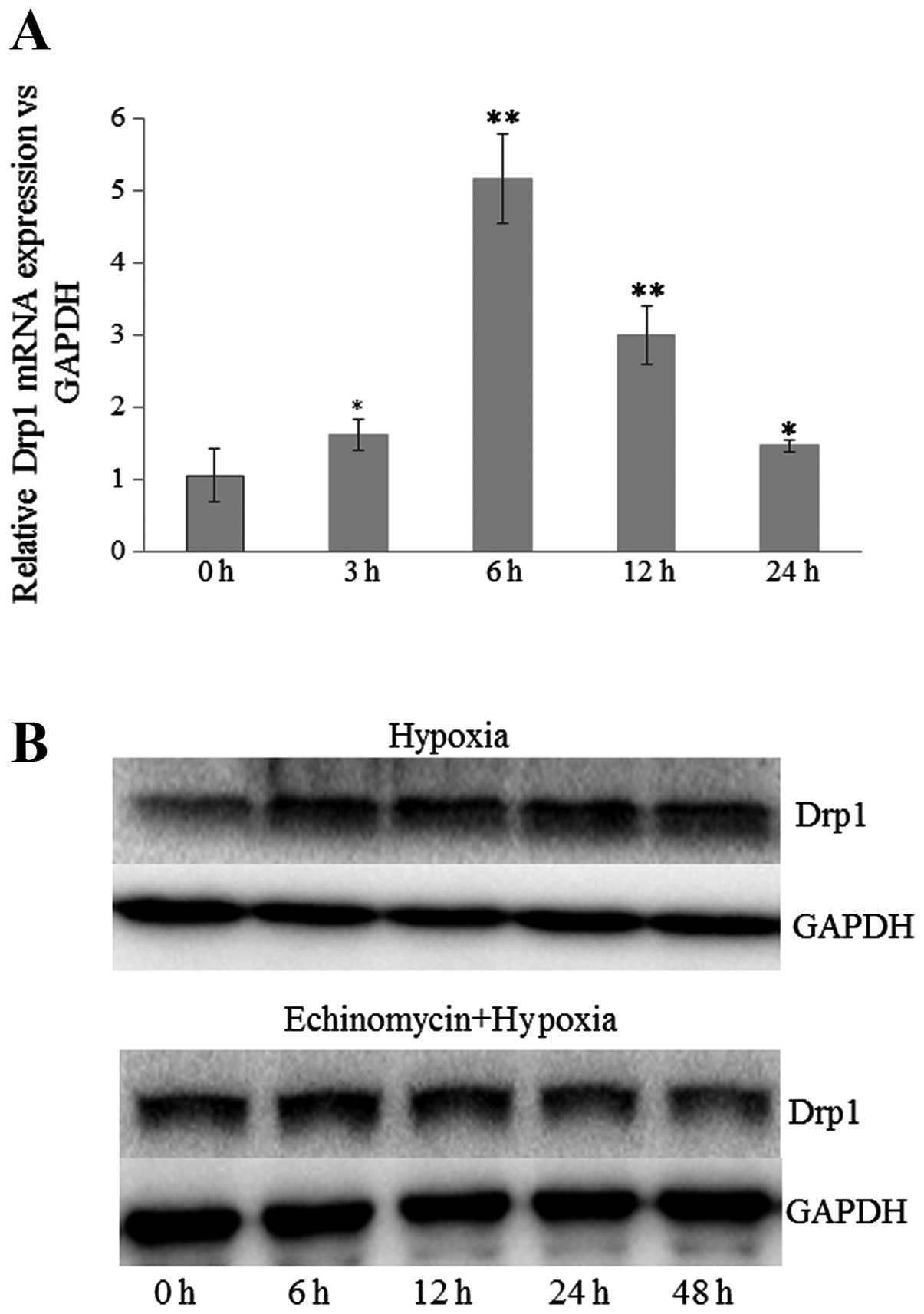
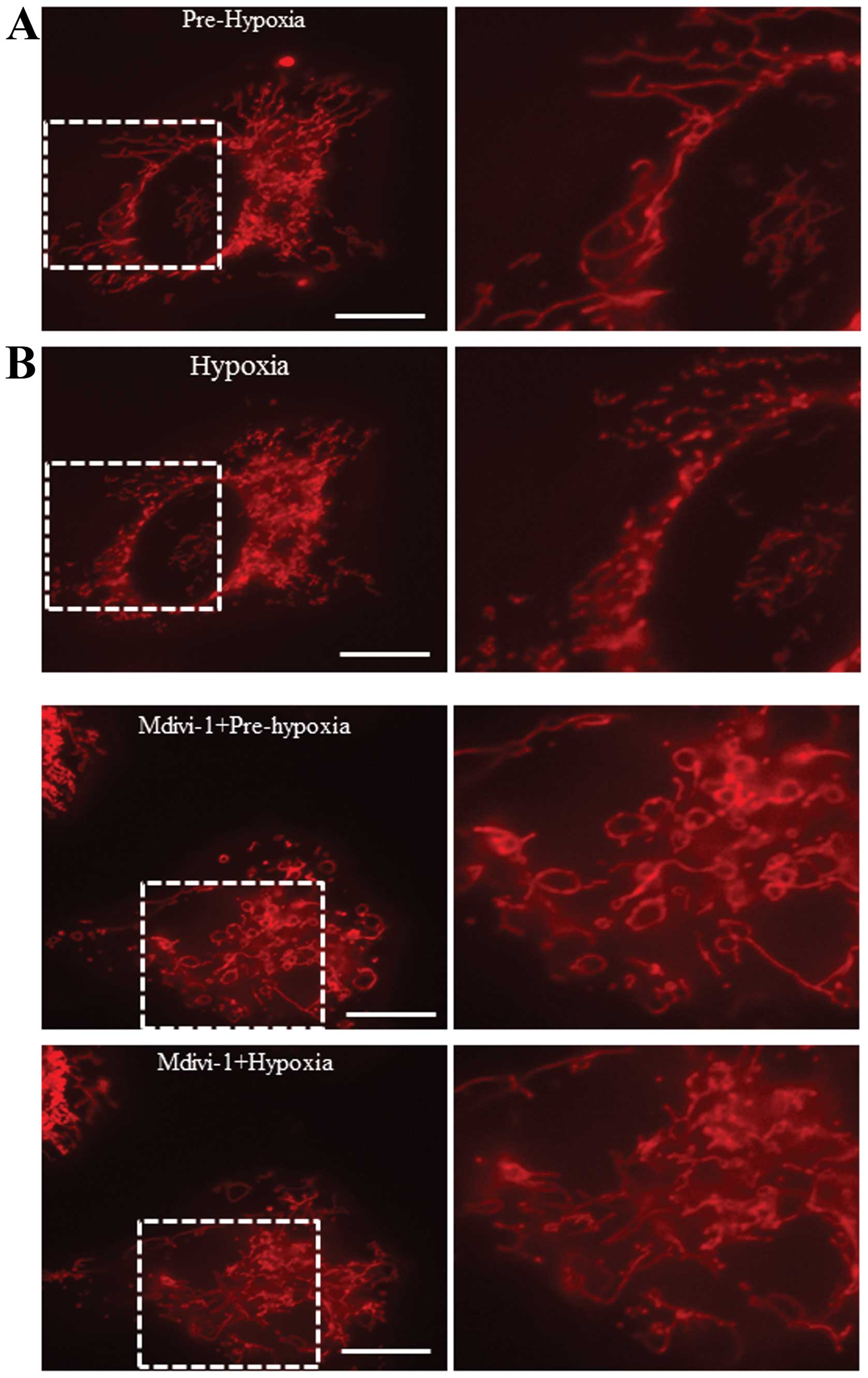
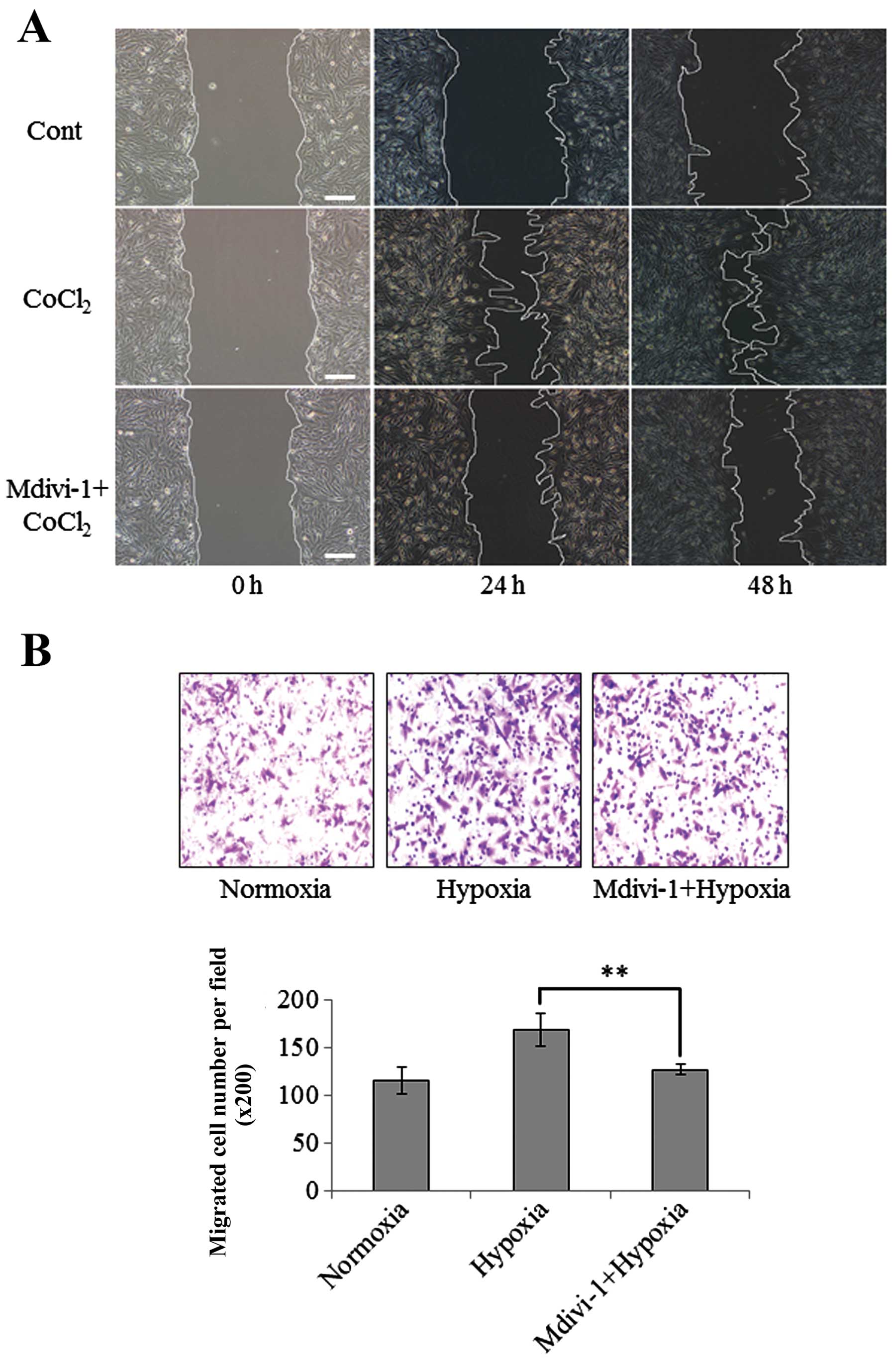
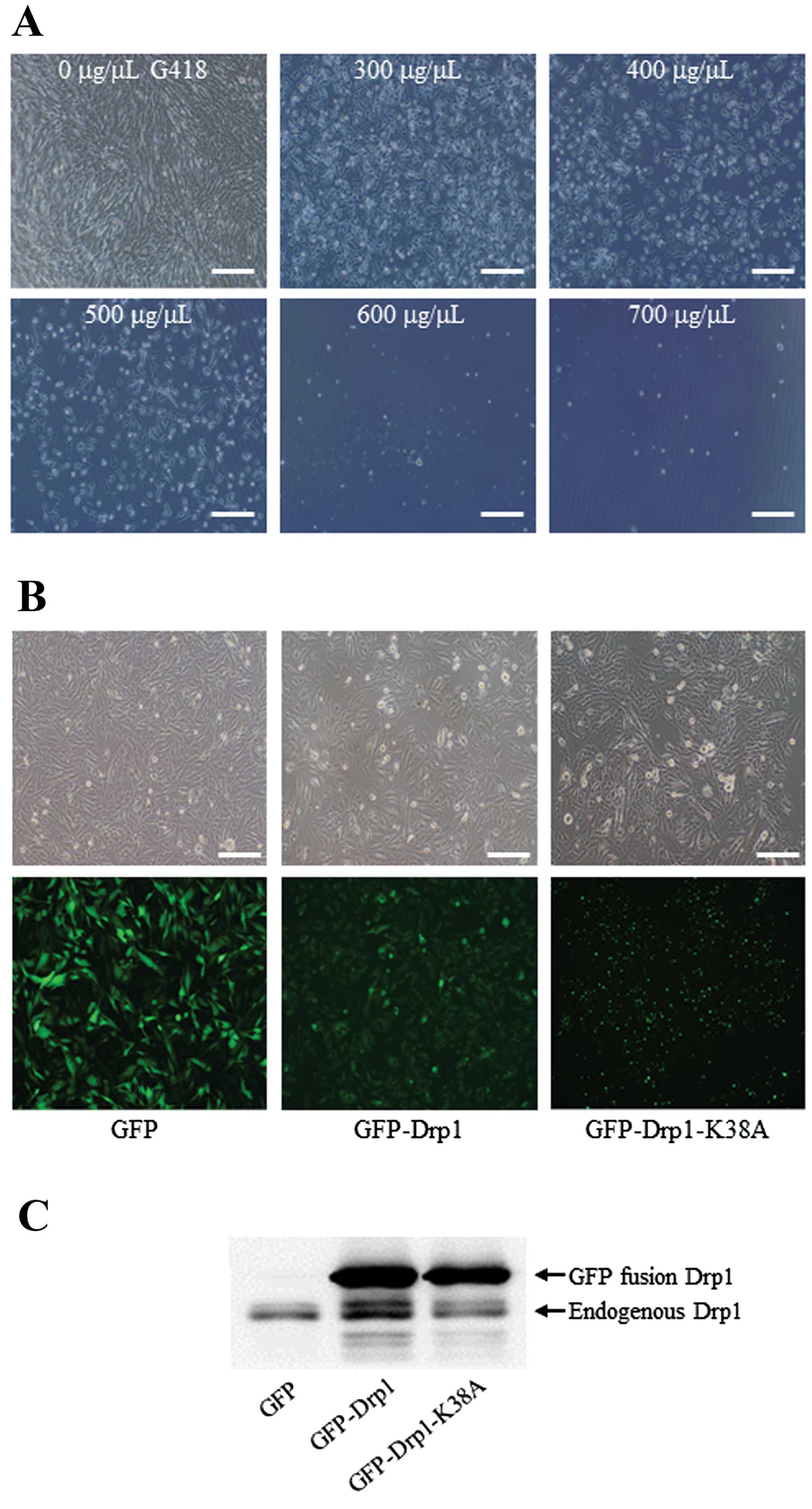
|
1
|
Behin A, Hoang-Xuan K, Carpentier AF and
Delattre JY: Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet. 361:323–331.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Claes A, Idema AJ and Wesseling P: Diffuse
glioma growth: a guerilla war. Acta Neuropathol. 114:443–458. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Anton K, Baehring JM and Mayer T:
Glioblastoma multiforme: overview of current treatment and future
perspectives. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 26:825–853. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chan DA and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia, gene
expression, and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:333–339.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wang F, Ling EA, Liu S,
Wang L, Yang Y, Yao L, Chen X, Wang F, Shi W, Gao M and Hao A:
Melatonin antagonizes hypoxia-mediated glioblastoma cell migration
and invasion via inhibition of HIF-1α. J Pineal Res. 55:121–130.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan DA, Sutphin PD, Yen SE and Giaccia
AJ: Coordinate regulation of the oxygen-dependent degradation
domains of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Mol Cell Biol.
25:6415–6426. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chan DA, Sutphin PD, Denko NC and Giaccia
AJ: Role of prolyl hydroxylation in oncogenically stabilized
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. J Biol Chem. 277:40112–40117.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Krishnamachary B, Berg-Dixon S, Kelly B,
Agani F, Feldser D, Ferreira G, Iyer N, LaRusch J, Pak B, Taghavi P
and Semenza GL: Regulation of colon carcinoma cell invasion by
hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cancer Res. 63:1138–1143.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Muñoz-Nájar UM, Neurath KM, Vumbaca F and
Claffey KP: Hypoxia stimulates breast carcinoma cell invasion
through MT1-MMP and MMP-2 activation. Oncogene. 25:2379–2392.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zagzag D, Zhong H, Scalzitti JM, Laughner
E, Simons JW and Semenza GL: Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor
1α in brain tumors: association with angiogenesis, invasion, and
progression. Cancer. 88:2606–2618. 2000.
|
|
11
|
Oakes SA and Korsmeyer SJ: Untangling the
web: mitochondrial fission and apoptosis. Dev Cell. 7:460–462.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Szabadkai G, Simoni AM, Chami M,
Wieckowski MR, Youle RJ and Rizzuto R: Drp-1-dependent division of
the mitochondrial network blocks intraorganellar Ca2+
waves and protects against Ca2+-mediated apoptosis. Mol
Cell. 16:59–68. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shaw JM and Nunnari J: Mitochondrial
dynamics and division in budding yeast. Trends Cell Biol.
12:178–184. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chan DC: Mitochondrial fusion and fission
in mammals. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:79–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grandemange S, Herzig S and Martinou JC:
Mitochondrial dynamics and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:50–56.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Rehman J, Zhang HJ, Toth PT, Zhang Y,
Marsboom G, Hong Z, Salgia R, Husain AN, Wietholt C and Archer SL:
Inhibition of mitochondrial fission prevents cell cycle progression
in lung cancer. FASEB J. 26:2175–2186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao J, Zhang J, Yu M, Xie Y, Huang Y,
Wolff DW, Abel PW and Tu Y: Mitochondrial dynamics regulates
migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
32:4814–4824. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hagenbuchner J, Kuznetsov AV, Obexer P and
Ausserlechner MJ: BIRC5/Survivin enhances aerobic glycolysis and
drug resistance by altered regulation of the mitochondrial
fusion/fission machinery. Oncogene. 32:4748–4757. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qian W, Choi S, Gibson GA, Watkins SC,
Bakkenist CJ and Van Houten B: Mitochondrial hyperfusion induced by
loss of the fission protein Drp1 causes ATM-dependent G2/M arrest
and aneuploidy through DNA replication stress. J Cell Sci.
125:5745–5757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Inoue-Yamauchi A and Oda H: Depletion of
mitochondrial fission factor DRP1 causes increased apoptosis in
human colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:81–85.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Parone PA, Da Cruz S, Tondera D,
Mattenberger Y, James DI, Maechler P, Barja F and Martinou JC:
Preventing mitochondrial fission impairs mitochondrial function and
leads to loss of mitochondrial DNA. PLoS One. 3:e32572008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu D, Wu J, Xu L, Zhang R and Chen L: A
method for the establishment of a cell line with stable expression
of the GFP-LC3 reporter protein. Mol Med Rep. 6:783–786.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marsboom G, Toth PT, Ryan JJ, et al:
Dynamin-related protein 1-mediated mitochondrial mitotic fission
permits hyperproliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and
offers a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary hypertension. Circ
Res. 110:1484–1497. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang GL and Semenza GL: Desferrioxamine
induces erythropoietin gene expression and hypoxia-inducible factor
1 DNA-binding activity: implications for models of hypoxia signal
transduction. Blood. 82:3610–3615. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cassidy-Stone A, Chipuk JE, Ingerman E,
Song C, Yoo C, Kuwana T, Kurth MJ, Shaw JT, Hinshaw JE, Green DR
and Nunnari J: Chemical inhibition of the mitochondrial division
dynamin reveals its role in Bax/Bak-dependent mitochondrial outer
membrane permeabilization. Dev Cell. 14:193–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lackner LL and Nunnari J: Small molecule
inhibitors of mitochondrial division: tools that translate basic
biological research into medicine. Chem Biol. 17:578–583. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Qian W, Wang J and Van Houten B: The role
of dynamin-related protein 1 in cancer growth: a promising
therapeutic target? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 17:997–1001. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kushnareva Y, Andreyev AY, Kuwana T and
Newmeyer DD: Bax activation initiates the assembly of a multimeric
catalyst that facilitates Bax pore formation in mitochondrial outer
membranes. PLoS Biol. 10:e10013942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pitts KR, Yoon Y, Krueger EW and McNiven
MA: The dynamin-like protein DLP1 is essential for normal
distribution and morphology of the endoplasmic reticulum and
mitochondria in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Cell. 10:4403–4417. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ong SB, Subrayan S, Lim SY, Yellon DM,
Davidson SM and Hausenloy DJ: Inhibiting mitochondrial fission
protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Circulation. 121:2012–2022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Taguchi N, Ishihara N, Jofuku A, Oka T and
Mihara K: Mitotic phosphorylation of dynamin-related GTPase Drp1
participates in mitochondrial fission. J Biol Chem.
282:11521–11529. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han XJ, Lu YF, Li SA, Kaitsuka T, Sato Y,
Tomizawa K, Nairn AC, Takei K, Matsui H and Matsushita M: CaM
kinase Iα-induced phosphorylation of Drp1 regulates mitochondrial
morphology. J Cell Biol. 182:573–585. 2008.
|
|
33
|
Cho DH, Nakamura T, Fang J, Cieplak P,
Godzik A, Gu Z and Lipton SA: S-nitrosylation of Drp1 mediates
β-amyloid-related mitochondrial fission and neuronal injury.
Science. 324:102–105. 2009.
|
|
34
|
Wang H, Song P, Du L, Tian W, Yue W, Liu
M, Li D, Wang B, Zhu Y, Cao C, Zhou J and Chen Q: Parkin
ubiquitinates Drp1 for proteasome-dependent degradation:
implication of dysregulated mitochondrial dynamics in Parkinson
disease. J Biol Chem. 286:11649–11658. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Harder Z, Zunino R and McBride H: Sumo1
conjugates mitochondrial substrates and participates in
mitochondrial fission. Curr Biol. 14:340–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Piret JP, Mottet D, Raes M and Michiels C:
CoCl2, a chemical inducer of hypoxia-inducible factor-1,
and hypoxia reduce apoptotic cell death in hepatoma cell line
HepG2. Ann NY Acad Sci. 973:443–447. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma J, Zhang Q, Chen S, Fang B, Yang Q,
Chen C, Miele L, Sarkar FH, Xia J and Wang Z: Mitochondrial
dysfunction promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion
through HIF1α accumulation via increased production of reactive
oxygen species. PLoS One. 8:e694852013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tochhawng L, Deng S, Pervaiz S and Yap CT:
Redox regulation of cancer cell migration and invasion.
Mitochondrion. 13:246–253. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chiche J, Rouleau M, Gounon P, et al:
Hypoxic enlarged mitochondria protect cancer cells from apoptotic
stimuli. J Cell Physiol. 222:648–657. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|