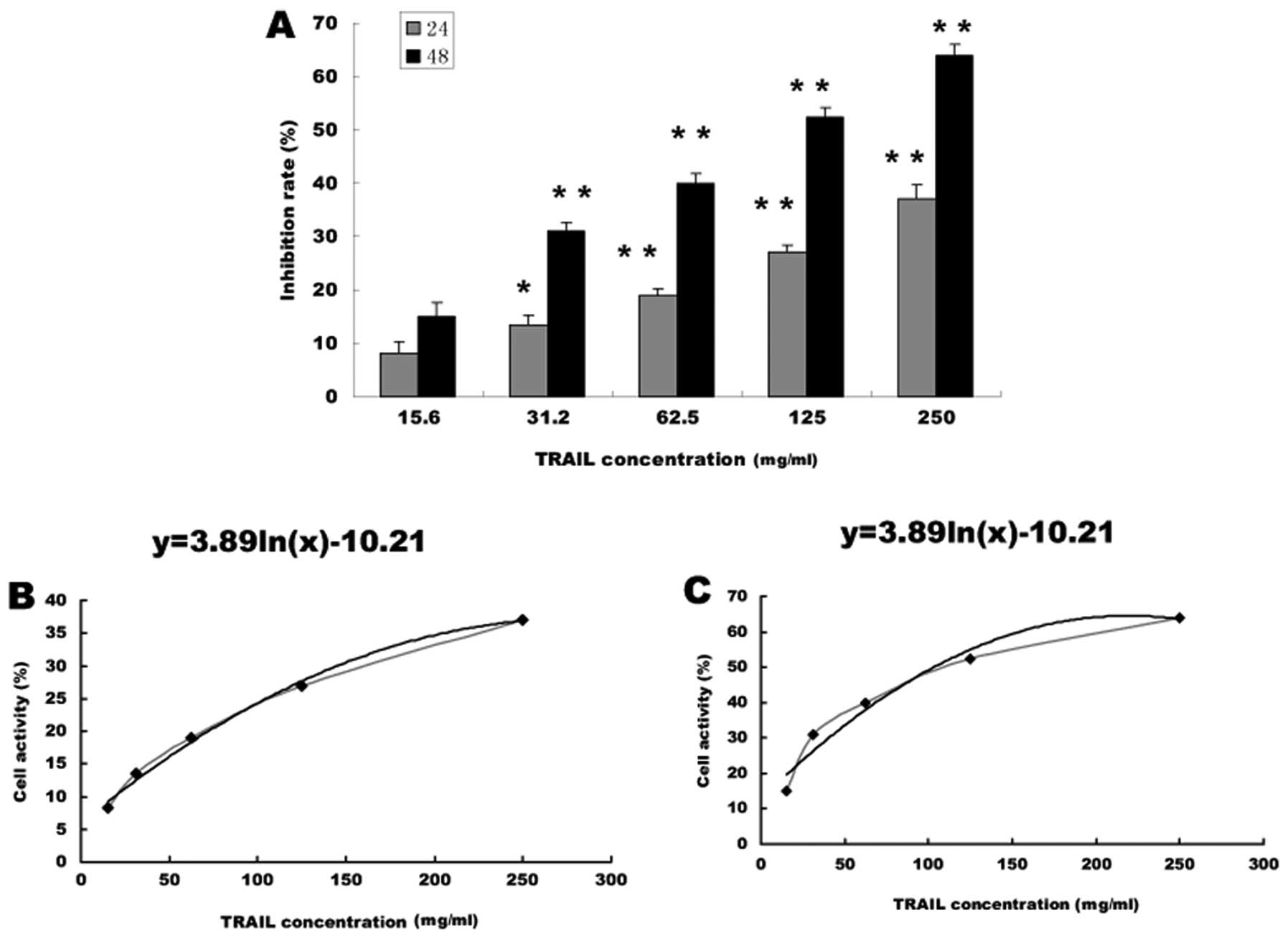
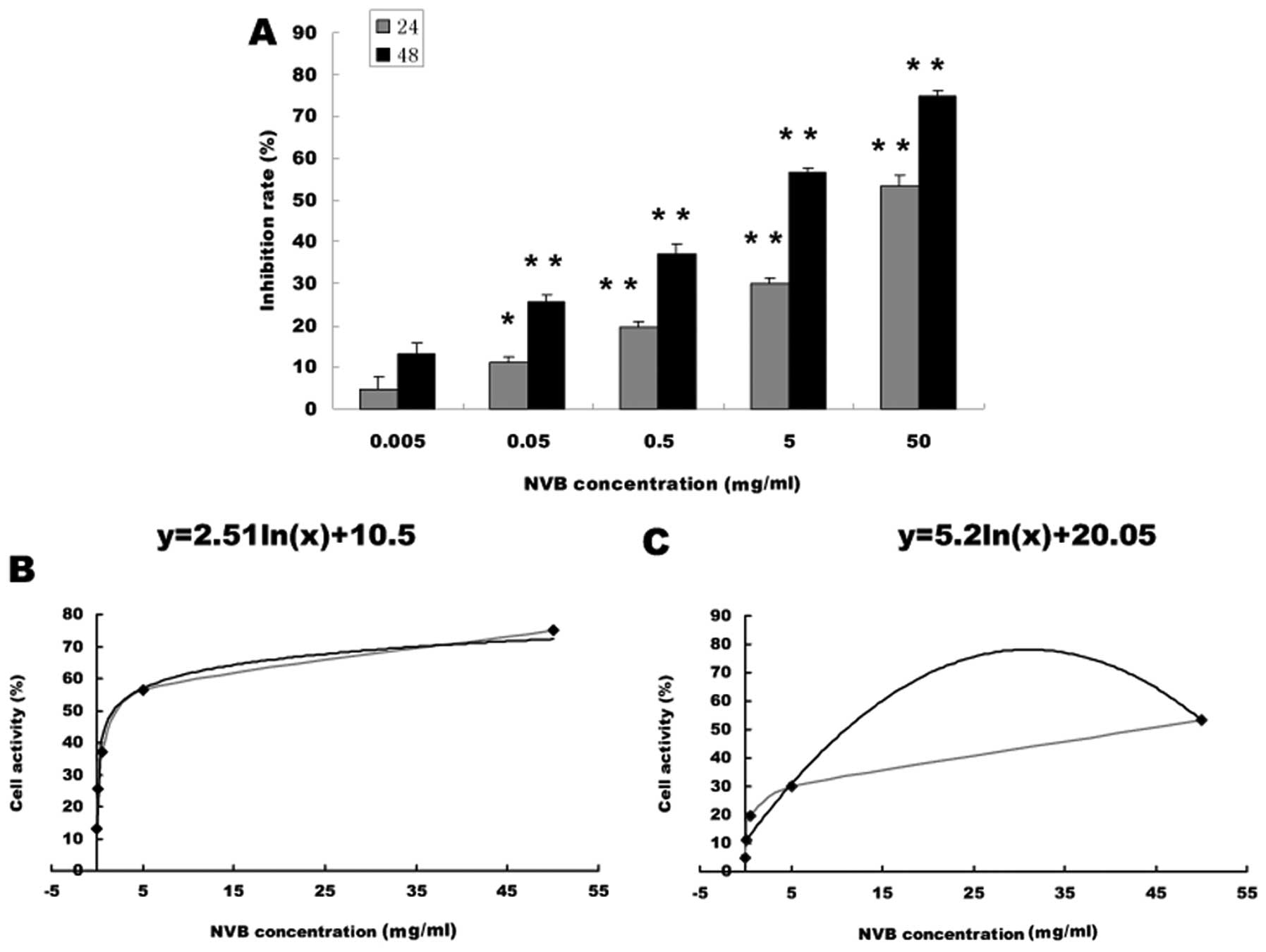
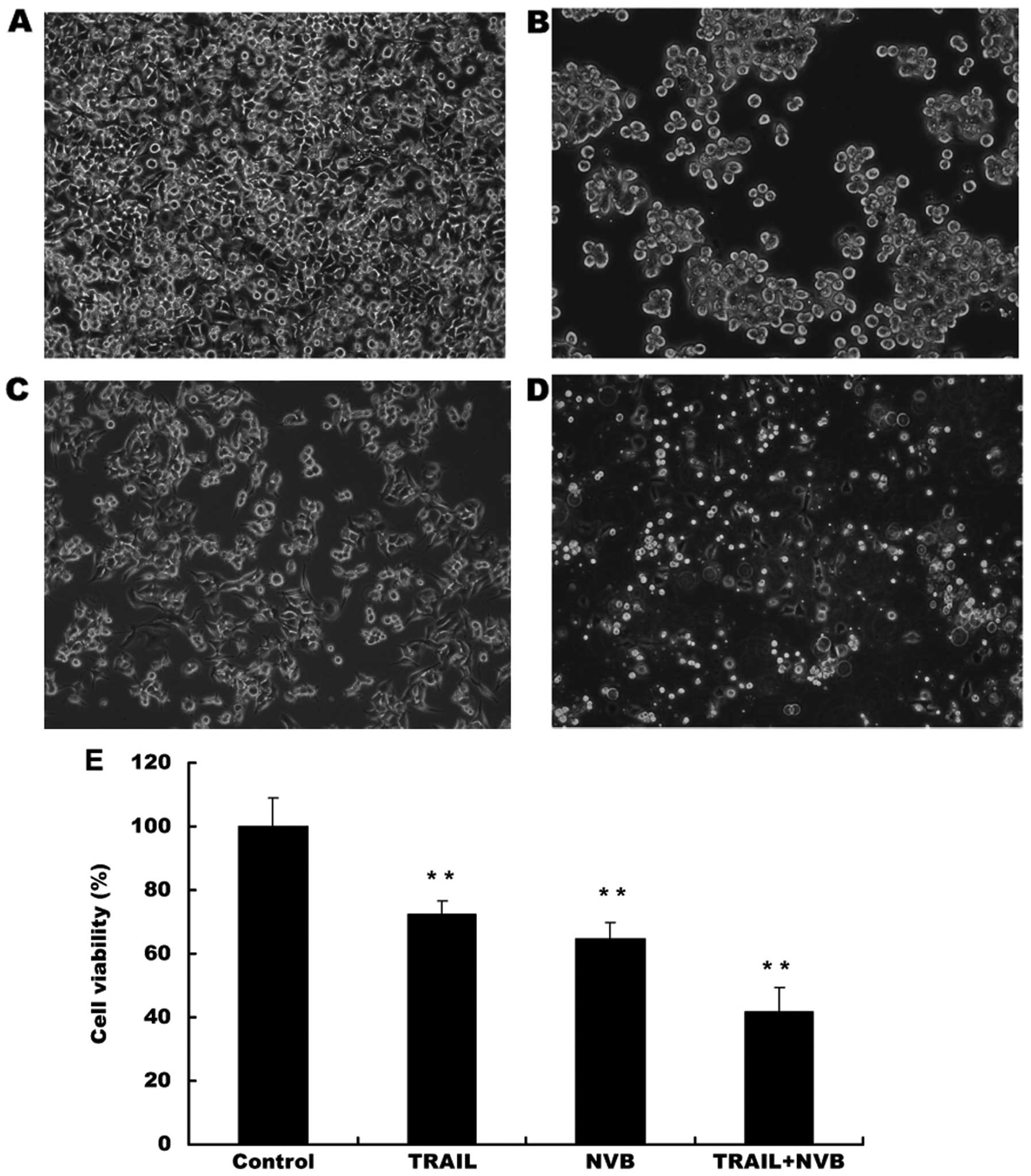
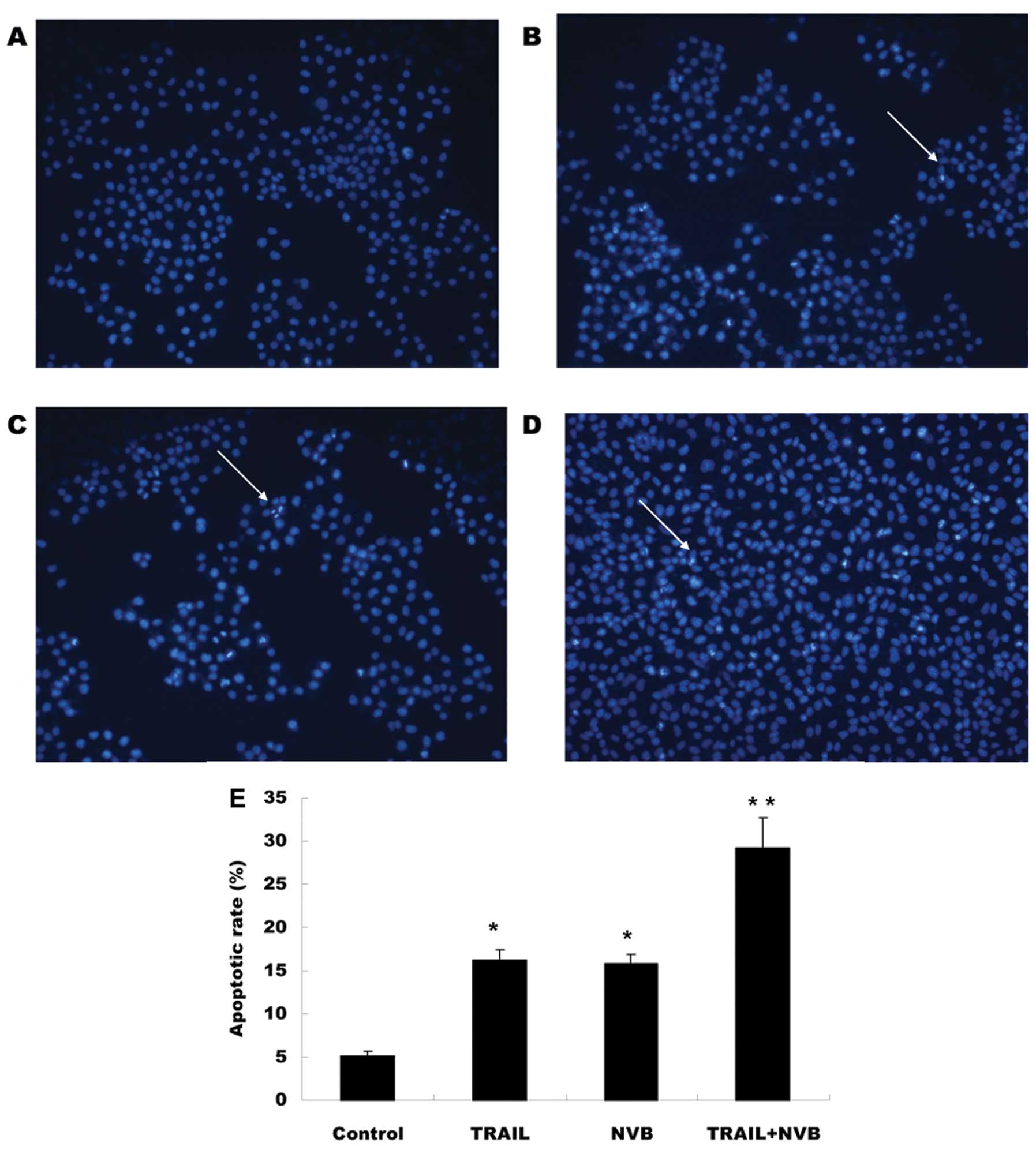
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lara PN, Lau DH and Gandara DR:
Non-small-cell lung cancer progression after first-line
chemotherapy. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 3:53–58. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP,
Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J and Johnson DH; Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group. Comparison of four chemotherapy
regimens for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. N Eng J Med.
346:92–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Davies A, Gandara DR, Lara P, Goldberg Z,
Roberts P and Lau D: Current and future therapeutic approaches in
locally advanced (stage III) non-small cell lung cancer. Semin
Oncol. 29(Suppl 12): S10–S16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Marinis F and De Petris L: Pemetrexed
in second-line treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncology.
18(Suppl 8): S38–S42. 2004.
|
|
7
|
Ashkenazi A, Holland P and Eckhardt SG:
Ligand-based targeting of apoptosis in cancer: the potential of
recombinant human apoptosis ligand 2/tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhApo2L/TRAIL). J Clin Oncol.
26:3621–3630. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, Din WS,
Huang CP, Nicholl JK, Sutherland GR, Smith TD, Rauch C, Smith CA,
et al: Identification and characterization of a new member of the
TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 3:673–682. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C,
Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JC and Lynch DH: Tumoricidal
activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ and Smyth MJ: The
TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 8:782–798. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ganten TM, Koschny R, Sykora J,
Schulze-Bergkamen H, Büchler P, Haas TL, Schader MB, Untergasser A,
Stremmel W and Walczak H: Preclinical differentiation between
apparently safe and potentially hepatotoxic applications of TRAIL
either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic drugs. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:2640–2646. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li F, Guo Y, Han L, Duan Y, Fang F, Niu S,
Ba Q, Zhu H, Kong F, Lin C and Wen X: In vitro and in
vivo growth inhibition of drug-resistant ovarian carcinoma
cells using a combination of cisplatin and a TRAIL-encoding
retrovirus. Oncol Lett. 4:1254–1258. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Mansour M and Mourad C: Phase II study of
single agent oral vinorelbine as first-line treatment in patients
with HER-2 negative metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 72:429–435. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saip P, Eralp Y, Sen F, Karaca H, Ozkan M,
Cetin B, Benekli M, Kucukoner M, Isikdogan A, Un O, Basaran G and
Onur H: Phase II study of lapatinib in combination with vinorelbine
in patients with HER2 positive recurrent or metastatic breast
cancer: A multicentric Turkish Oncology Group (TOG) trial. Breast.
22:628–633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan A, Conte PF, Petruzelka L,
Tubiana-Mathieu N, Ganju V, Llombart A, Espie M, Majois F, Gil MG,
Vaissiere N and Villanova G: Phase II study of a triple combination
of oral vinorelbine, capecitabine and trastuzumab as first-line
treatment in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer
Res. 33:2657–2664. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu YC, Wang HX, Tang L, Ma Y and Zhang FC:
A systematic review of vinorelbine for the treatment of breast
cancer. Breast J. 19:180–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
de Vries EG, Gietema JA and de Jong S:
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand pathway and
its therapeutic implications. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2390–2393.
2006.
|
|
18
|
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, Friesen
C, Li F, Tomaselli KJ, Debatin KM, Krammer PH and Peter ME: Two
CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J. 17:1675–1687. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gonzalvez F and Ashkenazi A: New insights
into apoptosis signaling by Apo2L/TRAIL. Oncogene. 29:4752–4765.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang H, Sui A, Wang Z, Liu S and Yao R:
Adenovirus-mediated TRAIL expression and downregulation of Bcl-2
expression suppresses non-small cell lung cancer growth in
vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med. 30:358–364.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Heber
A, DeForge L, Koumenis IL, Lewis D, Harris L, Bussiere J, Koeppen
H, Shahrokh Z and Schwall RH: Safety and antitumor activity of
recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gazitt Y: TRAIL is a potent inducer of
apoptosis in myeloma cells derived from multiple myeloma patients
and is not cytotoxic to hematopoietic stem cells. Leukemia.
13:1817–1824. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takimoto R and El-Deiry WS: Wild-type p53
transactivates the KILLER/DR5 gene through an intronic
sequence-specific DNA-binding site. Oncogene. 19:1735–1743. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oda K, Arakawa H, Tanaka T, Matsuda K,
Tanikawa C, Mori T, Nishimori H, Tamai K, Tokino T, Nakamura Y and
Taya Y: p53AIP1, a potential mediator of p53-dependent
apoptosis, and its regulation by Ser-46-phosphorylated p53. Cell.
102:849–862. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X: Smac,
a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Henry H, Thomas A, Shen Y and White E:
Regulation of the mitochondrial checkpoint in p53-mediated
apoptosis confers resistance to cell death. Oncogene. 21:748–760.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|