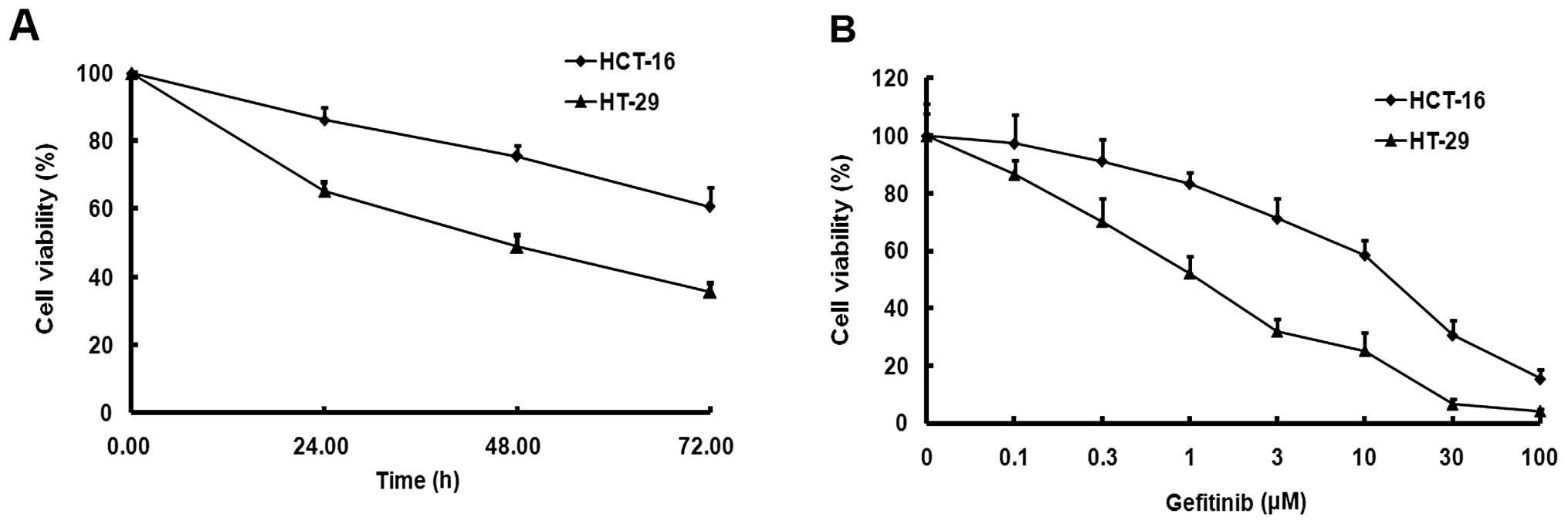
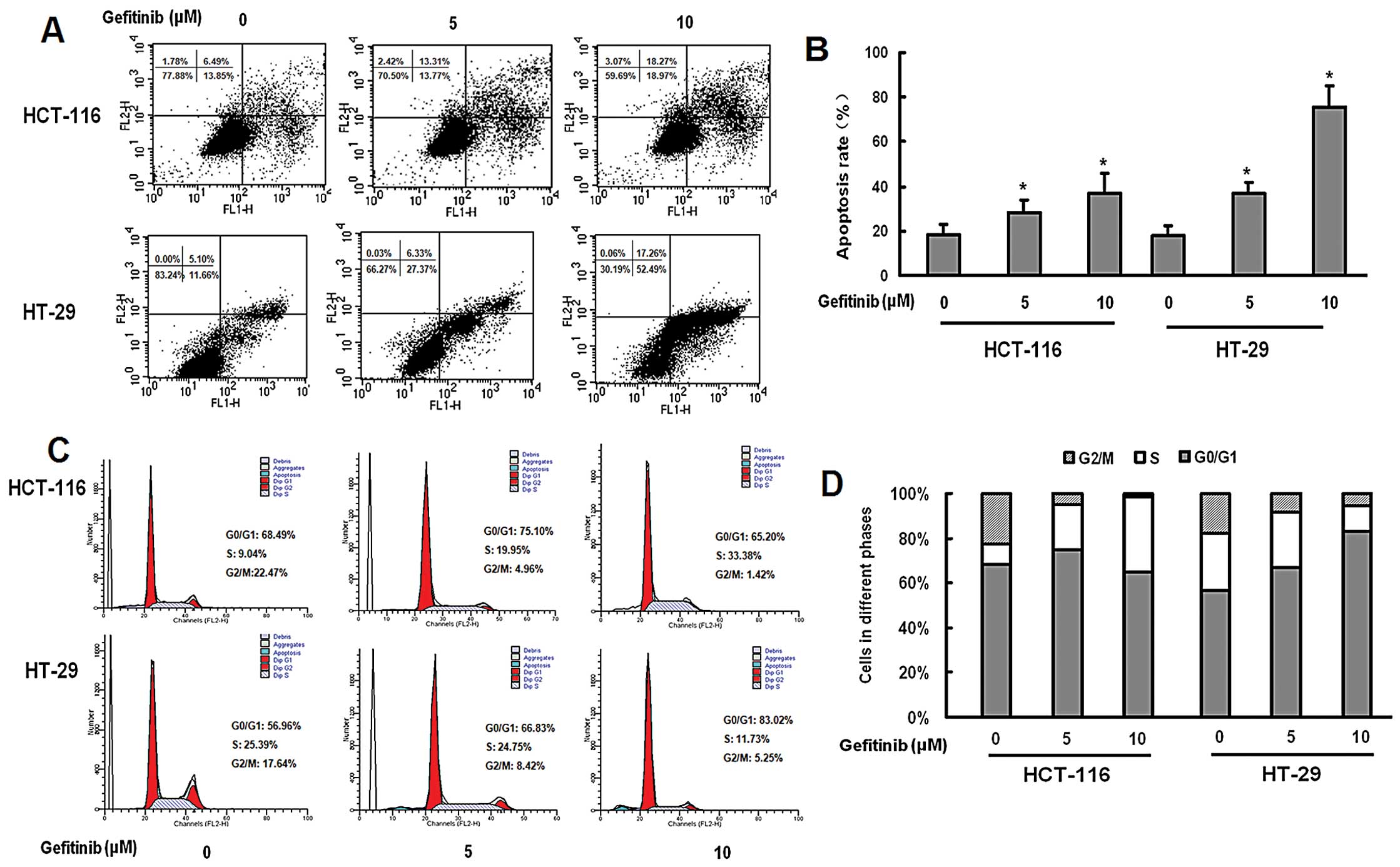
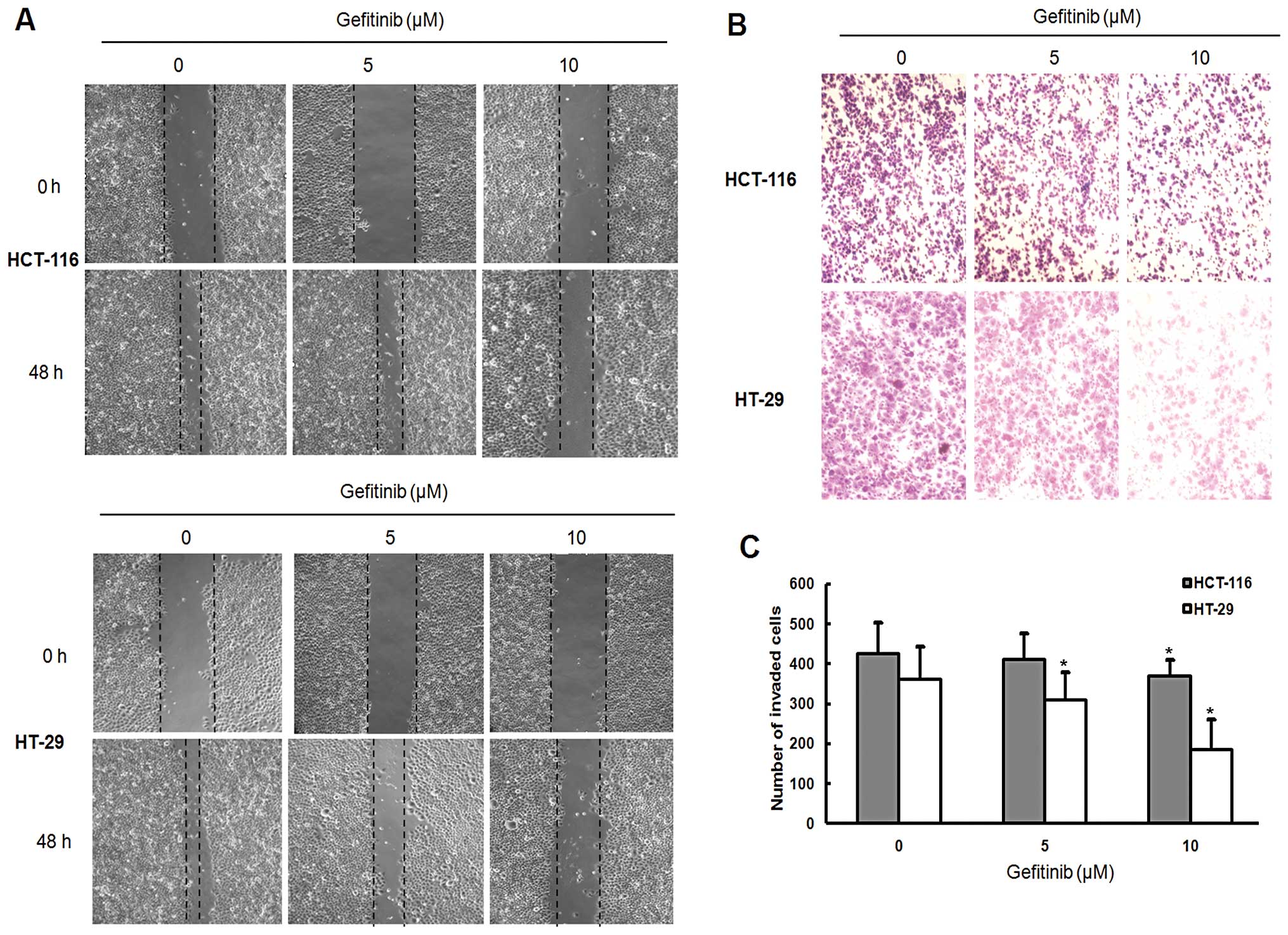
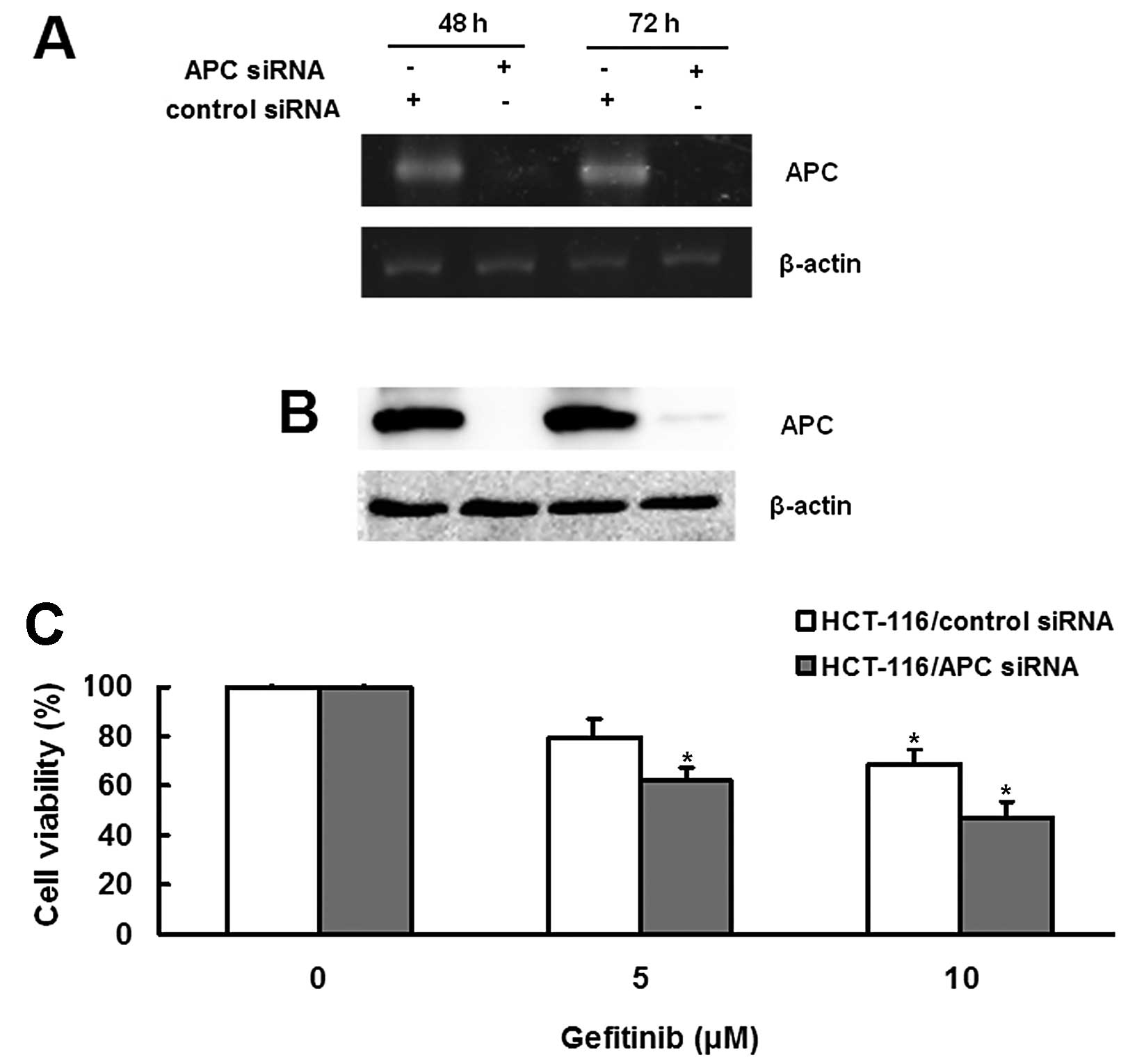
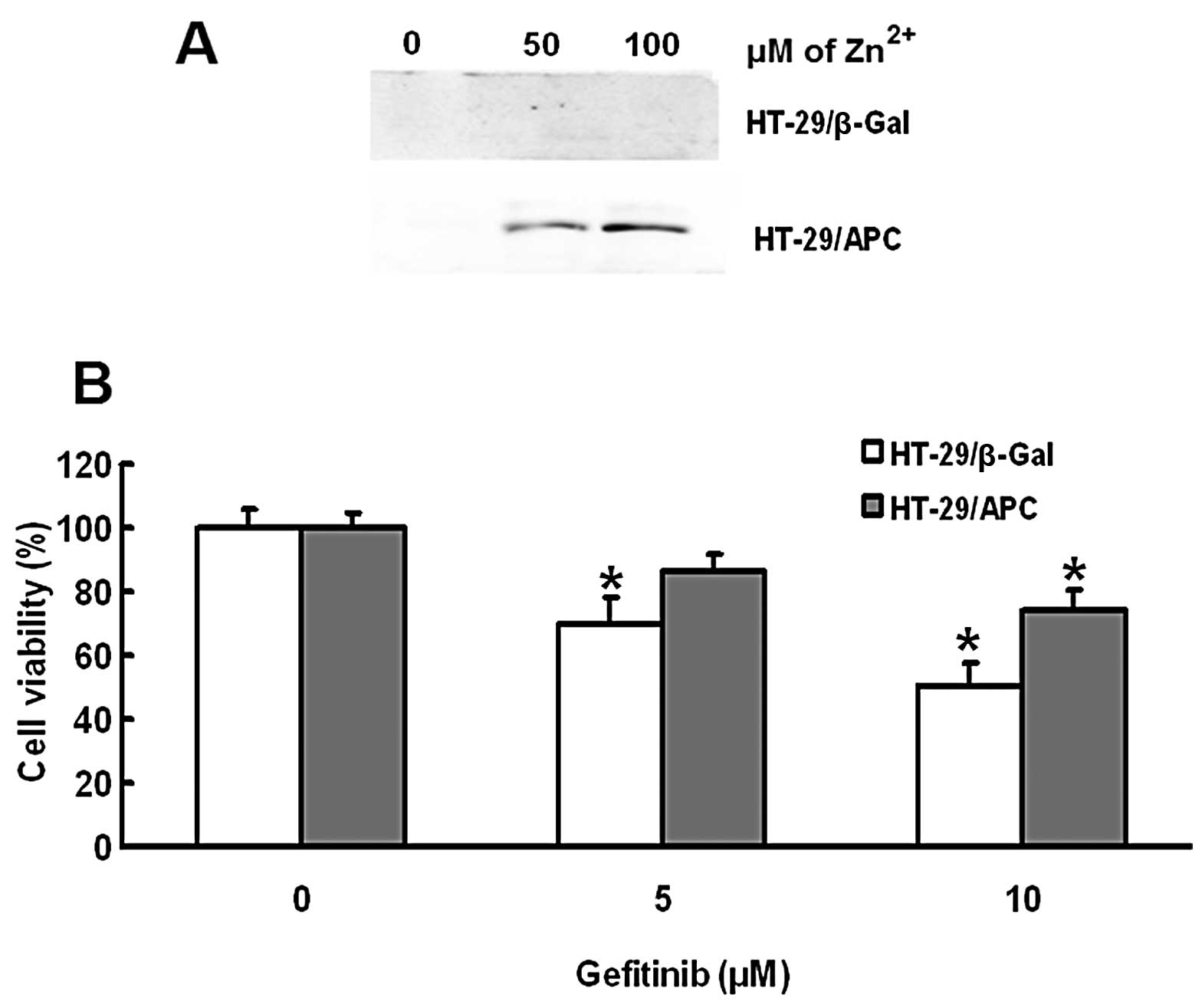
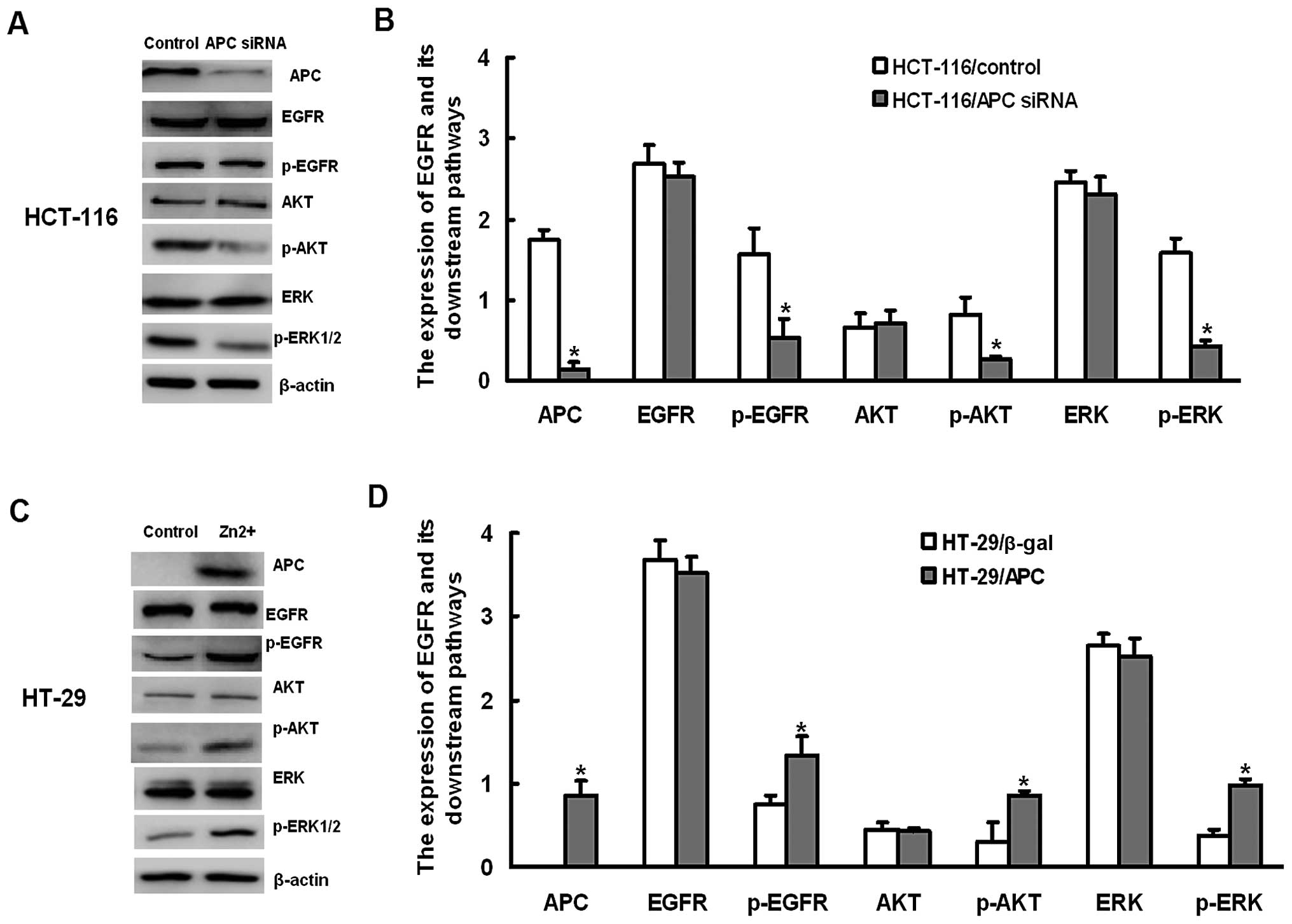
|
1
|
de Castro-Carpeno J, Belda-Iniesta C,
Casado Saenz E, Hernandez Agudo E, Feliu Batlle J and Gonzalez
Baron M: EGFR and colon cancer: a clinical view. Clin Transl Oncol.
10:6–13. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fischer von Weikersthal L, Schalhorn A,
Stauch M, et al: Phase III trial of irinotecan plus infusional
5-fluorouracil/folinic acid versus irinotecan plus oxaliplatin as
first-line treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer.
47:206–214. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krasinskas AM: EGFR signaling in
colorectal carcinoma. Patholog Res Int. 2011:9329322011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Wieduwilt MJ and Moasser MM: The epidermal
growth factor receptor family: biology driving targeted
therapeutics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:1566–1584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Citri A and Yarden Y: EGF-ERBB signalling:
towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:505–516. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yarom N and Jonker DJ: The role of the
epidermal growth factor receptor in the mechanism and treatment of
colorectal cancer. Discov Med. 11:95–105. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Albanell J and Gascon P: Small molecules
with EGFR-TK inhibitor activity. Curr Drug Targets. 6:259–274.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wakeling AE, Guy SP, Woodburn JR, et al:
ZD1839 (Iressa): an orally active inhibitor of epidermal growth
factor signaling with potential for cancer therapy. Cancer Res.
62:5749–5754. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ono M and Kuwano M: Molecular mechanisms
of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) activation and response
to gefitinib and other EGFR-targeting drugs. Clin Cancer Res.
12:7242–7251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al: Erlotinib
versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase
3 study. Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, et al:
Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with
mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi Y, Zhang L, Liu X, et al: Icotinib
versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer (ICOGEN): a randomised, double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority
trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:953–961. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mackenzie MJ, Hirte HW, Glenwood G, et al:
A phase II trial of ZD1839 (Iressa) 750 mg per day, an oral
epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Invest New Drugs.
23:165–170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rothenberg ML, LaFleur B, Levy DE, et al:
Randomized phase II trial of the clinical and biological effects of
two dose levels of gefitinib in patients with recurrent colorectal
adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 23:9265–9274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trarbach T, Reinacher-Schick A,
Hegewisch-Becker S, et al: Gefitinib in combination with
capecitabine as second-line therapy in patients with advanced
colorectal cancer (aCRC): a phase I/II study of the
Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie (AIO). Onkologie.
33:89–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vieitez JM, Valladares M, Pelaez I, et al:
A randomized phase II study of raltitrexed and gefitinib versus
raltitrexed alone as second line chemotherapy in patients with
colorectal cancer. (1839IL/0143). Invest New Drugs. 29:1038–1044.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Santoro A, Comandone A, Rimassa L, et al:
A phase II randomized multicenter trial of gefitinib plus FOLFIRI
and FOLFIRI alone in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer.
Ann Oncol. 19:1888–1893. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nathke IS: The adenomatous polyposis coli
protein: the Achilles heel of the gut epithelium. Annu Rev Cell Dev
Biol. 20:337–366. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fodde R: The APC gene in colorectal
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 38:867–871. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Barker N: The canonical Wnt/β-catenin
signalling pathway. Methods Mol Biol. 468:5–15. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Hu T and Li C: Convergence between
Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol Cancer.
9:2362010.
|
|
23
|
Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al:
Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor
underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to
gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 350:2129–2139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al: EGFR
mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to
gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cappuzzo F, Magrini E, Ceresoli GL, et al:
Akt phosphorylation and gefitinib efficacy in patients with
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
96:1133–1141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yuan G, Regel I, Lian F, et al: WNT6 is a
novel target gene of caveolin-1 promoting chemoresistance to
epirubicin in human gastric cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:375–387.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang X and Guo B: Adenomatous polyposis
coli determines sensitivity to histone deacetylase
inhibitor-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:9245–9251. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Narayan S, Jaiswal AS and Balusu R: Tumor
suppressor APC blocks DNA polymerase β-dependent strand
displacement synthesis during long patch but not short patch base
excision repair and increases sensitivity to methylmethane
sulfonate. J Biol Chem. 280:6942–6949. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Fang X, Gu P, Zhou C, et al: β-Catenin
overexpression is associated with gefitinib resistance in non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. May 23–2013.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
30
|
Park SH, Ha SY, Lee JI, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor mutations and the clinical outcome in male
smokers with squamous cell carcinoma of lung. J Korean Med Sci.
24:448–452. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kalikaki A, Koutsopoulos A, Trypaki M, et
al: Comparison of EGFR and K-RAS gene status between
primary tumours and corresponding metastases in NSCLC. Br J Cancer.
99:923–929. 2008.
|
|
32
|
Sasaki H, Shimizu S, Endo K, et al: EGFR
and erbB2 mutation status in Japanese lung cancer patients. Int J
Cancer. 118:180–184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barber TD, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW and
Velculescu VE: Somatic mutations of EGFR in colorectal
cancers and glioblastomas. N Engl J Med. 351:28832004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nagahara H, Mimori K, Ohta M, et al:
Somatic mutations of epidermal growth factor receptor in colorectal
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1368–1371. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park JJ, Yi JY, Jin YB, et al: Sialylation
of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates receptor activity and
chemosensitivity to gefitinib in colon cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 83:849–857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Milligan SA, Burke P, Coleman DT, et al:
The green tea polyphenol EGCG potentiates the antiproliferative
activity of c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 15:4885–4894.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
den Hartigh JC, van Bergen en Henegouwen
PM, Verkleij AJ and Boonstra J: The EGF receptor is an
actin-binding protein. J Cell Biol. 119:349–355. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|