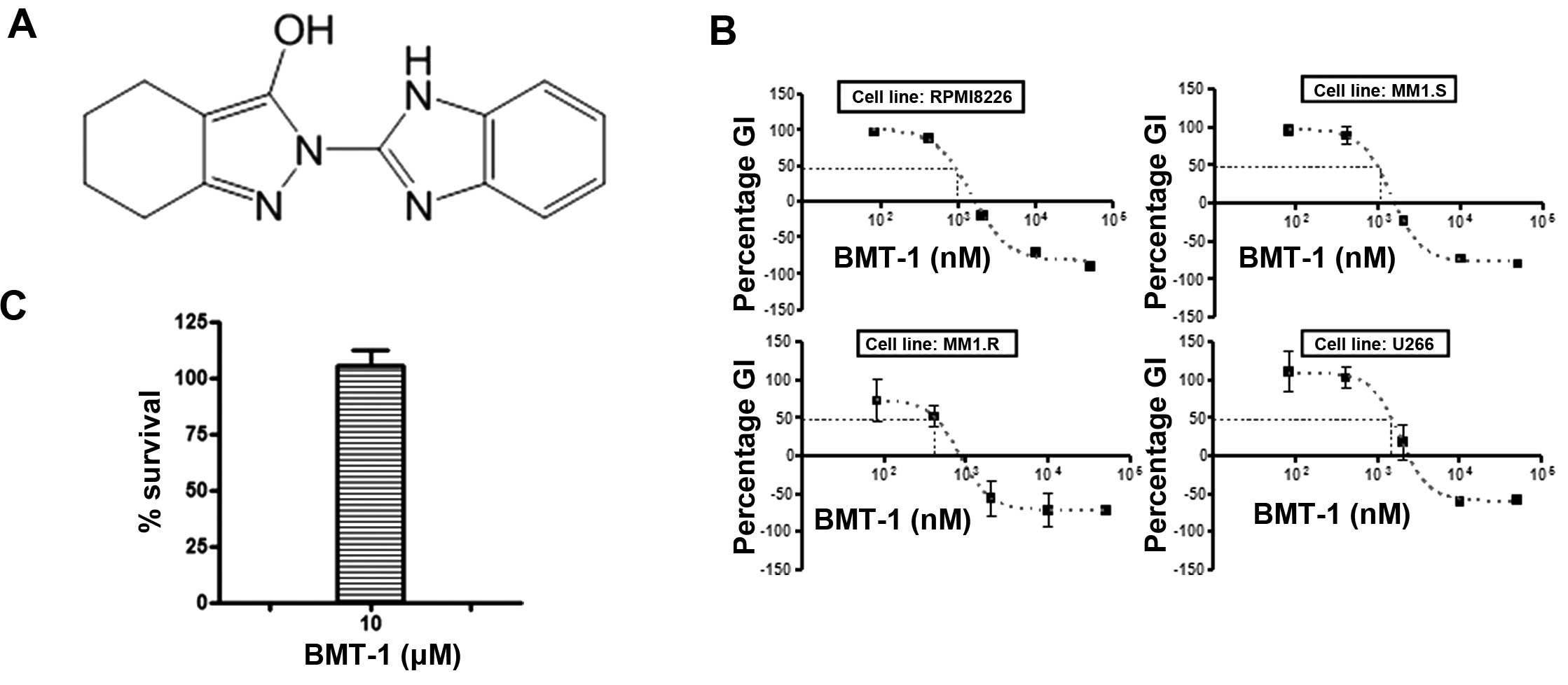
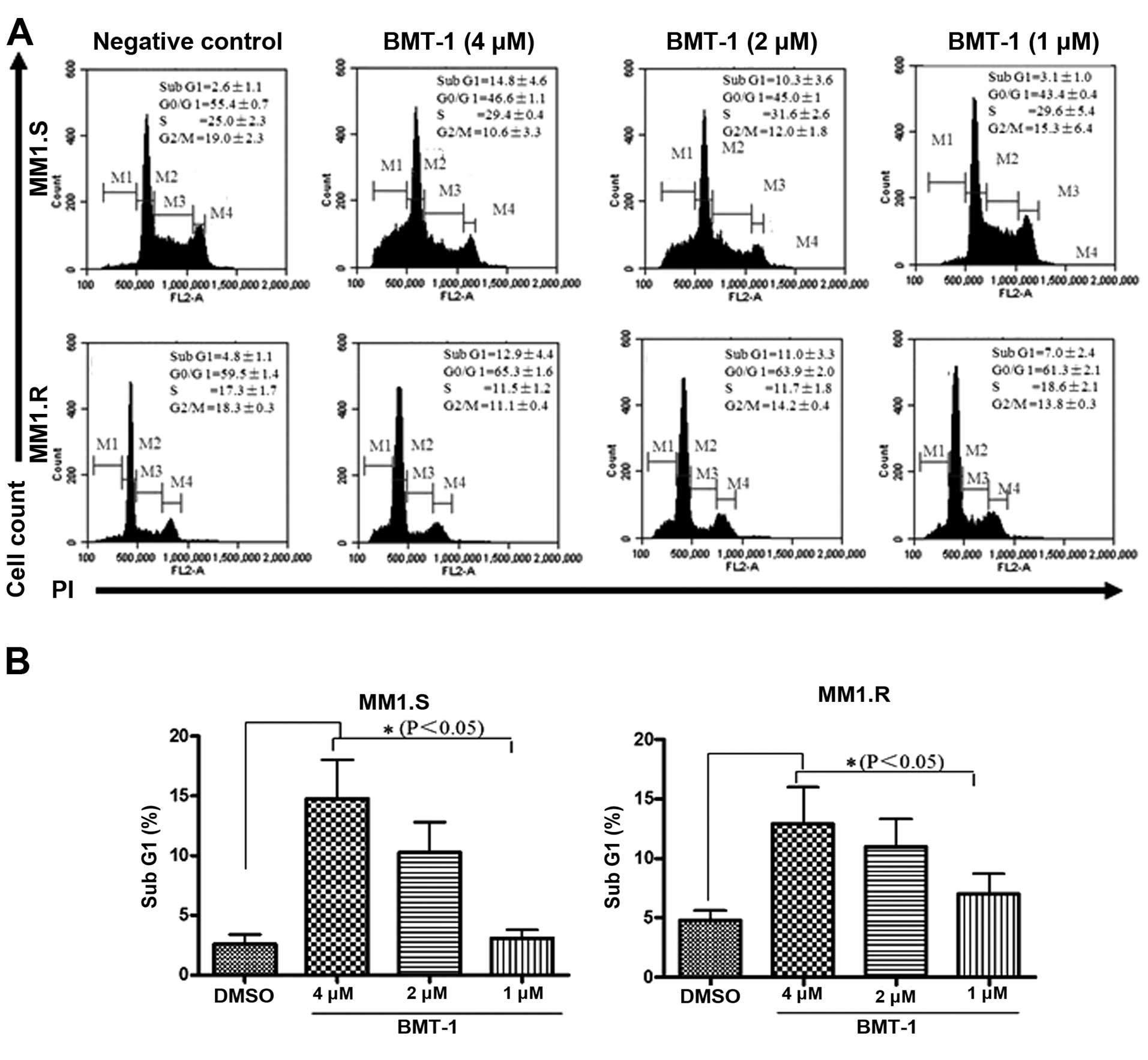
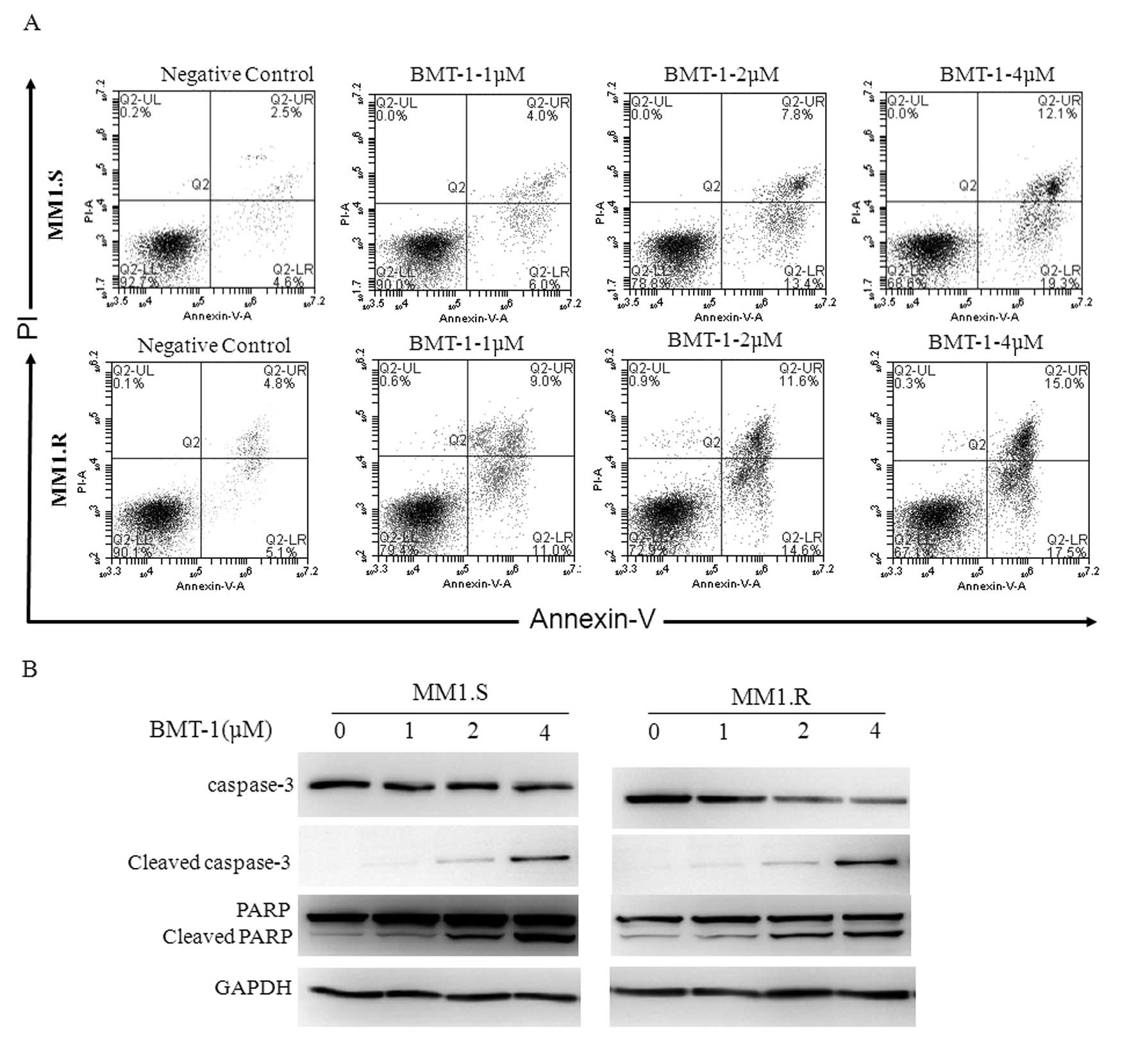
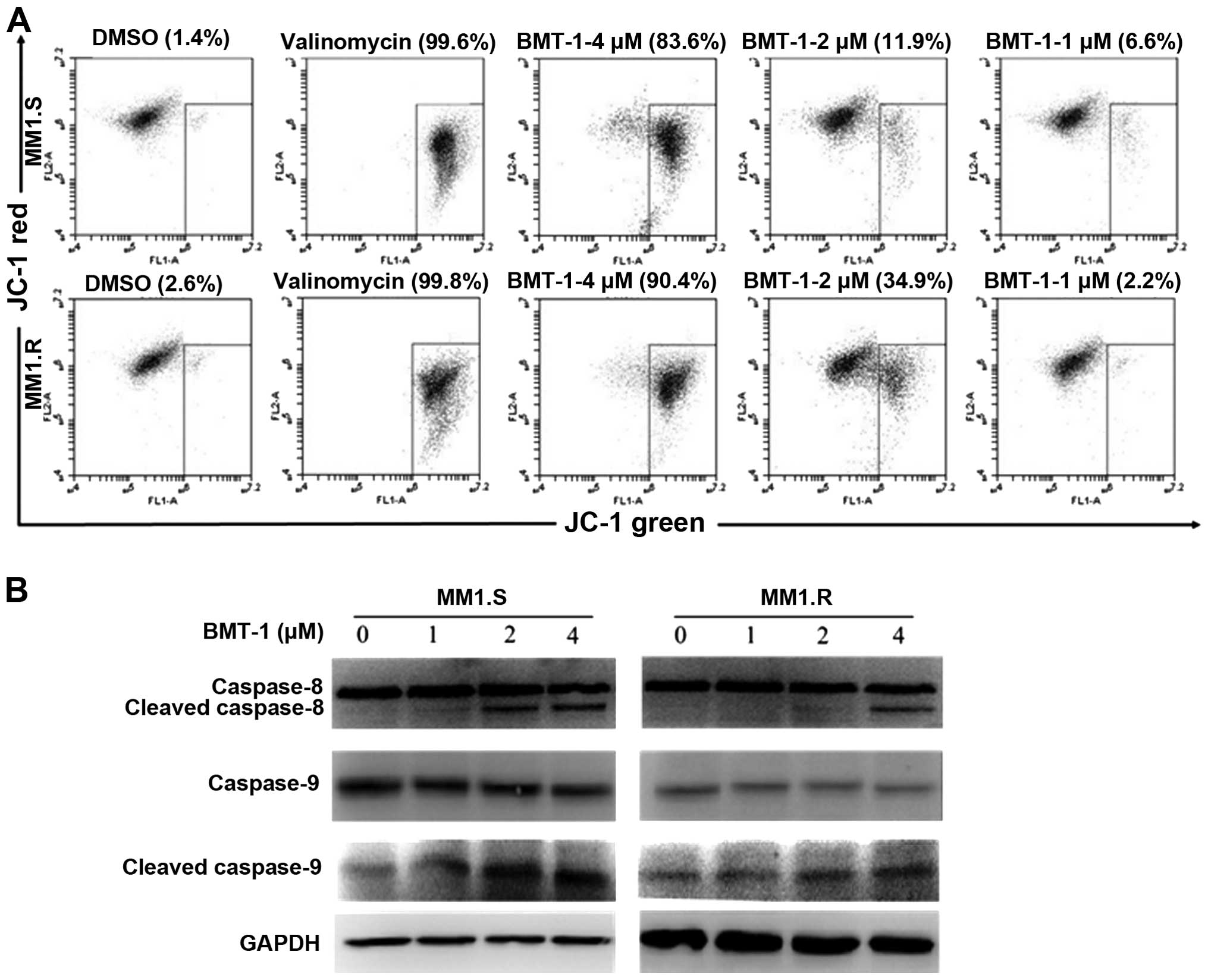
|
1
|
Kyle RA and Rajkumar SV: Criteria for
diagnosis, staging, risk stratification and response assessment of
multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 23:3–9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mahindra A, Laubach J, Raje N, Munshi N,
Richardson PG and Anderson K: Latest advances and current
challenges in the treatment of multiple myeloma. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 9:135–143. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jáuregui I, García-Lirio E, Soriano AM,
Gamboa PM and Antépara I: An overview of the novel H1-antihistamine
bilastine in allergic rhinitis and urticaria. Expert Rev Clin
Immunol. 8:33–41. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wexler RR, Greenlee WJ, Irvin JD, et al:
Nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists: the next generation
in antihypertensive therapy. J Med Chem. 39:625–656. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Navarrete-Vázquez G, Cedillo R,
Hernández-Campos A, et al: Synthesis and antiparasitic activity of
2-(trifluoromethyl)-benzimidazole derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 11:187–190. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sachs G, Shin JM, Vagin O, Lambrecht N,
Yakubov I and Munson K: The gastric H,K ATPase as a drug target:
past, present, and future. J Clin Gastroenterol. 41(Suppl 2):
S226–S242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim SK, Ahn CM, Choi SJ, Park YS, Cho HC
and Koh CM: The growth inhibitiory effect of new
pyrrolo[1,2-α]benzimidazole derivatives on human gastric cancer
cells. Arch Pharm Res. 20:410–413. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grimaudo S, Tolomeo M, Chimirri A, Zappala
M, Gancitano RA and D’Alessandro N: Selective induction of
apoptosis in multidrug resistant HL60R cells by the
thiazolobenzoimidazole derivative 1-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-1
H,3H-thiazolo [3,4-a] benzimidazole (TBZ). Eur J
Cancer. 34:1756–1763. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Al-Douh MH, Sahib HB, Osman H, Abd Hamid S
and Salhimi SM: Anti-proliferation effects of benzimidazole
derivatives on HCT-116 colon cancer and MCF-7 breast cancer cell
lines. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4075–4079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Youssef AM, Malki A, Badr MH, Elbayaa RY
and Sultan AS: Synthesis and anticancer activity of novel
benzimidazole and benzothiazole derivatives against HepG2 liver
cancer cells. Med Chem. 8:151–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin ML, Chen SS, Lu YC, et al: Rhein
induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress
and Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial death pathway in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 27:3313–3322.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shin JM and Kim N: Pharmacokinetics and
pharmacodynamics of the proton pump inhibitors. J
Neurogastroenterol Motil. 19:25–35. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Webb BA, Chimenti M, Jacobson MP and
Barber DL: Dysregulated pH: a perfect storm for cancer progression.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:671–677. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen M, Zou X, Luo H, et al: Effects and
mechanisms of proton pump inhibitors as a novel chemosensitizer on
human gastric adenocarcinoma (SGC7901) cells. Cell Biol Int.
33:1008–1019. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McCarty MF and Whitaker J: Manipulating
tumor acidification as a cancer treatment strategy. Altern Med Rev.
15:264–272. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fais S: Proton pump inhibitor-induced
tumour cell death by inhibition of a detoxification mechanism. J
Intern Med. 267:515–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Monks A, Scudiero D, Skehan P, et al:
Feasibility of a high-flux anticancer drug screen using a diverse
panel of cultured human tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst.
83:757–766. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Karali N: Synthesis and primary
cytotoxicity evaluation of new 5-nitroindole-2,3-dione derivatives.
Eur J Med Chem. 37:909–918. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Milito A, Iessi E, Logozzi M, et al:
Proton pump inhibitors induce apoptosis of human B-cell tumors
through a caspase-independent mechanism involving reactive oxygen
species. Cancer Res. 67:5408–5417. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nilsson C, Kågedal K, Johansson U and
Ollinger K: Analysis of cytosolic and lysosomal pH in apoptotic
cells by flow cytometry. Methods Cell Sci. 25:185–194. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cowling V and Downward J: Caspase-6 is the
direct activator of caspase-8 in the cytochrome c-induced
apoptosis pathway: absolute requirement for removal of caspase-6
prodomain. Cell Death Differ. 9:1046–1056. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen M, Guerrero AD, Huang L, et al:
Caspase-9-induced mitochondrial disruption through cleavage of
anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members. J Biol Chem. 282:33888–33895.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Perry SW, Norman JP, Barbieri J, Brown EB
and Gelbard HA: Mitochondrial membrane potential probes and the
proton gradient: a practical usage guide. Biotechniques. 50:98–115.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Smolka AJ, Goldenring JR, Gupta S and
Hammond CE: Inhibition of gastric H,K-ATPase activity and gastric
epithelial cell IL-8 secretion by the pyrrolizine derivative ML
3000. BMC Gastroenterol. 4:42004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morii M, Takata H, Fujisaki H and
Takeguchi N: The potency of substituted benzimidazoles such as
E3810, omeprazole, Ro 18-5364 to inhibit gastric H+,
K+-ATPase is correlated with the rate of acid-activation
of the inhibitor. Biochem Pharmacol. 39:661–667. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Beil W and Sewing KF: Inhibition of
partially purified K+/H+-ATPase from
guinea-pig isolated and enriched parietal cells by substituted
benzimidazoles. Br J Pharmacol. 82:651–657. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yeo M, Kim DK, Park HJ, Cho SW, Cheong JY
and Lee KJ: Blockage of intracellular proton extrusion with proton
extrusions with proton pump inhibitor induces apoptosis in gastric
cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:1852008.
|
|
28
|
Pinto MC, Dias DF, Del Puerto HL, et al:
Discovery of cytotoxic and pro-apoptotic compounds against leukemia
cells: Tert-butyl-4-[(3-nitrophenoxy)
methyl]-2,2-dimethyloxazolidine-3-carboxylate. Life Sci.
89:786–794. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang WL, Chang CS, Chiang PC, et al:
2-Phenyl-5-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzyl)-1H-benzimidazole,
a benzimidazole derivative, inhibits growth of human prostate
cancer cells by affecting tubulin and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Br J
Pharmacol. 160:1677–1689. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu JF, Huang YL, Yang WH, Chang CS and
Tang CH: 1-Benzyl-2-phenylbenzimidazole (BPB), a benzimidazole
derivative, induces cell apoptosis in human chondrosarcoma through
intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 13:16472–16488.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vasaitis T, Belosay A, Schayowitz A, et
al: Androgen receptor inactivation contributes to antitumor
efficacy of 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase inhibitor
3β-hydroxy-17-(1H-benzimidazole-1-yl)androsta-5,16-diene in
prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2348–2357. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu JF, Chang CS, Fong YC, Kuo SC and Tang
CH: FPipTB, a benzimidazole derivative, induces chondrosarcoma cell
apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase 1. Mol Carcinog. May 18–2011.(Epub ahead
of print).
|
|
33
|
Schultz BE and Chan SI: Structures and
proton-pumping strategies of mitochondrial respiratory enzymes.
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 30:23–65. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murakami T, Shibuya I, Ise T, et al:
Elevated expression of vacuolar proton pump genes and cellular pH
in cisplatin resistance. Int J Cancer. 93:869–874. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Streif D, Iglseder E, Hauser-Kronberger C,
Fink KG, Jakab M and Ritter M: Expression of the non-gastric
H+/K+ ATPase ATP12A in normal and
pathological human prostate tissue. Cell Physiol Biochem.
28:1287–1294. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|