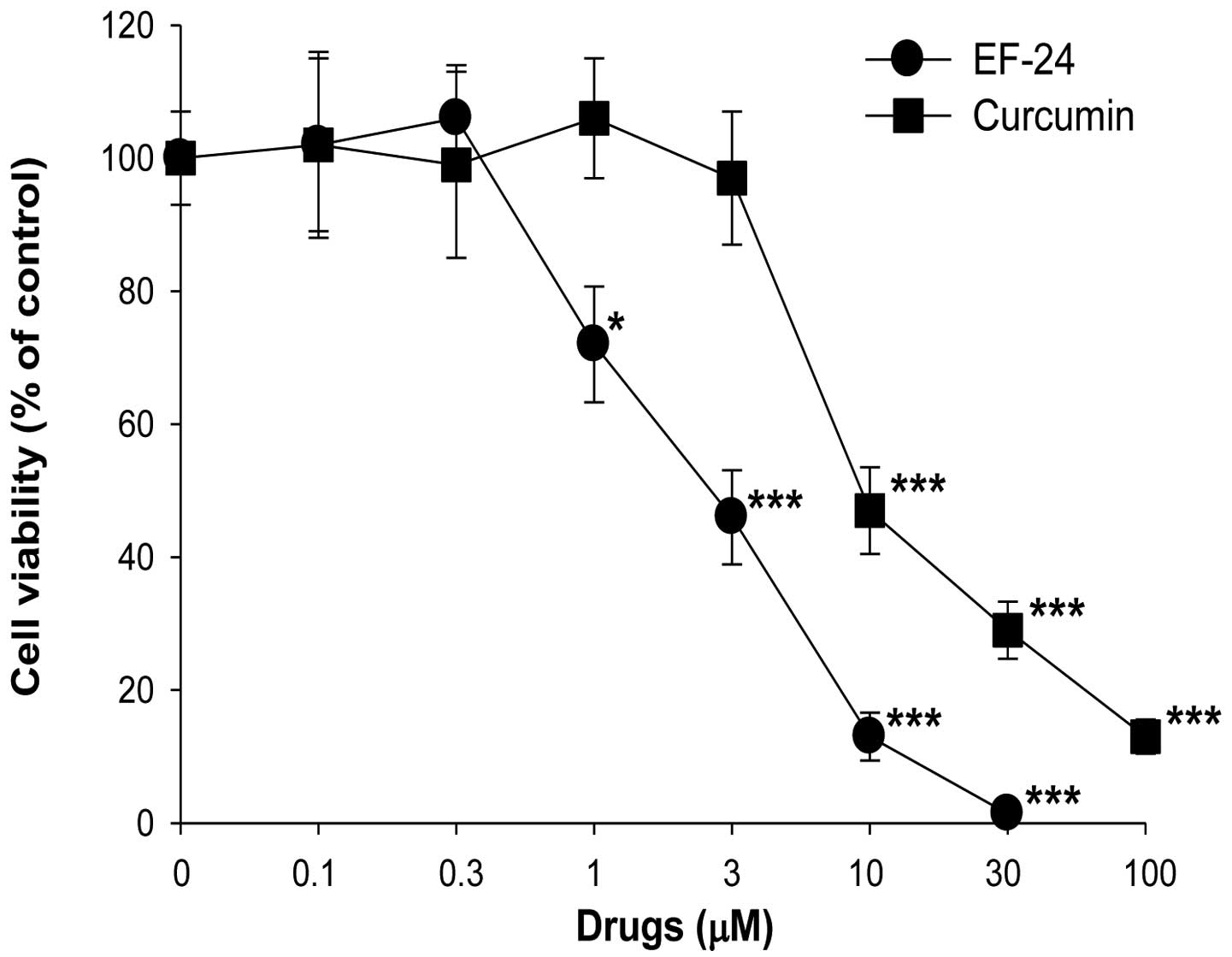
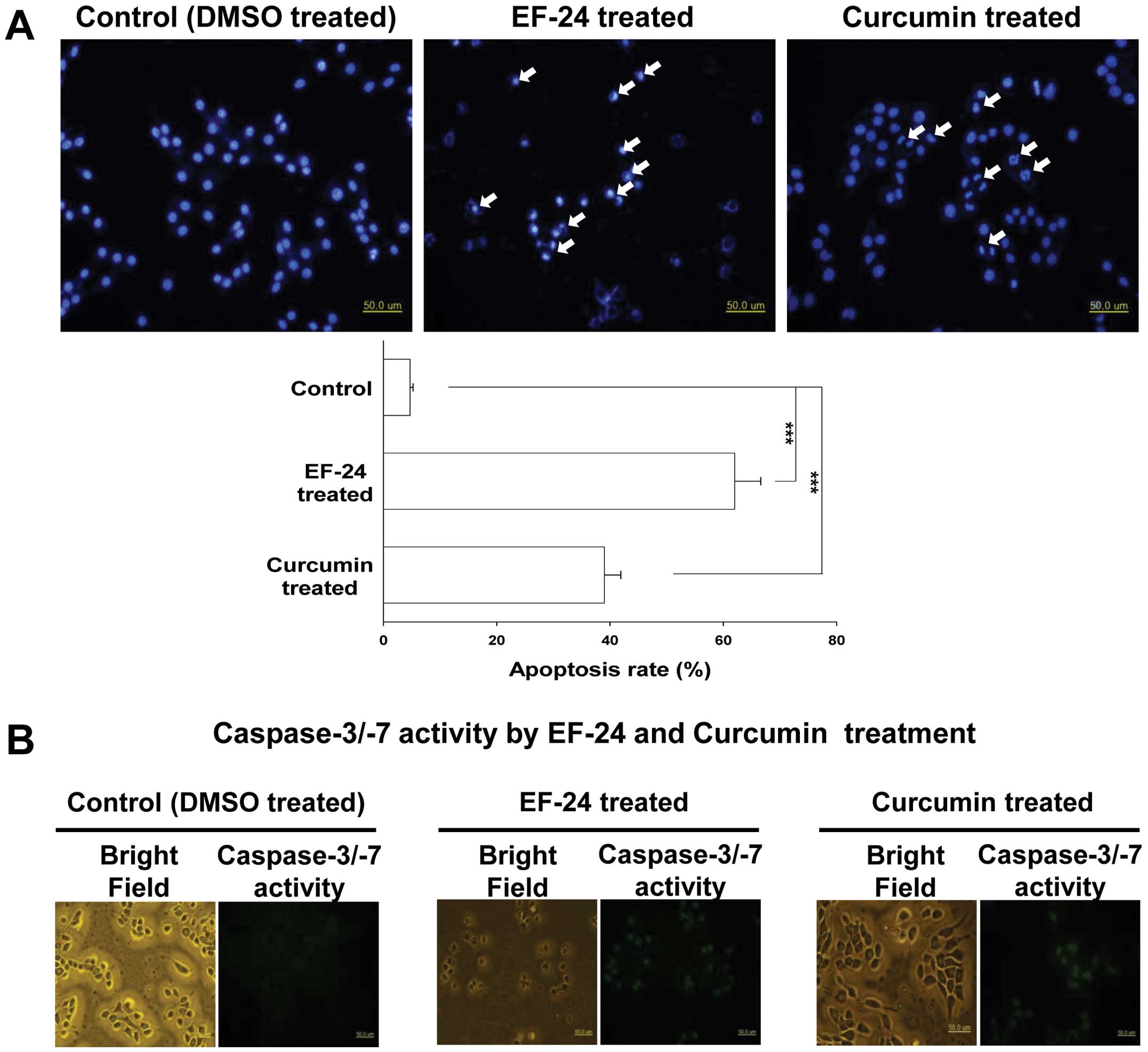
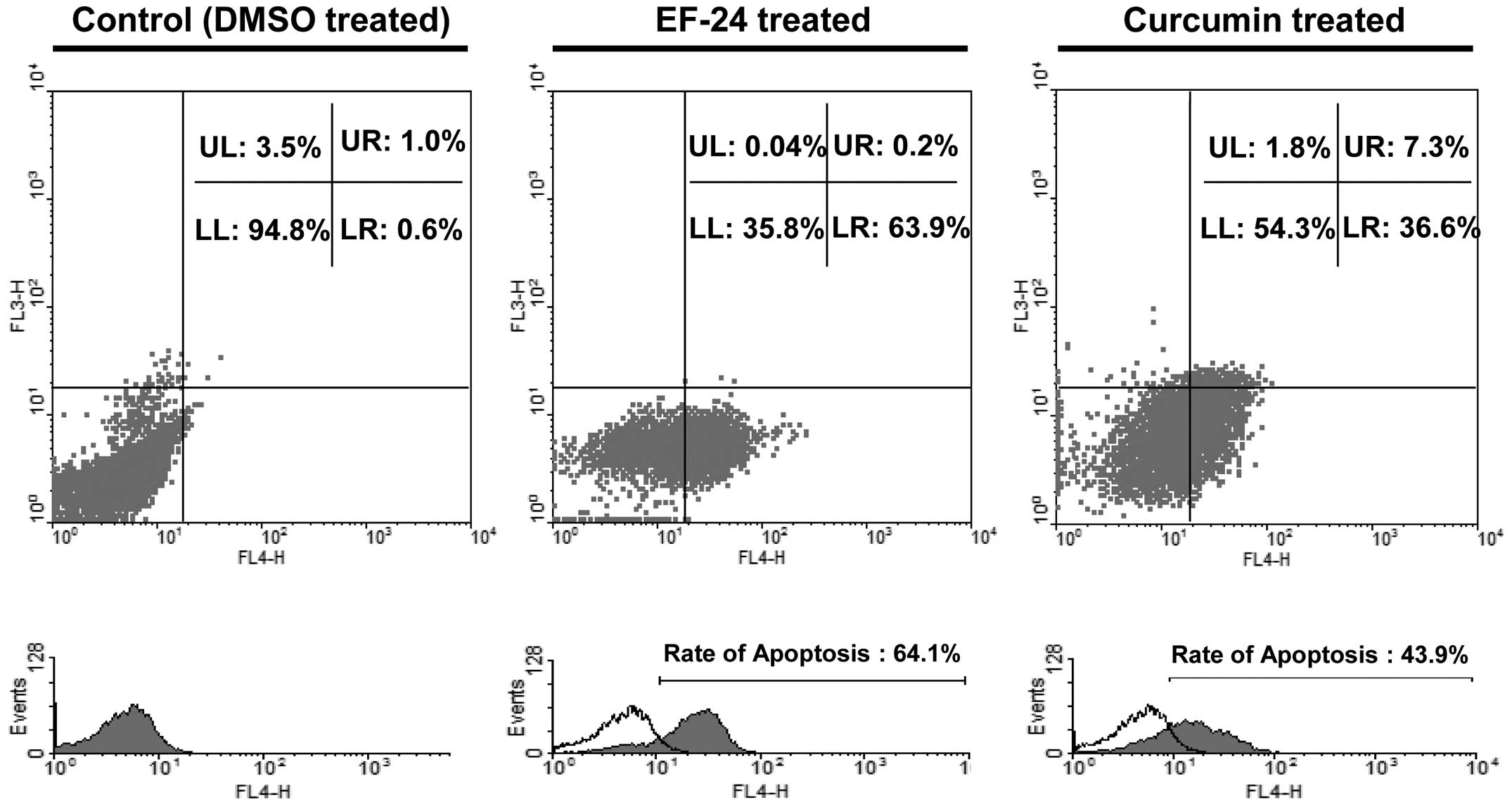
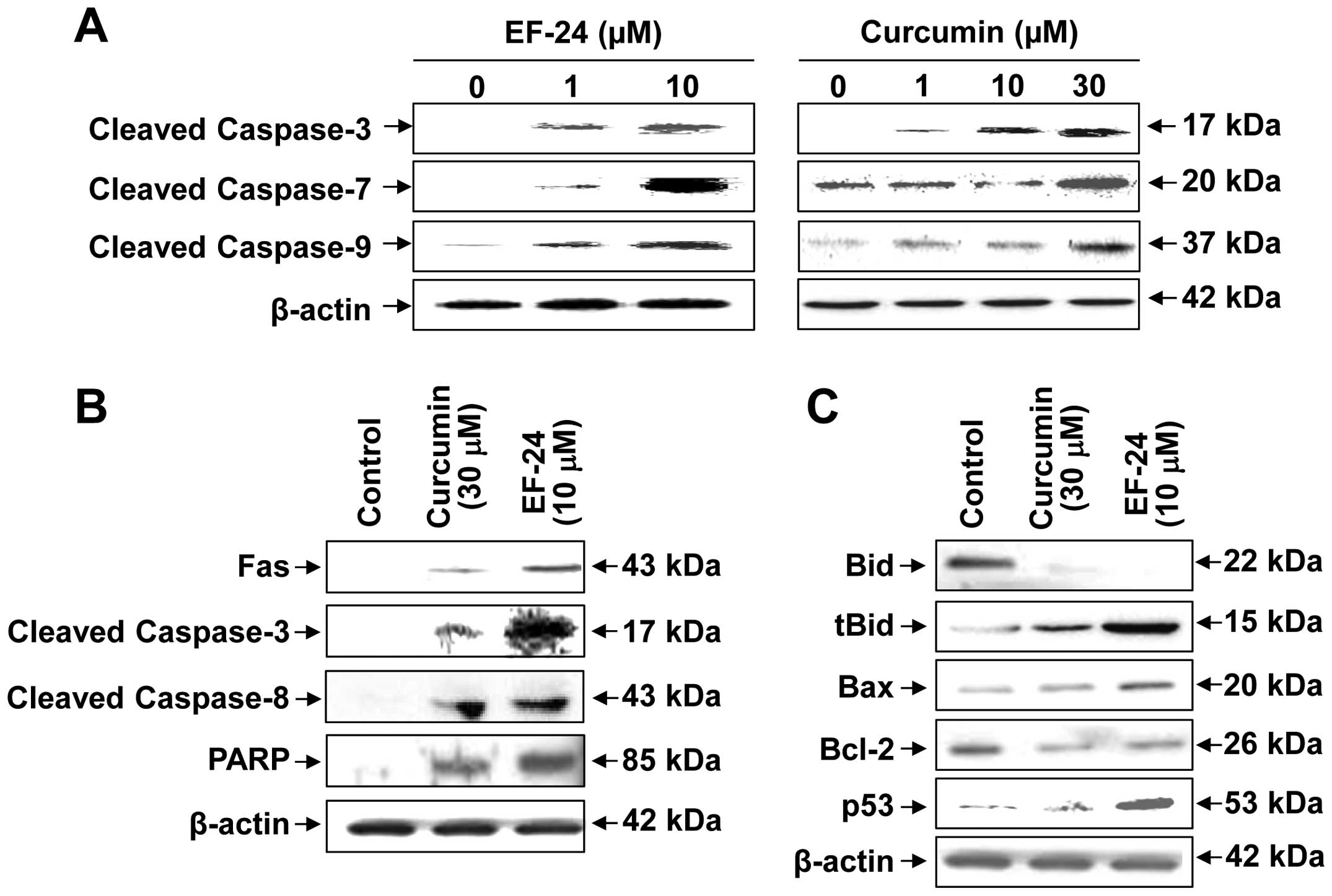
|
1
|
Daiy H, Huangy Y, Li Y, Meng G, Wang Y and
Guo QN: TSSC3 overexpression associates with growth inhibition,
apoptosis induction and enhances chemotherapeutic effects in human
osteosarcoma. Carcinogenesis. 33:30–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fuchs B and Pritchard DJ: Etiology of
osteosarcoma. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 397:40–52. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gibbs CP Jr, Weber K and Scarborough MT:
Malignant bone tumors. Instr Course Lect. 51:413–428. 2002.
|
|
4
|
Zhao Q, Wang C, Zhu J, Wang L, Dong S,
Zhang G and Tian J: RNAi-mediated knockdown of cyclooxygenase2
inhibits the growth, invasion and migration of Saos2 human
osteosarcoma cells: a case control study. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
30:262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mukherjee AK, Basu S, Sarkar N and Ghosh
AC: Advances in cancer therapy with plant based natural products.
Curr Med Chem. 8:1467–1486. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Smets LA: Programmed cell death
(apoptosis) and response to anti-cancer drugs. Anticancer Drugs.
5:3–9. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Paschka AG, Butler R and Young CYF:
Induction of apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines by the green
tea component, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Lett.
130:1–7. 1998.
|
|
8
|
Kaufmann SH and Hengartner MO: Programmed
cell death: alive and well in the new millennium. Trends Cell Biol.
11:526–534. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-regulating proteins as
targets for drug discovery. Trends Mol Med. 7:314–319. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banerjee M, Tripathi LM, Srivastava VM,
Puri A and Shukla R: Modulation of inflammatory mediators by profen
and curcumin treatment during chronic inflammation in rat.
Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 25:213–224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sahu RP, Batra1 S and Srivastava SK:
Activation of ATM/Chk1 by curcumin causes cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Br J Cancer.
100:1425–1433. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wahl H, Tan L, Griffith K, Choi M and Liu
JR: Curcumin enhances Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 105:104–112.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goel A, Kunnumakkara AB and Aggarwal BB:
Curcumin as ‘Curecumin’: from kitchen to clinic. Biochem Pharmacol.
75:787–809. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA and
Aggarwal BB: Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises.
Mol Pharm. 4:807–818. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adams BK, Cai J, Armstrong J, et al: EF24,
a novel synthetic curcumin analog, induces apoptosis in cancer
cells via a redox-dependent mechanism. Anticancer Drugs.
16:263–275. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Komatsu M, Kuroda M, Wang Y, et al:
Manganese superoxide dismutase overexpression changes plating
efficiency bidirectionally according to change in redox for SaOS2
human osteosarcoma cell line. Int J Oncol. 26:853–862. 2005.
|
|
18
|
Kim SG, Kim HH, Kim HK, et al:
Differential expression and functional characterization of system L
amino acid transporters in human normal osteoblast cells and
osteogenic sarcoma cells. Anticancer Res. 26:1989–1996. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Hu W and Kavanagh JJ: Anticancer therapy
targeting the apoptotic pathway. Lancet Oncol. 4:721–729. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Herrnring C, Reimer T, Jeschke U, et al:
Expression of the apoptosis-inducing ligands FasL and TRAIL in
malignant and benign human breast tumors. Histochem Cell Biol.
113:189–194. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li HJ, Wang CY, Mi Y, et al: FasL-induced
apoptosis in bovine oocytes via the Bax signal. Theriogenology.
80:248–255. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng YL, Lee SC, Lin SZ, et al:
Anti-proliferative activity of Bupleurum scrozonerifolium in
A549 human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett.
222:183–193. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tian Z, Chen S, Zhang Y, et al: The
cytotoxicity of naturally occurring styryl lactones. Phytomedicine.
13:181–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hauser PJ, Han Z, Sindhwani P and Hurst
RE: Sensitivity of bladder cancer cells to curcumin and its
derivatives depends on the extracellular matrix. Anticancer Res.
27:737–740. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kikuchi T, Pan X, Ishii K, et al:
Cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing activities of
12-O-Acetylazedarachin B from the fruits of Melia
azedarach in human cancer cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull.
36:135–139. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon
AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RCAA, LaFace DM and Green DR: Early
redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general
feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus:
inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med.
182:1545–1556. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X: DFF,
a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to
trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell. 89:175–184. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ryu DS, Lee HS, Lee GS and Lee DS: Effects
of the ethylacetate extract of Orostachys japonicus on
induction of apoptosis through the p53-mediated signaling pathway
in human gastric cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 35:660–665.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lavin MF and Gueven N: The complexity of
p53 stabilization and activation. Cell Death Differ. 13:941–950.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Heath-Engel HM, Chang NC and Shore GC: The
endoplasmic reticulum in apoptosis and autophagy: role of the BCL-2
protein family. Oncogene. 27:6419–6433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fisher DE: The p53 tumor suppressor:
critical regulator of life & death in cancer. Apoptosis.
6:7–15. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kluck RM, Esposti MD, Perkins G, et al:
The pro-apoptotic proteins, Bid and Bax, cause a limited
permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane that is
enhanced by cytosol. J Cell Biol. 147:809–822. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu CS, Huang AC, Lai KC, Huang YP, Lin MW,
Yang JS and Chung JG: Diallyl trisulfide induces apoptosis in human
primary colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 28:949–954.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C
and Wang X: Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c
release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface
death receptors. Cell. 94:481–490. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|