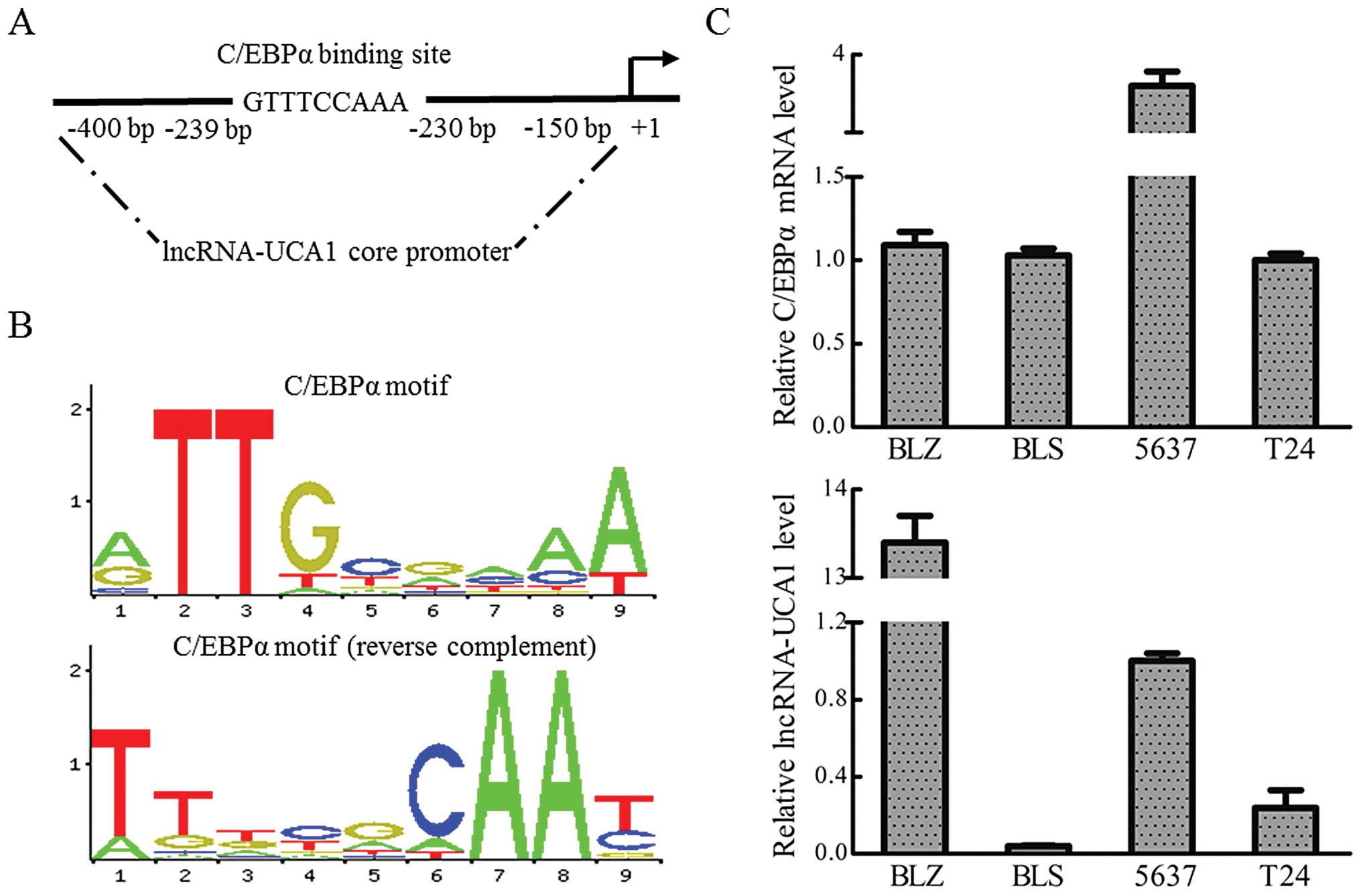
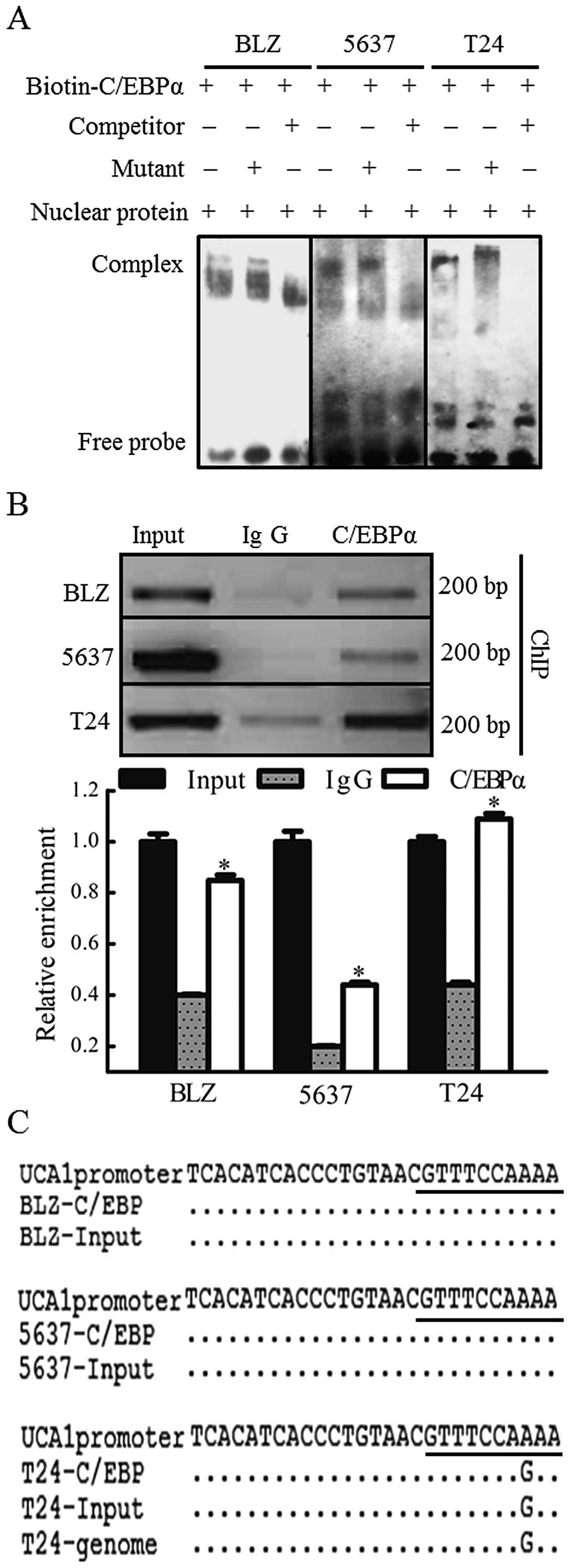
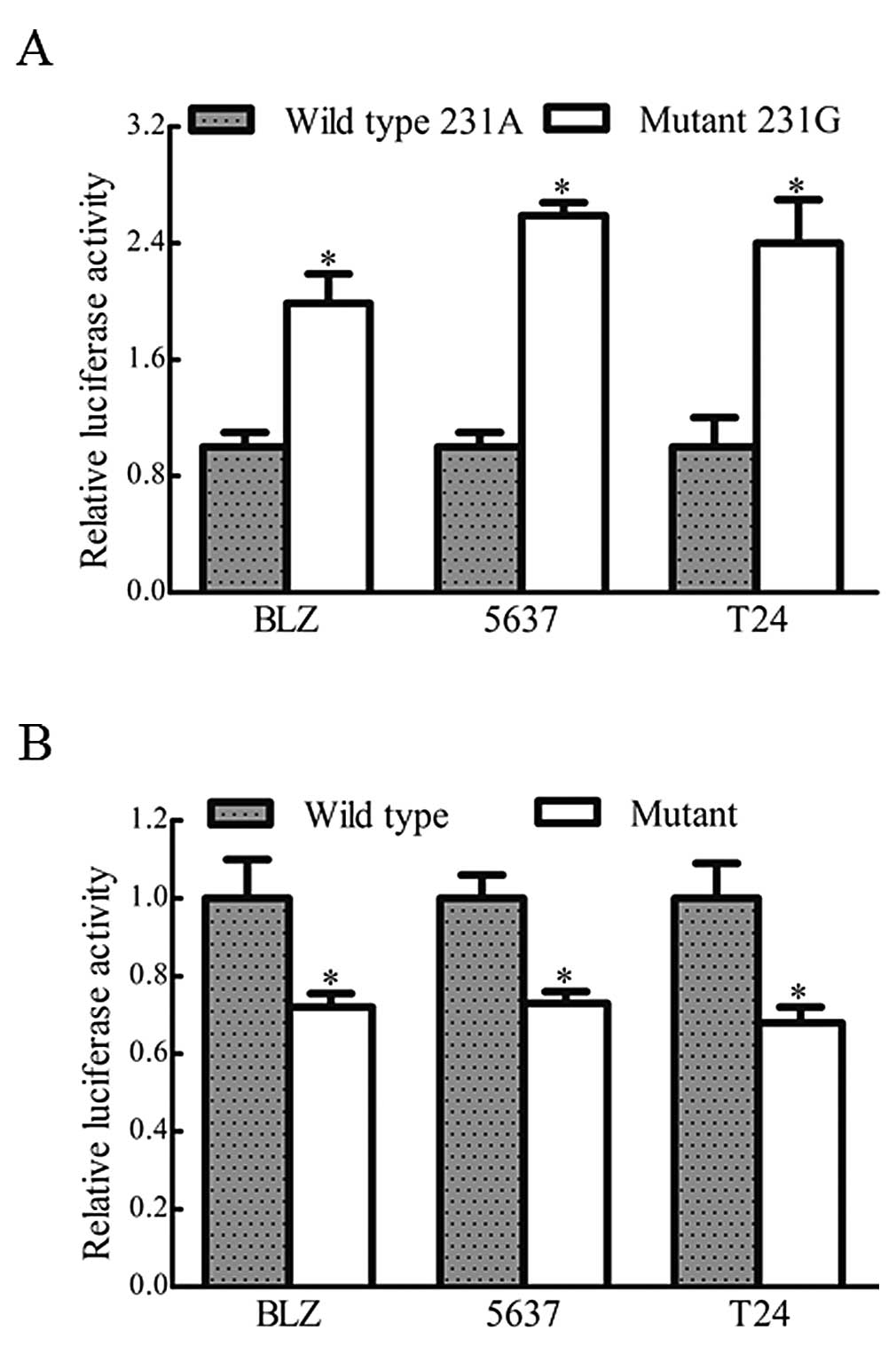
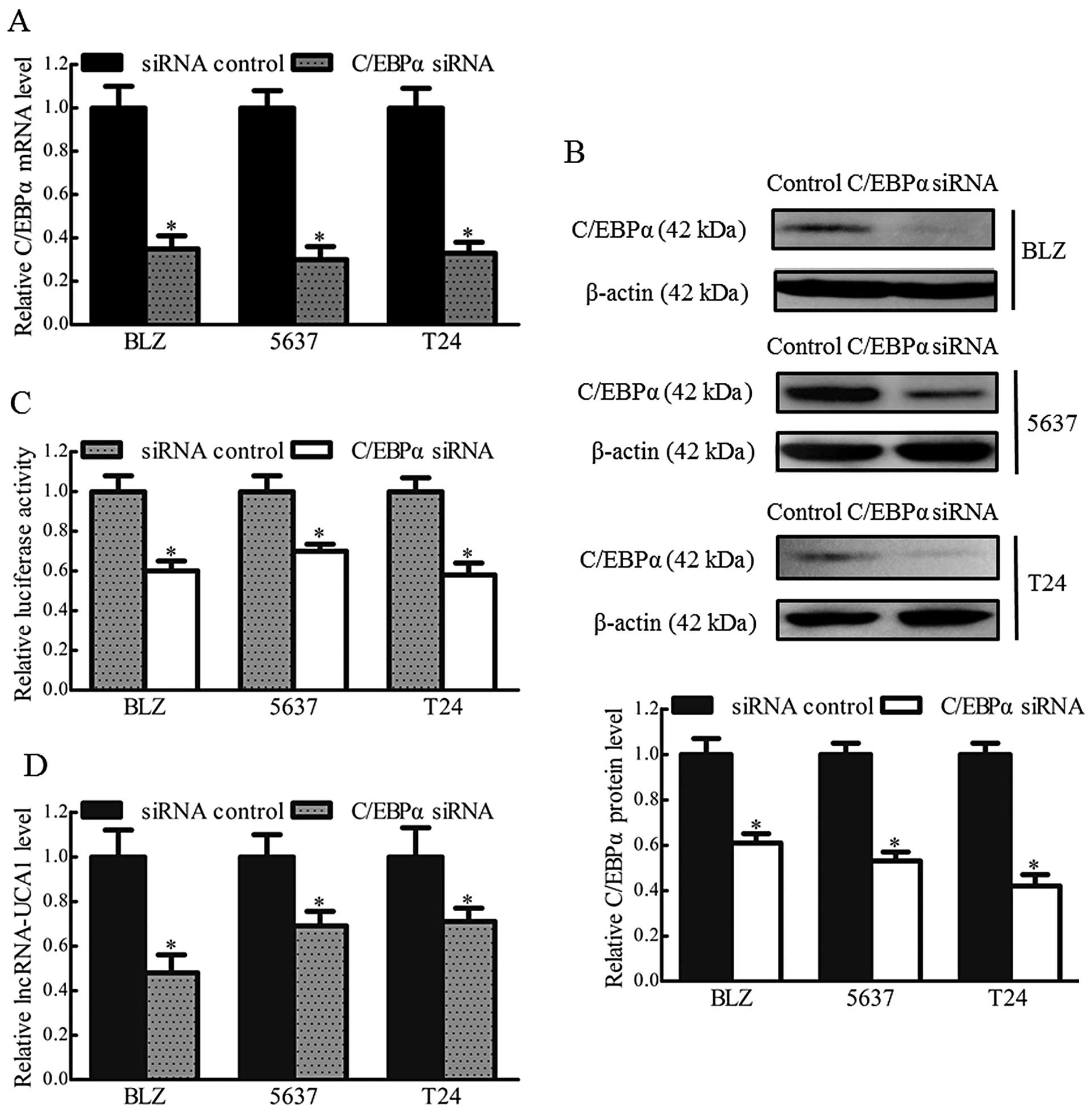
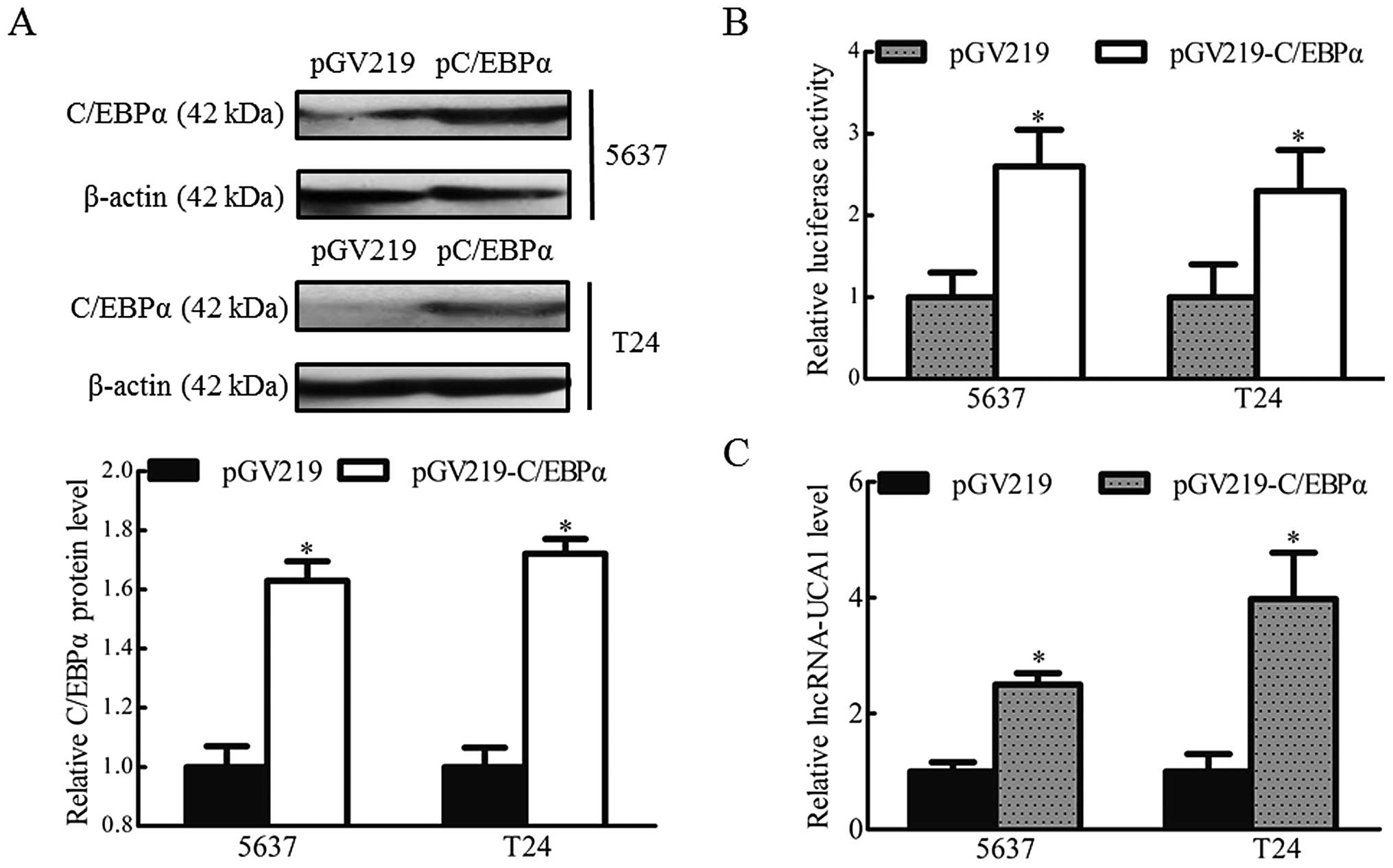
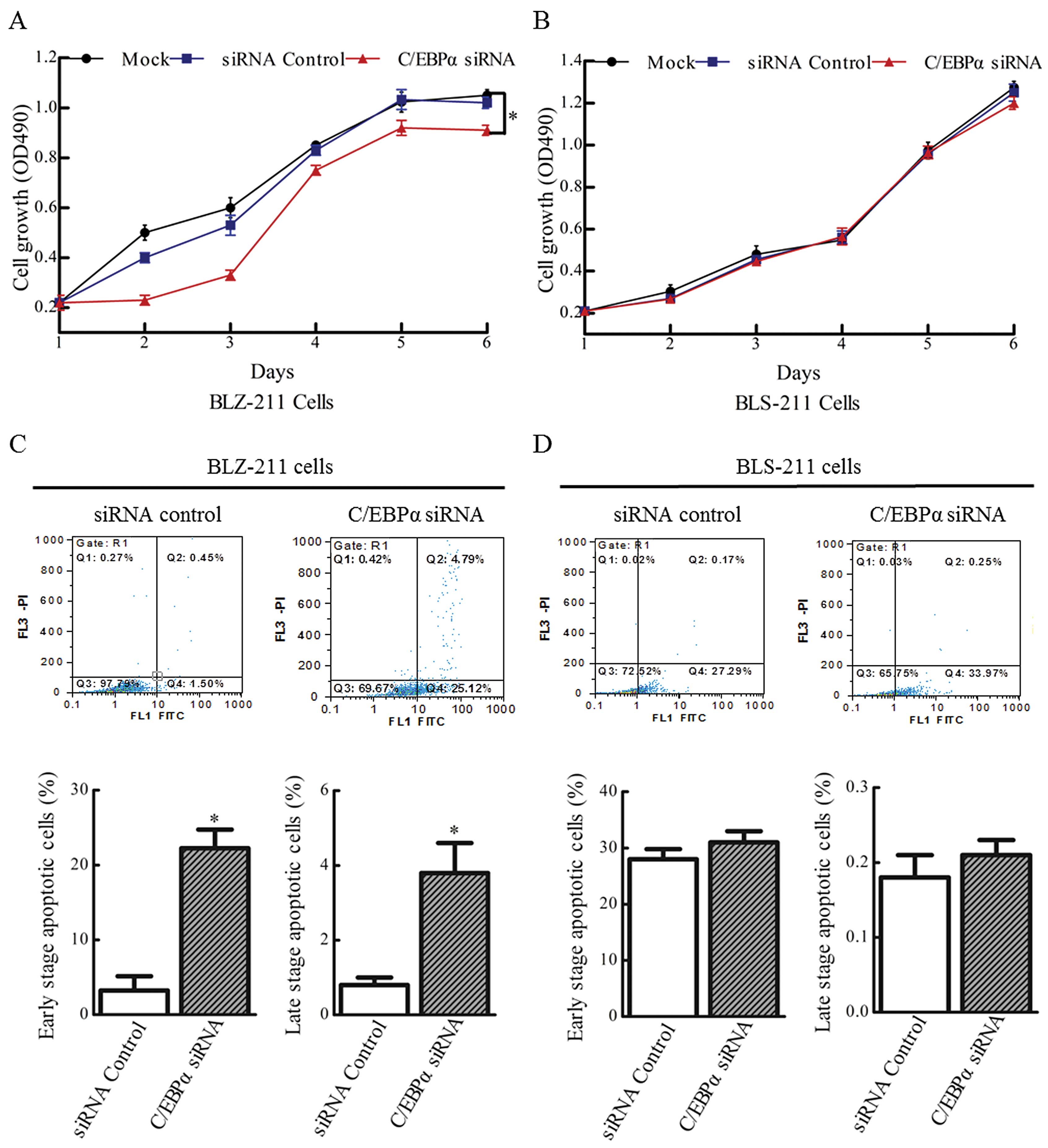
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jacobs BL, Lee CT and Montie JE: Bladder
cancer in 2010: how far have we come? CA Cancer J Clin. 60:244–272.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamat AM, Hegarty PK, Gee JR, et al:
ICUD-EAU International Consultation on Bladder Sancer 2012:
Screening, diagnosis, and molecular markers. Eur Urol. 63:4–15.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Orom UA, Derrien T, Beringer M, et al:
Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells.
Cell. 143:46–58. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guttman M, Donaghey J, Carey BW, et al:
lincRNAs act in the circuitry controlling pluripotency and
differentiation. Nature. 477:295–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JT: Epigenetic regulation by long
noncoding RNAs. Science. 338:1435–1439. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M and
Mattick JS: Non-coding RNAs: regulators of disease. J Pathol.
220:126–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gutschner T and Diederichs S: The
hallmarks of cancer: a long non-coding RNA point of view. RNA Biol.
9:703–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang XS, Zhang Z, Wang HC, et al: Rapid
identification of UCA1 as a very sensitive and specific unique
marker for human bladder carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4851–4858.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang F, Li X, Xie X, Zhao L and Chen W:
UCA1, a non-protein-coding RNA up-regulated in bladder carcinoma
and embryo, influencing cell growth and promoting invasion. FEBS
Lett. 582:1919–1927. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang C, Li X, Wang Y, Zhao L and Chen W:
Long non-coding RNA UCA1 regulated cell cycle distribution via CREB
through PI3-K dependent pathway in bladder carcinoma cells. Gene.
496:8–16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Chen W, Yang C, et al: Long
non-coding RNA UCA1a (CUDR) promotes proliferation and
tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. Int J Oncol. 41:276–284.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen G, Wang Z, Wang D, et al:
LncRNADisease: a database for long-non-coding RNA-associated
diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:D983–D986. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M, et al:
Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large
non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature. 458:223–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang JH, Li JH, Jiang S, Zhou H and Qu LH:
ChIPBase: a database for decoding the transcriptional regulation of
long non-coding RNA and microRNA genes from ChIP-Seq data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 41:D177–D187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang YC, Li X and Chen W: Characterization
of genes associated with different phenotypes of human bladder
cancer cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin. 38:602–610. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu W, Zhang S, Li X, et al: Ets-2
regulates cell apoptosis via the Akt pathway, through the
regulation of urothelial cancer associated 1, a long non-coding
RNA, in bladder cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e739202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brunner AL, Beck AH, Edris B, et al:
Transcriptional profiling of long non-coding RNAs and novel
transcribed regions across a diverse panel of archived human
cancers. Genome Biol. 13:R752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MM, Guelly C, et
al: Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking
up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA.
Gastroenterology. 132:330–342. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, et al: CREB
up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through
interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:5366–5383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huarte M, Guttman M, Feldser D, et al: A
large intergenic noncoding RNA induced by p53 mediates global gene
repression in the p53 response. Cell. 142:409–419. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang M, Zhang Z, Zhu H, et al: A novel
functional polymorphism C1797G in the MDM2 promoter is
associated with risk of bladder cancer in a Chinese population.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:3633–3640. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|