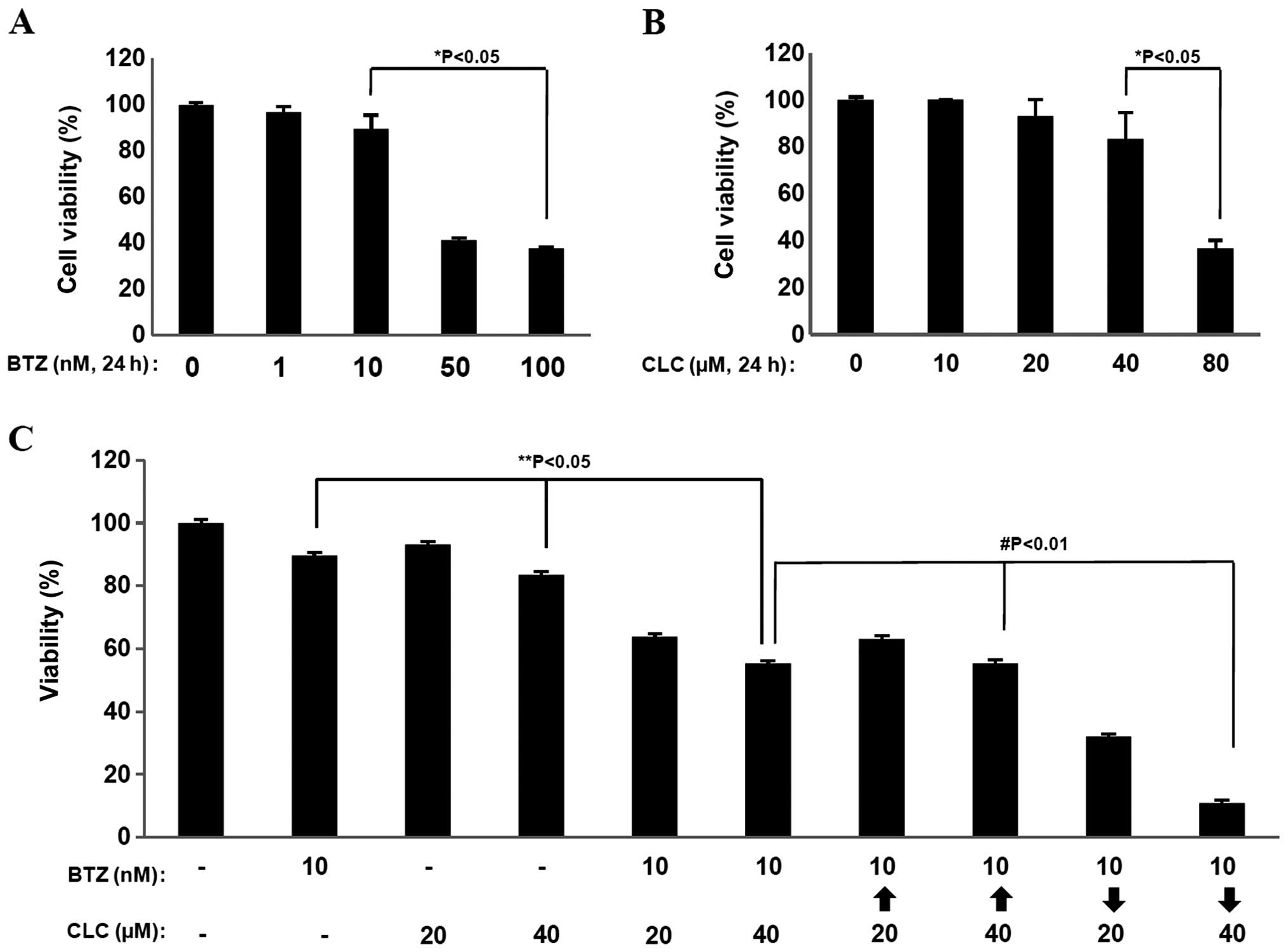
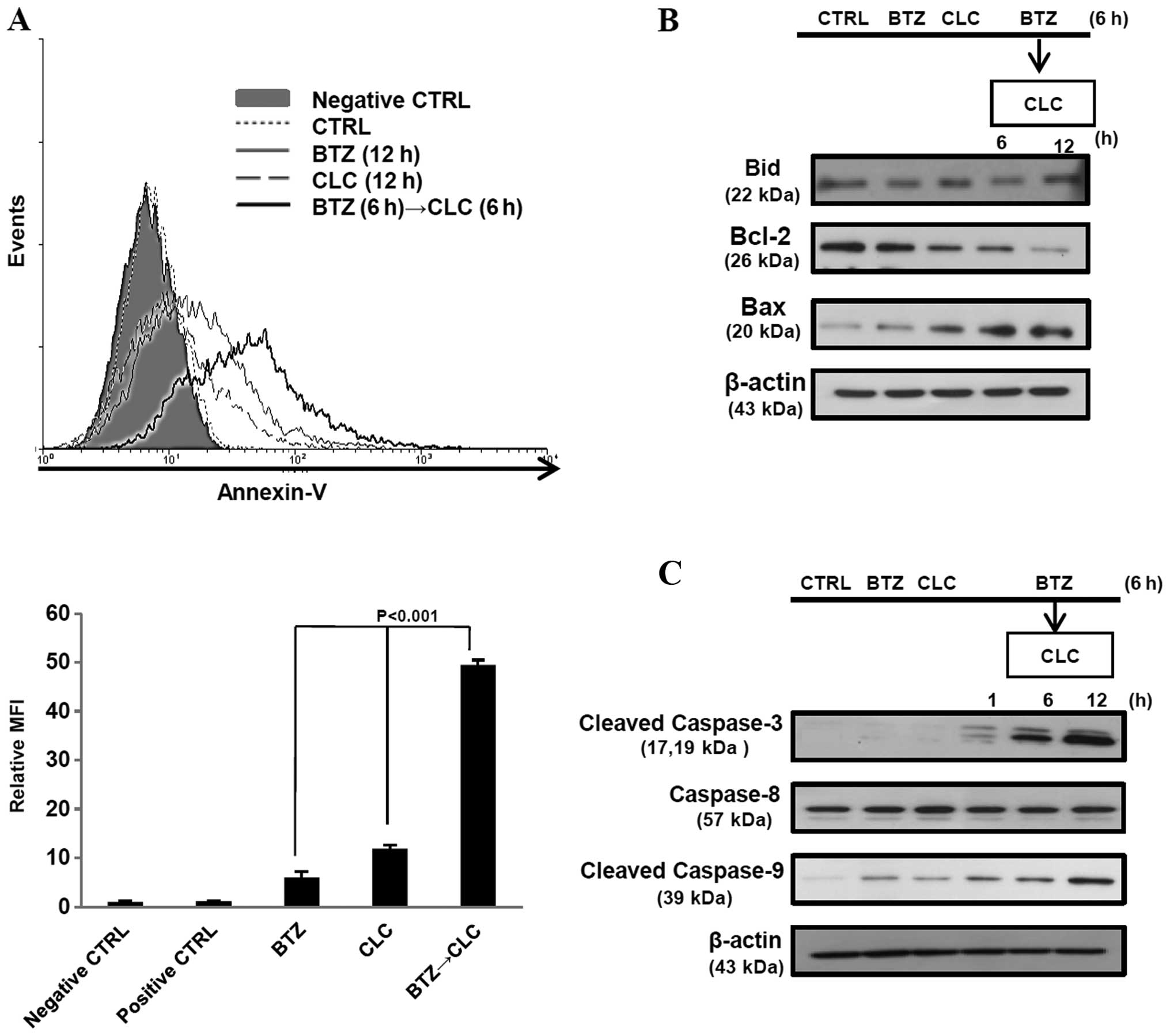
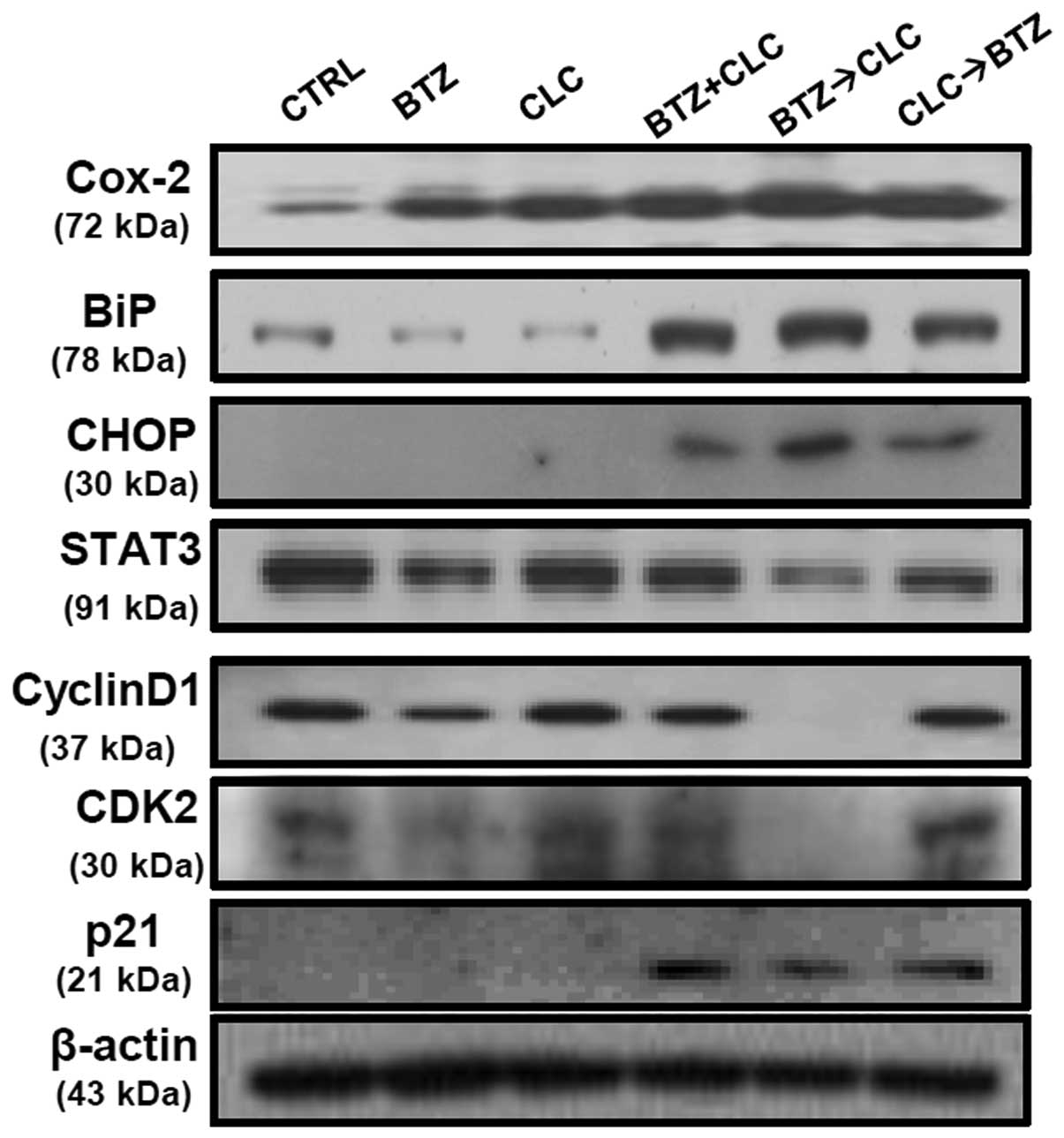
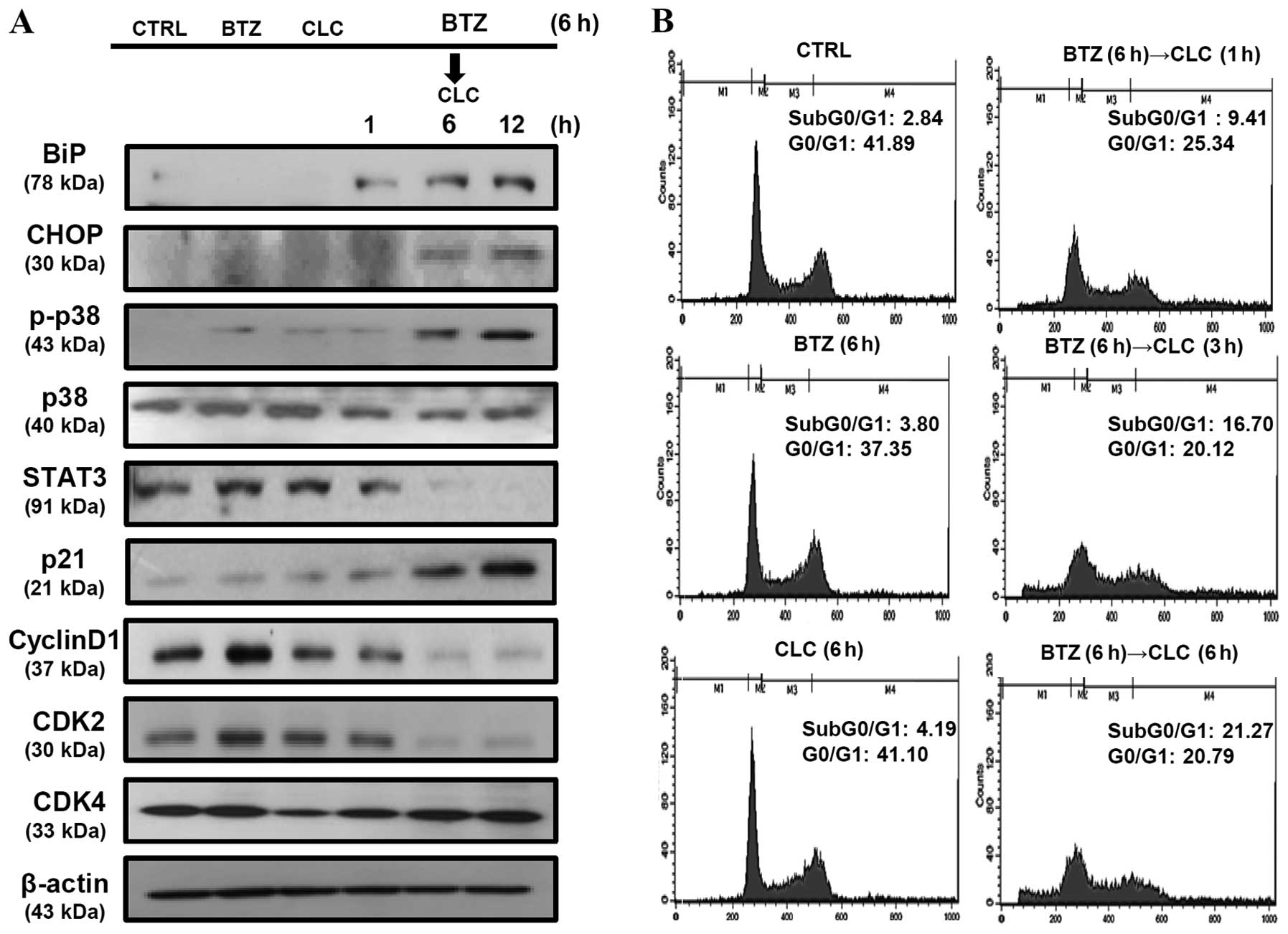
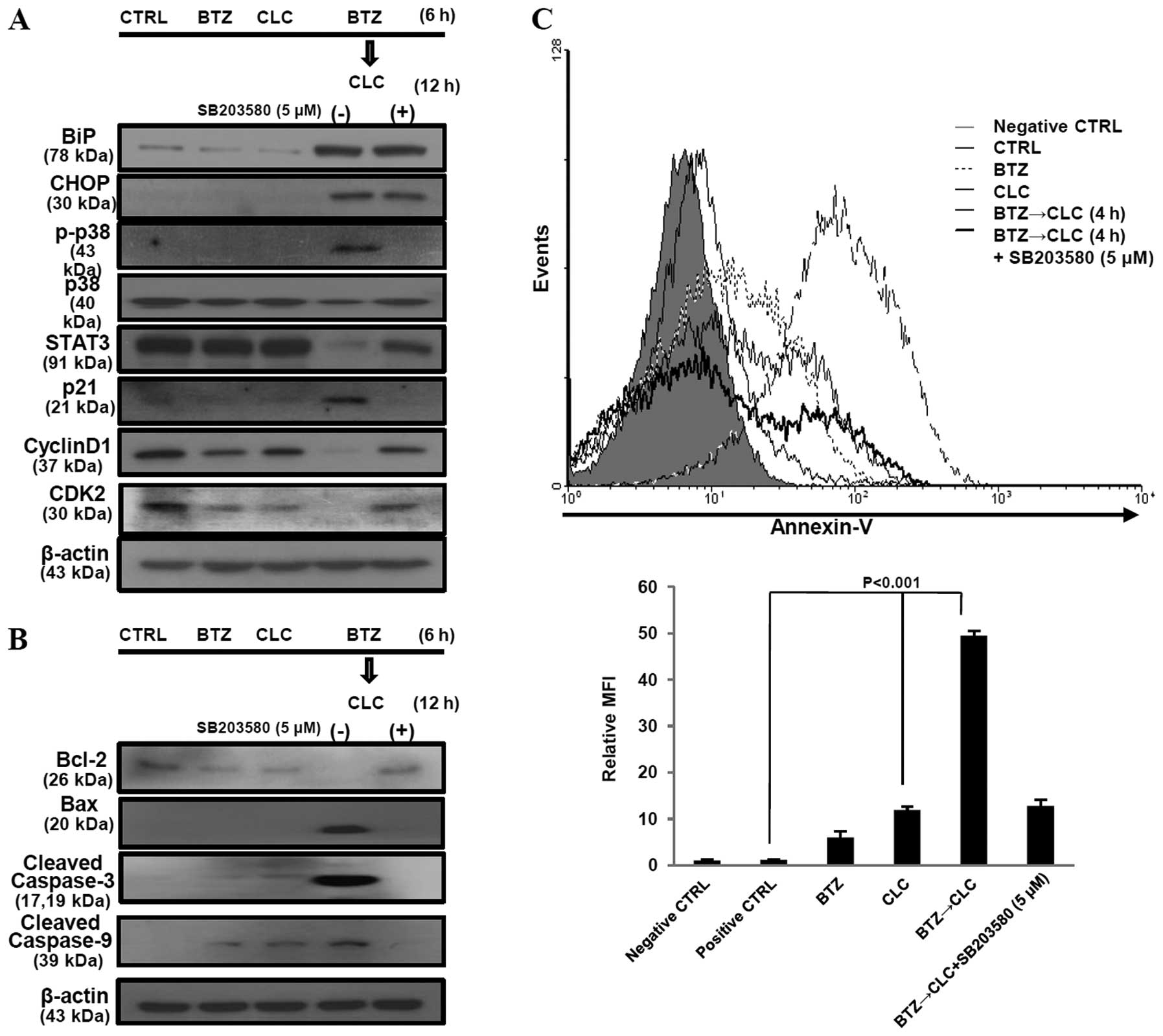
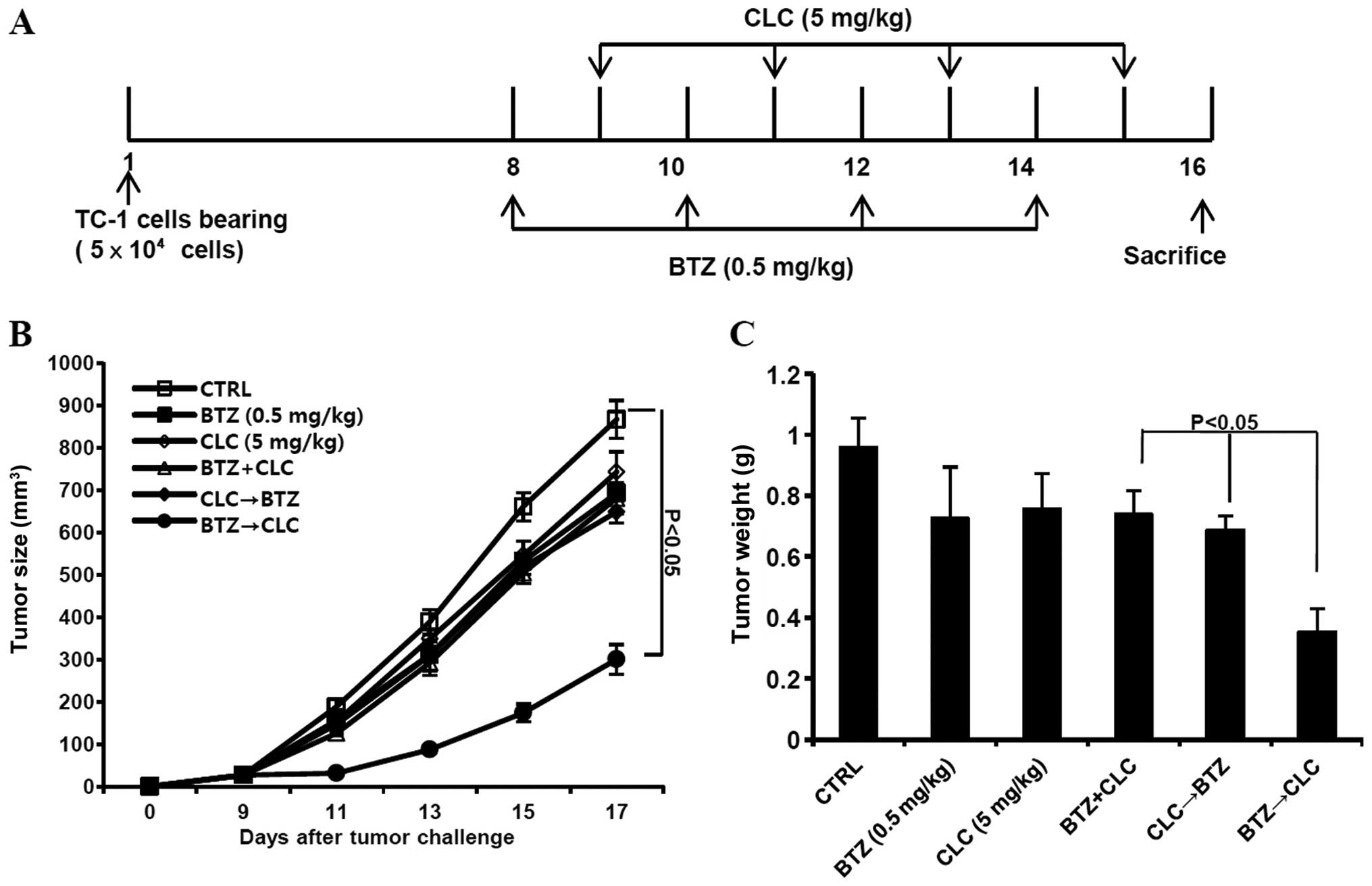
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
ZurHausen H and de Villiers EM: Human
papillomaviruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 48:27–47. 1994.
|
|
3
|
Maher DM, Bell MC, O’Donnell EA, Gupta BK,
Jaggi M and Chauhan SC: Curcumin suppresses human papillomavirus
oncoproteins, restores p53, Rb, and PTPN13 proteins and inhibits
benzo[a]pyrene-induced upregulation of HPV E7. Mol Carcinog.
50:47–57. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Werness BA, Levine AJ and Howley PM:
Association of human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 E6 proteins
with p53. Science. 248:76–79. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alani RM and Munger K: Human
papillomaviruses and associated malignancies. J Clin Oncol.
16:330–337. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M:
Cyclin D-dependent kinases, INK4 inhibitors and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1602:73–87. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: Living with or
without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev.
18:2699–2711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bahnassy AA, Zekri AR, Alam El-Din HM,
Aboubakr AA, Kamel K, El-Sabah MT and Mokhtar NM: The role of
cyclins and cyclin inhibitors in the multistep process of
HPV-associated cervical carcinoma. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst.
18:292–302. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin KY, Guarnieri FG, Staveley-O’Carroll
KF, Levitsky HI, August JT, Pardoll DM and Wu TC: Treatment of
established tumors with a novel vaccine that enhances major
histocompatibility class II presentation of tumor antigen. Cancer
Res. 56:21–26. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tseng CW, Monie A, Wu CY, Huang B, Wang
MC, Hung CF and Wu TC: Treatment with proteasome inhibitor
bortezomib enhances antigen-specific CD8+
T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity induced by DNA vaccination. J
Mol Med. 86:899–908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Malara N, Focà D, Casadonte F, Sesto MF,
Macrina L, Santoro L, Scaramuzzino M, Terracciano R and Savino R:
Simultaneous inhibition of the constitutively activated nuclear
factor kappaB and of the interleukin-6 pathways is necessary and
sufficient to completely overcome apoptosis resistance of human
U266 myeloma cells. Cell Cycle. 7:3235–3245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wen J, Feng Y, Huang W, Chen H, Liao B,
Rice L, Preti HA, Kamble RT, Zu Y, Ballon DJ and Chang CC: Enhanced
antimyeloma cytotoxicity by the combination of arsenic trioxide and
bortezomib is further potentiated by p38 MAPK inhibition. Leuk Res.
34:85–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eberhart CE, Coffey RJ, Radhika A,
Giardiello FM, Ferrenbach S and DuBois RN: Upregulation of
cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human colorectal adenomas and
adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology. 107:1183–1188. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kulkarni S, Rader JS, Zhang F, Liapis H,
Koki AT, Masferrer JL, Subbaramaiah K and Dannenberg AJ:
Cyclooxygenase-2 is overexpressed in human cervical cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 7:429–434. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Kim K, Jeon YT, Park IA, Kim JW, Park NH,
Kang SB, Lee HP and Song YS: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1171:111–115.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subbaramaiah K and Dannenberg AJ:
Cyclooxygenase-2 transcription is regulated by human papillomavirus
16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins: evidence of a corepressor/coactivator
exchange. Cancer Res. 67:3976–3985. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ferrandina G, Ranelletti FO, Legge F,
Lauriola L, Salutari V, Gessi M, Testa AC, Werner U, Navarra P,
Tringali G, Battaglia A and Scambia G: Celecoxib modulates the
expression of cyclooxygenase-2, ki67, apoptosis-related marker, and
microvessel density in human cervical cancer: a pilot study. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:4324–4331. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sareddy GR, Geeviman K, Ramulu C and Babu
PP: The nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug celecoxib suppresses
the growth and induces apoptosis of human glioblastoma cells via
the NF-κB pathway. J Neurooncol. 106:99–109. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kardosh A, Golden EB, Pyrko P, Uddin J,
Hofman FM, Chen TC, Louie SG, Petasis NA and Schönthal AH:
Aggravated endoplasmic reticulum stress as a basis for enhanced
glioblastoma cell killing by bortezomib in combination with
celecoxib or its non-coxib analogue, 2,5-dimethyl-celecoxib. Cancer
Res. 68:843–851. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mukhopadhyay I, Sausville EA, Doroshow JH
and Roy KK: Molecular mechanism of adaphostin-mediated G1 arrest in
prostate cancer (PC-3) cells: signaling events mediated by
hepatocyte growth factor receptor, c-Met, and p38 MAPK pathways. J
Biol Chem. 281:37330–37344. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fujita T, Doihara H, Washio K, Ino H,
Murakami M, Naito M and Shimizu N: Antitumor effects and drug
interactions of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib (PS341) in
gastric cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 18:677–686. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Morham SG, Langenbach R and Young
DA: Malignant transformation and antineoplastic actions of
nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) on cyclooxygenase-null
embryo fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 190:451–459. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nawrocki ST, Carew JS, Pino MS, Highshaw
RA, Dunner K Jr, Huang P, Abbruzzese JL and McConkey DJ: Bortezomib
sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptosis. Cancer Res. 65:11658–11666. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Obeng EA, Carlson LM, Gutman DM,
Harrington WJ Jr, Lee KP and Boise LH: Proteasome inhibitors induce
a terminal unfolded protein response in multiple myeloma cells.
Blood. 107:4907–4916. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fribley A and Wang CY: Proteasome
inhibitor induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Cancer Biol Ther. 5:745–748. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hanif R, Pittas A, Feng Y, Koutsos MI,
Qiao L, Staiano-Coico L, Shiff SI and Rigas B: Effects of
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on proliferation and on
induction of apoptosis in colon cancer cells by a
prostaglandin-independent pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 52:237–245.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kardosh A, Blumenthal M, Wang WJ, Chen TC
and Schönthal AH: Differential effects of selective COX-2
inhibitors on cell cycle regulation and proliferation of
glioblastoma cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther. 3:9–16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arico S, Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Gane P,
Barbat A, Codogno P and Ogier-Denis E: Celecoxib induces apoptosis
by inhibiting 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1
activity in the human colon cancer HT-29 cell line. J Biol Chem.
277:27613–27621. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawano M, Hirano T, Matsuda T, Taga T,
Horii Y, Iwato K, Asaoku H, Tang B, Tanabe O, Tanaka H, Kuramoto A
and Kishimoto T: Autocrine generation and requirement of BSF-2/IL-6
for human multiple myelomas. Nature. 332:83–85. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen J, Wang J, Lin L, He L, Wu Y, Zhang
L, Yi Z, Chen Y, Pang X and Liu M: Inhibition of STAT3 signaling
pathway by nitidine chloride suppressed the angiogenesis and growth
of human gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:277–287. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Li X, Lu X and Pi L: The
regulation of stat3 signal transduction pathway to G1 to S phase of
laryngocarcinoma cell. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za
Zhi. 22:699–703. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Ishii Y, Pirkmaier A, Alvarez JV, Frank
DA, Keselman I, Logothetis D, Mandeli J, O’Connell MJ, Waxman S and
Germain D: Cyclin D1 overexpression and response to bortezomib
treatment in a breast cancer model. J Natl Cancer Inst.
98:1238–1247. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Harper JV and Brooks G: The mammalian cell
cycle: an overview. Methods Mol Biol. 296:113–153. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang J, Wang Q, Cui Y, Liu ZY, Zhao W,
Wang CL, Dong Y, Hou L, Hu G, Luo C, Chen J and Lu Y: Knockdown of
cyclin D1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and attenuates
the invasive capacity of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol.
106:473–484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shapiro GI: Cyclin-dependent kinase
pathways as targets for cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol.
24:1770–1783. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Munagala R, Kausar H, Munjal C and Gupta
RC: Withaferin A induces p53-dependent apoptosis by repression of
HPV oncogenes and upregulation of tumor suppressor proteins in
human cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 32:1697–1705. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mihailidou C, Papazian I, Papavassiliou AG
and Kiaris H: CHOP-dependent regulation of p21/waf1 during ER
stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 25:761–766. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mori T, Hayashi T and Su TP: Compromising
sigma-1 receptors at the ER renders cytotoxicity to
physiologicallyrelevant concentrations of dopamine in a
NF-κB/Bcl-2-dependent mechanism: Potential relevance to Parkinson’s
disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 341:663–671. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shimazawa M, Miwa A, Ito Y, Tsuruma K,
Aihara M and Hara H: Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in
optic nerve degeneration following
N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced retinal damage in mice. J
Neurosci Res. 90:1960–1969. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang KH, Kuo KL, Chen SC, Weng TI, Chuang
YT, Tsai YC, Pu YS, Chiang CK and Liu SH: Down-regulation of
glucose-regulated protein (GRP) 78 potentiates cytotoxic effect of
celecoxib in human urothelial carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
7:e336152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shimada Y, Kobayashi H, Kawagoe S, Aoki K,
Kaneshiro E, Shimizu H, Eto Y, Ida H and Ohashi T: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress induces autophagy through activation of p38 MAPK
in fibroblasts from Pompe disease patients carrying c.546G>T
mutation. Mol Genet Metab. 104:566–573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee B, Kim CH and Moon SK: Honokiol causes
the p21WAF1-mediated G(1)-phase arrest of the cell cycle through
inducing p38 mitogen activated protein kinase in vascular smooth
muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 580:5177–5184. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hayslip J, Chaudhary U, Green M, Meyer M,
Dunder S, Sherman C, Salzer S, Kraft A and Montero AJ: Bortezomib
in combination with celecoxib in patients with advanced solid
tumors: a phase I trial. BMC Cancer. 7:2212007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|