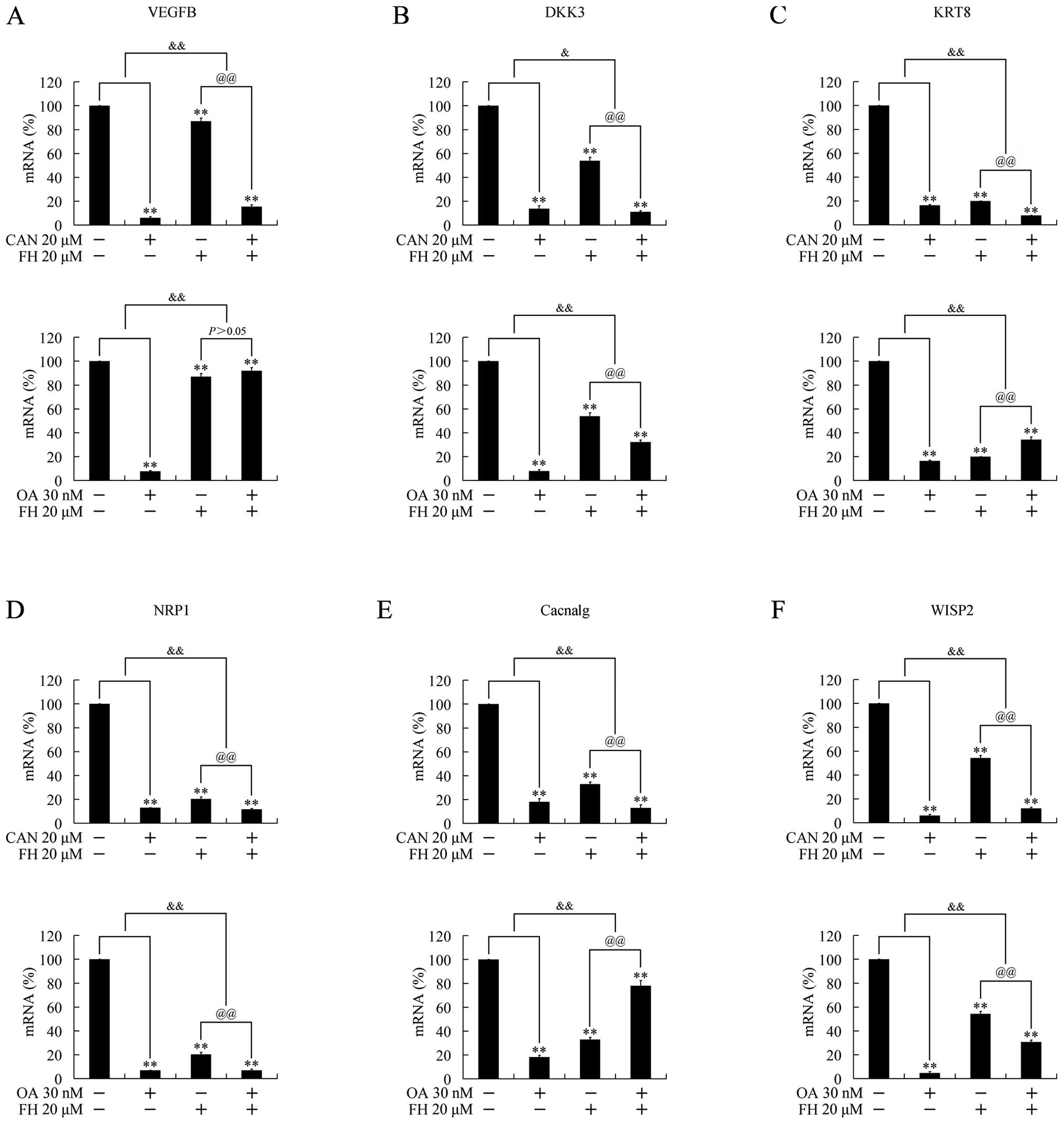
|
1
|
Wolfgang CL, Herman JM, Laheru DA, et al:
Recent progress in pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:318–348.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Paulson AS, Tran Cao HS, Tempero MA and
Lowy AM: Therapeutic advances in pancreatic cancer.
Gastroenterology. 144:1316–1326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li W, Xie L, Chen Z, et al: Cantharidin, a
potent and selective PP2A inhibitor, induces an oxidative
stress-independent growth inhibition of pancreatic cancer cells
through G2/M cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Sci.
101:1226–1233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li W, Chen Z, Zong Y, et al: PP2A
inhibitors induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1
through persistent phosphorylation of IKKα and sustained activation
of the NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett. 304:117–127. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li W, Chen Z, Gong FR, et al: Growth of
the pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1 is inhibited by protein
phosphatase 2A inhibitors through overactivation of the c-Jun
N-terminal kinase pathway. Eur J Cancer. 47:2654–2664. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shou LM, Zhang QY, Li W, et al:
Cantharidin and norcantharidin inhibit the ability of MCF-7 cells
to adhere to platelets via protein kinase C pathway-dependent
downregulation of α2 integrin. Oncol Rep. 30:1059–1066.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fearon ER: PARsing the phrase ‘all in for
Axin’-Wnt pathway targets in cancer. Cancer Cell. 16:366–368.
2009.
|
|
11
|
White BD, Chien AJ and Dawson DW:
Dysregulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in gastrointestinal
cancers. Gastroenterology. 142:219–232. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Bos CL, Kodach LL, van den Brink GR, et
al: Effect of aspirin on the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is mediated via
protein phosphatase 2A. Oncogene. 25:6447–6456. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna
JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated
colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer
Res. 47:936–942. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang C, Jacobson K and Schaller MD: MAP
kinases and cell migration. J Cell Sci. 117:4619–4628. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Handeli S and Simon JA: A small-molecule
inhibitor of Tcf/beta-catenin signaling down-regulates PPARgamma
and PPARdelta activities. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:521–529. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Burkadze G and
Kolar Z: Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and
carcinogenesis. Pathobiology. 73:213–223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamaguchi TP: Heads or tails: Wnts and
anterior-posterior patterning. Curr Biol. 11:R713–R724. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes
Dev. 14:1837–1851. 2000.
|
|
21
|
Takahashi-Yanaga F and Sasaguri T:
GSK-3beta regulates cyclin D1 expression: a new target for
chemotherapy. Cell Signal. 20:581–589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Papadopoulou S and Edlund H: Attenuated
Wnt signaling perturbs pancreatic growth but not pancreatic
function. Diabetes. 54:2844–2851. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zeng G, Germinaro M, Micsenyi A, et al:
Aberrant Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Neoplasia. 8:279–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chetty R, Serra S, Salahshor S, et al:
Expression of Wnt-signaling pathway proteins in intraductal
papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: a tissue microarray
analysis. Hum Pathol. 37:212–217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pasca di Magliano M, Biankin AV, Heiser
PW, et al: Common activation of canonical Wnt signaling in
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PloS One. 2:e11552007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang L, Heidt DG, Lee CJ, et al: Oncogenic
function of ATDC in pancreatic cancer through Wnt pathway
activation and beta-catenin stabilization. Cancer Cell. 15:207–219.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lowy AM, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Kim OJ, et
al: Dysregulation of beta-catenin expression correlates with tumor
differentiation in pancreatic duct adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
10:284–290. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Joo YE, Rew JS, Park CS and Kim SJ:
Expression of E-cadherin, alpha- and beta-catenins in patients with
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology. 2:129–137. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karayiannakis AJ, Syrigos KN,
Polychronidis A and Simopoulos C: Expression patterns of alpha-,
beta- and gamma-catenin in pancreatic cancer: correlation with
E-cadherin expression, pathological features and prognosis.
Anticancer Res. 21:4127–4134. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li YJ, Wei ZM, Meng YX and Ji XR:
Beta-catenin up-regulates the expression of cyclinD1, c-myc and
MMP-7 in human pancreatic cancer: relationships with carcinogenesis
and metastasis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:2117–2123. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qiao Q, Ramadani M, Gansauge S, Gansauge
F, Leder G and Beger HG: Reduced membranous and ectopic cytoplasmic
expression of beta -catenin correlate with cyclin D1 overexpression
and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 95:194–197.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Heiser PW, Cano DA, Landsman L, et al:
Stabilization of beta-catenin induces pancreas tumor formation.
Gastroenterology. 135:1288–1300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seeling JM, Miller JR, Gil R, Moon RT,
White R and Virshup DM: Regulation of beta-catenin signaling by the
B56 subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Science. 283:2089–2091.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li X, Yost HJ, Virshup DM and Seeling JM:
Protein phosphatase 2A and its B56 regulatory subunit inhibit Wnt
signaling in Xenopus. EMBO J. 20:4122–4131. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wey JS, Fan F, Gray MJ, et al: Vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1 promotes migration and
invasion in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer. 104:427–438.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bielenberg DR, Pettaway CA, Takashima S
and Klagsbrun M: Neuropilins in neoplasms: expression, regulation,
and function. Exp Cell Res. 312:584–593. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Frankel P, Pellet-Many C, Lehtolainen P,
et al: Chondroitin sulphate-modified neuropilin 1 is expressed in
human tumour cells and modulates 3D invasion in the U87MG human
glioblastoma cell line through a p130Cas-mediated pathway. EMBO
Rep. 9:983–989. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miao HQ, Lee P, Lin H, Soker S and
Klagsbrun M: Neuropilin-1 expression by tumor cells promotes tumor
angiogenesis and progression. FASEB J. 14:2532–2539. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wey JS, Gray MJ, Fan F, et al:
Overexpression of neuropilin-1 promotes constitutive MAPK
signalling and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 93:233–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Latil A, Bieche I, Pesche S, et al: VEGF
overexpression in clinically localized prostate tumors and
neuropilin-1 overexpression in metastatic forms. Int J Cancer.
89:167–171. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hansel DE, Wilentz RE, Yeo CJ, Schulick
RD, Montgomery E and Maitra A: Expression of neuropilin-1 in
high-grade dysplasia, invasive cancer, and metastases of the human
gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 28:347–356. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ochiumi T, Kitadai Y, Tanaka S, Akagi M,
Yoshihara M and Chayama K: Neuropilin-1 is involved in regulation
of apoptosis and migration of human colon cancer. Int J Oncol.
29:105–116. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zenzmaier C, Hermann M, Hengster P and
Berger P: Dickkopf-3 maintains the PANC-1 human pancreatic tumor
cells in a dedifferentiated state. Int J Oncol. 40:40–46.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fortier AM, Asselin E and Cadrin M:
Keratin 8 and 18 loss in epithelial cancer cells increases
collective cell migration and cisplatin sensitivity through
claudin1 up-regulation. J Biol Chem. 288:11555–11571. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Toyota M, Ho C, Ohe-Toyota M, Baylin SB
and Issa JP: Inactivation of CACNA1G, a T-type calcium channel
gene, by aberrant methylation of its 5′ CpG island in human tumors.
Cancer Res. 59:4535–4541. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lory P, Bidaud I and Chemin J: T-type
calcium channels in differentiation and proliferation. Cell
Calcium. 40:135–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Panner A and Wurster RD: T-type calcium
channels and tumor proliferation. Cell calcium. 40:253–259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Taylor JT, Huang L, Pottle JE, et al:
Selective blockade of T-type Ca2+channels suppresses
human breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett. 267:116–124.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Jiang D, et al:
Inhibition of T-type Ca2+channels by endostatin
attenuates human glioblastoma cell proliferation and migration. Br
J Pharmacol. 166:1247–1260. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brigstock DR: The CCN family: a new
stimulus package. J Endocrinol. 178:169–175. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Davies SR, Davies ML, Sanders A, Parr C,
Torkington J and Jiang WG: Differential expression of the CCN
family member WISP-1, WISP-2 and WISP-3 in human colorectal cancer
and the prognostic implications. Int J Oncol. 36:1129–1136.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Aikawa T, Gunn J, Spong SM, Klaus SJ and
Korc M: Connective tissue growth factor-specific antibody
attenuates tumor growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis in an
orthotopic mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther.
5:1108–1116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Millward TA, Zolnierowicz S and Hemmings
BA: Regulation of protein kinase cascades by protein phosphatase
2A. Trends Biochem Sci. 24:186–191. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Janssens V, Goris J and Van Hoof C: PP2A:
the expected tumor suppressor. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:34–41. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|