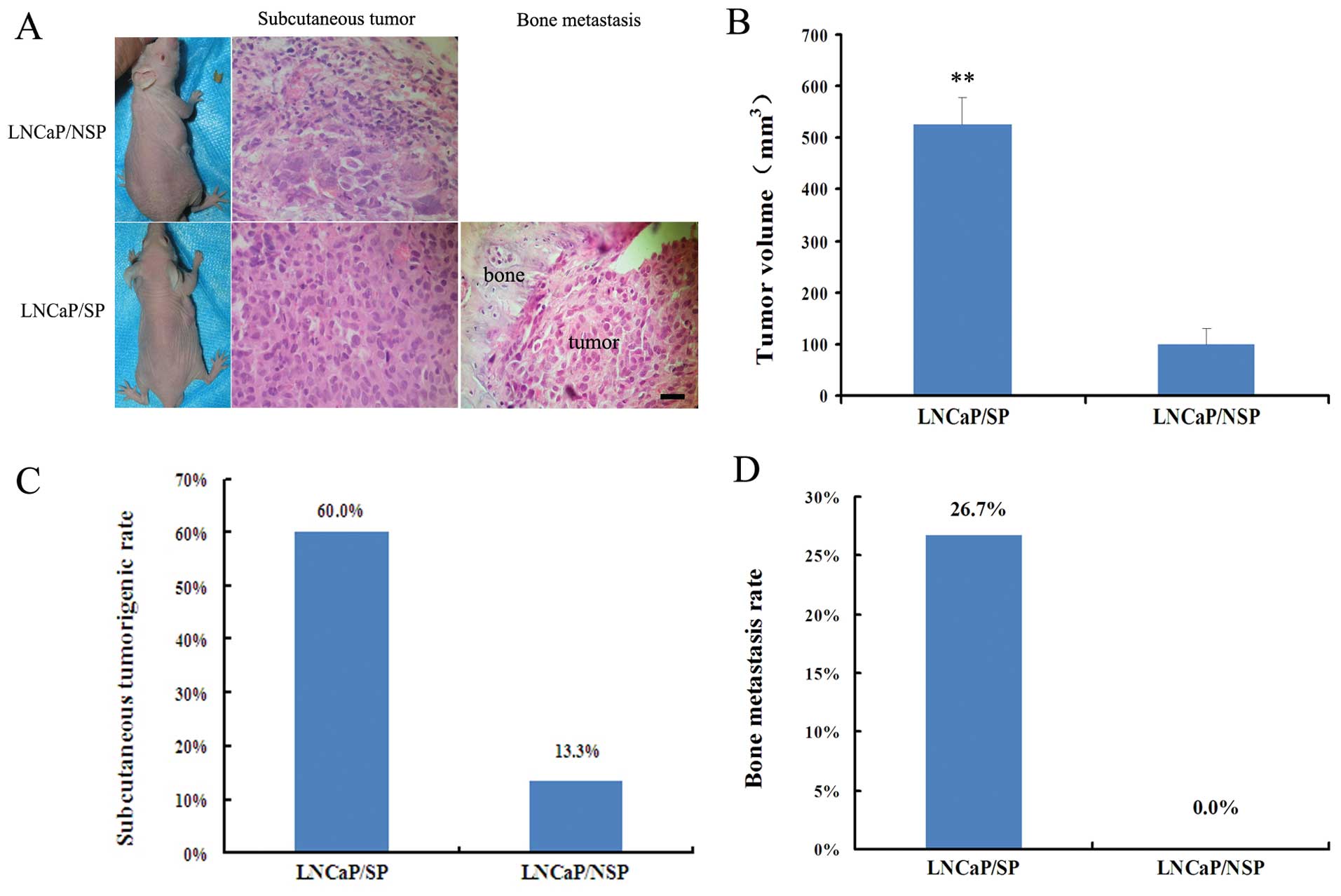
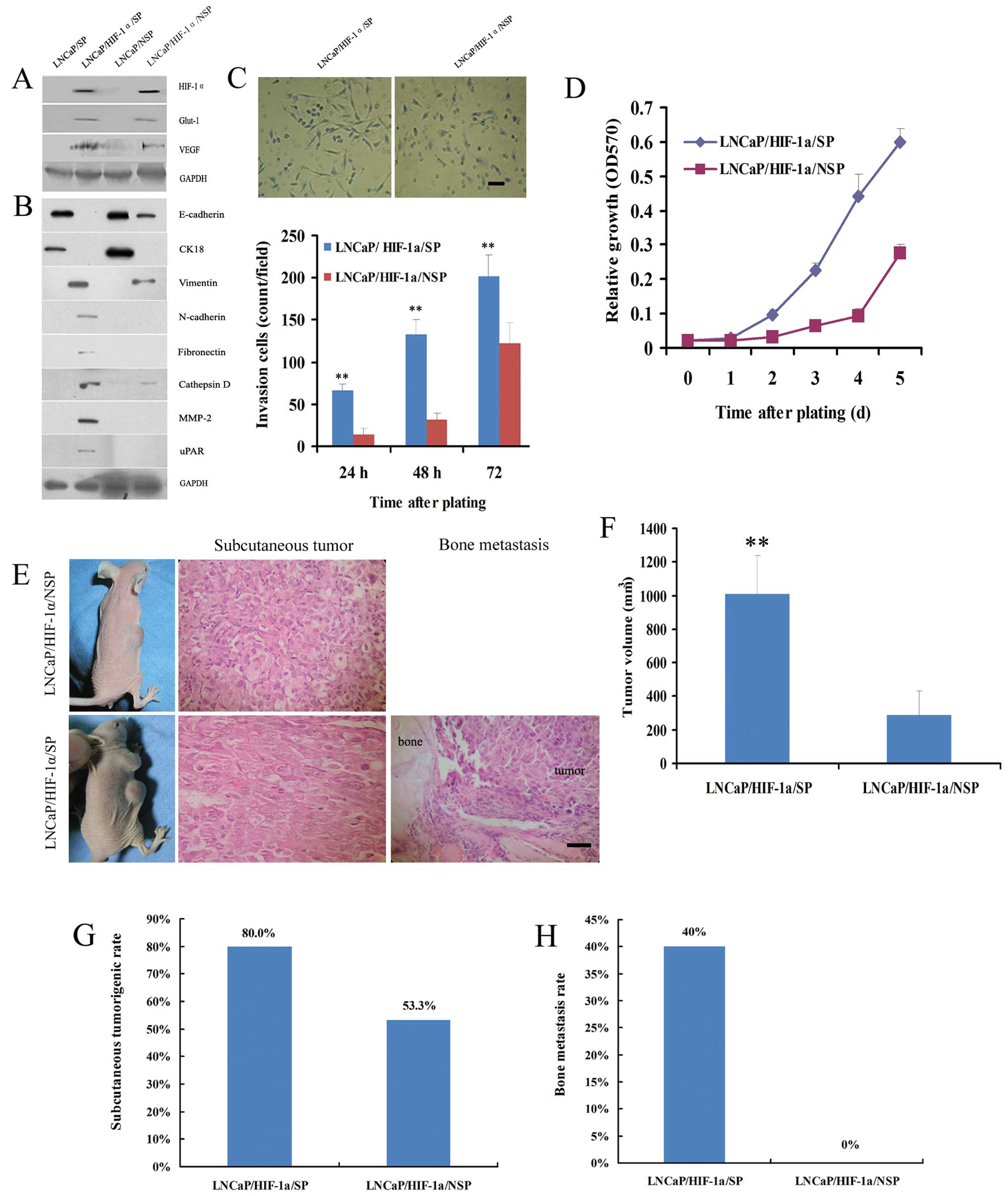
Luo Y, He DL, Ning L, Shen SL, Li L, Li X,
Zhau HE and Chung LW: Over-expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α increases the invasive potency of LNCaP cells in
vitro. BJU Int. 98:1315–1139. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang YG, Luo Y, He DL, Li X, Zhang LL,
Peng T, Li MC and Lin YH: Role of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human prostate
cancer induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Int J Urol.
14:1034–1039. 2007.
|
|
15
|
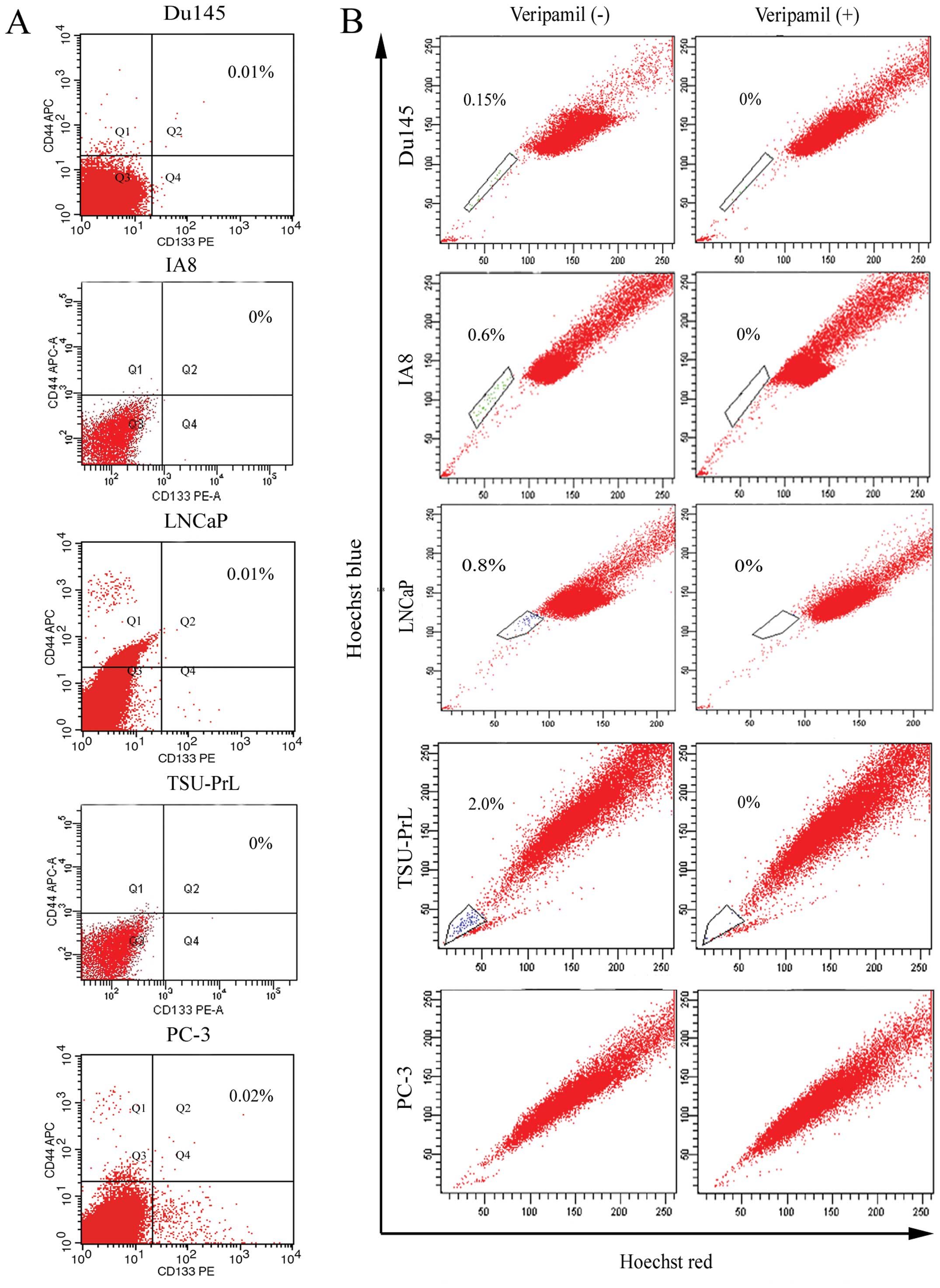
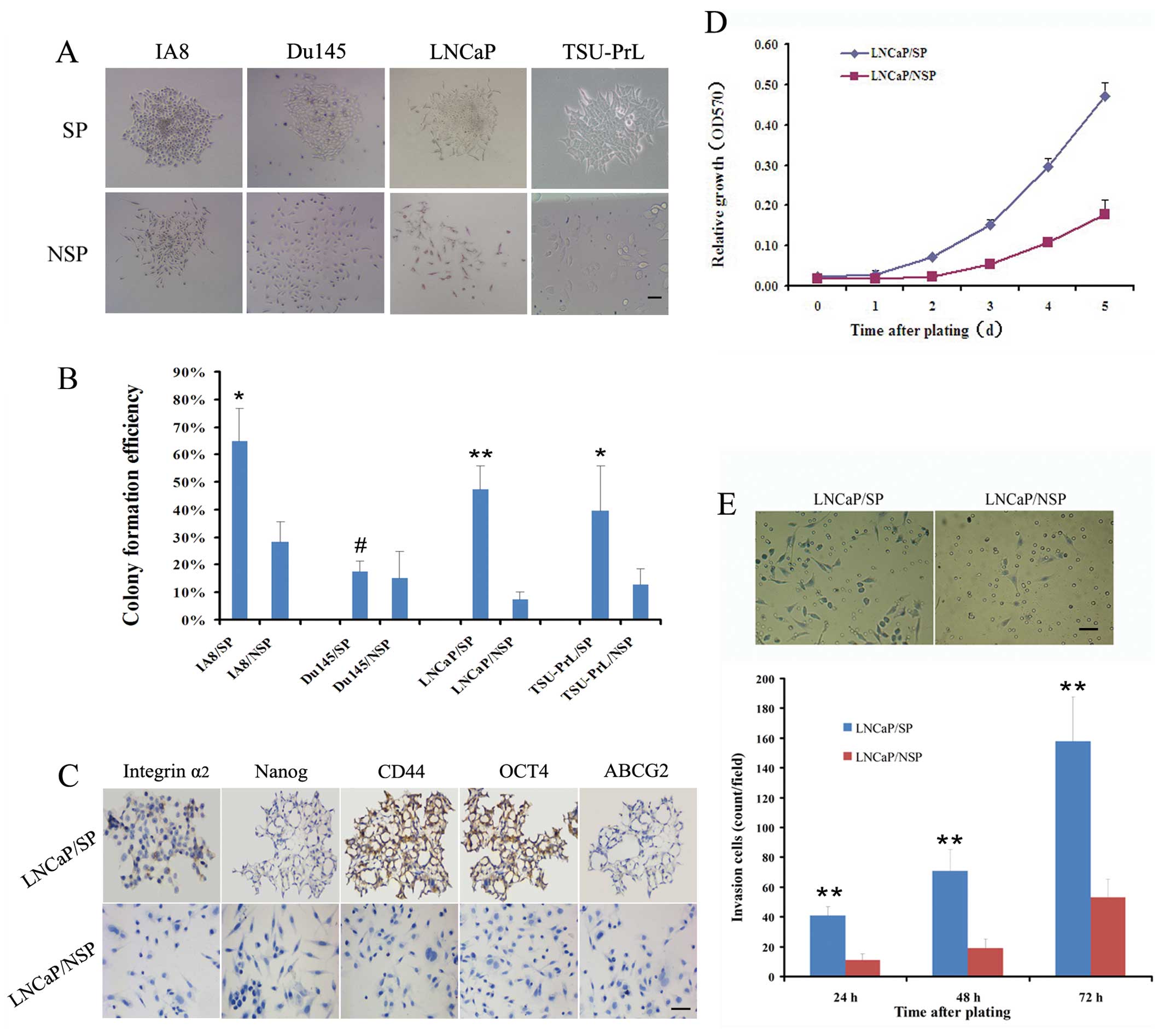
Yu SC and Bian XW: Enrichment of cancer
stem cells based on heterogeneity of invasiveness. Stem Cell Rev.
5:66–71. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oates JE, Grey BR, Addla SK, Samuel JD,
Hart CA, Ramani VA, Brown MD and Clarke NW: Hoechst 33342 side
population identification is a conserved and unified mechanism in
urological cancers. Stem Cells Dev. 18:1515–1522. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou J, Wang H, Cannon V, Wolcott KM, Song
H and Yates C: Side population rather than CD133+ cells
distinguishes enriched tumorigenicity in hTERT-immortalized primary
prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:1122011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
May CD, Sphyris N, Evans KW, Werden SJ,
Guo W and Mani SA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
stem cells: a dangerously dynamic duo in breast cancer progression.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:2022011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cano A and Nieto MA: Non-coding RNAs take
centre stage in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Trends Cell
Biol. 18:357–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Y, VandenBoom TG II, Kong D, Wang Z,
Ali S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH: Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7
by natural agents leads to the reversal of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:6704–6712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC,
Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, Waldvogel B, Vannier C, Darling D,
zur Hausen A, Brunton VG, Morton J, Sansom O, Schüler J, Stemmler
MP, Herzberger C, Hopt U, Keck T, Brabletz S and Brabletz T: The
EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing
stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 11:1487–1495. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, Gong
C, Huang Y, Hu X, Su F, Lieberman J and Song E: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brabletz T, Jung A, Spaderna S, Hlubek F
and Kirchner T: Opinion: migrating cancer stem cells - an
integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:744–749. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Albino D, Longoni N, Curti L, Mello-Grand
M, Pinton S, Civenni G, Thalmann G, D’Ambrosio G, Sarti M, Sessa F,
Chiorino G, Catapano CV and Carbone GM: ESE3/EHF controls
epithelial cell differentiation and its loss leads to prostate
tumors with mesenchymal and stem-like features. Cancer Res.
72:2889–2900. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Banerjee S,
Ahmad A, Li Y, Azmi AS, Miele L and Sarkar FH: Over-expression of
FoxM1 leads to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem
cell phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
112:2296–2306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang R, Li Y, Xu Y, Zhou Y, Pang Y, Shen
L, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhou J, Wang X and Liu Q: EMT and CSC-like
properties mediated by the IKKβ/IκBα/RelA signal pathway via the
transcriptional regulator, Snail, are involved in the
arsenite-induced neoplastic transformation of human keratinocytes.
Arch Toxicol. 87:991–1000. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jo M, Eastman BM, Webb DL, Stoletov K,
Klemke R and Gonias SL: Cell signaling by urokinase-type
plasminogen activator receptor induces stem cell-like properties in
breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:8948–8958. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Li Y, Ahmad
A, Banerjee S, Azmi AS, Miele L and Sarkar FH: Notch-1 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell
phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 307:26–36. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Morel AP, Lièvre M, Thomas C, Hinkal G,
Ansieau S and Puisieux A: Generation of breast cancer stem cells
through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One. 3:e28882008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou Y, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, Campbell
LL, Polyak K, Brisken C, Yang J and Weinberg RA: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lan L, Luo Y, Cui D, Shi BY, Deng W, Huo
LL, Chen HL, Zhang GY and Deng LL: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition triggers cancer stem cell generation in human thyroid
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:113–120. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Biddle A, Liang X, Gammon L, Fazil B,
Harper LJ, Emich H, Costea DE and Mackenzie IC: Cancer stem cells
in squamous cell carcinoma switch between two distinct phenotypes
that are preferentially migratory or proliferative. Cancer Res.
71:5317–5326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen C, Wei Y, Hummel M, Hoffmann TK,
Gross M, Kaufmann AM and Albers AE: Evidence for
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer stem cells of head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e164662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han M, Liu M, Wang Y, Chen X, Xu J, Sun Y,
Zhao L, Qu H, Fan Y and Wu C: Antagonism of miR-21 reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype
through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS One.
7:e395202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chiou GY, Cherng JY, Hsu HS, Wang ML, Tsai
CM, Lu KH, Chien Y, Hung SC, Chen YW, Wong CI, Tseng LM, Huang PI,
Yu CC, Hsu WH and Chiou SH: Cationic polyurethanes-short branch
PEI-mediated delivery of Mir145 inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal
transdifferentiation and cancer stem-like properties and in lung
adenocarcinoma. J Control Release. 159:240–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Nalls D, Tang SN, Rodova M, Srivastava RK
and Shankar S: Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for
treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer
stem cells. PLoS One. 6:e240992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bao B, Ali S, Kong D, Sarkar SH, Wang Z,
Banerjee S, Aboukameel A, Padhye S, Philip PA and Sarkar FH:
Anti-tumor activity of a novel compound-CDF is mediated by
regulating miR-21, miR-200, and PTEN in pancreatic cancer. PLoS
One. 6:e178502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bao B, Ali S, Banerjee S, Wang Z, Logna F,
Azmi AS, Kong D, Ahmad A, Li Y, Padhye S and Sarkar FH: Curcumin
analogue CDF inhibits pancreatic tumor growth by switching on
suppressor microRNAs and attenuating EZH2 expression. Cancer Res.
72:335–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|