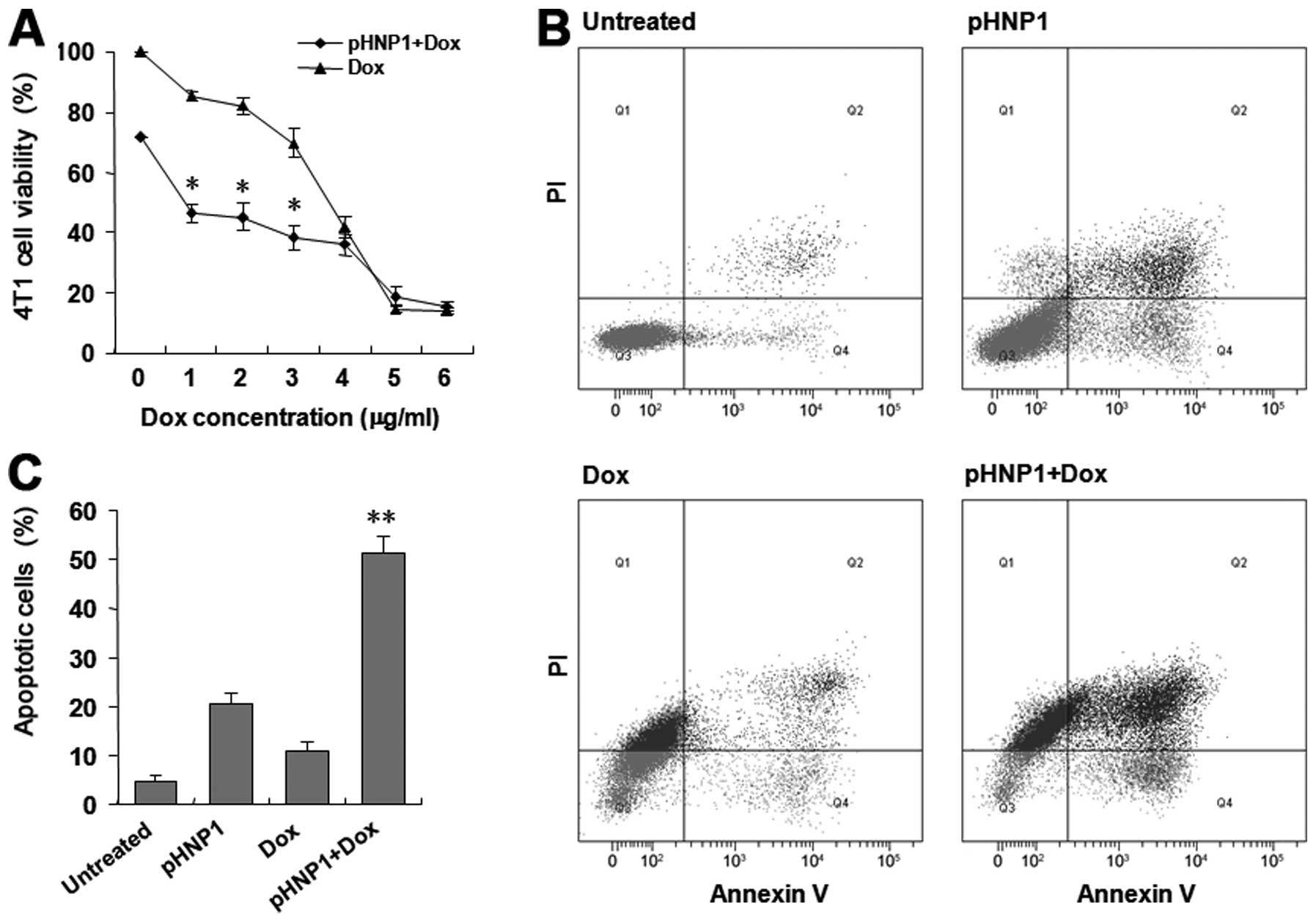
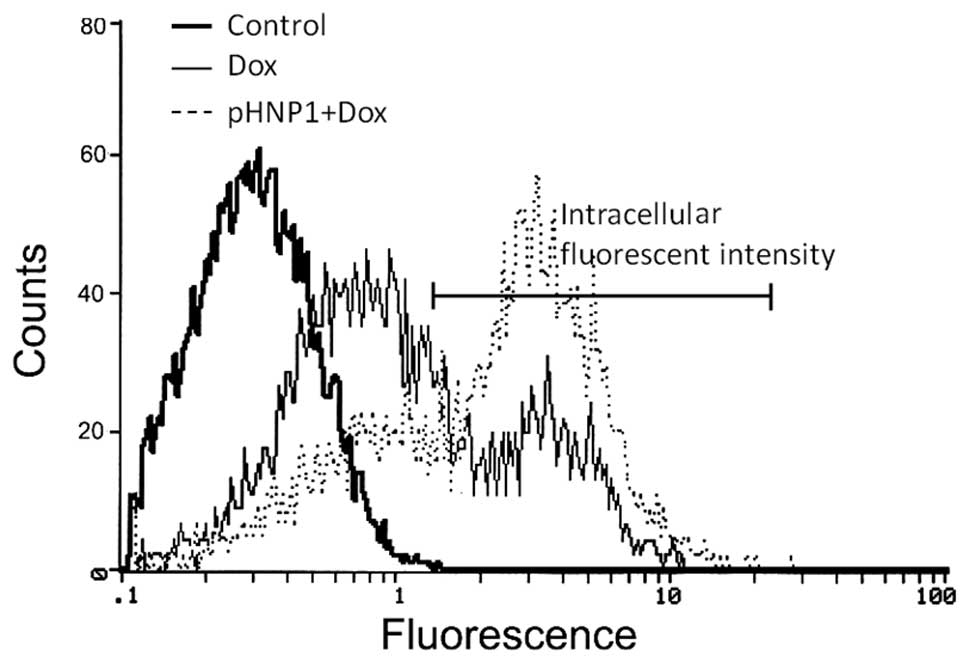
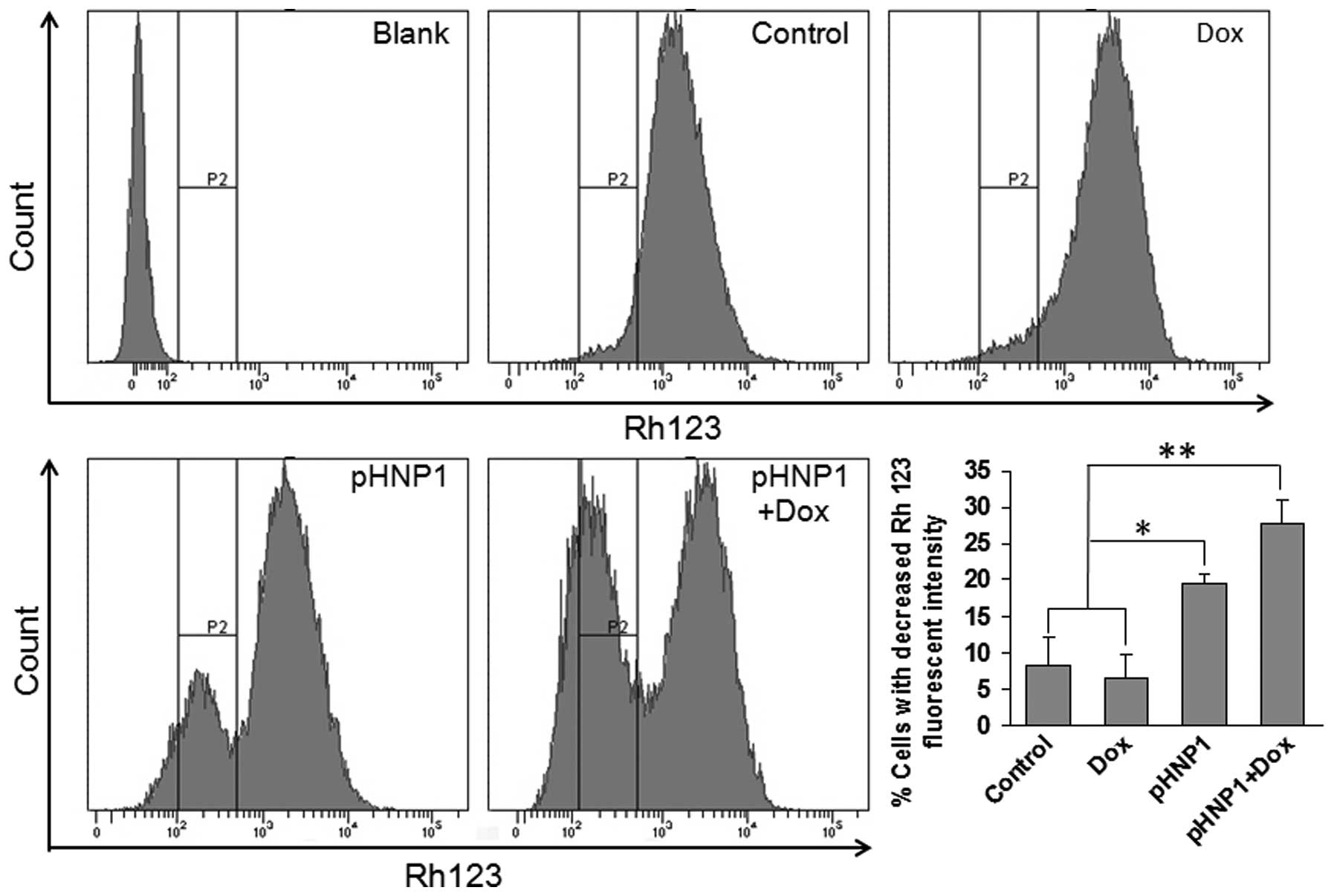
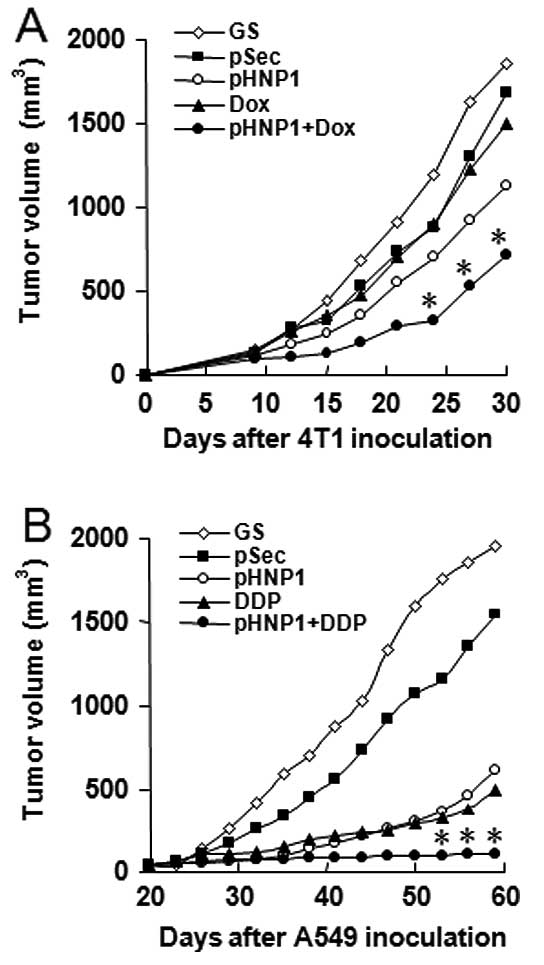
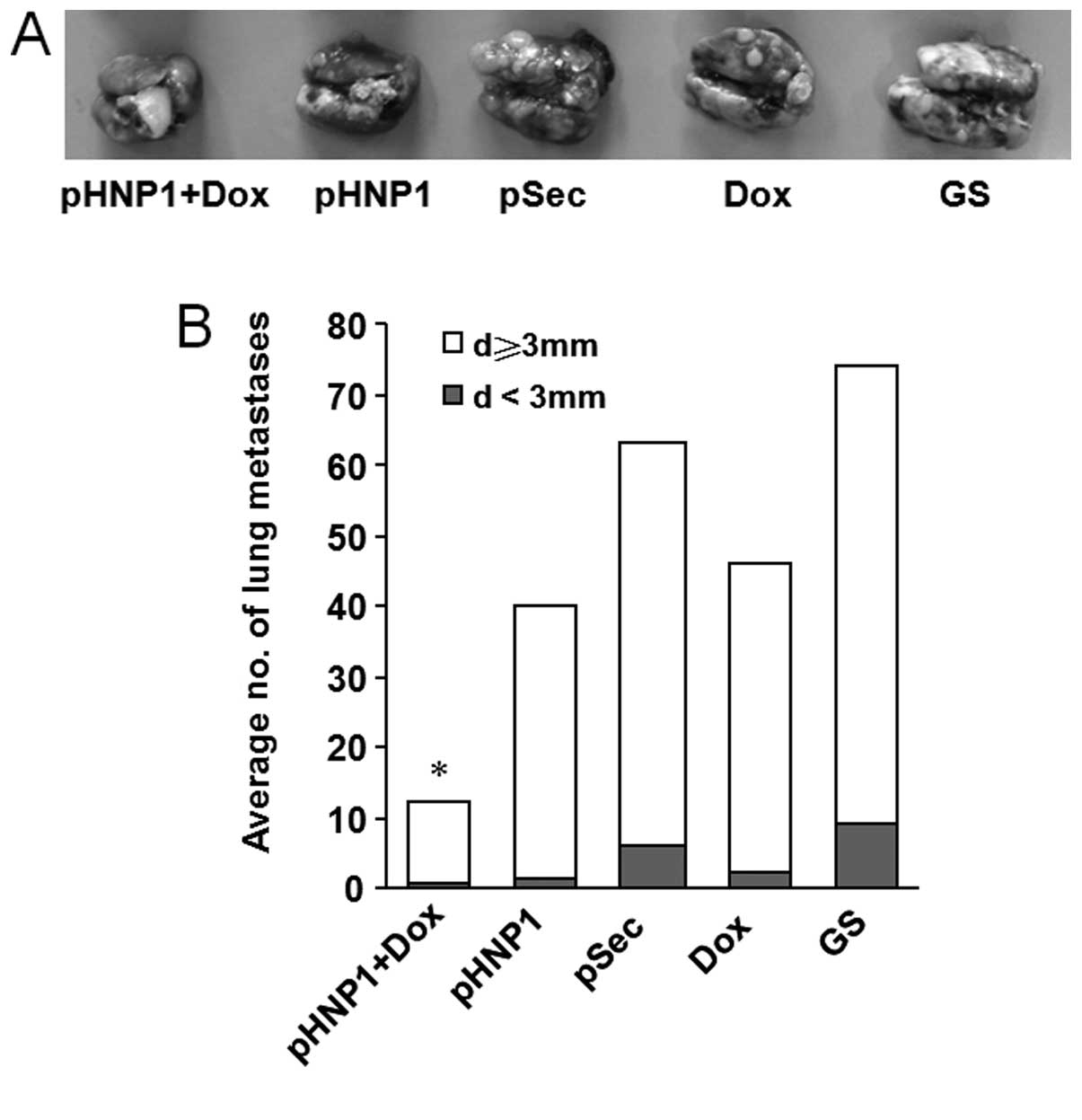
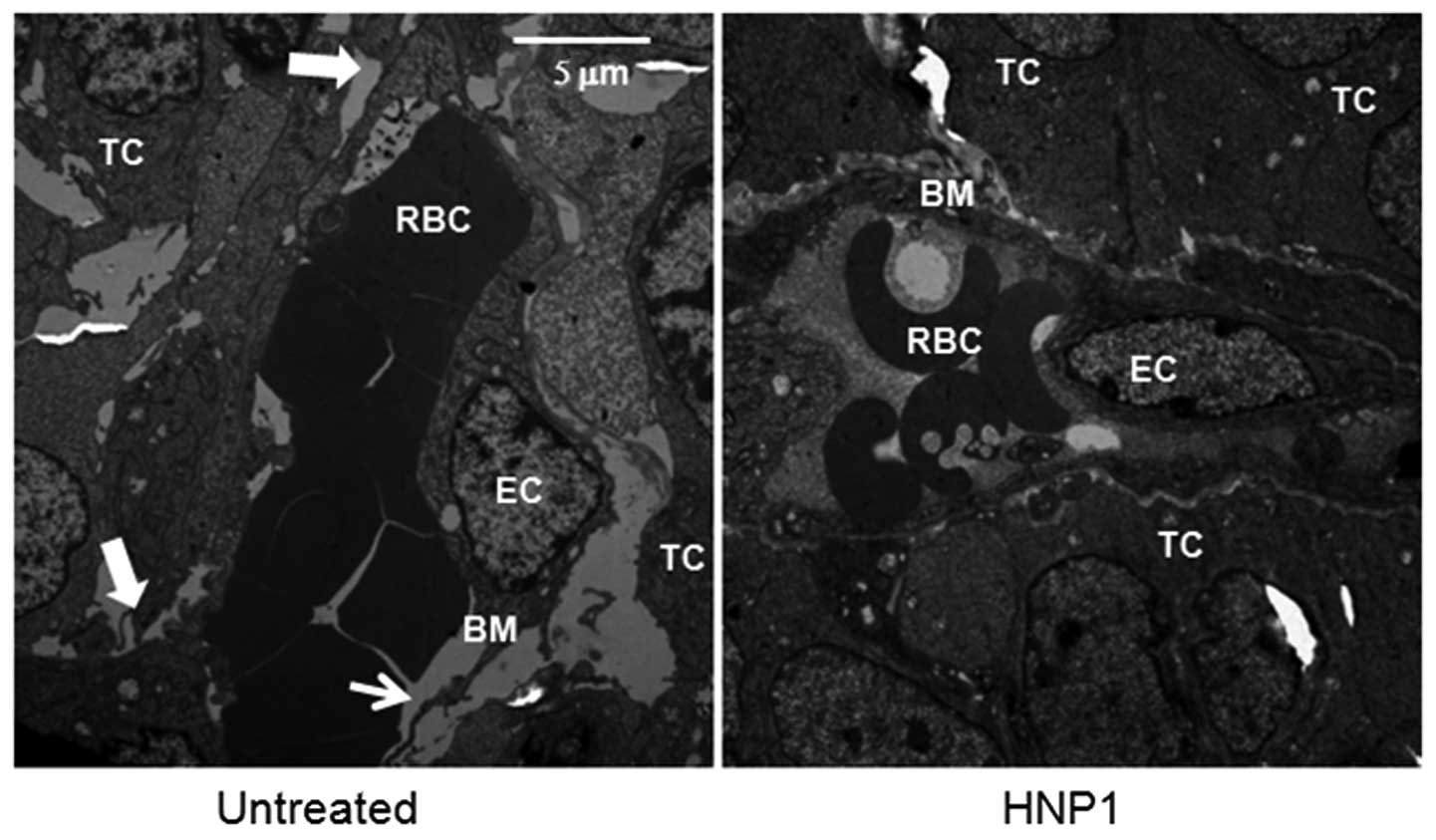
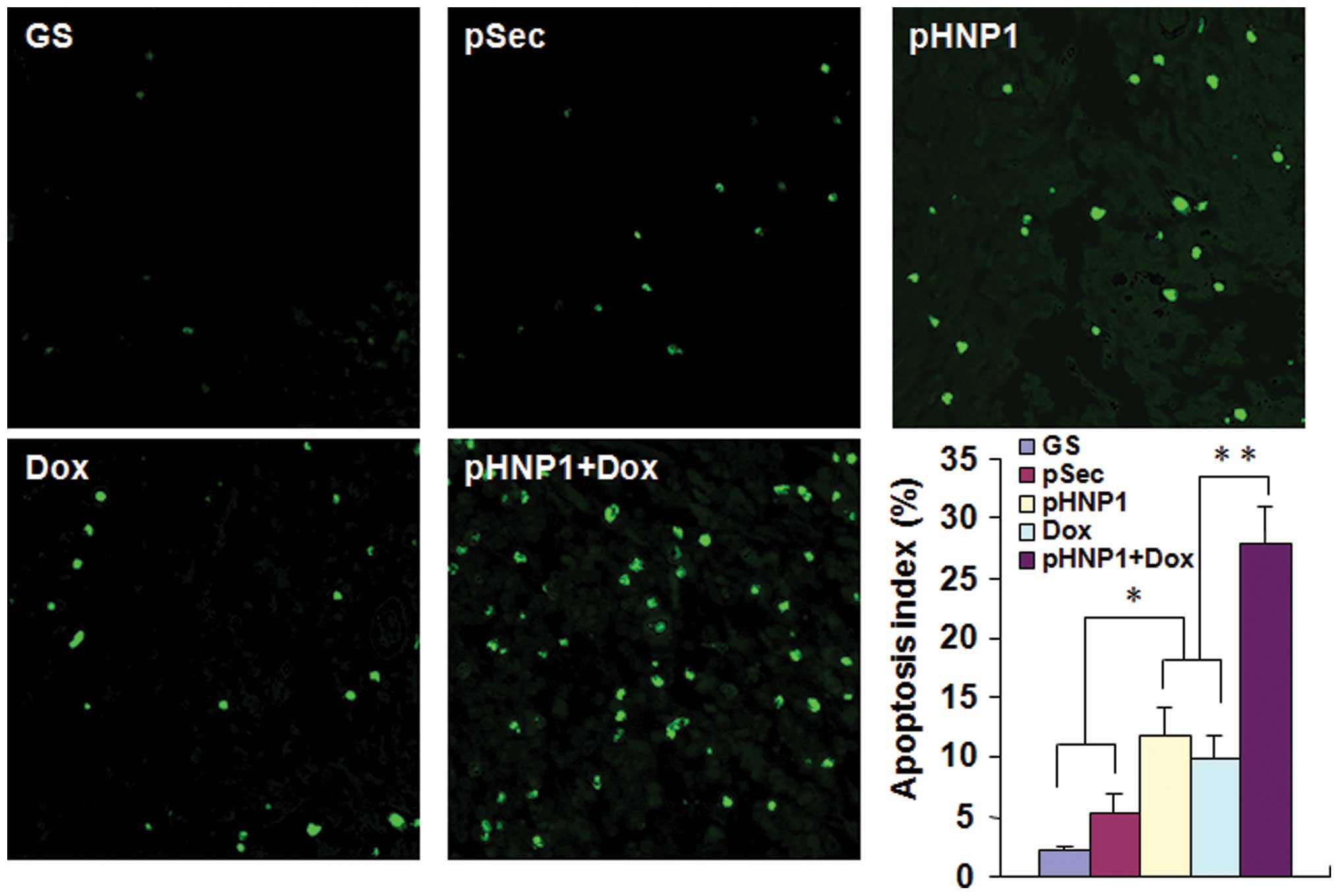
|
1
|
Franceschini G, Terribile D, Magno S, et
al: Update in the treatment of locally advanced breast cancer: a
multidisciplinary approach. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 11:283–289.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, et al:
Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast
cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:1784–1792. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schott AF and Hayes DF: Defining the
benefits of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 30:1747–1749. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dong J, Yang G and McHaourab HS:
Structural basis of energy transduction in the transport cycle of
MsbA. Science. 308:1023–1028. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agerberth B, Charo J, Werr J, et al: The
human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides LL-37 and α-defensins
are expressed by specific lymphocyte and monocyte populations.
Blood. 96:3086–3093. 2000.
|
|
6
|
Obata-Onai A, Hashimoto S, Onai N, et al:
Comprehensive gene expression analysis of human NK cells and
CD8+ T lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 14:1085–1098. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ganz T, Selsted ME and Lehrer RI:
Defensins. Eur J Haematol. 44:1–8. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Müller CA, Markovic-Lipkovski J, Klatt T,
et al: Human α-defensins HNPs-1, -2, and -3 in renal cell
carcinoma: influences on tumor cell proliferation. Am J Pathol.
160:1311–1324. 2002.
|
|
9
|
Lundy FT, Orr DF, Gallagher JR, et al:
Identification and overexpression of human neutrophil α-defensins
(human neutrophil peptides 1, 2 and 3) in squamous cell carcinomas
of the human tongue. Oral Oncol. 40:139–144. 2004.
|
|
10
|
Melle C, Ernst G, Schimmel B, et al:
Discovery and identification of α-defensins as low abundant,
tumor-derived serum markers in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
129:66–73. 2005.
|
|
11
|
Holterman DA, Diaz JI, Blackmore PF, et
al: Overexpression of α-defensin is associated with bladder cancer
invasiveness. Urol Oncol. 24:97–108. 2006.
|
|
12
|
Bateman A, Singh A, Jothy S, Fraser R,
Esch F and Solomon S: The levels and biologic action of the human
neutrophil granule peptide HP-1 in lung tumors. Peptides.
13:133–139. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Zhao J, Yu X, et al: Identification
of biomarkers for breast cancer in nipple aspiration and ductal
lavage fluid. Clin Cancer Res. 11:8312–8320. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lichtenstein A, Ganz T, Selsted ME and
Lehrer RI: In vitro tumor cell cytolysis mediated by peptide
defensins of human and rabbit granulocytes. Blood. 68:1407–1410.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barker E and Reisfeld RA: A mechanism for
neutrophil-mediated lysis of human neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res.
53:362–367. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
McKeown ST, Lundy FT, Nelson J, et al: The
cytotoxic effects of human neutrophil peptide-1 (HNP1) and
lactoferrin on oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) in vitro. Oral
Oncol. 42:685–690. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu N, Wang YS, Pan WB, et al: Human
α-defensin-1 inhibits growth of human lung adenocarcinoma xenograft
in nude mice. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1588–1597. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Wang YS, Li D, Shi HS, et al: Intratumoral
expression of mature human neutrophil peptide-1 mediates antitumor
immunity in mice. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6901–6911. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chavakis T, Cines DB, Rhee JS, et al:
Regulation of neovascularization by human neutrophil peptides
(α-defensins): a link between inflammation and angiogenesis. FASEB
J. 18:1306–1308. 2004.
|
|
20
|
Shen G, Li Y, Du T, et al: SKLB1002, a
novel inhibitor of VEGF receptor 2 signaling, induces vascular
normalization to improve systemically administered chemotherapy
efficacy. Neoplasma. 59:486–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dickson PV, Hamner JB, Sims TL, et al:
Bevacizumab-induced transient remodeling of the vasculature in
neuroblastoma xenografts results in improved delivery and efficacy
of systemically administered chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3942–3950. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bruno NA and Slate DL: Effect of exposure
to calcium entry blockers on doxorubicin accumulation and
cytotoxicity in multidrug-resistant cells. J Natl Cancer Inst.
82:419–424. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aarbiou J, Tjabringa GS, Verhoosel RM, et
al: Mechanisms of cell death induced by the neutrophil
antimicrobial peptides α-defensins and LL-37. Inflamm Res.
55:119–127. 2006.
|
|
24
|
Pulaski BA, Terman DS, Khan S, Muller E
and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Cooperativity of Staphylococcal
aureus enterotoxin B superantigen, major histocompatibility
complex class II, and CD80 for immunotherapy of advanced
spontaneous metastases in a clinically relevant postoperative mouse
breast cancer model. Cancer Res. 60:2710–2715. 2000.
|
|
25
|
Boucher Y, Baxter LT and Jain RK:
Interstitial pressure gradients in tissue-isolated and subcutaneous
tumors: implications for therapy. Cancer Res. 50:4478–4484.
1990.
|
|
26
|
Minchinton AI and Tannock IF: Drug
penetration in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:583–592. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang SH, Wientjes MG, Lu D and Au JL: Drug
delivery and transport to solid tumors. Pharm Res. 20:1337–1350.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Economopoulou M, Bdeir K, Cines DB, et al:
Inhibition of pathologic retinal neovascularization by α-defensins.
Blood. 106:3831–3838. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Zasloff M: Antimicrobial peptides of
multicellular organisms. Nature. 415:389–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McPhee JB and Hancock RE: Function and
therapeutic potential of host defence peptides. J Pept Sci.
11:677–687. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mader JS, Salsman J, Conrad DM and Hoskin
DW: Bovine lactoferricin selectively induces apoptosis in human
leukemia and carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:612–624.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moore AJ, Devine DA and Bibby MC:
Preliminary experimental anticancer activity of cecropins. Pept
Res. 7:265–269. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jacob L and Zasloff M: Potential
therapeutic applications of magainins and other antimicrobial
agents of animal origin. Ciba Found Symp. 186:197–216.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hui L, Leung K and Chen HM: The combined
effects of antibacterial peptide cecropin A and anti-cancer agents
on leukemia cells. Anticancer Res. 22:2811–2816. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Johnstone SA, Gelmon K, Mayer LD, Hancock
RE and Bally MB: In vitro characterization of the anticancer
activity of membrane-active cationic peptides. I. Peptide-mediated
cytotoxicity and peptide-enhanced cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin
against wild-type and P-glycoprotein over-expressing tumor cell
lines. Anticancer Drug Des. 15:151–160. 2000.
|
|
36
|
Lincke CR, van der Bliek AM, Schuurhuis
GJ, van der Velde-Koerts T, Smit JJ and Borst P: Multidrug
resistance phenotype of human BRO melanoma cells transfected with a
wild-type human mdr1 complementary DNA. Cancer Res.
50:1779–1785. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ohsaki Y, Gazdar AF, Chen HC and Johnson
BE: Antitumor activity of magainin analogues against human lung
cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 52:3534–3538. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fojo AT and Menefee M: Microtubule
targeting agents: basic mechanisms of multidrug resistance (MDR).
Semin Oncol. 32(Suppl 7): S3–S8. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Doyle L and Ross DD: Multidrug resistance
mediated by the breast cancer resistance protein BCRP (ABCG2).
Oncogene. 22:7340–7358. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gottesman MM, Fojo T and Bates SE:
Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters.
Nat Rev Cancer. 2:48–58. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu RH, Pelicano H, Zhou Y, et al:
Inhibition of glycolysis in cancer cells: a novel strategy to
overcome drug resistance associated with mitochondrial respiratory
defect and hypoxia. Cancer Res. 65:613–621. 2005.
|
|
42
|
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, et al:
Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain
tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1,
and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell. 6:553–563. 2004.
|
|
43
|
Baluk P, Morikawa S, Haskell A, Mancuso M
and McDonald DM: Abnormalities of basement membrane on blood
vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors. Am J Pathol.
163:1801–1815. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Morikawa S, Baluk P, Kaidoh T, Haskell A,
Jain RK and McDonald DM: Abnormalities in pericytes on blood
vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors. Am J Pathol.
160:985–1000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Adams RH and Alitalo K: Molecular
regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:464–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, et al:
Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other
diseases. Physiol Rev. 91:1071–1121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huang Y, Yuan J, Righi E, et al: Vascular
normalizing doses of antiangiogenic treatment reprogram the
immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and enhance immunotherapy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:17561–17566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|