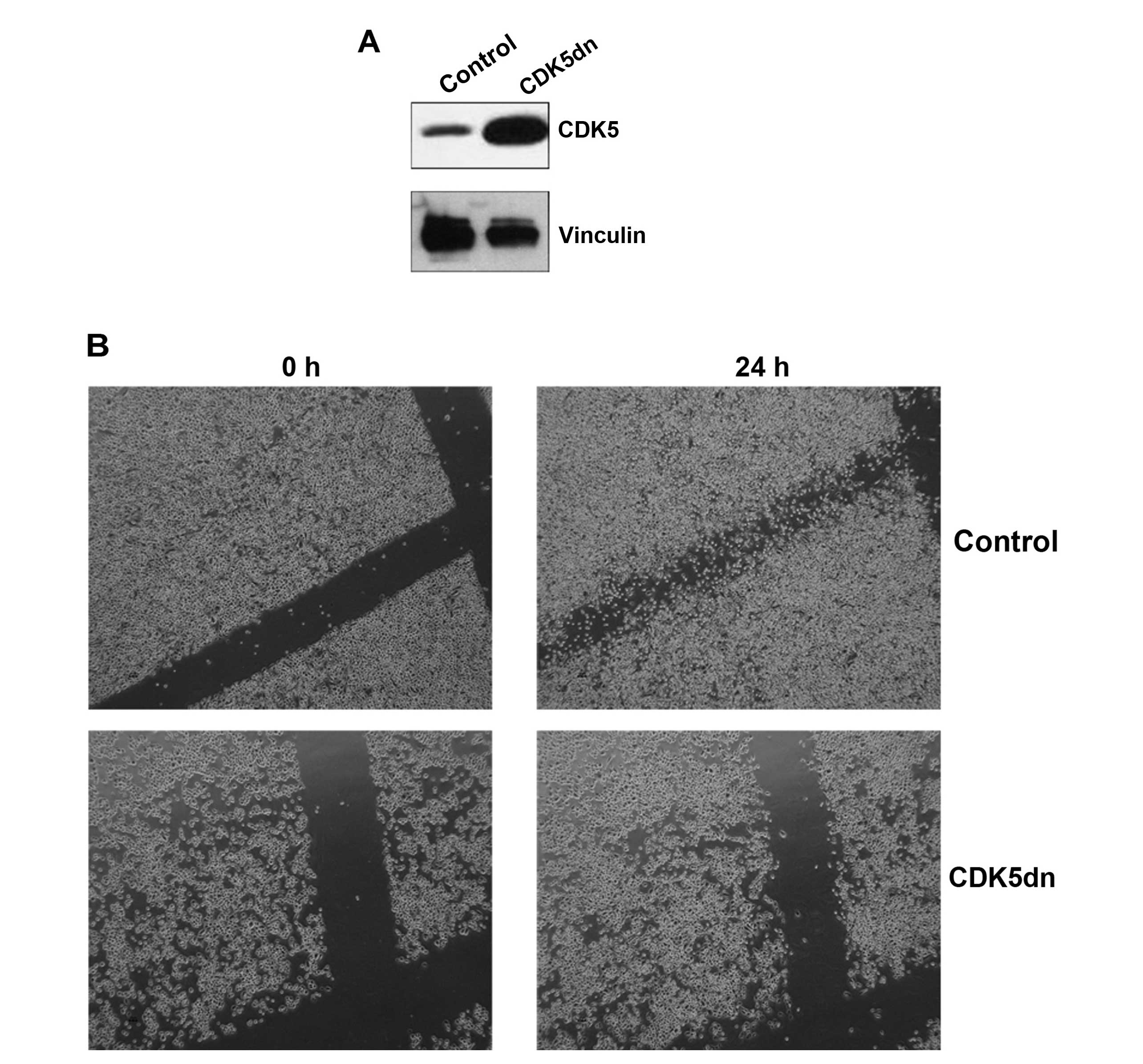
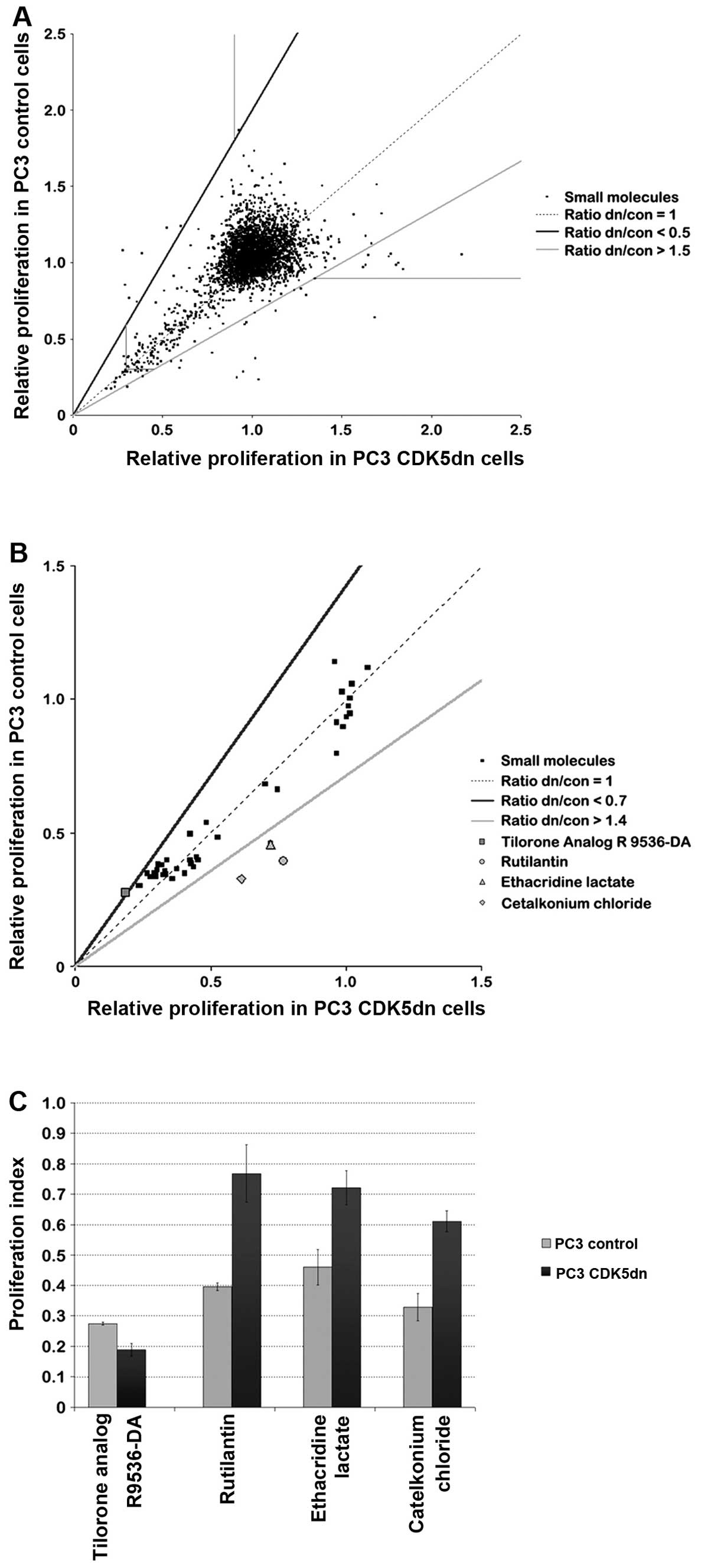
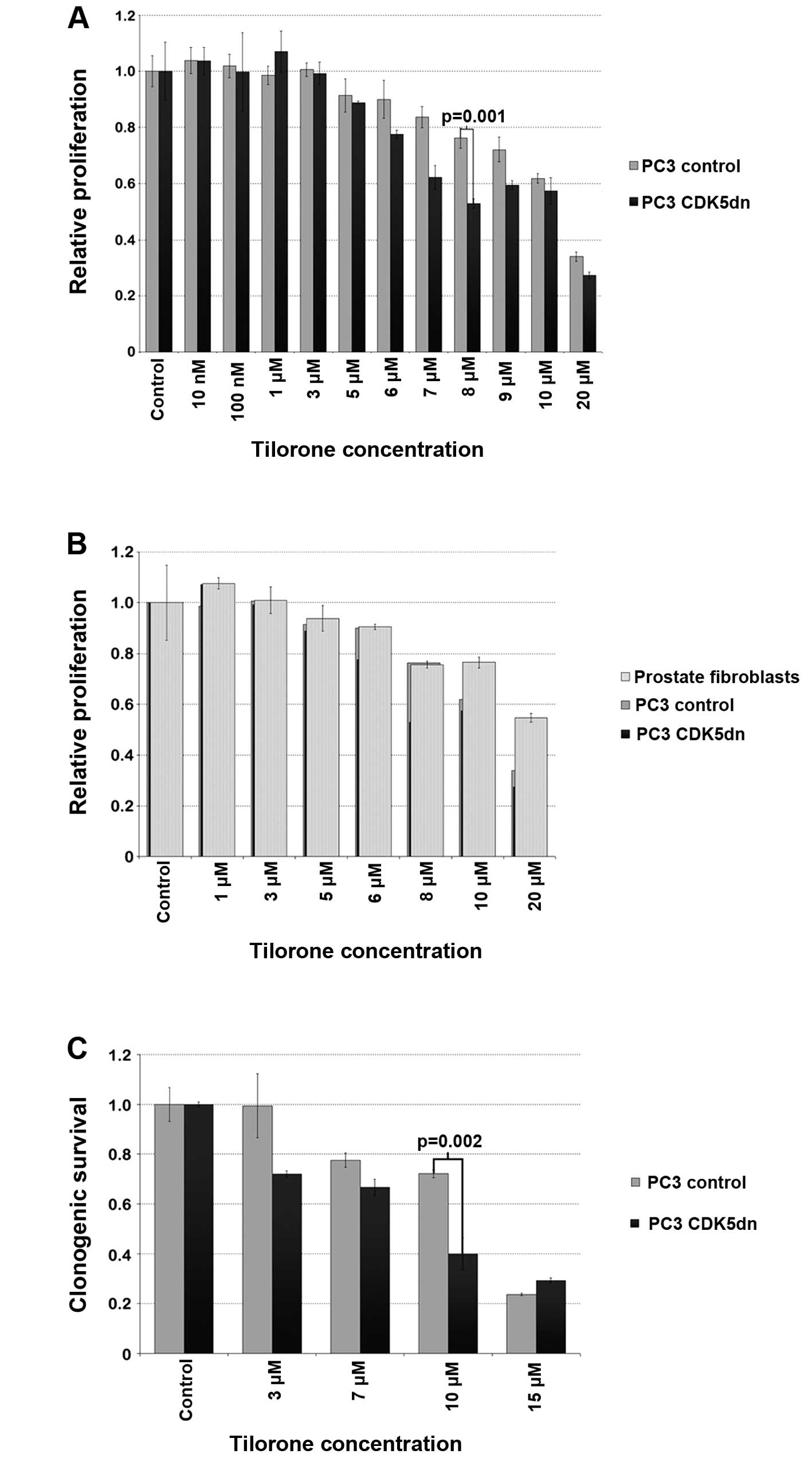
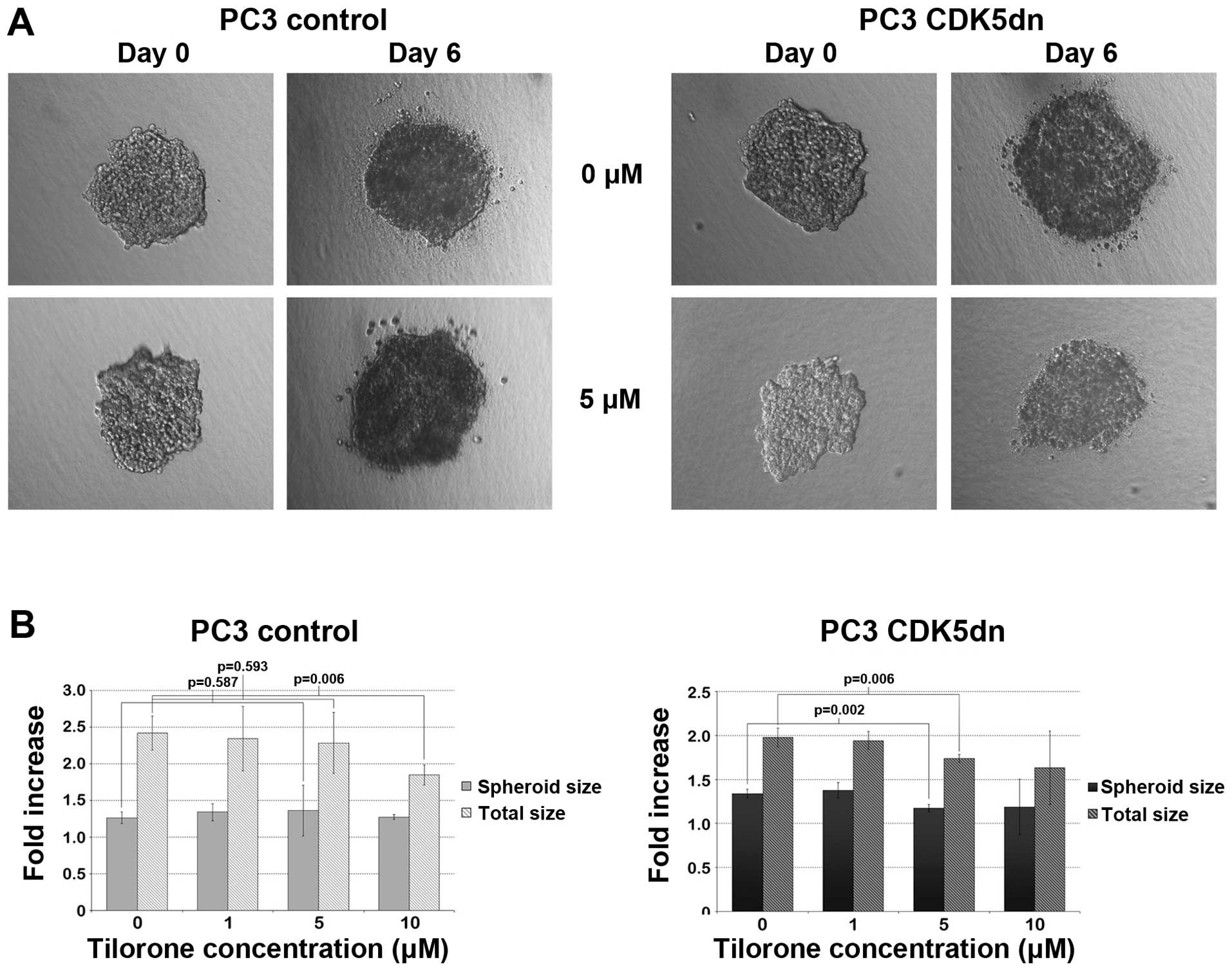
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tarricone C, Dhavan R, Peng J, Areces LB,
Tsai LH and Musacchio A: Structure and regulation of the
CDK5-p25(nck5a) complex. Mol Cell. 8:657–669. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rosales JL and Lee KY: Extraneuronal roles
of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Bioessays. 28:1023–1034. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lalioti V, Pulido D and Sandoval IV: Cdk5,
the multifunctional surveyor. Cell Cycle. 9:284–311. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dhavan R and Tsai LH: A decade of CDK5.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:749–759. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cicero S and Herrup K: Cyclin-dependent
kinase 5 is essential for neuronal cell cycle arrest and
differentiation. J Neurosci. 25:9658–9668. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Strock CJ, Park JI, Nakakura EK, Bova GS,
Isaacs JT, Ball DW and Nelkin BD: Cyclin-dependent kinase 5
activity controls cell motility and metastatic potential of
prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:7509–7515. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feldmann G, Mishra A, Hong SM, et al:
Inhibiting the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK5 blocks pancreatic
cancer formation and progression through the suppression of Ras-Ral
signaling. Cancer Res. 70:7509–7515. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu FN, Chen MC, Chiang MC, et al:
Regulation of androgen receptor and prostate cancer growth by
cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J Biol Chem. 286:33141–33149. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Demelash A, Rudrabhatla P, Pant HC, et al:
Achaete-scute homologue-1 (ASH1) stimulates migration of lung
cancer cells through Cdk5/p35 pathway. Mol Biol Cell. 23:2856–2866.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsu FN, Chen MC, Lin KC, et al:
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 modulates STAT3 and androgen receptor
activation through phosphorylation of Ser727on STAT3 in
prostate cancer cells. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
305:E975–E986. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pozo K, Castro-Rivera E, Tan C, et al: The
role of Cdk5 in neuroendocrine thyroid cancer. Cancer Cell.
24:499–511. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chong CR, Qian DZ, Pan F, Wei Y, Pili R,
Sullivan DJ and Liu JO: Identification of type 1 inosine
monophosphate dehydrogenase as an antiangiogenic drug target. J Med
Chem. 49:2677–2680. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chong CR, Xu J, Lu J, Bhat S, Sullivan DJ
and Liu JO: Inhibition of angiogenesis by the antifungal drug
itraconazole. ACS Chem Biol. 2:263–270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rudin CM, Liu W, Desai A, et al:
Pharmacogenomic and pharmacokinetic determinants of erlotinib
toxicity. J Clin Oncol. 26:1119–1127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang H, Qian DZ, Tan YS, et al: Digoxin
and other cardiac glycosides inhibit HIF-1alpha synthesis and block
tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:19579–19586. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wissing MD, Mendonca J, Kim E, et al:
Identification of cetrimonium bromide and irinotecan as compounds
with synthetic lethality against NDRG1 deficient prostate cancer
cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:401–410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nikolic M, Dudek H, Kwon YT, Ramos YF and
Tsai LH: The cdk5/p35 kinase is essential for neurite outgrowth
during neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev. 10:816–825. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kachhap SK, Rosmus N, Collis SJ, et al:
Downregulation of homologous recombination DNA repair genes by HDAC
inhibition in prostate cancer is mediated through the E2F1
transcription factor. PLoS One. 5:e112082010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O’Meara S, Al-Kurdi D, Ologun Y and
Ovington LG: Antibiotics and antiseptics for venous leg ulcers.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD0035572010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hou SP, Fang AH, Chen QF, Huang YM, Chen
OJ and Cheng LN: Termination of second-trimester pregnancy by
mifepristone combined with misoprostol versus intra-amniotic
injection of ethacridine lactate (Rivanol®): a
systematic review of Chinese trials. Contraception. 84:214–223.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Daull P, Lallemand F and Garrigue JS:
Benefits of cetalkonium chloride cationic oil-in-water
nanoemulsions for topical ophthalmic drug delivery. J Pharm
Pharmacol. May 26–2013.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hume V, Westwood JC and Appleyard G: The
anti-viral action of Rutilantin A. J Gen Microbiol. 38:143–151.
1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krueger RE and Mayer GD: Tilorone
hydrochloride: an orally active antiviral agent. Science.
169:1213–1214. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mayer GD and Krueger RF: Tilorone
hydrochloride: mode of action. Science. 169:1214–1215. 1970.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tazulakhova EB, Parshina OV, Guseva TS and
Ershov FI: Russian experience in screening, analysis, and clinical
application of novel interferon inducers. J Interferon Cytokine
Res. 21:65–73. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Adamson RH: Antitumor activity of tilorone
hydrochloride against some rodent tumors: preliminary report. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 46:431–434. 1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cummings FJ, Gelman R, Skeel RT, Kuperminc
M, Israel L, Colsky J and Tormey D: Phase II trials of Baker’s
antifol, bleomycin, CCNU, streptozotocin, tilorone, and
5-fluorodeoxyuridine plus arabinosyl cytosine in metastatic breast
cancer. Cancer. 48:681–685. 1981.
|
|
29
|
Chong CR and Sullivan DJ: New uses for old
drugs. Nature. 448:645–646. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shim JS, Matsui Y, Bhat S, et al: Effect
of nitroxoline on angiogenesis and growth of human bladder cancer.
J Natl Cancer Inst. 102:1855–1873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shim JS, Rao R, Beebe K, Neckers L, Han I,
Nahta R and Liu JO: Selective inhibition of HER2-positive breast
cancer cells by the HIV protease inhibitor nelfinavir. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 104:1576–1590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang HC, Xing S, Shan L, et al:
Small-molecule screening using a human primary cell model of HIV
latency identifies compounds that reverse latency without cellular
activation. J Clin Invest. 119:3473–3486. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lisianyi MI and Skitiak SA: Use of amiksin
in complex therapy of cerebral gliomas. Lik Sprava. 121–123.
2002.(In Ukranian).
|
|
34
|
Karimova FS, Ivanchenko GF and Grigorian
SS: The treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis with interferon
inducers. Vestn Otorinolaringol. 54–57. 2000.(In Russian).
|
|
35
|
Zhou D, Tuo W, Hu H, et al: Synthesis and
activity evaluation of tilorone analogs as potential anticancer
agents. Eur J Med Chem. 64:432–441. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ratan RR, Siddiq A, Aminova L, et al:
Small molecule activation of adaptive gene expression: tilorone or
its analogs are novel potent activators of hypoxia inducible
factor-1 that provide prophylaxis against stroke and spinal cord
injury. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1147:383–394. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Schrimpf MR, Sippy KB, Briggs CA, et al:
SAR of α7 nicotinic receptor agonists derived from tilorone:
exploration of a novel nicotinic pharmacophore. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 22:1633–1638. 2012.
|