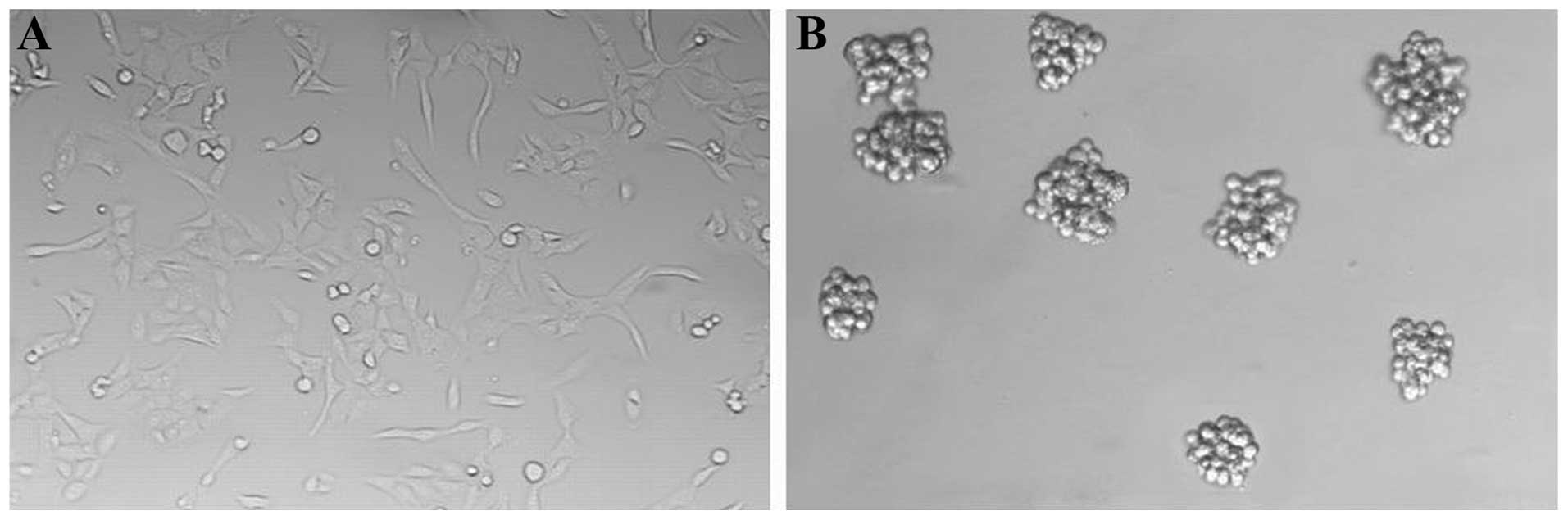
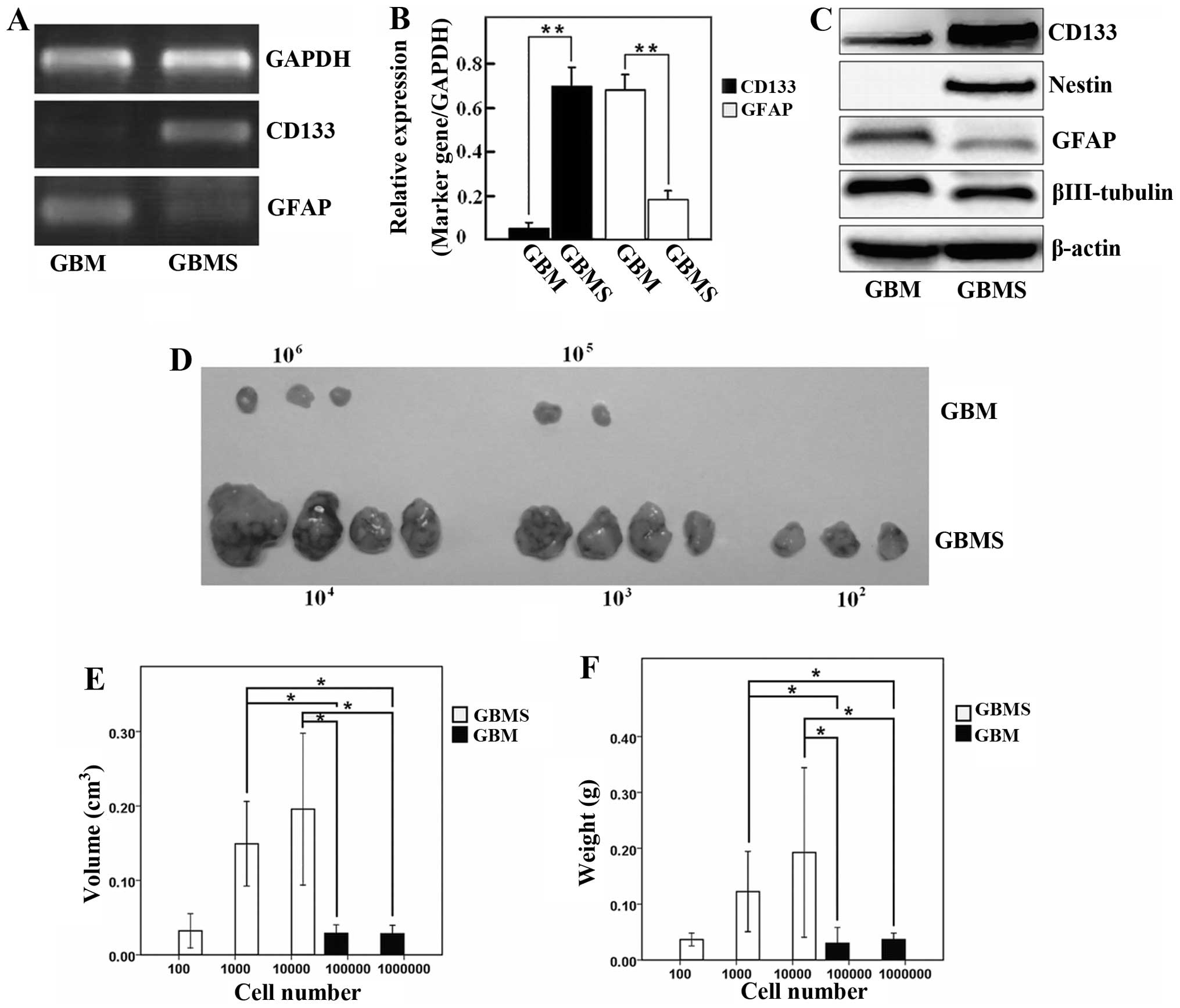
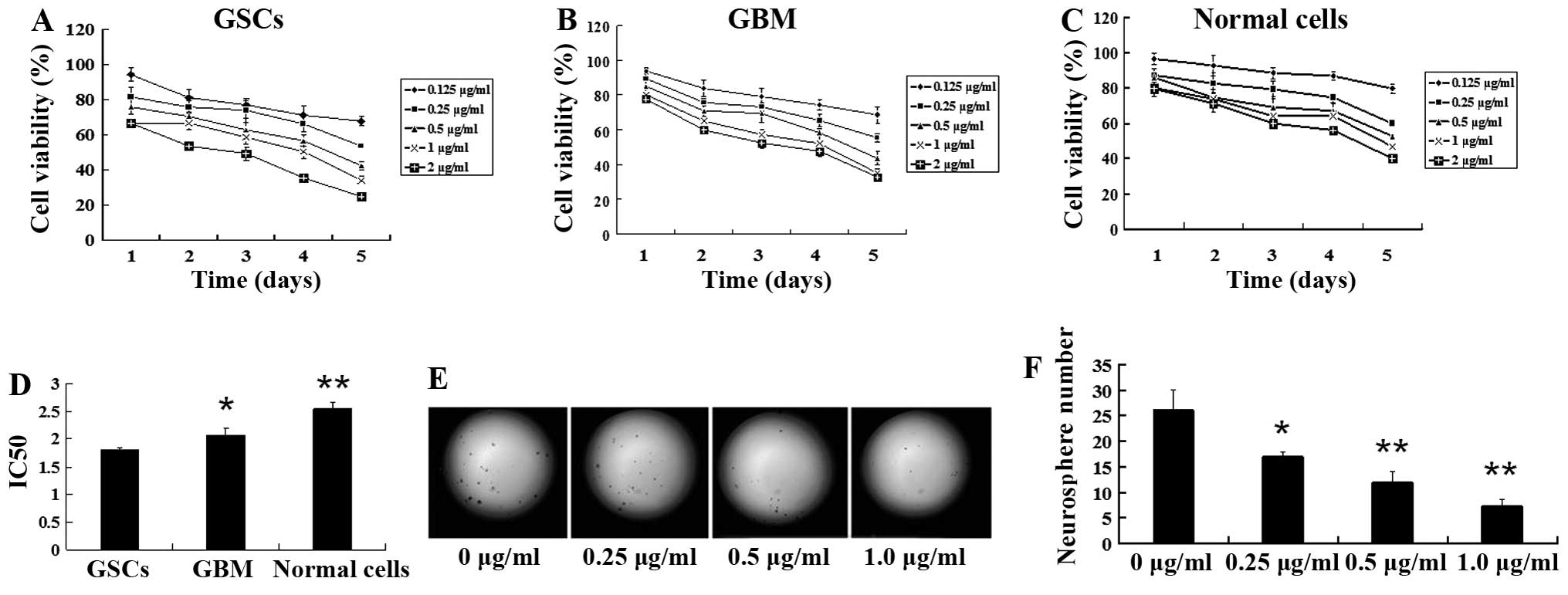
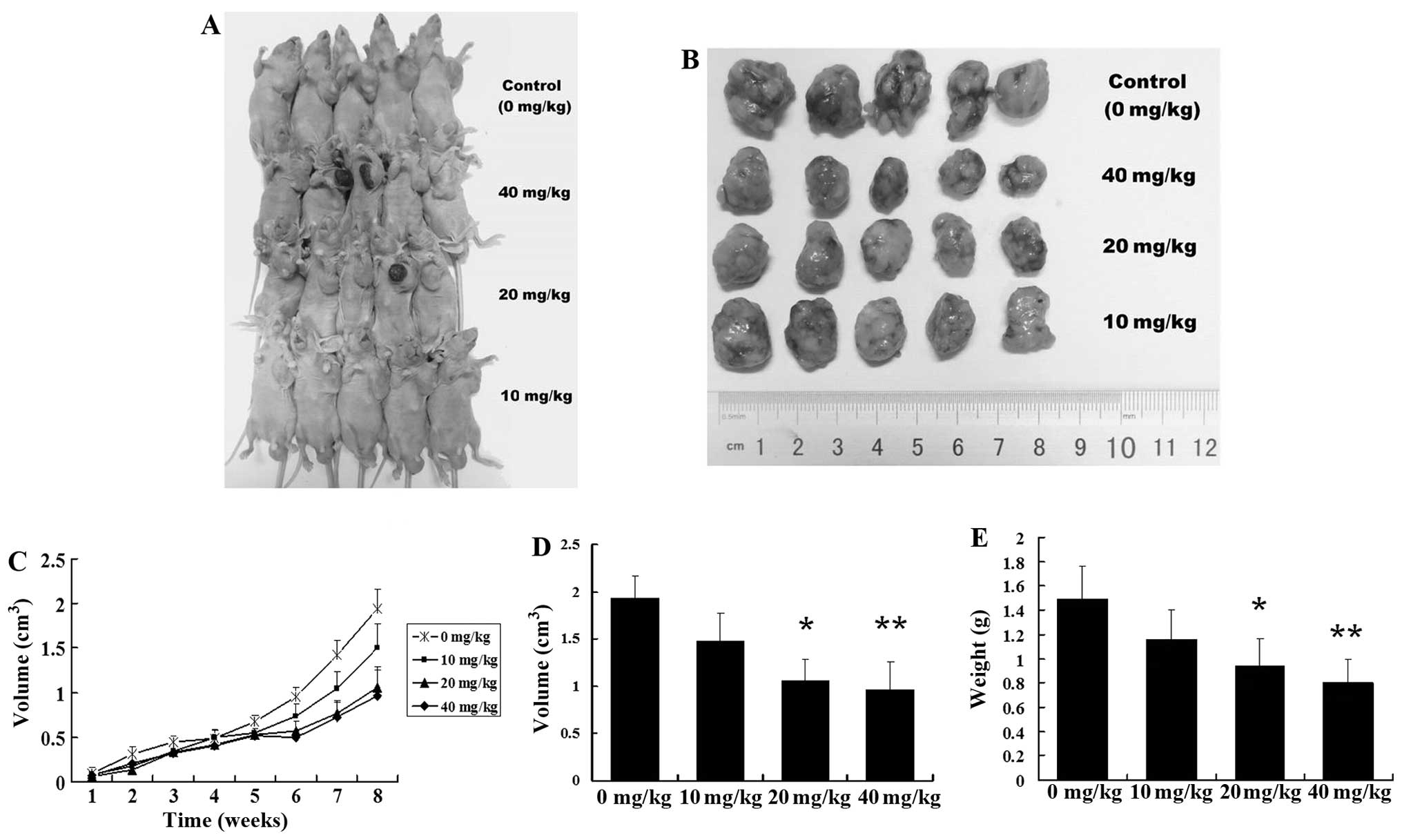
|
1
|
Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer B, O’Fallon J
and Kelly P: Grading of astrocytomas, a simple and reproducible
method. Cancer. 62:2152–2165. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith JS and Jenkins RB: Genetic
alterations in adult diffuse glioma: occurrence, significance, and
prognostic implications. Front Biosci. 5:D213–D231. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang L, Liu Z, Balivada S, Shrestha T,
Bossmann S, Pyle M, Pappan L, Shi J and Troyer D: Interleukin-1β
and transforming growth factor-β cooperate to induce neurosphere
formation and increase tumorigenicity of adherent LN-229 glioma
cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 3:52012.
|
|
4
|
Jordan CT: Cancer stem cells:
controversial or just misunderstood? Cell Stem Cell. 4:203–205.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ignatova TN, Kukekov VG, Laywell ED,
Suslov ON, Vrionis FD and Steindler DA: Human cortical glial tumors
contain neural stem-like cells expressing astroglial and neuronal
markers in vitro. Glia. 39:193–206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, Squire JA,
Bayani J, Hide T, Henkelman RM, Cusimano MD and Dirks PB:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, Cipelletti
B, Gritti A, De Vitis S, Fiocco R, Foroni C, Dimeco F and Vescovi
A: Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural
precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 64:7011–7021. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q,
Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Glioma stem
cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA
damage response. Nature. 444:756–760. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bao S, Wu Q, Sathornsumetee S, Hao Y, Li
Z, Hjelmeland AB, Shi Q, McLendon RE, Bigner DD and Rich JN: Stem
cell-like glioma cells promote tumor angiogenesis through vascular
endothelial growth factor. Cancer Res. 66:7843–7848. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eramo A, Ricci-Vitiani L, Zeuner A,
Pallini R, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E, Larocca LM, Peschle C and
De Maria R: Chemotherapy resistance of glioblastoma stem cells.
Cell Death Differ. 13:1238–1241. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rich JN: Cancer stem cells in radiation
resistance. Cancer Res. 67:8980–8984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H,
Abdulkadir IR, Lu L, Irvin D, Black KL and Yu JS: Analysis of gene
expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem
cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Hide T and Dirks PB:
Cancer stem cells in nervous system tumors. Oncogene. 23:7267–7273.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin X, Yin Y, Cao FL, Chen YF, Peng Y, Hou
WG, Sun SK and Luo ZJ: Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory
response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in
adult rats. PLoS One. 7:e383812012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dai ZK, Qin JK, Huang JE, Luo Y, Xu Q and
Zhao HL: Tanshinone IIA activates calcium-dependent apoptosis
signaling pathway in human hepatoma cells. J Nat Med. 66:192–201.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chiu TL and Su CC: Tanshinone IIA induces
apoptosis in human lung cancer A549 cells through the induction of
reactive oxygen species and decreasing the mitochondrial membrane
potential. Int J Mol Med. 25:231–236. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren ZH, Tong YH, Xu W, Ma J and Chen Y:
Tanshinone IIA attenuates inflammatory responses of rats with
myocardial infarction by reducing MCP-1 expression. Phytomedicine.
17:212–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fan GW, Gao XM, Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Hu
LM, Su YF, Kang LY and Zhang BL: The anti-inflammatory activities
of tanshinone IIA, an active component of TCM, are mediated by
estrogen receptor activation and inhibition of iNOS. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 113:275–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen W, Tang F, Xie B, Chen S, Huang H and
Liu P: Amelioration of atherosclerosis by tanshinone IIA in
hyperlipidemic rabbits through attenuation of oxidative stress. Eur
J Pharmacol. 674:359–364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Wei Y, Yuan S, Liu G, Lu Y, Zhang
J and Wang W: Potential anticancer activity of tanshinone IIA
against human breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 116:799–807. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Su CC and Lin YH: Tanshinone IIA inhibits
human breast cancer cells through increased Bax to Bcl-xL ratios.
Int J Mol Med. 22:357–361. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Wang G and Struhl
K: Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their
dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:1397–1402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Korkaya H, Liu S and Wicha MS: Regulation
of cancer stem cells by cytokine networks: attacking cancer’s
inflammatory roots. Clin Cancer Res. 17:6125–6129. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jang SI, Jeong SI, Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Yu HH,
Park R, Kim HM and You YO: Tanshinone IIA from Salvia
miltiorrhiza inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase
expression and production of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL6 in
activated RAW 264.7 cells. Planta Med. 69:1057–1059.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Wang X, Jiang S, Lin P, Zhang J,
Wu Y, Xiong Z, Ren JJ and Yang H: Establishment of a new human
glioblastoma multiforme cell line (WJ1) and its partial
characterization. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 27:831–843. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee J, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Li A, Su
Q, Donin NM, Pastorino S, Purow BW, Christopher N, Zhang W, Park JK
and Fine HA: Tumor stem cells derived from glioblastomas cultured
in bFGF and EGF more closely mirror the phenotype and genotype of
primary tumors than do serum-cultured cell lines. Cancer Cell.
9:391–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J:
Cell sensitivity assays: the MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol.
731:237–245. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim MJ, Kim YJ, Park HJ, Chung JH, Leem KH
and Kim HK: Apoptotic effect of red wine polyphenols on human colon
cancer SNU-C4 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 44:898–902. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yuan X, Curtin J, Xiong Y, Liu G,
Waschsmann-Hogiu S, Farkas DL, Black KL and Yu JS: Isolation of
cancer stem cells from adult glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene.
23:9392–9400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kapoor S: Tanshinone IIA: a potent,
natural anti-carcinogenic agent for the management of systemic
malignancies. Chin J Integr Med. 15:1532009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma H, Fan Q, Yu J, Xin J and Zhang C:
Novel microemulsion of tanshinone IIA, isolated from Salvia
miltiorrhiza Bunge, exerts anticancer activity through inducing
apoptosis in hepatoma cells. Am J Chin Med. 41:197–210.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friedman MD, Jeevan DS, Tobias M, Murali R
and Jhanwar-Uniyal M: Targeting cancer stem cells in glioblastoma
multiforme using mTOR inhibitors and the differentiating agent
all-trans retinoic acid. Oncol Rep. 30:1645–1850.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jin X, Kim SH, Jeon HM, Beck S, Sohn YW,
Yin J, Kim JK, Lim YC, Lee JH, Kim SH, Kang SH, Pian X, Song MS,
Park JB, Chae YS, Chung YG, Lee SH, Choi YJ, Nam DH, Choi YK and
Kim H: Interferon regulatory factor 7 regulates glioma stem cells
via interleukin-6 and Notch signalling. Brain. 135:1055–1069. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang H, Lathia JD, Wu Q, Wang J, Li Z,
Heddleston JM, Eyler CE, Elderbroom J, Gallagher J, Schuschu J,
MacSwords J, Cao Y, McLendon RE, Wang XF, Hjelmeland AB and Rich
JN: Targeting interleukin 6 signaling suppresses glioma stem cell
survival and tumor growth. Stem Cells. 27:2393–2404. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guryanova OA, Wu Q, Cheng L, Lathia JD,
Huang Z, Yang J, MacSwords J, Eyler CE, McLendon RE, Heddleston JM,
Shou W, Hambardzumyan D, Lee J, Hjelmeland AB, Sloan AE, Bredel M,
Stark GR, Rich JN and Bao S: Nonreceptor tyrosine kinase BMX
maintains self-renewal and tumorigenic potential of glioblastoma
stem cells by activating STAT3. Cancer Cell. 19:498–511. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bromberg J and Darnell JE Jr: The role of
STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular
function. Oncogene. 19:2468–2473. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schindler C, Levy DE and Decker T:
JAK-STAT signaling: from interferons to cytokines. J Biol Chem.
282:20059–20063. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|