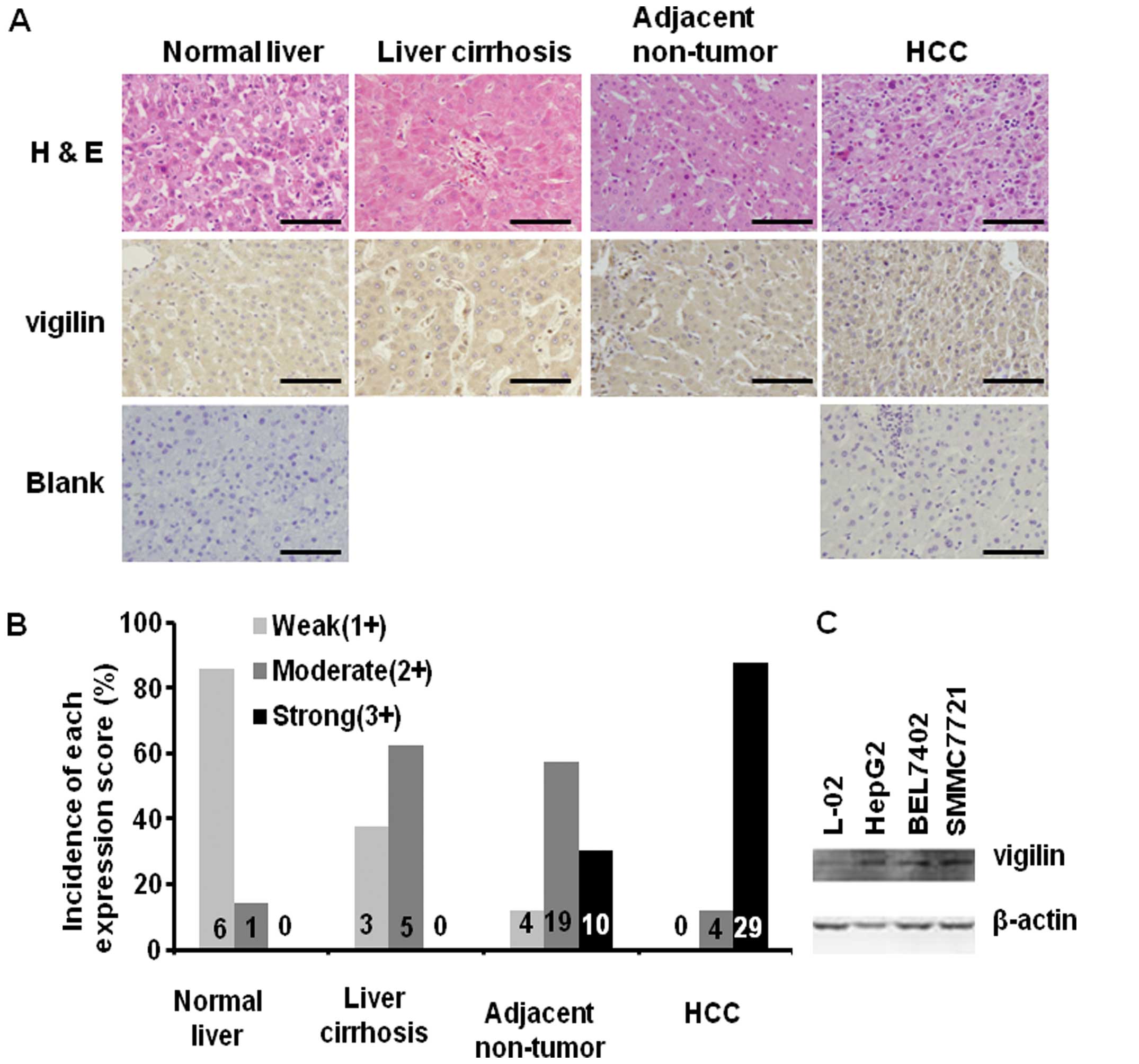
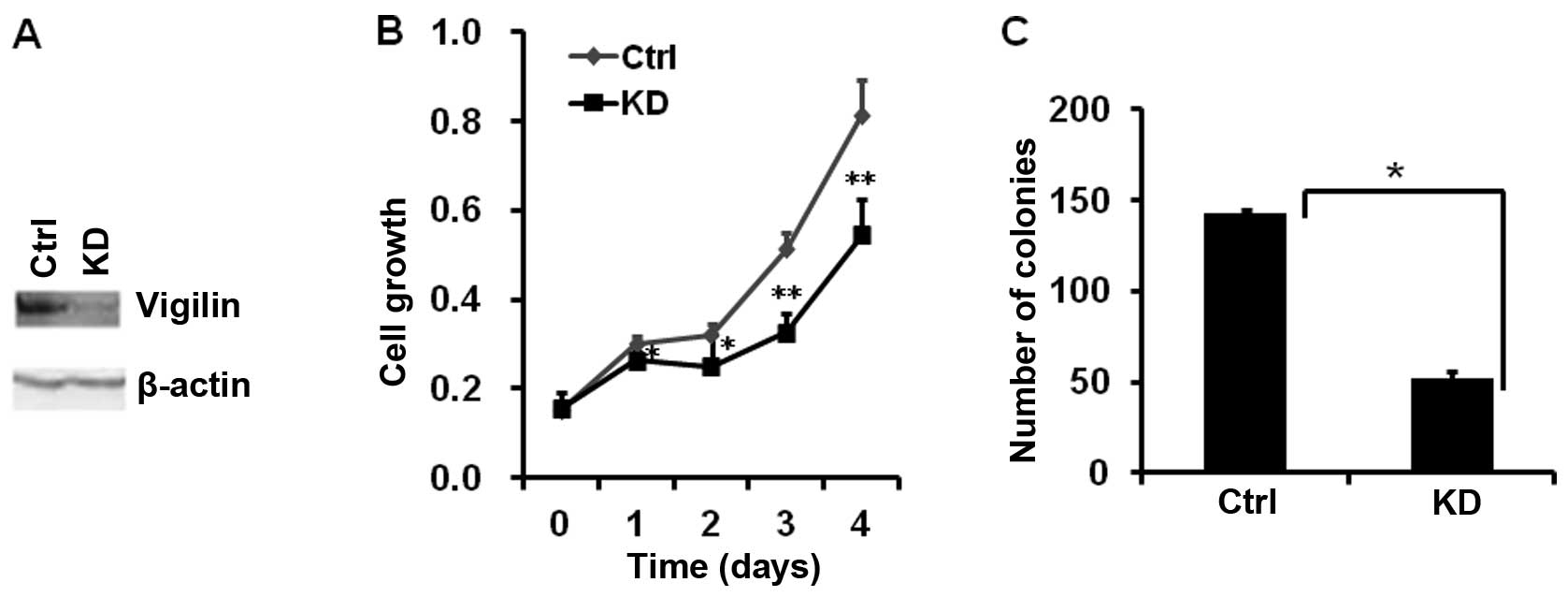
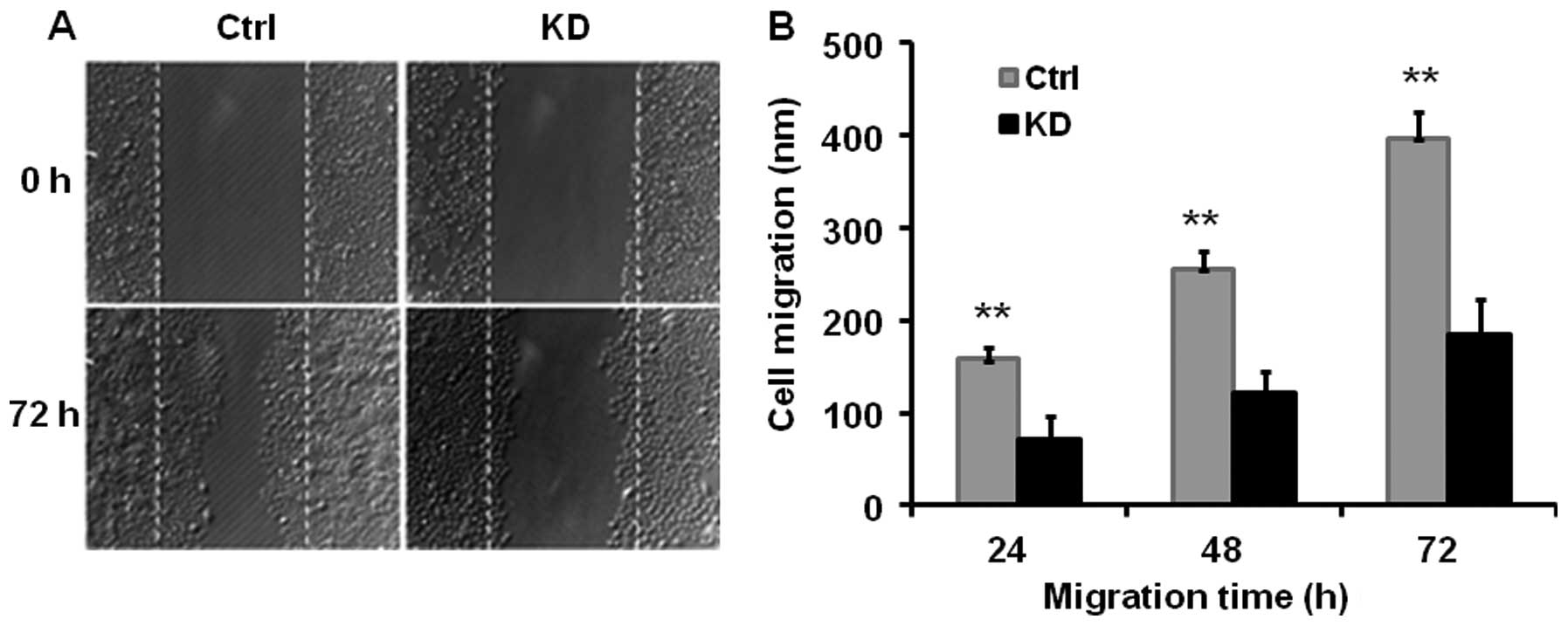
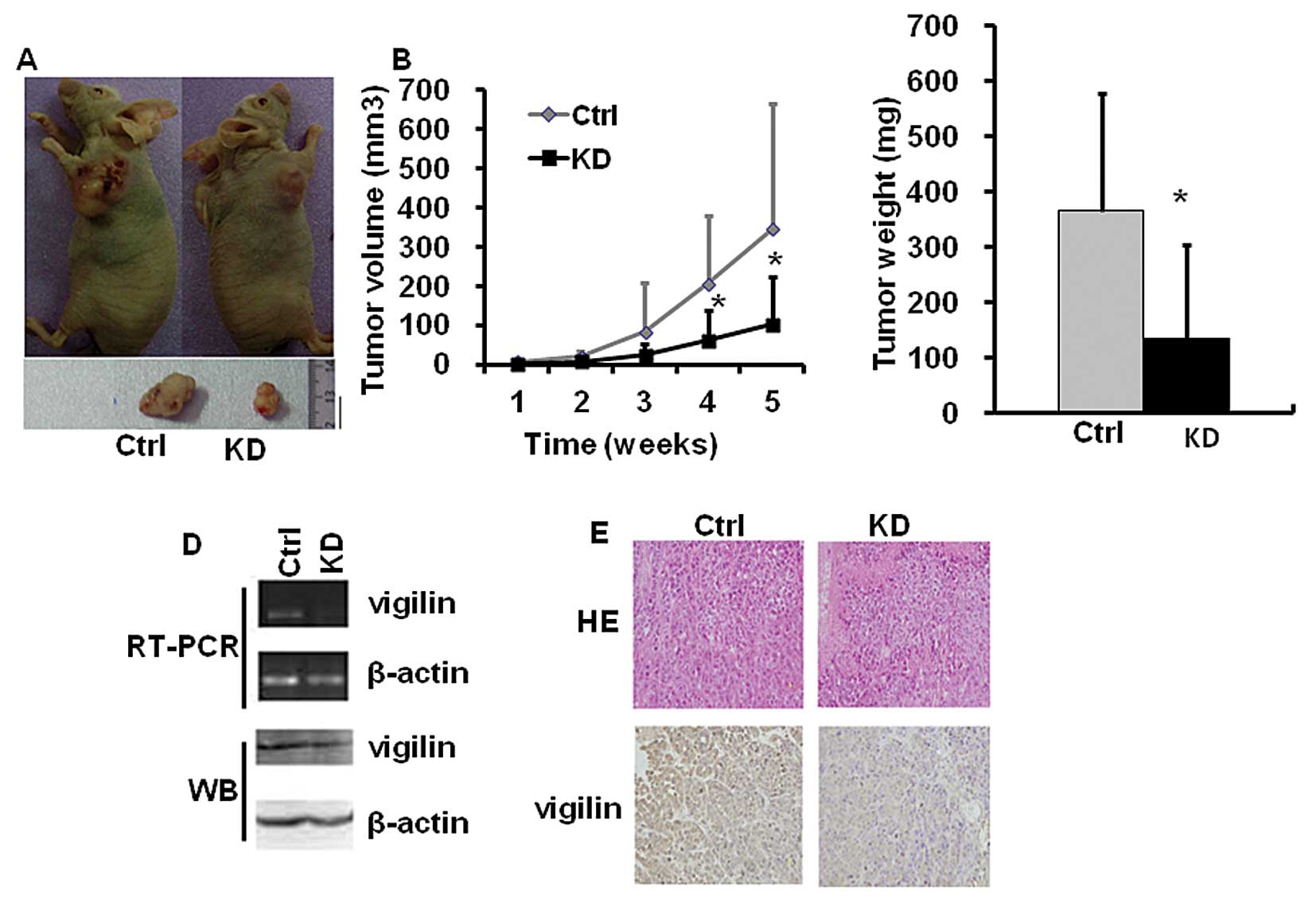
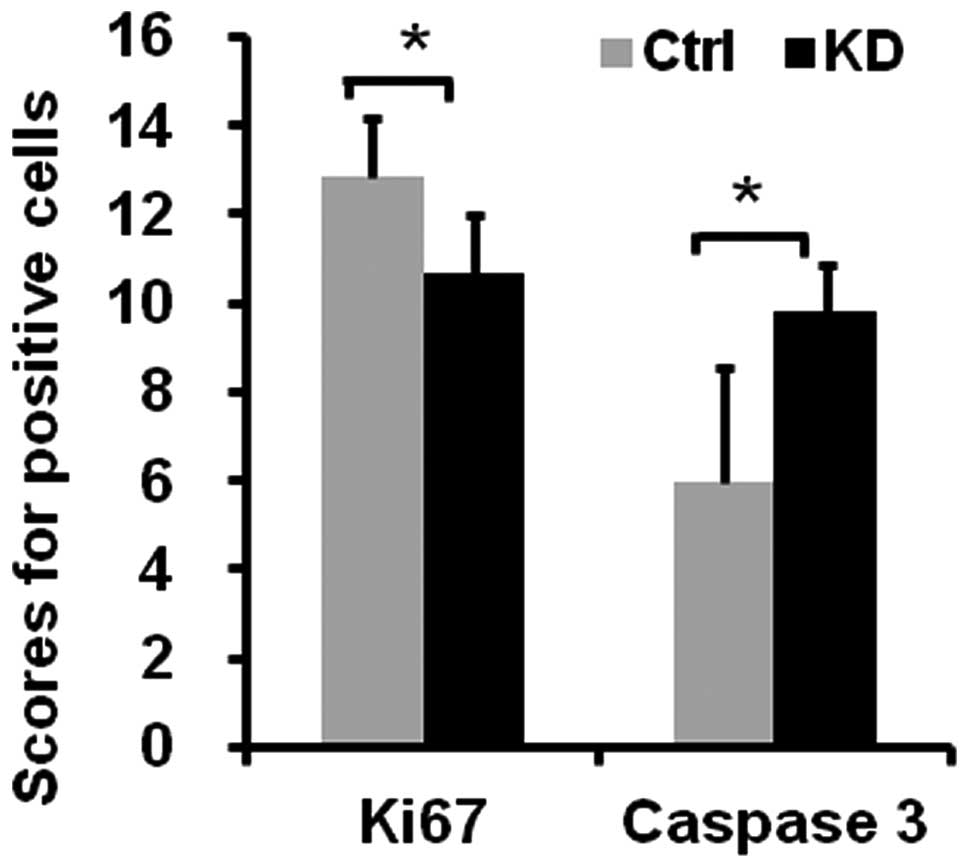
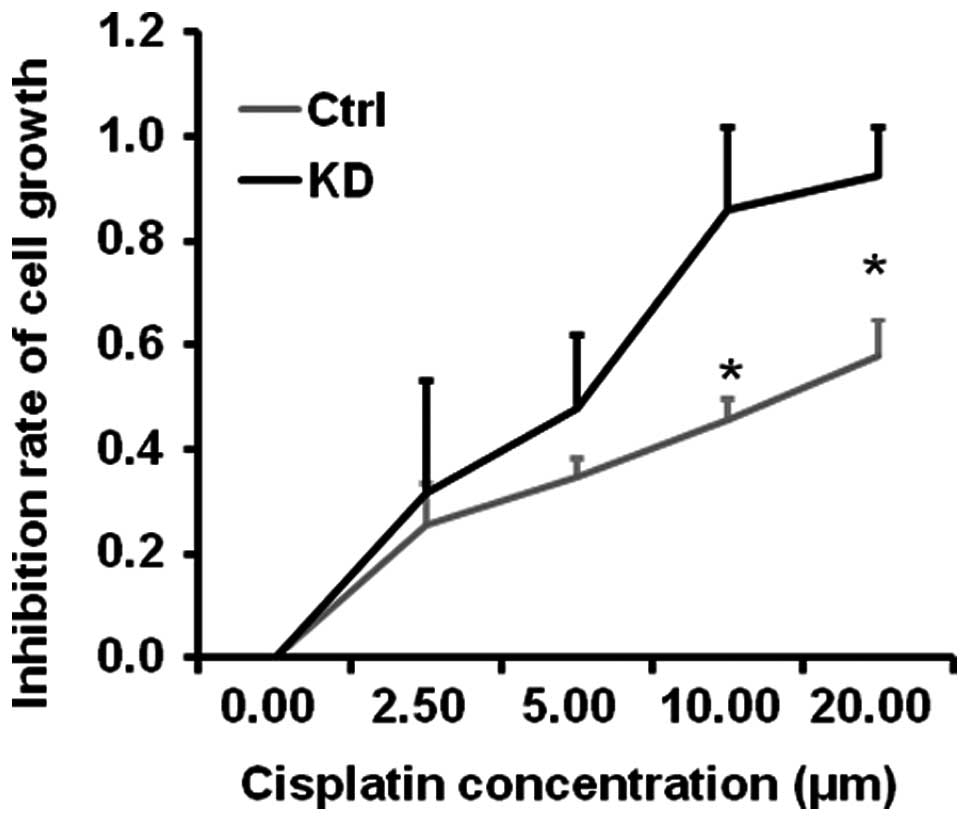
|
1
|
Leong TY and Leong AS: Epidemiology and
carcinogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB. 7:5–15. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wintersberger U, Kühne C and Karwan A:
Scp160p, a new yeast protein associated with the nuclear membrane
and the endoplasmic reticulum, is necessary for maintenance of
exact ploidy. Yeast. 11:929–944. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kügler S, Grünweller A, Probst C, et al:
Vigilin contains a functional nuclear localisation sequence and is
present in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. FEBS Lett.
382:330–344. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vollbrandt T, Willkomm D, Stossberg H, et
al: Vigilin is co-localized with 80S ribosomes and binds to the
ribosomal complex through its C-terminal domain. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 36:1306–1318. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Frey S, Pool M and Seedorf M: Scp160p, an
RNA-binding, polysome-associated protein, localizes to the
endoplasmic reticulum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a
microtubule-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 276:15905–15912. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lang BD and Fridovich-Keil JL: Scp160p, a
multiple KH-domain protein, is a component of mRNP complexes in
yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:1576–1584. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baum S, Bittins M, Frey S and Seedorf M:
Asc1p, a WD40-domain containing adaptor protein, is required for
the interaction of the RNA-binding protein Scp160p with polysomes.
Biochem J. 380:823–830. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Klinger MH and Kruse C: Immunocytochemical
localization of vigilin, a tRNA-binding protein, after cell
fractionation and within the exocrine pancreatic cell of the rat.
Ann Anat. 178:331–335. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hilgendorf I, Gellersen O, Emmrich J, et
al: Estradiol has a direct impact on the exocrine pancreas as
demonstrated by enzyme and vigilin expression. Pancreatology.
1:24–29. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kruse C, Grünweller A, Willkomm DK, et al:
tRNA is entrapped in similar, but distinct, nuclear and cytoplasmic
ribonucleoprotein complexes, both of which contain vigilin and
elongation factor 1 α. Biochem J. 329:615–621. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kruse C, Willkomm D, Gebken J, et al: The
multi-KH protein vigilin associates with free and membrane-bound
ribosomes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 60:2219–2227. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cunningham KS, Dodson RE, Nagel MA, et al:
Vigilin binding selectively inhibits cleavage of the vitellogenin
mRNA 3′-untranslated region by the mRNA endonuclease polysomal
ribonuclease 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:12498–12502.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou J, Wang Q, Chen LL and Carmichael GG:
On the mechanism of induction of heterochromatin by the RNA-binding
protein vigilin. RNA. 14:1773–1781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Plenz G, Kügler S, Schnittger S, et al:
The human vigilin gene: identification, chromosomal localization
and expression pattern. Hum Genet. 93:575–582. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiu DS, Oram JF, LeBoeuf RC, et al:
High-density lipoprotein-binding protein (HBP)/vigilin is expressed
in human atherosclerotic lesions and colocalizes with
apolipoprotein E. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 17:2350–2358.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gagné JP, Gagné P, Hunter JM, et al:
Proteome profiling of human epithelial ovarian cancer cell line
TOV-112D. Mol Cell Biochem. 275:25–55. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim H and Lubman DM: Micro-proteome
analysis using micro-chromatofocusing in intact protein
separations. J Chromatogr A. 1194:3–10. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Evans CO, Moreno CS, Zhan X, et al:
Molecular pathogenesis of human prolactinomas identified by gene
expression profiling, RT-qPCR, and proteomic analyses. Pituitary.
11:231–245. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim NS, Hahn Y, Oh JH, et al: Gene
cataloging and expression profiling in human gastric cancer cells
by expressed sequence tags. Genomics. 83:1024–1045. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Woo HH, Yi X, Lamb T, et al:
Posttranscriptional suppression of proto-oncogene c-fms
expression by vigilin in breast cancer. Mol Cell Biol. 31:215–225.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei L, Zhang CL, Jiang L, et al:
Expression of human VIGILIN N terminus and observation of
subcellular localization. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
40:185–189. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Reiner A, Neumeister B, Spona J, et al:
Immunocytochemical localization of estrogen and progesterone
receptor and prognosis in human primary breast cancer. Cancer Res.
50:7057–7061. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stewart SA, Dykxhoorn DM, Palliser D, et
al: Lentivirus-delivered stable gene silencing by RNAi in primary
cells. RNA. 9:493–501. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goolsby KM and Shapiro DJ: RNAi-mediated
depletion of the 15 KH domain protein, vigilin, induces death of
dividing and non-dividing human cells but does not initially
inhibit protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:5644–5653. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liang CC, Park AY and Guan JL: In vitro
scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of
cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2:329–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Galvez AF, Chen N, Macasieb J and de Lumen
BO: Chemopreventive property of a soybean peptide (lunasin) that
binds to deacetylated histones and inhibits acetylation. Cancer
Res. 61:7473–7478. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Robinson WS: The role of hepatitis B virus
in the development of primary hepatocellular carcinoma: part I. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:622–638. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wadle A, Mischo A, Imig J, et al:
Serological identification of breast cancer-related antigens from a
Saccharomyces cerevisiae surface display library. Int J
Cancer. 117:104–113. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kalnin̦a Z, Silin̦a K, Meistere I, et al:
Evaluation of T7 and lambda phage display systems for survey of
autoantibody profiles in cancer patients. J Immunol Methods.
334:37–50. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Neu-Yilik G, Zorbas H, Gloe TR, et al:
Vigilin is a cytoplasmic protein. A study on its expression in
primary cells and in established cell lines of different species.
Eur J Biochem. 213:727–736. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schuh A, Assmuth K, Hilgendorf I, et al:
Protein synthesis of eucaryotic cells could be decreased by
antisense-DNA of the multi KH domain protein vigilin. Int J Mol
Med. 12:35–43. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oh-Ishi M and Maeda T: Disease proteomics
of high-molecular-mass proteins by two-dimensional gel
electrophoresis with agarose gels in the first dimension (Agarose
2-DE). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 849:211–222.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|